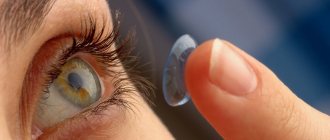
Contact lenses for the eyes, just like glasses, are used to correct refractive errors without surgery. With their help, you can easily eliminate vision defects such as myopia (nearsightedness), hypermetropia (farsightedness), and astigmatism.
The history of the creation of lenses for contact vision correction (CL) dates back to 1500, when they were first described by Leonardo da Vinci. Over the next centuries, there were many attempts to make such optical devices from various materials (glass, plastic), but most of them did not end entirely successfully, since the lenses caused significant discomfort during operation.
The first successful examples were created in the 1960–1970s by Bausch & Lomb, at which time they became available to patients with refractive errors as an alternative to spectacle vision correction. The following decades were very fruitful in the development of contact lenses. A large number of new and biocompatible materials were invented, several lens surface designs were developed, even tinted and multi-colored lenses appeared, and it became possible to wear some contact lenses for a long time without taking them off at night, without damaging vision.
Advantages and disadvantages of contact vision correction
Patients who have chosen contact lenses to correct their vision note the following advantages and positive properties compared to glasses:
- Due to its small size and location directly on the surface of the eyeball, CL provides much better peripheral vision and is also characterized by significantly less optical distortion.
- If a person has a large difference in vision (dioptres) between the two eyes, then CLs provide better correction in this case, as they are well tolerated (many patients cannot wear glasses due to side effects such as dizziness, headaches and optical distortions Images).
- During operation, CLs do not produce such negative phenomena as glare, reflection from the surface, and visual aberrations, unlike spectacle lenses.
- A contact lens has no limitation in the field of vision, and when wearing glasses, the field of vision is clearly limited by the size of the spectacle lens.
- CLs are much more convenient and safer to use with an active lifestyle, playing sports, they do not impair vision in various weather conditions (rain, snow, wind, fog, frost).
- There are special cases when it is impossible to achieve good vision correction with glasses, for example, with keratoconus, corneal injuries, after eye surgery, a high degree of astigmatism, in such situations only CL can restore clear vision without surgical intervention.
- Vision in CL is natural, that is, a person sees all objects in real size and the distance to them is not distorted, as when wearing glasses.
- Lenses do not appear in any way on a person’s appearance; they are practically invisible to outsiders.
Contact correction allows you to achieve ideal clarity of vision in people with various refractive errors.
At the same time, we should not forget that even the most modern lens is a foreign object for the eye, so you need to know the arguments against contact vision correction:
- There is a period of adaptation to CL; unfortunately, not everyone succeeds in going through it, which forces them to abandon such vision correction.
- It is necessary to develop skills in handling contact lenses, strictly observe hygiene and not neglect the rules of wearing contact lenses.
- Wearing contact lenses is a constant expense, since you need to constantly buy a new pair of lenses, solutions and containers for their storage and processing, and other consumables.
- The CL user should visit an ophthalmologist at least once every 6 months.
- High risk of allergic eye damage, as well as infection if the rules for handling CL are violated, and the development of specific complications (for example, vascularization of the cornea).
What are contact lenses made of?
Depending on the type of lens material, they can be divided into two large groups:
- Rigid contact lenses (RCLs) are gas-permeable and gas-tight.
- Soft contact lenses (SCL) – hydrogel, silicone hydrogel.
LCDs made from a material called polymethyl methacrylate, or organic glass, were the first to be invented. Such lenses were durable and optically transparent, but did not transmit oxygen to the cornea at all, which caused many side effects during long-term use. To solve this problem, experts added silicone to the source material. Thus, LCLs became gas-permeable, but this also led to a decrease in the strength of products and a complication of the technological process of manufacturing LCLs.
Modern hard lenses are made from gas-permeable polymers. Their advantages over soft ones:
How to properly put on and remove contact lenses
- Higher degree of oxygen permeability when compared with hydrogel SCLs.
- Very good visual clarity.
- Good vision correction for pathologies such as high degrees of astigmatism, keratoconus, post-traumatic or postoperative deformations of the cornea.
- Resistant to damage, ruptures, accumulation of protein and lipid deposits on the surface.
- They are characterized by a long period of operation, which significantly saves the user’s money.
The disadvantages of LCD include:
- Long and difficult period of adaptation.
- The small size of the lens itself, when compared with SCLs, increases the chance of it falling out of the eye and being lost.
Today, ophthalmologists recommend using GCL for the following indications:
- A person does not have enough of the clarity of vision that SCLs provide (with a high degree of astigmatism, during vision correction for professional athletes).
- Keratoconus.
- After eye surgery to correct refraction.
- For therapeutic purposes to correct myopia.
An ideal material for CL should be highly permeable to oxygen and contain a large amount of moisture.
Soft contact lenses are made from hydrogel and silicone hydrogel polymers. Their main feature is their moisture content; they are able to bind water molecules, which allows oxygen to penetrate to the cornea. SCLs immediately became popular because they have good elasticity, moisture content, oxygen permeability, and are much easier to adapt to and select the right optical device for a particular patient. A real breakthrough in modern contact vision correction has become silicone hydrogel SCLs, which are distinguished not only by a high percentage of moisture content, but also by a very high oxygen permeability, for which they are often called “breathable”.
What are eye lenses made of?
About 2% of the world's population uses eye lenses to correct their vision. This invention of human thought has greatly simplified life, allowing you to see more and look better at the same time. Having made them an important attribute of their lives, few people think about the question of what eye lenses are made of.
Lenses can be divided into soft and hard. The first appeared at the end of the 19th century, remaining relevant until the 1960s. They were hard and made of plexiglass. Over time, silicone-based lenses began to be produced, which are capable of better correcting vision, achieving maximum sharpness even with serious eye diseases. Silicone-based hard lenses have higher oxygen saturation. The downside of these lenses is that they require getting used to and more careful selection based on the anatomical features of the eyes.
The vast majority of people prefer to wear soft lenses, which have the following advantages:
- soft lenses are universal;
- they are saturated with moisture and allow sufficient oxygen to pass through;
- have a wide range of uses from vision correction to cosmetic effects.
Lenses become soft due to the presence of water: the more moisture in the lens, the softer and more flexible it is. The optimal water content was experimentally determined to be 70%. When the water content is above this level, the lenses become too soft and uncomfortable to use; if the contact lenses are made with less ability to absorb water, the eye feels dry and uncomfortable.
Read more about comfortable daily lenses at www.ochkov.net/odnodnevnye-linzy/.
Soft eye lenses are made from two main types of hydrophilic polymers: hydrogel and silicone hydrogel. The first polymer is characterized by weak oxygen permeability to the eye cornea, as a result of which hydrogel lenses are intended only for daytime wear and require frequent changes. The second polymer partially eliminates the disadvantages of the first. Silicone hydrogel lenses have a high gas permeability, so they can be worn for several days without removing them without the threat of eye hypoxia. However, increasing the proportion of silicone reduces the moisture content of the lens, making it more rigid and brittle.
Although the production of lenses has long been established: consumers choose the best for themselves and are generally satisfied with the quality, complaints remain about rapid eye fatigue and a feeling of dryness. Therefore, in May 2021, Alcon presented its innovative development - water-gradient lenses made using a special technology for combining materials. These new generation lenses have increased moisture content, which is 80% inside and reaches 100% on the surface, making them almost invisible to the eye. Essentially, contactless lenses were offered to Alcon.
Note that materials for making contact lenses can be precious. Thus, the Indian Sanjay Shah introduced the public to women with diamond sparkle eyes. The basis of his designer lenses, which cost a fortune and weigh about 6 grams, are yellow or white gold with diamond inclusions. A water cushion is provided between the lens and the eye for comfortable wearing. Having an idea of the material from which the lenses are made, you can choose the optimal quality for your eyes according to your wallet.
26.09.2016
Leave a comment Cancel reply
| Tell your friends about it → |
Classification
In addition to dividing CL into hard and soft, there are several other classifications.
Considering the wearing mode, lenses are:
- Daytime - they are put on in the morning for the whole day, and must be taken off before going to bed.
- Flexible - the same as daytime ones, but in some situations such contact lenses can be worn without taking them off for 1-2 nights.
- Extended - may not be removed for up to seven days.
- Long-term continuous wear - the lenses can be left in place for the period specified by the manufacturer (as a rule, they are two weeks, but there are models that can be worn for up to 30 days).
Considering the CL replacement mode, lenses are:
- Daily contact lenses – use a new pair of lenses every day.
- With frequent scheduled replacement - a new pair is used every 1-2 weeks.
- With planned replacement – lenses are changed every 1–3 months.
- Traditional - replacement every 6-12 months.
Ultra Flex 3 month tint contact lenses are ideal for light eyes.
Considering the surface design, CLs are:
- Spherical.
- Aspherical.
- Toric.
- Multifocal.
- Keratoconus.
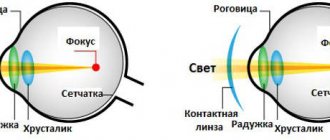
An extremely important criterion for a lens is its optical power. It is this parameter that is required to be indicated in the prescription for CL and is expressed in diopters. Lenses can be plus (to correct myopia) and minus (to correct farsightedness).
CLs also differ in such an important parameter as the radius of curvature of the cornea (the degree of convexity of its surface), this indicator is expressed in millimeters. The base curvature of the back surface of the lens should match the curvature of the cornea as closely as possible. Only in this case the CL will fit perfectly on the eye and will not cause discomfort to the patient.
Spherical CLs have the same optical power over their entire surface. They are suitable for patients with myopia, hypermetropia and slight astigmatism.
Aspherical CLs differ in the shape of their surface, due to which their radius of curvature, as well as optical power, gradually decrease from the center to the periphery. This modification can significantly reduce the number of visual aberrations (distortions). The indications for wearing them are the same as for spherical ones.
Toric (astigmatic) CLs have different optical powers in different meridians, thus, they correct the astigmatism present in the patient and at the same time negative or positive vision (hypermetropia, myopia).
Toric lenses allow you to correct vision with astigmatism.
Multifocal (bifocal and progressive) CLs are used to correct age-related farsightedness - presbyopia. The principle of their operation is as follows: they have several optical zones, which are responsible for good vision near, at an average distance and into the distance. Simple bifocal lenses have three zones. The top one is for near vision, the bottom one is for distance vision, and the middle one is for viewing objects at a medium distance. The difference in diopters of these zones should not be more than 2–3 units. Progressive lenses are characterized by the absence of sharp jumps in optical power between lens zones; they decrease or increase smoothly, which ensures less visual distortion and better tolerance of such vision correction.
What are contact lenses made of?
Hydrogel lenses.
The first hydrogel polymer materials for contact lenses (in particular, HEMA hydroxyethyl methacrylate) were synthesized in the 60s of the 20th century.
These polymers were hydrophilic, i.e. ability to attract water. 38% of these polymers consisted of water, which actually transfers oxygen to the cornea of the eye. For normal oxygen supply to the eyes, tear fluid must continuously flow under the surface of the lens. The Bausch&Lomb company, around the end of the 60s, acquired a license for the production of HEMA material and the technology for molding soft contact lenses. The company began to improve the hydrophilicity of contact lenses, launched hydrogel contact lenses Optima FW, Soflens 59 and others, constantly improving their properties and increasing the hydrophilicity of soft contact lenses. However, the peculiarity of this material has limitations and today, almost all gyrogel contact lenses from all manufacturers have equal indicators for moisture content and oxygen transmission to the cornea (For hydrogel products this indicator is usually 20-30 * 10-9 Dk/t) . By the way, for safe daytime wearing, the oxygen transmittance coefficient (Dk) should be 24 - 26 units. Like any item that makes our life easier, hydrogel contact lenses have a number of pros and cons. Pros.
- Low cost contact lenses.
- Easy selection and replacement. Quickly adjust the eyes to the material.
Minuses.
- Only daytime wearing of lenses.
- Low level of gas transmission, as a result - hypoxia and redness of the eyes when wearing lenses in enclosed spaces.
Silicone hydrogel lenses.
At their core, silicone hydrogel contact lenses are a combination of two copolymers - hydrogel and silicone. Hydrogel is the basis of the material, and silicone added to the chemical composition is hydrophobic, that is, the contact lens already contains water. In this regard, the silicone hydrogel lens allows more oxygen to pass through (– 70-170*10-9 Dk/t) and this allows you to wear contact lenses not only during the day, but also in a prolonged state - continuously, for a week! At the same time, the eyes do not experience hypoxia (oxygen starvation).
Minuses:
- Higher cost of lenses
- Some period of getting used to the lens itself.
- Individual intolerance to the material.
- Tendency to dry out.
Some features of silicone hydrogel lenses that cannot be ignored. The presence of silicone in the lens material increases the elastic modulus of the lens. This means that the more silicone the lenses contain, the harder they become. This affects the properties of the lenses, because with an increase in the elastic modulus, the lenses become fragile. Also, as the silicone content in contact lenses increases, the moisture content decreases. The lens dries out and becomes less comfortable.
Pros:
- Possibility of wearing contact lenses in extended mode (without removing them at night).
- Higher level of breathability.
Which material to choose? What's better?
Research statistics in recent years indicate an increase in demand specifically for silicone hydrogel lenses (up to 40%). Experts say that soon almost all manufacturers will switch to the production of silicone hydrogel contact lenses. This is primarily due to advances in research in the field of silicone hydrogel materials. Manufacturers have found a balance between the interaction of indicators such as breathability, moisture content and elastic modulus in combination with high optical performance and wearing comfort of silicone hydrogel contact lenses. Which material to choose is, of course, chosen by the consumer himself, based on his personal preferences and capabilities.
For our part, we would advise you to follow simple rules:
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly (less than 2 times a year) to check your vision and eye condition. Purchase and use vision correction products selected by a competent specialist.
- Take vitamin complexes regularly for eye health
- spend more time outdoors
- do eye exercises for at least 10 minutes a day.
- Do not purchase contact lenses and care products of questionable quality and from random manufacturers.
Special types of lenses
There are several other types of unusual CLs. Let's look at them.
Scleral
These lenses have a much larger diameter, in some cases they are worn almost over the entire eye. They are used for special indications when wearing regular contact lenses does not help correct refraction:
- Congenital or acquired (due to injury, surgery) irregular shape of the cornea.
- Keratoconus.
- Severe dry eye syndrome.
Scleral lenses are also used for cosmetic purposes to create a particular theatrical image.
The photo shows scleral cosmetic contact lenses without pupils.
Orthokeratological
These are therapeutic contact lenses that allow you to temporarily correct myopia up to 6 diopters and myopic astigmatism up to 1.75 diopters. What are these lenses made of? All of them are rigid gas permeable. They are worn at night, during which time the lens changes the shape and thickness of the cornea, which leads to a change in its optical power and improved vision. The effect can last up to several days. This method of vision correction is chosen by people who cannot wear conventional lenses, for example, when working in dusty rooms.
Cosmetic
At the very beginning, such CLs were used only for medical reasons in order to hide an existing eye defect. But today, such lenses are worn by many users who want to change their eye color or add uniqueness to their image.
Mirrored cosmetic lenses will allow you to create an interesting and unique image.
Thus, the modern market offers dozens of options for beautiful multi-colored lenses with and without diopters for users with dark eyes and light ones.
Lenses with vertical pupils will help create the perfect image of a catwoman.
Complications and contraindications of contact vision correction
It is prohibited to use CL in the following cases:
- Strabismus.
- Low sensitivity of the cornea.
- Ptosis (drooping eyelid).
- Blepharitis (inflammation of the eyelid).
- Diagnosed lens subluxation.
- Violation of the quantitative and qualitative composition of the tear fluid.
- Inflammatory diseases of the membranes of the eyes and auxiliary visual apparatus (conjunctivitis, keratitis, dacryocystitis).
- Xerophthalmia;
- Glaucoma.
- Immunodeficiency syndrome (congenital or acquired).
- Tuberculosis infection.
Reviews
Natalya, 29 years old: “I have been using soft contact lenses for two years now. I am very pleased with this method of vision correction. Before that, I wore glasses, but it was very difficult with them - I had to constantly adjust them, and they often fogged up in winter. There are no such problems with lenses at all. I've tried so many models! But the Biofinity lenses from Cooper Vision suited me best.”
Anton, 45 years old: “Recently my eyesight has deteriorated greatly, which I attributed to constant work at the computer, but it turned out that it was due to age. The doctor suggested trying special contact lenses for correction. No matter how hard I tried to stick them into the eye, the blink reflex turned out to be stronger. That’s why I now wear glasses for near vision.”
Alina, 35 years old: “I have been wearing contact lenses for about 10 years. During this time, whatever vision I started with, I stayed with it, that is, they do not reduce vision, as many say. During this time, I tried everything that the market offers, and before I even wore hard ones. I have my favorite lenses – Air Optics Sakwa, but, unfortunately, they have become very expensive lately, so I have to choose from a more affordable segment.”
Contact lenses are a unique, fast and effective way of non-surgical vision correction for refractive errors. But it is important to understand that there are a large number of varieties of this optical device, and only a specialist should select the CLs you need, taking into account all the above-described features.
Composition of soft lenses
Soft ones can be made of hydrogel and silicone hydrogel, both of which use hydrogel.
Material for silicone hydrogel lenses
The main materials for production are silicone and hydrogel.
Silicone is hydrophobic, which means it already contains water. Pros :
- high level of breathability and the possibility of prolonged wear, that is, without taking it off at night and feeling a lack of oxygen.
The disadvantages include:
- individual intolerance, some patients cannot use them;
- presence of a period for adaptation;
- relatively high cost.
Hydrogel lens material
For the first time, hydrogel material became known in the sixties of the last century.
Pros:
- The main quality of these materials is hydrophilicity, that is, they attract water. They perfectly transport oxygen to the cornea of the eye, since they consist of more than 35% water;
- The advantages include easy selection and lack of addiction, as well as a relatively low price.
Minuses:
- Disadvantages include the ability to be worn only during the day and low gas permeability.
Water content in soft lenses
Based on water content, they are divided into three types:
- with high moisture content - more than 60%;
- with an average moisture content of about 50–60%;
- with low moisture content - less than 40%.
Important! The higher the percentage of water content, the more comfortable the products are to wear, and therefore, the more comfortable they are to wear.