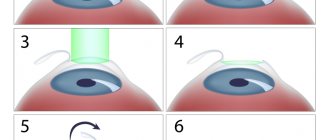
Laser correction is one of the most effective and minimally invasive methods to help restore vision. However, it is still an operation, which means it has certain contraindications. They are determined by the attending physician, based on the results of the examination. Read about contraindications on Ochkov.Net.
In this article
- What methods exist?
- Absolute contraindications for LASIK surgery
- Relative contraindications for LASIK laser correction
- Absolute contraindications for PRK
- Relative contraindications for PRK
- How long should I wait for surgery if there are relative contraindications?
Contraindications to surgery can be very different, ranging from a common cold to serious diseases of the body’s immune system. In modern ophthalmology, a division into two groups is accepted: relative and absolute contraindications. The first category includes those indications that are considered temporary, that is, after a certain period of time, it will become possible to perform eye surgery.
The second group includes those contraindications for which laser vision correction is strictly prohibited. Considering that every year the methods are improved and the technologies are improved, the number of contraindications to the operation is reduced. For example, some diseases from the “absolute” group are transferred to the “relative” group, and some are even completely crossed out from the list.
What methods exist?
Today, modern ophthalmology clinics perform two types of laser eye surgeries. The first technique is called LASIK. The name of this technology comes from the acronym LASIK (Laser-Assisted in Situ Keratomileusis), which in “medical language” means laser keratomileusis, that is, literally, separation of a flap of the cornea, entailing correction of its internal layers and then, upon completion of the operation, return flap to its original location. Indications for LASIK are:
- myopia no more than -15;
- farsightedness no more than +4;
- astigmatism from +3 to -3.
You can often find the terms Super LASIK or NASA LASIK used in medical journals or topical programs. As ophthalmologists say, this is still the same laser correction procedure, no different. According to their assumptions, such names were invented by employees of medical clinics who wanted to attract additional attention from patients.
Another technology that allows operations to be performed using a laser beam is PRK or photorefractive keratectomy. It involves removing the top layer of the cornea using an excimer laser. One of the most tangible benefits of PRK is the reduction in physical impact, which eliminates the risk of human error and the complete absence of any mechanical manipulation. Indications for laser vision correction using this method are:
- myopia up to -6;
- farsightedness up to +3;
- astigmatism from -1.5 to -3.
Each operation we presented above has certain contraindications. Some of them may be duplicated, preventing the patient from undergoing either operation. Others may be included in one list, for example, they are a contraindication for PRK, but at the same time allow LASIK laser correction.
Laser assisted keratomileusis (LASIK)
This is a more modern, effective and painless method of laser vision correction. This technique guarantees the correction of ametropia even in people with high degrees (up to 15 diopters) of myopia. The recovery period after it, in comparison with PRK, is also much shorter (one week).
LASIK is a combined technique that combines laser technologies and microsurgical techniques.
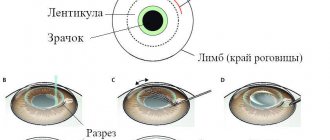
At the first stage of the operation, a superficial corneal flap is formed using a microkeratome (an automatic instrument). This flap is further moved back to access the deeper tissues of the cornea. The entire procedure is completely painless and lasts no more than 5 seconds. Then the laser stage begins, during which the stromal tissue is evaporated to the required depth with an excimer laser so that the cornea acquires the desired curvature. At the end of the intervention, the epithelial layer of the cornea is returned to its place. At the same time, the duration of the entire operation does not exceed 15 minutes, and after just a few hours, the patient can leave the medical facility and return home.
Experts include the following advantages of LASIK: painless operation and recovery period; preservation of the anatomical layers of the cornea; absence of rough postoperative scars; high predictability of results.
Among the disadvantages of the method, it is worth noting: the possibility of the occurrence of Hayes phenomena due to cicatricial changes in the cornea and halo effects. In addition, even in the distant future, the patient remains at risk of dislocation of the corneal flap due to injury.
Absolute contraindications for LASIK surgery
Among the general list of contraindications, in the presence of which laser vision correction is contraindicated, absolute ones play a special role. Their group includes those in which LASIK is not only prohibited, but can also lead to very negative consequences. Ophthalmologists distinguish the following:
- the presence of vascular diseases or diseases of the immune system, including: AIDS, systemic lupus erythematosus, multiple sclerosis, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.;
- keratoconus is an ophthalmological pathology in which the cornea of the eye, due to thinning, takes the shape of a cone;
- regular use of medications, for example, corticosteroids, one of the side effects of which is a negative effect on the visual organs;
- retinal detachment of the eye, not operated on in a timely manner;
- actively developing cataracts, reducing visual acuity;
- the thickness of the cornea is less than 400-450 micromillimeters;
- having only one eye.
In order to avoid negative consequences, before the operation, the ophthalmologist will definitely refer you to a general practitioner, who will have to conduct his own examination, and carefully study the patient’s medical history or write out a conclusion, or refer you to related specialists for these purposes, for example, an endocrinologist or rheumatologist.
Contraindications
The operation is not performed in the following cases:
- Age up to 18 years. Before adulthood, the formation of the eyeball occurs, so it is better to wait until the end of the process for adequate correction.
- Retinal detachment, glaucoma and cataracts. Such diseases make it difficult to accurately identify refractive problems caused by ametropia. Therefore, before prescribing laser corneal correction, it is recommended to get rid of the above pathologies.
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding.
- Keratotonus. This disease causes thinning of the cornea and changes in its shape. Exposure to it can lead to increased atrophic processes.
- Diabetes mellitus, vascular pathologies. In such cases, the blood supply to the retina is often disrupted and retinopathy develops.
- Dry eye syndrome, decreased sensitivity of the cornea.
- Inflammatory diseases in acute or chronic stages.
- Oncological processes.
- Severe mental illness.
Relative contraindications for LASIK laser correction
If the patient has relative contraindications, laser vision correction can be performed. However, this may take some time until the patient recovers completely or his condition cannot be assessed by an ophthalmologist as extremely severe, requiring emergency laser vision correction. The category of relative contraindications includes:
- the patient's age is less than 18 years;
- operated retinal detachment in the past;
- too rapid development of myopia;
- pregnancy or lactation period;
- tendency to allergic reactions and regular use of antihistamines;
- general infectious diseases of the body;
- dry eye syndrome;
- diabetes.
As a rule, the list of relative contraindications may vary depending on the patient's condition. That is why, before performing vision correction using an excimer laser, ophthalmologists recommend that you undergo other doctors who will give their opinion on the possibility of performing this operation.
Limitations after laser vision correction
The postoperative period after laser correction has many limitations. The main task of this stage is to allow the eyes to rest and recover effectively.
Therefore, for a week until the cornea recovers, it is prohibited:
- Wash and touch your eyes
- Use cosmetics;
- Strain the visual apparatus (any type of reading, needlework, watching TV, etc. is excluded).
For six months after surgery you cannot:
- Visit ponds, baths, saunas, swimming pools;
- Exercise;
- Drink alcohol;
- Smoking;
- Look at a source of bright light (applies to the rays of a strobe light, fireworks);
- Get pregnant.
It is also necessary to avoid exposure to direct sunlight, and therefore it is recommended to wear sunglasses even in cloudy weather. A number of other restrictions may be added to the above list at the discretion of the attending physician.
Absolute contraindications for PRK
The list of contraindications that completely exclude the possibility of performing photorefractive keratectomy on the eyes is not as wide as a similar list for laser vision correction using LASIK. These include:
- autoimmune diseases of the body, for example: systemic lupus erythematosus, myasthenia gravis, goiter, rheumatoid polyarthritis, scleroderma;
- disruption of processes associated with regenerative processes, in connection with which tumor-like growths of coarse fibrous connective tissue of the skin can form on the skin.
As you can see, the list of contraindications for laser PRK correction is much shorter than for LASIK surgery. Despite this, LASIK is, today, the most advanced method of vision correction.
Types of operation
There are two main methods of correction - PRK (photorefractive keratectomy) and LASIK (laser keratomyelosis). The first operation allows you to correct myopia up to 6 diopters, astigmatism up to 2.5-3 diopters. Both types of laser correction are carried out sequentially: first on one eye, then on the other. But this happens within the framework of one operation.
For laser correction of farsightedness and myopia complicated by astigmatism, Lasik is more often used. This is because PRK requires a long (up to 10 days) healing time. Each type of operation has its pros and cons, but still Lasik is a more promising direction, so this method is most often preferred.
Photorefractive keratectomy
The operation is performed under local anesthesia.
The doctor treats the eyelid and eyelashes with an antiseptic. Sometimes an additional antibiotic is instilled to prevent infection. The eye is fixed using an eyelid speculum and washed with saline solution. At the first stage, the doctor removes the epithelium. He can do this surgically, mechanically and laser. After this, the process of evaporation of the cornea begins. It is carried out only with a laser.
The method is limited by the required residual thickness of the cornea. To perform its functions, it must be at least 200-300 microns (0.2-0.3 mm). To determine the optimal shape of the cornea and, accordingly, the degree of its evaporation, complex calculations are carried out using special computer programs. The shape of the eyeball, the ability of the lens to accommodate, and visual acuity are taken into account.
In some cases, it is possible to refuse excision of the epithelium. Then the operations are faster and with less risk of complications. In Russia, a domestically produced Profile-500 installation is used for this purpose.
Laser intrastromal keratomyelosis
Preparations are similar to those for PRK. The cornea is marked with safe ink. A metal ring is placed over the eye, which additionally secures it in one position.
The operation takes place under local anesthesia in three stages. At first, the surgeon creates a flap from the cornea. He detaches the superficial layer, leaving it attached to the underlying tissue, using a microkeratome instrument—specially modeled for eye microsurgery.
laser vision correction: progress of the operation
The doctor removes excess fluid with a sterile swab. At the second stage, he bends the flap and performs laser evaporation of the cornea. The entire process takes less than one minute. During this time, the flap is also covered with a sterile swab. At the third stage, the separated piece is placed in its place, according to the previously applied marks. After rinsing the eye with sterile water, the doctor smoothes the flap. No sutures are required; the cut-off piece is fixed on its own due to negative pressure inside the cornea.
The possibility of performing an operation is determined largely by the anatomical structure of the patient's eye. To implement this, it is necessary that the cornea of the eye is of sufficient size. The flap must have a thickness of at least 150 microns. The deep layers of the cornea remaining after evaporation are at least 250 microns.
Video: how laser vision correction is done
Relative contraindications for PRK
As we said earlier, relative contraindications are not unconditional and undeniable taboos when performing laser correction. However, not responding to them would not only be wrong, but also dangerous to health. Such contraindications include:
- chronic infections of the eyes and eyelids, especially in the acute stage;
- pronounced lagophthalmos - a pathology in which the process of closing the eyelids is disrupted;
- viral keratitis and its consequences;
- neurotrophic diseases that provoke a decrease in the sensitivity of the cornea;
- cases of congenital cataracts;
- pregnancy and lactation;
- diseases that cause hormonal dependence.
Surely, you have noticed that some contraindications overlap with those indicated in the indications that temporarily prohibit LASIK laser vision correction. This is explained by the fact that despite the fact that the techniques are different, they have much in common.
Rehabilitation after laser correction
Rehabilitation after laser correction takes approximately the first six months, during which restrictions must be strictly observed, and, if necessary, continues for up to a year. After this period, one can reasonably judge the effectiveness of the surgical intervention.
Thus, laser vision correction is an excellent way to improve the quality of vision, but it must be remembered that it is not a panacea. In 15-20 years, or even earlier, the effect of the surgical intervention will disappear, and vision will begin to deteriorate again.
Also, the operation does not affect degenerative changes in the retina, which progress despite the surgically achieved 100% visual acuity. Therefore, it is much easier and more effective to protect your eyesight from a young age: maintain a work and rest schedule, do not read or watch TV in the dark, and perform special exercises.
How long should I wait for surgery if there are relative contraindications?
Many patients who have been given relative contraindications for laser correction are interested in the question of how long they will have to wait until the operation becomes available to them. If we are talking about such a prohibition as pregnancy and lactation, then in this case it is necessary to wait until the end of the moment when the woman stops feeding the child on her own.
This is due to the fact that after laser vision correction, patients are prescribed antibiotic drops that promote faster healing of the affected tissues. Another contraindication to surgery is rapidly progressing myopia. In this case, the decision about the possibility of vision correction directly depends on the attending ophthalmologist. If the degree of myopia has reached a critical level, then laser surgery can be performed, since in this case the risk from using an excimer laser is much less than the consequences of the lack of timely treatment for this refractive error.