Properties of tetracycline ointment
Tetracycline is a potent bacteriostatic antibiotic. The action of the substance is to disrupt the binding of RNA and ribosomes in microbial cells, which leads to protein destruction. Without it, cells cannot develop and divide, the infection stops spreading through the tissues and inflammation stops.
Tetracycline ointment can be a first aid drug for eye inflammation. It copes with inflammatory processes caused by various gram-positive and gram-negative microorganisms. The exceptions are fungal and viral pathogens, as well as group A streptococci.
Scope of action of tetracycline:
- gram-positive microorganisms: staphylococci (Staphylococcus aureus), streptococci (pneumococcus), actinomycetes, listeria, clostridia, anthrax pathogens;
- gram-negative microorganisms: hemophilus influenzae, Ducray's bacillus, pertussis bacillus;
- enterobacteria: Escherichia coli, Klebsiella, rickettsia, Salmonella, Shigella, plague bacillus, Brucella;
- causative agents of venereal and inguinal lymphogranuloma;
- Treponema.
Tetracycline ointment is absolutely ineffective against some pathogens, so it should be used only after diagnosis and correct diagnosis. The most reliable way to check the type of infection is a laboratory test of a smear from the mucous membrane of the eye, although most ophthalmologists rely only on symptoms.
pharmachologic effect
Tetracycline eye ointment has an antimicrobial effect. It also has antibacterial properties. The drug disrupts the formation of the complex between transfer RNA and the ribosome. As a result, the production of protein components deteriorates.
Tetracycline has a wide spectrum of action. It is active against many gram-positive and gram-negative bacteria. The drug has an effect on rickettsia, leptospira, spirochetes.
The active substance enters various organs and tissues. It also easily penetrates biological fluids. The drug selectively accumulates in teeth, tumor formations, liver, and bone tissue.
The substance is able to cross the placental barrier and enter breast milk. Tetracycline is not metabolized. It leaves the body through the kidneys and bile.
What concentration of ointment is needed for eye inflammation
The product is available in the form of tablets, ointment for external use and eye ointment. The main substance is the antibiotic tetracycline. To give the desired consistency, Vaseline and lanolin are additionally used. The composition of the drugs differs only in the percentage of antibiotic content. In ophthalmic ointment, the proportion of tetracycline is no more than 1%, and in ointment for external use – 3%.
Tetracycline ointment 3% is not used in ophthalmology. Due to the high concentration of the antibiotic, it can cause burns to the mucous membrane and other unpleasant consequences. If a product with a high concentration was used by mistake, it is necessary to rinse the eye under clean running water and consult an ophthalmologist.
Compound
Tetracycline ointment is available in the form of an ointment with a concentration of 1 and 3%. The product has a yellowish tint and an opaque consistency. It is characterized by an unobtrusive aroma.
In ophthalmic practice, a product containing 1% active substance is used. A more concentrated drug is suitable for the treatment of dermatological pathologies.
The active component of the product is tetracycline hydrochloride. Tetracycline ointment also contains petroleum jelly and paraffin.
The product is available in aluminum tubes, which can contain 3 or 10 g of ointment. Each tube along with instructions is in a cardboard box. The product should be stored in a dry place out of reach of children. This must be done at a temperature of +15-25 degrees for 3 years. After the expiration date, the product should not be used.
Indications and contraindications
Tetracycline ointment is a universal remedy for infectious lesions of the skin and mucous membranes. An antibiotic not only destroys infectious agents, but also prevents their spread. An ointment with a concentration of 3% helps to cope with infectious foci on the skin (eczema, boils, rashes). Tetracycline is used in the treatment of herpes, but the drug is useless as the only therapeutic measure. Sometimes tetracycline ointment is used in gynecology.
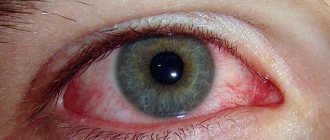
Tetracycline ophthalmic ointment is prescribed to patients with inflammation of the ocular mucosa. The greatest effectiveness is observed for bacterial and chlamydial infections when treatment is started at the onset of inflammation. Many parents note the benefits of the product for barley in children.
Indications for tetracycline ointment in ophthalmology:
- conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye);
- keratoconjunctivitis (damage to the cornea and conjunctiva);
- blepharitis (inflammation of the edges of the eyelids);
- blepharoconjunctivitis (damage to the eyelids and conjunctiva);
- keratitis (inflammation of the cornea);
- meibomitis (inflammatory processes in the glands of the eyelid);
- trachoma (inflammation of the connective membrane);
- barley (inflammatory process in the hair follicle of the eyelash);
- eye damage due to rosacea.
People with chronic pathologies of the liver and kidneys can use tetracycline ointment only with the permission and under the supervision of the attending physician.
Contraindications to tetracycline:
- age up to 5 years;
- individual sensitivity to tetracycline;
- mycosis (fungal inflammation);
- exacerbation of chronic liver diseases.
Doctors prescribe tetracycline with caution to patients who have gastric ulcers, kidney or liver failure. It is undesirable to use an antibiotic for leukopenia and allergies to antibiotics from this group.
Side effects
They reported about the low-grade side effects of the post-mortem stage that often occur after treatment.
From the side of the organs:
blurred vision, swollen liver, acute pain, itchy eyes or eyes, conjunctival hyperemia, swelling of the eyes, increased lacrimation and pain in the eyes.
On the side of the immune system:
Local allergic reactions – dermatitis, visip, itching, photodermatitis (sensitivity to sleepy light and UV damage); generalized allergic reactions, sore throat, angioedema, itching and swelling of the face, tongue, throat, confusion, buttocks. In such cases, the ointment will stagnate.
On the side of the scolio-intestinal tract:
decreased appetite, boredom, vomiting, diarrhea, possible burning processes in the tongue, stomatitis, gastritis, proctitis.
Tetracycline ointment during pregnancy
In the early stages, the use of drugs with tetracycline can be dangerous, because the antibiotic can affect the formation of fetal organs. Tetracycline interferes with normal bone mineralization, which in the future leads to pathologies of the bone frame in the child. During pregnancy and breastfeeding, tetracycline is prescribed exclusively in small dosages. Before use, it is advisable to check the woman’s body’s response to tetracycline using laboratory methods.
A doctor can recommend tetracycline ointment to a pregnant woman only for infectious forms of conjunctivitis, but the state of the woman’s immunity and nutrition must be taken into account. If you use tetracycline with a very weak immune system, viral inflammation can join the infection of the mucous membrane.
Interactions with other medicinal drugs and other types of interactions
In case of local ophthalmic stasis of tetracycline, it is important to note that its bacteriostatic action may interfere with the bactericidal action of penicillins, cephalosporins and aminoglycosides. A trace of the uniqueness of their one-hour stagnation, both local and systemic.
The use of tetracycline in patients who use the drug for contact lenses containing 0.004% thiomersal is associated with eye reactions varying in severity (red eyes, irritation, blepharitis), etc. To avoid one-hour stagnation.
A trace of the uniqueness of one-hour ophthalmic administration of tetracycline and local corticosteroids (section “Peculiarities of administration”).
To enhance activity, it is possible to combine it with erythromycin, oleandomycin, and drugs of the nitrofuran series.
Use of tetracycline ointment
Tetracycline ointment is suitable for treating mucous membranes for infectious eye lesions. Self-medication with eye antibiotics is undesirable, since due to an excess of potent substances, scars can form on the mucous membrane.
Both patients and specialists note the high effectiveness of tetracycline ointment precisely at the initial stage of inflammation. Styes, blepharitis and conjunctivitis are treated with tetracycline ointment until symptoms disappear and for another 2 days. For prophylaxis before and after ophthalmic surgery, 3 days are enough.
The ointment is applied to the lower eyelid several times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor, taking into account the severity of the disease and the speed of recovery. Usually this is 3-5 applications per day in a weekly course. When treating eye diseases with tetracycline ointment, caution must be exercised; increasing the dose leads to an allergic reaction and deterioration of the mucous membrane.
If conjunctivitis affects only one eye, tetracycline ointment is applied twice a day to the affected eye and once to the healthy eye for prevention. The course of treatment is continued until the symptoms disappear completely and for several more days after, in order to destroy hidden remnants of the infection and prevent its secondary spread.
Conjunctivitis caused by chlamydia takes longer to cure. Improvement can be achieved within 2-3 weeks of using antibiotics and antibacterial drugs, which help avoid damage to the cornea and scarring of the eyelids. For chlamydial conjunctivitis, the ointment is applied 2-3 times a day. After completing the course of treatment - for prevention - you can use the product for another week, once a day.
For trachoma, therapy will include not only an antibiotic, but also antiseptic drugs. To relieve the symptoms of chronic inflammation, 2-3 weeks of intensive treatment are usually required.
Tetracycline ointment is used to prevent infectious diseases after injury to the eyeball or skull, as well as to prevent complications after surgery. The product is applied once a day for several days.
Treatment of burns with ointment
Exposure to high temperatures (over 60°C), chemical compounds, and electric current cause burns. Not only the skin is damaged, but also the mucous membranes of the eyes, nose, and mouth. At the initial stage of treatment, medications are used to relieve pain and cool injuries. Many of them contain dexpanthenol, which promotes rapid tissue healing.
Traumatologists prescribe tetracycline ointment for burns when weeping wounds form on the skin. Pathogenic bacteria penetrate into them from the surrounding space and begin to actively multiply. Despite the use of antiseptics, tissue restoration does not occur. On the contrary, the edges of the wound begin to redden and become inflamed, and suppuration appears. Only the use of ointments with antibiotics can quickly cope with infection and speed up regeneration.
Eye burns
Most often, ophthalmologists diagnose retinal burns that occur under the influence of temperature.
But the most dangerous injuries are caused by the ingress of chemicals - acids, alkalis, heavy metals.
In such cases, only timely medical care can help a person preserve his vision. After an eye burn, the following symptoms quickly appear:
- severe lacrimation;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- increased sensitivity to light.
Tetracycline 1% ointment is used immediately at the initial stage of treatment of a chemical burn. When used, it is possible to prevent the development of edema and inflammation caused by pathogenic microbes. Ophthalmologists recommend placing an antibacterial agent behind the eyelid even at the stage of providing first aid to the victim.
Chemical burn
Chemical burns of the skin or mucous membranes can occur both at home and at work. The most dangerous injuries are caused by alkalis—lime, ammonia solution, and cleaning agents. When concentrated chemicals come into contact with the skin, a wound surface immediately forms. Even timely treatment with an antiseptic is not able to prevent infection. Traumatologists prescribe ointments to patients for 3-4 times application to the affected surface:
- Levomekol;
- Tetracycline;
- Levomycetinic.
The active ingredients of antibacterial ointments quickly penetrate into inflammatory foci and destroy pathogens.
Using these medications also helps prevent the formation of scars and scars.
Radiation influence
Eye damage is often caused by ultraviolet radiation, for example, during gas welding work. 1st or 2nd degree skin burns occur due to prolonged exposure to the sun.
Such lesions are very painful and, if left untreated, can become inflamed and infected. It is necessary to apply antibacterial ointments when redness and swelling spread to healthy areas of the skin.
Quite rarely, burns occur as a result of ionizing radiation. It is actively used in instrumental diagnosis of the disease and chemotherapy. Such skin damage can only be caused by exceeding a certain level of radiation dose.
Principles of first aid for burns
After removing the source of the burn, the damaged areas must be cooled under running water. This is especially true when injured by chemicals, as it allows you to quickly wash off the acid or alkali. The skin should be cooled under running water for 15-20 minutes, after which it is treated with antiseptics:
Tetracycline ointment for a child
Tetracycline is prescribed to children from 5 to 8 years of age with great caution. If the expected benefit greatly outweighs the risk of side effects, use the minimum dose for a short course. This is due to the negative effect of tetracycline on the tissue of baby teeth.
Indications for the use of tetracycline ointment in children are the same as in adults: conjunctivitis, blepharitis, trachoma, keratitis. It is worth noting the high effectiveness of the product at the initial stage of barley development. Analogues of tetracycline ointment do not cope with this disease so well and quickly.
In the case of children, the product can be used only as prescribed by an ophthalmologist, since the effect of the antibiotic on a growing organism is many times stronger. Despite the fact that the instructions for the ointment indicate a restriction on the use of tetracycline ointment up to 8 years of age, many pediatricians recommend the drug for the treatment of eye diseases in young children. In special cases, tetracycline ointment can be used to eliminate infection in a child up to a year. The use of tetracycline during teething is undesirable.
The frequency of use of the product should be determined by the treating ophthalmologist after examining the child. Usually two ointments a day are enough to get rid of the infection. For mild inflammation, a few days of treatment are sufficient, but in rare cases, tetracycline ointment is prescribed to children for up to a month.
Contraindications
Key contraindications to the use of Tetracycline ointment include the following:
- hypersensitivity to the active substance and similar antibacterial drugs;
- intolerance to additional components;
- pregnancy;
- lactation;
- children under 11 years of age;
- fungal infections in the organ of vision;
- systemic lupus erythematosus;
- complex forms of burns;
- puncture or deep wounds;
- leukopenia.
Sometimes the drug provokes unwanted side effects. They manifest themselves in the form of allergies - rashes or Quincke's edema. A person may also experience swelling of the eyelids, a temporary decrease in the clarity of visual perception, irritation in the form of itching and hyperemia.
If unwanted side effects occur, you should consult your doctor. The same must be done if reactions occur that are not in the instructions.
People whose vision is temporarily impaired after administration of the ointment should not drive a car or operate complex machinery, since clear vision is required immediately after using the product.
During pregnancy and lactation, the use of the substance is prohibited. The product contains lanolin, which can provoke local dermatological reactions. If a person’s condition does not return to normal within a few days, it is worth consulting a doctor.
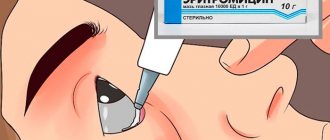
How to Apply Eye Ointment
Before applying the ointment, wash your hands. The tube must not come into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye: microbes can get inside and cause secondary infection. After the procedure, it is advisable to wipe the tip of the tube with a cotton swab.
It is convenient to use a special medical stick to apply eye ointments. It is necessary to pull back the lower eyelid and apply 5-6 mm of the product from such a stick on it. In order for the ointment to be distributed evenly, you need to close your eyelids and move your eyes. Remains of tetracycline ointment can be removed from eyelashes with a cotton swab. After applying the ointment, vision is temporarily blurred, so you cannot return to working with complex equipment or driving vehicles for 10-15 minutes.
Side effects of tetracycline ointment
Treatment with tetracycline ointment can cause general and local side effects. Within the visual system, these are itching, burning, swelling of the eyelids, photophobia, and a characteristic allergic reaction. General side effects in eye treatment are rare, since in ophthalmic practice a low-concentrated version of tetracycline ointment is used.
If the patient has already had a negative reaction to any drug, especially antibiotics, this should be reported to the doctor. Most often, an allergy to tetracycline manifests itself in the form of a rash, although serious disorders (Quincke's edema) are also possible.
Common side effects from tetracycline use:
- nausea and vomiting;
- rash;
- digestive disorders (bloating, loss of appetite, impaired peristalsis);
- diarrhea or constipation;
- swelling of soft tissues;
- swallowing disorder;
- inflammation of the tongue;
- symptoms of oral microflora imbalance.
Long-term tetracycline therapy causes yellowing of teeth. The most intense yellowing occurs when tetracycline is taken orally, when it is absorbed in large quantities into the circulatory system. If the patient notices a change in the color of the teeth, it is necessary to discuss the issue of changing the drug with the doctor. When this is not possible, a break in a long course of tetracycline can be taken to reduce the concentration of the active substance.
Restrictions on use and side effects
Tetracycline ointment is not prescribed for the treatment of pregnant and breastfeeding women. The fetus or infant may experience impaired development of bone structures and develop hypoplasia of tooth enamel. Use during pregnancy is possible only when the benefit from treating the mother justifies the risk to the child.
Tetracycline therapy is not recommended for stomach ulcers. The use of the drug is incompatible with taking cephalosporins, penicillins, and retinol.
The combination with colestipol, which is part of drugs that prevent the absorption of bile acids and cholesterol in the intestines, is excluded. The absorption of the antibacterial agent decreases.
In addition, tetracycline forms poorly soluble combinations with metals. Therefore, while using the drug, it is not recommended to eat apricots, apples, greens, buckwheat, peas, and foods containing calcium, including milk.
Allergic reactions may occur as a side effect. Headache, dizziness, nausea and vomiting may also occur. The drug can negatively affect the composition of the blood, the condition of the liver and kidneys. Its use together with vitamin A helps to increase blood pressure.
Possible photosensitivity - increased sensitivity to sunlight.
In case of side effects, you should stop using the drug and consult a doctor.
Contraindications of the drug
Tetracycline-based ointment is contraindicated for leukopenia, liver failure and extensive fungal infection.
Individual intolerance to the components of the product is possible, which manifests itself in the form of itching, rash, and increased redness.
To check for allergies, apply a small amount of the drug to the crook of your elbow. If after a few hours no allergic reaction appears, then treatment can begin.
In the situation with the drug at a concentration of 1%, the ointment is contraindicated in children under 8 years of age. If the product is required to be used at a concentration of 3%, the child must be at least 11 years old.
Analogues of the drug
An effective tetracycline-based ointment is by no means the only remedy that can be used for burns. There are drugs with no less, or even greater therapeutic effectiveness: balms, ointments, gels on a hydrophilic basis.
Interaction with other drugs
Antibiotics penicillins, cephalosporins and aminoglycosides have the opposite effect of tetracycline. When taking retinol simultaneously with tetracycline, intracranial pressure may increase. The interaction of insulin and tetracycline leads to hypoglycemia (a drop in blood glucose levels). Drugs containing metal ions form inactive chelate complexes with tetracycline.
Colestipol and Cholestyramine can weaken the effect of tetracycline. Tetracycline combines favorably with erythromycin, oleandomycin and polymyxin. These drugs enhance its antibacterial properties.
Analogs of tetracycline ophthalmic ointment
As a replacement for tetracycline ointment, you can choose Tobrex, Floxal, Tobropt eye drops, as well as erythromycin, chloramphenicol or ditetracycline ointments. If tetracycline ointment is ineffective, a doctor should select a replacement, since many drugs have different compositions and differ in their characteristics of use.
Analogues of tetracycline in ophthalmology:
- Gentamicin, Levomycetin, Erythromycin. These products are available in the form of drops and ointments. The effect of gentamicin, erythromycin, chloramphenicol and tetracycline ointments is approximately the same. The cost of these drugs usually does not exceed 100 rubles.
- Tobrex. Eye drops effective against conjunctivitis, stye and other eye infections. For a week, it is necessary to instill a drop every 4 hours for adults and a drop 5 times a day for children. The drug is approved for use in children under one year of age.
- Phloxal. The drug is available in the form of drops and ointments. Floxal is prescribed for inflammation of the eyelids and mucous membranes of the eye, as well as for the prevention of infection after injury. The drug can be used almost from birth.
- Futaron. Drops are prescribed for the treatment of bacterial eye infections in adults and children. Main indications: barley, conjunctivitis, keratitis, blepharitis, dacryocystitis. Futaron drops should be prescribed to patients over one year of age. Dispensed by prescription.
Tetracycline ointment, like any potent antibiotic, can be dangerous if used incorrectly. If you consult with an ophthalmologist and follow all his recommendations, the risk of adverse reactions is minimal, but the chances of a full and quick recovery are high.
Sources used:
- Taking care of your eyes. Vision problems from dry eye syndrome to macular degeneration / Jennifer S. Weiser, Joshua D. Stein. - M.: Art-Rodnik, 2012.
- Directory. Eye symptoms, syndromes, diseases / R.I. Korovenkov. - M.: Khimizdat, 2001.
- Emergency ophthalmology / Edited by E.A. Egorova. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2005.
- University of Nebraska Medical Center