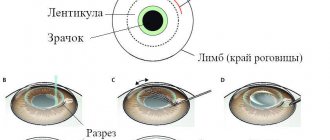
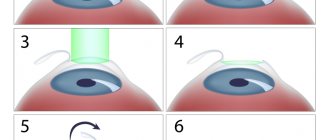
Laser vision correction (LASIK) is a surgery performed for refractive errors. Many patients, especially middle-aged and elderly patients, are concerned about the safety of this procedure. According to ophthalmologists, the optimal period for such surgical intervention is the age from 18 to 45 years.
Why are these particular age limits set? This is due to ongoing processes in the visual system, which are directly related to the aging of the body. For example, people under 18 years of age are not recommended to undergo this operation, since their eyeball is still growing, which means that their vision may well change. In patients of the older age group, other problems are observed. First of all, this concerns eye diseases, but there are other restrictions on this procedure.
Content:
- 1 Rules for using the acquired vision
- 2 Professional restrictions in connection with LASIK
- 3 High myopia
- 4 Progression of high myopia
- 5 Retinal damage in high myopia
- 6 Excursion into non-traditional ophthalmology
Description
↑ Rules for using the acquired vision
First rule
— in case of injury or eye surgery, tell your doctor that you had laser correction.
The corneal flap adheres very tightly to the cornea, but remains a flap. Therefore, in the event of a serious injury or eye surgery, the cornea, which contains a sublayer - a corneal flap, will behave differently than a normal one: the injury will affect it differently, and it will need to be treated differently and longer, and vision it will be more difficult to return. We are talking about really serious injuries that will not go unnoticed even for an unoperated eye.
All of the above applies to surgical trauma. The most common cause of significant vision loss in adulthood and old age, along with glaucoma, is cataract - clouding of the lens. You can delay its development by instilling vitamin drops (Quinax, Oftan-Katachrome), but the only way to return satisfactory visual acuity today is only surgery. The incision for cataract removal is made mainly on the cornea or at the border of the cornea and sclera.
This incision can be considered an operational eye injury. When performing cataract surgery on a patient who has previously undergone laser correction, one problem arises. Instead of a clouded lens, an artificial one is placed during surgery - an intraocular lens (IOL). There may be problems with accurately calculating the optical power of the IOL. That is, after cataract surgery, the patient may be left with slight nearsightedness or farsightedness. If the thickness of the cornea allows, then no earlier than 3 months after the operation, laser additional correction can be done and residual ametropia can be eliminated.
Second rule
— it is advisable to conduct regular comprehensive ophthalmological examinations in clinics that provide laser vision correction, and be sure to inform the doctor about previously performed laser vision correction.
The fact is that all people, without exception, who have reached the age of forty, need to be checked by an ophthalmologist once a year.
The main goal of such examinations is the early diagnosis of glaucoma.
The most common method of this diagnosis is measuring intraocular pressure. It is measured through the cornea by either “shooting” a portion of air at it (non-contact pneumotonometry) or placing weights on it (Maklakov tonometry). The essence of these methods is to measure the resistance of the cornea to a strictly defined pressure force (air or weight). Based on the degree of this resistance, a conclusion is made about the level of intraocular pressure. In the last three to four years, ophthalmological science has noticed that the thickness of the cornea also affects the data of such measurements.
After laser correction, the thickness of the cornea is significantly reduced, not to mention the reduction in its biomechanical resistance capabilities. Accordingly, the data obtained during tonometry ceases to be objective and accurate.
There are devices that allow you to diagnose glaucoma in patients who have undergone laser correction, but the doctor must know that you have undergone laser correction.
“The fact that ophthalmologists themselves are not particularly keen to do laser correction is confusing”
— Pavel Cheslavovich, tell me, have you ever performed surgery on your colleagues?
— I often hear a similar statement about ophthalmologists. Of course, I performed laser vision correction on my colleagues just like other patients. These were not only doctors of other specialties, but also ophthalmologists.
Let me give you a few examples: in our team, more than 80% of employees who were forced to use glasses or contact lenses have already undergone surgery. We are confident that an employee should demonstrate by example the safety of the methods we use.
Why do some doctors or nurses continue to use glasses or contact lenses? Firstly, laser vision correction requires a normal cornea before surgery. Unfortunately, some of our employees, like our patients, have contraindications. Secondly, some of our employees have presbyopia (age-related farsightedness), which requires the use of glasses for near vision. Presbyopia cannot be corrected by laser vision correction.
I consider the results of our work highly appreciated by the performance of laser vision correction by our colleagues, including ophthalmologists from other regions.
↑ Professional restrictions in connection with LASIK
It may be difficult for the driver to drive at night.
It is better to undergo a medical examination for admission to work or upon admission to work (work at height, driver, etc.) no earlier than a month after laser correction.
Persons whose professional activities or hobbies are associated with a high risk of injury (boxers, rapid response law enforcement officers, etc.) should take into account that after LASIK, the likelihood of an unfavorable outcome from the treatment of SEVERE eye injury increases.
Some categories of military personnel and civilians (including cadets of military schools, flight attendants, persons entering law enforcement agencies and special services, etc.) before undergoing laser correction should clarify the specifics of admission to perform professional duties according to orders and regulatory documents.
Young people called up for compulsory military service are given a deferment of at least six months after undergoing refractive surgery. For those who had high myopia before correction, the diagnosis is usually written in the statement: “Condition after laser correction. High myopia." Yes, no one can cancel the diagnosis, because, despite the absence of minus diopters, the size of the eyeball remains large and all the consequences of high myopia on the retina remain. So get all the possible papers about the condition of your eye and prove to the medical board of the military registration and enlistment office your right to the category “limitedly fit in wartime.”
It's not about your desire to serve or not to serve. With your diagnosis, there is a very high risk of getting a total retinal detachment due to injury - irreversible blindness, disability for life. Don't risk joining the army after getting laser correction. Article 34 of the order of the Russian Ministry of Defense, which guides the commissions of military registration and enlistment offices, does not talk about myopia, but only about dioptres (6 dioptres for the army, -6.25 dioptres for a “white” ticket). However, there are other subparagraphs, except for “d”, and other articles, except for the 34th.
Prove that you are right, get a consultation report on the condition of your retina, and request additional examination. You can't join the army! As for strengthening the retina (preventive laser coagulation of the retina), this procedure only reduces the risk of occurrence, but does not completely eliminate it.
For those who are “mowing down” from the army, I must add the following. Ophthalmology is not a field in which you can easily and simply “squint”.
↑ High myopia
The range of low myopia is three diopters (up to -3 diopters), the range of moderate myopia is also three (from -3 to -6 diopters), but high myopia has no upper limit (above 6 diopters). Ophthalmologists sometimes use the term “extreme myopia,” but this is not the official terminology. High myopia is -7 diopters, -15 diopters, and -35 diopters.
It is in this uncertainty that lies the catch not only for laser correction, but also for all refractive surgery for high myopia, which consists of two problems: the progression of myopia and retinal damage.
↑ Progression of high myopia
There is a rule:
if myopia does not progress for 2-3-5 years, then it is considered stable and refractive surgery can be performed. This stereotypical algorithm of doctor behavior does not reflect the true picture. Unfortunately, it is impossible to guarantee stabilization of high myopia in each specific case. Most often, myopia (myopia) as a refractive error stops growing at the age of 18-20 years. But there is also the concept of “myopic disease”. This is no longer a refractive error, but a serious disease characterized by a gradual, slow, but steady increase in the size of the eyeball (and, accordingly, “minus” - myopia) throughout the patient’s life and progressive degenerative lesions of the retina.
When diagnosing myopic disease, the main difficulty is not to confuse it with myopia, a refractive error. Such differentiation is possible in severe myopic disease. But early diagnosis here is controversial and often subjective. Myopic disease is the progression of myopia and changes in the fundus. But high myopia can also progress and be accompanied by changes in the fundus. Up to a certain level of pathological changes, these two processes in most cases proceed the same way, sometimes not even differing in the degree of damage and speed of development. And such identity is observed precisely in the age range in which laser correction is so in demand among patients - 18-25 years.
If we return to practical advice, I repeat - not a single doctor can guarantee with 100% certainty that after eliminating high myopia using laser correction, myopia will not progress in the future. Of course, the patient's chance of getting high myopia again is negligible. Most likely, progression over the years can lead to mild myopia, but it will be difficult to live without glasses all the time. Not everyone can wear contact lenses after laser correction. If there is a margin of corneal thickness left, additional correction can be done.
To prevent the progression of myopia
(or to improve the tolerance of residual myopia), various traditional and non-traditional treatment methods can be used.
“I’m waiting for a year to pass after my second birth. I didn’t see any point in having surgery before giving birth.”
— Are there any restrictions?
— Laser vision correction is always preceded by a very important diagnostic stage. Based on objective data, we accurately identify the cause of vision loss and predict changes in the future. There are a lot of publications about laser vision correction, pregnancy and childbirth, explaining why laser vision correction can be performed before pregnancy.
In our clinic, laser vision correction is not performed on pregnant women or while breastfeeding. This is justified, on the one hand, by altered hormonal levels and the properties of connective tissue, and on the other hand, by the need to use drops after surgery.
↑ Retinal damage in high myopia
Not a single person is immune from retinal damage, especially a person with high myopia.
A large eyeball with high myopia leads to stretching of the retina and disruption of its nutrition. Malnutrition worsens metabolic processes in tissues, which leads to dystrophy (degeneration) of the retina. Peripheral and/or central chorioretinal dystrophy develops. In the worst case, a “dry” or “wet” form of damage to the macular region of the retina (from stage I to IV) may appear, leading to significant (sometimes complete) and irreversible loss of visual acuity. In case of serious pathological changes in the retina, a diagnosis of “myopic disease” is made.
Myopic
the disease develops rarely. For the vast majority of people, high myopia remains a common and harmless refractive error. Laser correction can neither lead to myopic disease nor cure it.
To prevent complications of high myopia in the fundus, it is advisable to regularly carry out a complex of conservative treatment. Regardless of whether you have had laser vision correction or not.
How to get rid of myopia? How to cure farsightedness? How to restore your vision after laser correction? The author of the book “Seeing Without Glasses,” Michael Richardson, will answer this and many other questions.
A course of drug treatment for high myopia. A preventive course of treatment should be carried out 1-2 times a year. The set of medications for the course of treatment depends on the degree of development of retinal lesions and is prescribed by a doctor. Excessive amounts of medications are not so much helpful as they are harmful to health.
To prevent complications of myopia and its progression, the following are prescribed:
calcium gluconate (0.5 g 3-4 times a day, 10 days) ascorbic acid (0.05 -0.1 g 2-3 times a day, 3-4 weeks) or ascorutin (2-3 times a day) day) nicotinic acid (0.01 - 0.05 g 3 times a day after meals, 15-20 days) halidor (0.05 - 0.1 g 2 times a day, 2-3 weeks) 0.125 -0.25 g 3 times a day after meals, 1 month) trental (0.05 - 0.1 g 3 times a day after meals, 1 month). Vasodilators should not be prescribed in the presence of retinal hemorrhages.
In the initial period of development of chorioretinal dystrophies, angioprotectors (ascorutin, dicinone, prodectin, doxium), hemostatic agents (calcium chloride, vikasol, aminocaproic acid), antiplatelet agents (ticlid and trental) are used.
Serious complications are treated with the administration of various drugs through intramuscular, intravenous and parabulbar injections. Physiotherapy is used - phonophoresis of aloe extract, magnetic therapy, microwave and laser therapy. Electrophoresis is undesirable - according to some data, it increases the risk of retinal detachment.
The drugs myrtilen-forte, blueberry-forte, strix, lecithin, etc. are gaining popularity.
“The laser will burn the retina”
- Is it really possible?
— Excimer laser vision correction is performed using a special laser that remodels the surface of the transparent cornea. The impact usually affects tens of micrometers of tissue (this is comparable to the thickness of a hair). Laser beams do not penetrate deeper into the eye. To affect the retina, the excimer laser beam must penetrate at least another 20,000 microns of tissue, which is impossible in principle.
The presence of myopia is often accompanied by changes in the retina, which can be detected before surgery. Such pathological changes also require treatment, which is carried out before laser correction.