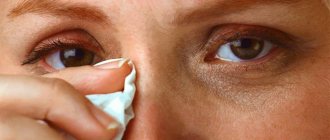
Why do my eyes hurt when I have a fever?
- With colds or viral diseases that are accompanied by fever, our body is greatly weakened. When it increases, inflammatory processes begin in the body, which indirectly provoke pain in the eyes. Experts name two main reasons for this phenomenon.
Spread of toxins. Viruses and bacteria in the body begin to release decomposition products. At elevated temperatures, blood flow increases and toxins enter the body's muscles, causing weakness and pain.
- The second reason is sinusitis, inflammation of the paranasal sinuses. When you have a cold, the nasal mucosa swells. It is necessary to take vasoconstrictors, otherwise it becomes difficult to breathe through the nose, and the pressure in the sinuses increases. It is its increase that causes pain in the frontal part of the head and around the eyes.
Eye pain occurs for various reasons depending on the disease. We’ll tell you more about this, as well as ways to get rid of pain symptoms.
Treatment with drugs
We have found out why the eyes hurt when a child or adult has a cold, and now we will look at ways to deal with unpleasant sensations. The symptom can be caused by different diseases, therefore the treatment methods may be different, depending on the clinical case. At the same time, there is one general recommendation that allows you to quickly remove eye pain from a cold. It is necessary to establish a drinking regime in order to quickly remove toxins from the body, and you should also rest more.
In case of a cold in which the eyes hurt without fever or with a slight increase in temperature (up to 37 degrees), you can take a drug based on paracetamol or NSAIDs. They normalize temperature and relieve inflammation, having a beneficial effect on the body and eliminating headaches and eye pain.
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) include Nise and Ibuprofen, which effectively fight muscle pain, and they often provoke soreness in the eyes during a cold.
Powders containing paracetamol and decongestant components also help:
- Fervex;
- Rinza;
- Coldrex;
- TeraFlu.
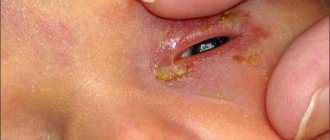
They relieve painful symptoms and eliminate tearing, itching and burning. When conjunctivitis develops along with a cold, it is better to see an ophthalmologist or tell your therapist about it. Without a doctor, it is not easy to cure such a complication, and it can become chronic. Bacteria will simply lose sensitivity to the components of the drugs. Most often, doctors prescribe medications for patients with conjunctivitis for colds such as:
- Sulfacyl Sodium;
- Albucid;
- Tsipromed.
These are all topical antibiotics instilled into the eyes. If conjunctivitis during a cold is viral, careful eye hygiene is necessary with rinsing with Furacilin solution and the use of interferons (for example, Actipol).
In serious cases of pain in the eyes due to a cold, doctors prescribe eye ointments to patients, and Tetracycline is especially common. Sometimes doctors use antibacterial drops, including:
- Torbex;
- Gentamicin;
- Tsiprolet.
It is important not to start treatment for sinusitis, since advanced stages require a puncture of the sinus. In the initial stages, vasoconstrictor drops and local antibiotics help, as well as regular rinsing 3-4 times a day. Additionally, doctors recommend taking vitamins and doing phototherapy, which relieves discomfort and improves the condition of the patient’s nervous system.
Why do your eyes hurt when you have a cold?
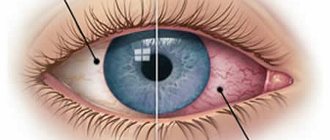
Eye pain due to colds is usually caused by sinusitis. At the same time, the conjunctiva turns red, the nasal sinuses swell, and profuse lacrimation begins. There is a cutting pain in the eyes. The first signs of ARVI or a cold are fever and weakness. Sinusitis can also cause a severe headache in the frontal region; it becomes painful even just to raise your eyes up. In such a situation, you should clear your nose of mucus in a timely manner so that it does not clog the tear ducts and germs do not enter the nasal sinuses, otherwise this may aggravate the course of the disease. It is best to use disposable paper tissues. Drops that relieve swelling and constrict blood vessels help well. When the swelling subsides, the pain in the eyes should go away.
What is the danger of eye pain due to coronavirus?
Ophthalmologists at a Moscow clinic stated that the coronavirus has affected all medical branches, and eye pathologies are no exception:
- The most common complications of Covid-19 are conjunctivitis and blepharoconjunctivitis.
- Existing disorders in the blood coagulation system can cause thrombosis of retinal vessels and a natural decrease in vision.
- Cases of immune vasculitis of the fundus have already been described in scientific sources.
- After the end of the disease, cases of weakening of accommodation caused by stress in the body and its decompensation against the background of the destructive activity of the RNA virus were discovered.
Important!
Doctors noted that in many cases, patients experienced progression of an existing disease and the need for previously deferred surgical intervention. For example, immediate treatment of cataracts due to rapid clouding of the eye lens, which is not typical in the normal state.
How to get rid of headaches during illness
Of course, the whole body should be treated, then the accompanying symptoms will go away. But there are general recommendations for illness that will help you get rid of viruses faster. To do this, it is recommended to drink as much warm liquid as possible - herbal decoctions, berry fruit drinks, tea with lemon and honey. For colds and acute respiratory viral infections, the drug “Rinza” helps well, which has a complex effect: it removes nasal congestion and reduces temperature. Also, in the room where the patient is, you need to darken the windows so that the eyes are not irritated by daylight. If you follow bed rest and follow all instructions, the disease will go away in the shortest possible time.
MagazinLinz.ru team
An atypical symptom of coronavirus – eyes hurt
Ophthalmological complications occur in 5-7% of patients. One of the main signs of damage to the organ of vision is eye pain, which resembles the sensations of increased intraocular pressure. Several factors contribute to the appearance of ophthalmic symptoms during COVID-19 infection:
- the presence of ophthalmological diseases that, due to the penetration of the virus, enter the acute stage;
- inflammation of the eye membranes under the influence of a virus;
- vasospasm;
- increased intraocular pressure;
- the effects of toxins on nerve receptors located on the surface of the eyeball;
- increase in body temperature above 39 degrees.
Usually, with coronavirus, the eyes hurt when the body temperature increases. Doctors recommend giving the organ of vision the opportunity to relax at this time in order to prevent lens spasm. Therefore, it is advisable to spend a minimum of time at the computer and TV.
Symptoms
The spread of influenza to the eye area is accompanied by the following clinical symptoms:
- malaise (weakness, fatigue, drowsiness, lethargy);
- irritation, pain, burning, itching in the area of the superficial tissues of the eyes;
- inflammation and swelling of the eyelids and mucous membranes;
- redness of the conjunctiva, small hemorrhages rarely form, which subsequently resolve on their own;
- dizziness, headache, migraine;
- headache radiating to various parts of the head (ears, temples, back of the head);
- increased pain in the eye area with tension, for example, due to watching TV, prolonged work at the computer, or using the phone;
- nausea, vomiting;
- chills, accompanied by fever, with a change in body temperature from subfebrile values (37-37.5 degrees) to high (38.5 and above).
Complications from the flu may include one or more symptoms. Based on them, the doctor can suggest a diagnosis, which will be confirmed using laboratory and instrumental examination methods.
Delfanto® capsules – a modern remedy for dry and red eyes
Delfanto® is an innovative product based on the standardized MaquiBright® extract. It is used to treat and prevent xerophthalmia syndrome, and also helps eliminate itching, redness and other unpleasant symptoms associated with dry cornea.
Delfanto® capsules contain at least 35% antioxidants, which help fight the effects of oxidative stress. Polyphenolic anthocyanins present in the composition of the product help restore damaged cells of the lacrimal glands, normalize the production of tear secretions, which allows for natural hydration of the conjunctiva and cornea. The innovative tool has several advantages:
- convenient release form;
- a wide range of possibilities (restoring the functions of the lacrimal glands, moisturizing the conjunctiva and cornea with your own tears, eliminating discomfort, relieving fatigue);
- Possibility of simultaneous use with ophthalmic solutions.
Delfanto® capsules can be used to prevent xerophthalmia. Therefore, they are recommended for people whose activities involve high visual loads.
Traditional methods of treatment
Today traditional medicine remains very popular. If a patient with a cold has pain in the eyes when moving or at rest, the following treatment methods are recommended:
- washing the eyes with decoctions of medicinal plants (calendula, chamomile, etc.). They help relieve pain and swelling, and also have an anti-inflammatory effect;
- compresses based on a decoction of medicinal herbs. To do this, use a decoction of wild rosemary, St. John's wort, calendula, eucalyptus and other plants. A cotton pad should be moistened in the solution and applied to the eyes for 10-15 minutes;
- washing with a solution of strong tea (very often used for barley).
It is important to note that all manipulations must be carried out with solutions at room temperature and observing all septic rules (hand washing, using sterile cotton pads, etc.). Self-medication does not always bring positive results; it often leads to the development of serious complications. Therefore, at the first unpleasant symptoms, it is better to immediately consult a doctor.
Why do my eyes “burn”?
Many people periodically experience an unpleasant burning sensation in their eyes. Often, no special attention is paid to the problem, and the issue is solved by simple methods: rubbing your eyes, washing your face, blinking, or using eye drops. But, in fact, these sensations can signal serious health problems, which means not paying attention and hoping that everything will go away on its own is, at a minimum, stupid, and at a maximum – very dangerous for your health in the future.
Burning eyes can be associated with various health-related factors. And the reason is not always ophthalmological.
The most harmless of the cases when the eyes “burn” is fatigue of the visual organs during prolonged exposure to a TV, monitor or phone screen, watching a movie in a 3D cinema, or reading in low light. Components such as dry air or smoke in the room can significantly aggravate the situation and accelerate the onset of symptoms. This is where the problem can be solved by resting and using drops. But, eyes can “burn” due to other factors.
- Allergy. Dust, fur, pollen and many other allergens not only cause a person to sneeze, but sometimes also cause a burning sensation in the eyes. You can relieve the symptom with eye drops, after consulting with your doctor. But it is not possible to cure allergies this way. Once the effects of the drops wear off, the symptoms will return.
- Demodex mite activity. The microscopic mite lives on the skin and causes problems with hair, eyes, and facial skin. To get rid of it, you need to carefully monitor your face: wash your face, use medications. If the fact of demodex infection is established, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment.
- Reaction to a chemical stimulus. Some gases, aerosols and chemicals can cause itching if they come into contact with the eyes, respiratory tract or even exposed skin. If contact is accidental, most often it is enough to rinse your eyes as soon as possible. But, the reaction can be to dye or hairspray, deodorants. In this case, the substance causing irritation must be washed off completely. It is also recommended to consult a doctor, since such a reaction may not go away without leaving a trace.
- Inflammatory diseases of the mucous organs. Inflammation is the body’s protective reaction to pathogenic microflora. The burning sensation in the eyes in this case is a consequence of the body’s defense against infection.
- Mechanical effects on the eyes. The longer people rub their eyelids, the more itchy their eyes become. To stop this, you just need to remove the mechanical impact: stop rubbing and give your eyes a rest. However, eye rubbing is a consequence. But the reasons why a person may voluntarily or involuntarily rub his eyes can be very different. For example, a sharp deterioration in vision.
- Thermal or chemical burns. Itching in this case is the body's reaction to injury. It is urgently necessary to consult a specialist for examination and receive a recommendation for treatment.
- Lack of vitamin A. Causes dry mucous membranes, including the eyes. To normalize the level of vitamin in the body, you can buy special supplements at the pharmacy or eat foods containing it: fish, carrots, cheese. But first of all, you need to see a doctor and undergo a comprehensive examination.
- Hormonal disbalance. At the same time, many functions of the body begin to work incorrectly: there is a lack of vitamins A and C, which causes a burning sensation.
- Metabolic disorder. The eyes “burn” due to a lack of special proteins in the lens and the accumulation of harmful substances in the eyeball.
- Side effects of drugs. Itching may occur due to individual intolerance to certain components of the medications.
Due to any of these factors, the production of the lacrimal glands is disrupted. The amount of tears is not enough to completely moisturize the eyeball, so the person feels a burning sensation. If measures are not taken for a long time, regardless of the reasons for the appearance of symptoms, damage to the visual organs and specifically vision can become irreversible.
Treatment
To eliminate complications from influenza, complex therapy is used:
- antiviral agents aimed at eliminating the pathogen;
- antiseptics, antibacterial drugs, which are prescribed locally or systemically, they are aimed at destroying the infection that has developed as a result of complications;
- antipyretic drugs used every 4 hours when the temperature reaches 38.5 degrees or more;
- gargling with antiseptics and herbal solutions every hour to eliminate sore throat, inflammation and swelling;
- moisturizing drops in the eyes aimed at eliminating dryness and preventing damage to the cornea.
In addition to medications, it is necessary to adhere to bed rest, food used during the disease must contain useful substances, vitamins, trace elements, and minerals. It is important to drink at least 2 liters of water per day.
Features of the structure of the eye
The visual apparatus is quite complex.
This small organ contains many pain receptors, as well as nerve endings. This anatomical structure makes the eye very vulnerable to external environmental influences and pathological changes in internal organs. This reaction of the eyeball is normal. Pain in the eyes is caused by various disorders in the body. In addition to infectious diseases such as influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, this unpleasant symptom is caused by disorders in the lacrimal glands. Unpleasant sensations in the eyes are caused by hypertension and other somatic disorders. Obviously, this problem is a symptom of more complex diseases in the body.
Classification of eye complications
Complications of influenza on the eyes are divided into several types. Each of them has its own treatment:
- Inflammation of the cornea. The patient develops acute inflammation, redness, and swelling of the cornea. Body temperature rises. If the condition is not eliminated, a complication will arise in the form of decreased visual acuity.
- Inflammation of the iris. Inflammation, swelling and redness of the area develops. The shape of the pupil changes, which reduces the perception of surrounding objects. The condition is dangerous because the infection can spread to the internal structures of the eyeballs.
- Development of herpes. This pathogen is constantly present in the patient’s nerve fibers and blood. With complications from the flu, herpes is activated, which complicates the patient’s condition and worsens his well-being.
To prevent the development of complications from influenza infection, it is necessary to promptly consult a doctor and carry out treatment.