One of the most insidious diseases is hypertension. It may not manifest itself at all, but at the same time cause significant harm to the body, affecting not only the kidneys, heart, cardiovascular system, but also the fundus of the eye. Along with this disease, hypertension can also lead to irreversible consequences for the eyes.
Hypertension and hypertension are diseases associated with high blood pressure. Their difference is that with hypertension the pressure is accompanied by sharp jumps, and with hypertension it is often not even noticed by the patient, since this phenomenon is constant and the body gets used to it. Both diseases negatively affect a person’s vision in their own way.
Vision at low and high pressure
Few people realize that blood pressure and vision are closely interrelated. It often happens that a person with hypertension begins to see poorly. However, vision deterioration can also occur with low blood pressure. Therefore, if you experience problems with blood pressure, you should pay attention to your well-being. Vision can be significantly reduced regardless of high or low blood pressure.
Relationship
High pressure
Hypertension has a detrimental effect on visual functions and leads to the following pathologies:
- glaucoma;
- angiopathy;
- retinal disinsertion;
- thrombosis;
- hemorrhages.
Disruption of normal blood supply is the main cause of visual impairment.
With frequent jumps in blood pressure, the arteries located in the retina swell, the lumen of the vessels decreases, which impairs the outflow of blood from the eye. Also, high pressure leads to damage to the walls of arterioles, which causes hemorrhage. Long-term exposure to these factors increases the risk of papilledema. The result may be complete or partial loss of visual function.
Low pressure
Hypotension has a negative effect on vision. Darkening of the eyes often occurs, and visual function also decreases for a short period. This happens due to a sharp change in eye pressure. This pathology also has a detrimental effect on the central nervous system. Constant overload leads to short-term loss of consciousness at low pressure, a symptom of which is darkening in the eyes.
Formation of edema
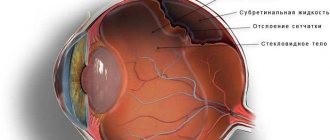
The occurrence of retinal edema and optic disc in the fundus of the eye during hypertension indicates a malignant course of hypertension. The accumulation of edematous fluid due to impaired blood supply leads to an increase in protein content. As a result, the retina becomes opaque.
Swelling of the optic nerve can be in various forms - from mild to the development of congestive optic disc syndrome with hemorrhages, exudates in the central zone of the retina and foci of local infarction.
The combination of signs of angiopathy described above, edema, hemorrhages and exudates are a typical picture of hypertensive neuroretinopathy (damage to the retina and optic nerve of a non-inflammatory nature). In its late stage, irreversible destruction of the vitreous body is observed.
Manifestations of pathology
Hypertensive disease disrupts the functions of the entire body. There are four stages of pathology, which are presented in the table:
| Stages of pathology | Manifestations |
| 1 | Arterioles narrow |
| The walls of blood vessels harden | |
| The shape of the lumen is disrupted | |
| 2 | Intersecting veins are compressed |
| 3 | Plasma penetrates the retina, which leads to the appearance of degenerative centers |
| 4 | The optic nerve swells. |
Return to contents
High blood pressure and vision
Changes in blood pressure disrupt normal blood flow in the organs of vision, which leads to the development of many pathological processes. The retina of the eye contains miniature arteries that are very susceptible to such changes. They swell and thicken as pressure increases. This causes a narrowing of the vessels between them and difficulty in the outflow of blood. As a result of prolonged hypertension, damage occurs to the walls of the retinal arteries, causing hemorrhage in the eye tissue. This can cause swelling of the optic nerve and lead to serious consequences, including loss of vision.
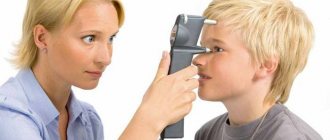
However, initially the process of destruction of retinal vessels proceeds unnoticed. A person may be bothered only by minor fluctuations in the clarity of vision. Sometimes during an attack, fog or a veil appears before the eyes, but these symptoms disappear on their own after the pressure normalizes. In some cases, you may notice slight hemorrhages in the eye. However, only a qualified ophthalmologist can detect pathological changes in the retina at the initial stage of development of hypertension when performing ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye).
A systematic increase in blood pressure causes various changes in the tissues and blood vessels of the eyes, which lead to a number of serious diseases. Patients with diabetes and glaucoma are especially at risk. Doctors say that the basis of all eye diseases caused by hypertension is damage to the eye vessels. The severity of pathologies is influenced by various factors, such as the height of blood pressure (mm Hg), the duration of hypertension, as well as the individual characteristics of the human body.
How does blood pressure affect vision?
- Initially, slight fluctuations in visual clarity appear;
- With a systematic increase in pressure, inevitable destruction of the blood vessels of the eyes occurs, which leads to a number of serious consequences: hypertensive retinopathy, hypertension of the visual organs, retinal detachment, angiopathy, papilledema, etc.
Diagnostics
Examinations are carried out using multiple measurements of the patient’s blood pressure. The disease is examined using a tonometer with a rubber cuff. For more accurate results, automatic devices are also used that take measurements throughout the day. An echocardiogram is required both at rest and under stress. Monitoring of cardiac activity is carried out using the Holter method (24-hour ECG). Diagnostic methods include examination of the fundus of the eyeball, during which the degree of change in the retinal vessels is examined. This indicates the degree of hypertension. To diagnose problems with eye pressure, you should consult an ophthalmologist. The patient is prescribed MRI and ultrasound. Most often, a Maklakov tonometer is used for measurements. This technique gives accurate results that will help identify the causes of the disease.
Stages of treatment and prevention
Therapy involves several types of treatment:
- stationary;
- outpatient clinic;
- sanatorium-resort.
After treatment at a day hospital, the patient is transferred to a local doctor, who monitors the further dynamics of the patient’s recovery. It is useful to undergo a course of therapy in a cardiac rehabilitation department, created on the basis of health resorts. Since hypertension cannot be treated, the patient must follow a certain daily routine and diet. At the end of the working day, a 2-hour rest is required. The duration of night sleep should be at least 9 hours, and daytime sleep - 2 hours. It is important to avoid stressful situations, conflicts at work, etc. All this leads to increased blood pressure. Following these rules will reduce the risk of vision impairment.
Source
Hypertonic disease
Hypertension, or arterial hypertension, is a disease accompanied by a systematic increase in blood pressure. It can be elevated constantly, or increase during stress, psycho-emotional and physical stress.
Blood pressure is considered elevated if it rises above the level of 140 and 90 mm. Hg Art.
As such, visual
in the early stages of hypertension is not observed.
Patients may be bothered by symptoms
such as dizziness, spots before the eyes, darkening of the eyes, for example, when standing up suddenly. The cause of visual impairment in this case is an increase in blood pressure and disruption of normal blood flow in the vessels of the orbit.
Other symptoms of hypertension:
- headache;
- weakness, fatigue;
- skin redness, sweating.
A reliable method for diagnosing hypertension is dynamic measurement of blood pressure using a tonometer. If blood pressure increases and concomitant vision deterioration, an appropriate study must be carried out to exclude pathologies of the kidneys, nervous system, endocrine system, and atherosclerosis.
The basis of treatment for arterial hypertension is the prescription of medications that lower blood pressure.
High blood pressure: the main causes of hypertension
Many people are faced with a disease such as hypertension, or a persistent increase in blood pressure. In normal condition, this figure is 120/80 mm Hg. Art. For some people, it may vary slightly to a lesser or greater extent, which is due to the individual characteristics of the body. However, if high blood pressure is constantly observed - from 140/90 mm Hg. Art. and more, a cardiologist diagnoses hypertension. This disease is very insidious because at first it can be asymptomatic. This is due to the fact that the body gets used to high blood pressure, so a person can feel good even with a reading of 180-200 mmHg. Art. At the same time, hypertension quietly has a destructive effect on the kidneys, heart, vascular system and fundus of the eye.
The reasons for the development of this pathology are very diverse. The occurrence of the disease may be associated with a hereditary factor, systematic stress, excess salt in the body, low physical activity, as well as excessive alcohol consumption, smoking and various diseases: endocrine, kidney, neurological, etc. As a rule, hypertension is diagnosed in people after 40 years of age However, according to cardiologists, recently the disease has become noticeably “younger”. Increasingly, increased blood pressure is diagnosed in people 25-30 years old with an active rhythm of life, who are susceptible to stress and increased mental stress.
An attack of hypertension is often accompanied by acute headache, tinnitus, rapid heartbeat, pulsation in the head, internal tension, anxiety, numbness of the fingers and swelling of the extremities, as well as redness of the face and pain in the heart area. Many people are interested in how increased blood pressure affects the human visual system. Let's take a closer look at what kind of relationship exists.
Stroke
Stroke is an acute condition characterized by a significant disruption of cerebral circulation as a result of blockage of a cerebral vessel, or cerebral hemorrhage.
In this case, entire groups of nerve cells are left without oxygen, as a result of which they can die. A stroke is characterized by the development of paralysis of the muscles of half the body and impaired sensitivity. At the same time, vision deterioration may occur in one or both eyes. The most common types of visual dysfunction are:
- complete blindness of one or both eyes;
- scotoma is a dark spot that is located in one half of the visual field, or in its center.
Sometimes these disorders may subsequently resolve on their own or as a result of treatment.
A stroke is easily diagnosed when a patient is examined by a doctor. The patient should be immediately admitted to the intensive care unit for treatment. Studies such as a biochemical blood test, a blood clotting test, CT and MRI of the brain, spinal puncture, etc. are prescribed.
The prognosis for a stroke depends on the extent of brain damage. Deterioration of vision in this case is not the leading symptom - there are more significant impairments.
Variants of visual disorders
The doctor may suspect that vision loss is due to cervical osteochondrosis during the initial examination of the patient and listening to his complaints. This is indicated by concomitant symptoms of grade 2 or 3 severity. The leading signs of osteochondrosis of any localization are pain when bending and turning the head, combined with stiffness of movements. But cervical pathology manifests itself in numerous symptoms of neurogenic origin. These include paresthesia, migraine-type headaches, dizziness, lack of coordination, and even fainting. The instability of visual disturbances becomes a definite clue to the doctor. For example, with a sudden movement or change in body position, colored circles appear before the eyes, disappearing within a few minutes.
The flickering of flies before the eyes and the flickering of colored circles are short-lived.
How does cervical osteochondrosis affect vision:
- “flies” flash periodically;
- often darkens in the eyes,
- the appearance of colored spots;
- “fog” appears before the eyes;
- objects double;
- field of view decreases;
- visual acuity decreases.
The peculiarity of neurogenic symptoms is that their severity does not increase with the progression of cervical osteochondrosis. The incidence of sudden visual disturbances increases as spinal structures deform and blood flow deteriorates.
The decrease in visual acuity in most cases is reversible. When the blood supply to the brain with oxygen and nutrients is normalized, all visual functions are restored.
Double vision
Diplopia is the simultaneous presentation of one object in two images. They can be shifted horizontally, vertically, diagonally, and sometimes even rotated relative to each other. In normal health, double vision does not occur due to the binocular effect, which expands the field of vision by covering elements common to both eyes. Such visual impairment with cervical osteochondrosis occurs for the following reasons:
- circulatory disorder in the cervical vertebral segments affected by pathology disrupts the work of all centers coordinating the functioning of the extraocular muscles;
- the signals received by them are distorted and unreliably display information, which provokes a temporary disruption in the functioning of muscle fibers;
- signals sent to the brain are processed incorrectly, and the perceived image loses clarity;
- to compensate for signal transmission disorders, the body increases the tone of the extraocular muscles;
- within a short time, clarity of vision fully or partially returns.
So there is “double vision” before your eyes.
The oculomotor muscles are not able to remain in a state of tension for a long period, so soon objects begin to double again. In the absence of medical intervention, diplopia becomes permanent and irreversible.
Another feature of this visual disturbance in cervical osteochondrosis is double vision of objects located close to the person. Doctors explain this by the fact that the extraocular muscles are exposed to maximum stress.
Decreased visual acuity
In rare cases, temporary loss of vision is observed with cervical osteochondrosis due to acute oxygen starvation. But much more often there is a decrease in its severity. If the patient does not see a doctor, then this condition becomes permanent. Clarity of vision is due to a certain curvature of the lens, which moves and changes thickness thanks to a group of special muscles. With cervical osteochondrosis, their coordinated work is disrupted for the following reasons:
- insufficient supply of parts of the brain with molecular oxygen and nutrients;
- infringement of sensitive nerve endings located near the cervical vertebrae.
With cervical osteochondrosis, visual acuity decreases.
When these negative factors combine, the muscles that move the lens weaken and lose their ability to function properly. The “lens” does not have time to adapt, which causes the unclear image. Vision is impaired according to the type of myopia, that is, the patient still sees distant objects well.
Flashing of black spots and colored circles before the eyes
The appearance of glare and “flies” in front of the eyes is a specific and very common visual disorder in cervical osteochondrosis. The reasons for this symptom are the same as doubling of objects or their unclear display. With a sudden movement or change in body position, the muscles located near the destroyed intervertebral discs spasm. There is a mechanical narrowing of the lumen of the vertebral arteries that carry blood to the brain. As a result, photopsia arise - a type of entoptic visual phenomena that manifests itself in the form of false flashes in the eyes, lightning, luminous sparks, zigzags, lines, and fiery flashes. The disorders are temporary, disappearing after the brain normalizes blood supply through reserve vessels (anastomoses).
Hypotension
Hypotension is reduced blood pressure, usually below 110 and mm. Hg Hypotension is not as dangerous a condition as hypertension. It may also be accompanied by some visual impairment.
With hypotension, the patient is concerned about the following symptoms:
- dizziness, headaches, pallor, cold sticky sweat;
- deterioration of vision in the form of “floaters before the eyes”, darkening of the eyes, especially with a sharp transition from a horizontal to a vertical position;
- decreased overall vitality, fatigue, weakness.
Retinal vascular thrombosis
Retinal vascular thrombosis is characterized by the formation of blood clots in the ocular arteries. This can occur as a result of diseases such as:
- increased blood clotting;
- hypertonic disease;
- diabetes mellitus, especially type 1;
- atherosclerosis.
Retinal vascular thrombosis is accompanied by deterioration of vision, which is characterized by a gradual decrease in its acuity. This process occurs very slowly over a long period of time. Complete loss of vision occurs extremely rarely, in cases where the pathology was not treated at all.
The diagnosis of retinal artery thrombosis is established after examining the patient by an ophthalmologist. Then conservative treatment is prescribed, which helps slow down the process of blood clots and vision deterioration. Surgical treatment has to be resorted to very rarely, only in advanced situations.
How does hypertension affect the retina?
One of the dangerous consequences of a persistent increase in blood pressure is hypertensive retinopathy. This is a disease associated with damage to the retina and disruption of its blood supply due to hypertension. The severity of this pathology is assessed using a special Keith-Wagener-Barker scale. During the examination, the ophthalmologist determines the degree of general and local narrowing of the arterioles, as well as the presence of hemorrhages. These changes are extremely dangerous, since in an advanced form they can lead to serious consequences, such as the appearance of scotoma (partial loss of an image fragment from the field of view), as well as the death of retinal cells and swelling of the optic nerve. It causes partial or complete blindness.
Diseases of the nervous system (migraine, epilepsy)
Epilepsy and migraine are two different diseases, however, they cause very similar visual impairments.
Epilepsy is a disease characterized by the appearance of a focus of pathological impulses in the cerebral cortex. In this case, convulsive seizures or other manifestations may occur. Deterioration in vision is usually noted immediately before the attack:
- dark spots and shadows in the eyes;
- bright flashes, spots of light before the eyes;
- creepy, pretentious images before the eyes, hallucinations.
Similar manifestations can be observed before migraine attacks - a very severe headache that occurs in one half of the head.
Source
Eye pressure - signs, symptoms, norms and abnormalities
Hello, readers of my blog.
Let's continue about the eyes ;). Unfortunately, no one is immune from such a disease as eye pressure . I have a friend, and she has been struggling with this dirty trick for a long time. After searching the Internet, this is what I found:
Eye pressure is a very common pathology. Increased pressure can be felt if you lightly press on closed eyelids with a finger, but most often people complain of the so-called “bloating.” At an appointment with an ophthalmologist, you need to disclose all your feelings. The pressure is very noticeable against the background of a number of diseases, among which are headaches and various viral diseases.
Constantly increased eye pressure, or glaucoma as it is also called, can lead not only to poor vision, but also to complete blindness. For this reason, at the first symptoms, you should urgently consult a doctor and strictly follow all instructions and prescriptions and undergo treatment.
Normal eye pressure is from 8 to 26 mmHg. Art. If the indicators do not go beyond the norm, we feel great. But if malfunctions occur in the body that negatively affect the secretion of natural fluids of the eye (strengthening it), as well as disrupting the functioning of blood vessels and the functioning of the heart, then this leads to pressure surges. Doctors list stress, increased physical and mental stress, and a recent illness as the main causes of failures. Another reason for increased eye pressure is a change in the structure (anatomical) of the eye.
Pressure accompanies many eye diseases. Accordingly, the ophthalmologist, before starting to examine the signs, first measures the pressure of the eyes. Elevated values indicate that eye function is impaired.
Accordingly, this disease must be treated with full responsibility.
Treatment of high eye pressure
At home, the patient can use only one method available to him - palpating the eyeball through the eyelids, determining by touch the degree of its density.
If the pressure is normal, then with gentle pressure you should feel a moderately elastic round ball under your fingers. With an increased IOP, it will be quite hard and not prone to deformation, but with a decreased IOP, on the contrary, it will sag. Of course, this method does not give correct readings and can only be used to understand the approximate condition, although people suffering from elevated IOP acquire the necessary skills over time. The exact data can be found in the doctor’s office, where he will conduct an examination using special instruments and also examine your fundus.
Tonometric measurement method. This is done using a tonometer. There are several types of them, but the most famous and common are Maklakov tonometer and Goldman tonometer. We will not go into technical details and a description of the measurement procedure, the only important thing is that these methods will help determine the exact intraocular pressure.
Non-contact blood pressure monitors. Sophisticated electronic devices that are used more and more often today, as this method gives even more accurate readings. If, with the help of the first two tonometers, a direct effect is made on the eye, drugs are used to anesthetize the cornea, since there is a physical effect on the organ of vision, then with the help of a non-contact tonometer, measurements are carried out using a stream of air directed at the cornea.
Today, the most common and accessible way to reduce increased ophthalmotonus is the use of special drops that normalize it. But you also need to take into account the reasons that provoked the increase in IOP, eliminating or treating them if possible. In addition to drops, there are also several other methods of combating high eye pressure.
The most drastic way to normalize blood pressure is surgery. There are also several types of them: goniotomy, trabeculectomy and the most advanced method - laser surgery. With the help of a laser beam, the outflow pathways of intraocular fluid are opened, as a result of which the ophthalmotonus decreases.
What to do if you are at risk? First of all, adjust your diet, thus promoting IOP stability. It is necessary to minimize the consumption of salt, sugar, fast carbohydrates and include the following foods in the daily diet: dark chocolate, nuts, eggs, red vegetables and fruits. It is also necessary to maintain a sufficient amount of vitamins E, ascorbic acid and beta-carotene in the body.
In addition to nutrition, you also need to follow simple recommendations from doctors, adhering to a healthy lifestyle: spend more time in the fresh air, give up smoking and alcohol, do not eat foods containing high amounts of cholesterol, do not spend long periods of time looking at gadgets and computer screens, and do special exercises for eyes.
According to various experts, changes in the fundus of the eye in hypertension are observed in 50-95% of patients. Periodic examinations by an ophthalmologist are one of the mandatory types of diagnostic tests for such patients. Monitoring the condition of target organs is carried out for the following purposes:
- determining the prognosis of arterial hypertension (AH);
- monitoring the course of the disease and visual impairment;
- assessment of the effectiveness and safety of therapeutic techniques.
In modern international recommendations for the management of patients with arterial hypertension, a system of criteria characterizing the risk and degree of damage to various organs in hypertension is constantly updated and developed. Fundus changes in hypertension are especially important in the initial stages of this disease, since the deterioration of the condition is often asymptomatic.
The blood supply to the optic nerve inside the orbit is via the posterior ciliary arteries. Blood circulation in the retina is provided by the retinal central vein. Impaired blood flow under the influence of unfavorable factors leads to a deterioration in metabolism in the retina and optic nerve.
In ophthalmology, there are 2 types of changes in the fundus – with and without retinopathy. In the first case, initial transformations of the vascular network are observed; the arteries still have a straight course, but their walls are already becoming dense and putting pressure on the veins, reducing their lumen. With a long-term condition, retinopathy occurs, complicated by hemorrhages and exudate from small arteries.
In the fundus of the eye with hypertension, the following pathological processes occur:
- angiopathy;
- arteriosclerosis;
- retino- and neuroretinopathy.
A photo of the fundus of the eye with hypertension, depending on the nature of the lesions, is presented below.
Eye pressure (norms): symptoms, treatment, pressure drops
Experts advise regularly measuring eye pressure, because it can reliably indicate the normal functioning of your visual system or warn of visual impairment. Moreover, both an increase and a decrease in pressure inside the eyeball is a bad sign.
Since it is the normal value of this indicator that contributes to the correct distribution of nutrients throughout the tissues and parts of the eye.
Particularly dangerous is the fact that increased eye pressure may not externally manifest itself in any way and may not affect the patient’s well-being, causing irreparable damage to the visual apparatus until it is no longer possible to reverse the process.
Increased eye pressure
Quite often, an increase in pressure in the eye leads to the destruction of the cells that make up the retina and negatively affects the metabolic processes of the eyeball. This condition is extremely dangerous for the patient, as it gradually changes the normal functioning of the visual apparatus and can provoke the development of various diseases.
Sometimes an increase in this indicator accompanies the development of glaucoma. Considering the fact that with such a disease, the filtration angle of the visual apparatus changes, a gradual increase in eye pressure within the departments of the visual system is understandable. Initially, the angle of vision narrows, and then can close completely.
By the way, such signs of pressure are accompanied by a drop in visual acuity and pain inside the eye.
Causes
There are several types of increased pressure inside the eyes:
- The transient type is caused by a short-term change in the indicator and its subsequent return to normal.
- Labile pressure also changes temporarily with subsequent normalization, but such changes occur regularly.
- Stable high blood pressure is constant, making it the greatest danger to humans.
After all, degenerative processes gradually progress and contribute to complete loss of vision or irreversible changes in the structure of the visual system.
The reasons for such phenomena can be a lot from hypertension or excessive load on the eyeball, to stress or nervous strain. Also, the root cause of increased eye pressure may well be the presence of heart failure or dysfunction of the genitourinary system in the patient.
A disorder of the endocrine system or age-related changes in the body (mainly menopause in women) can also provoke such a pathology. And sometimes the cause of a sharp increase in pressure inside the eyeball can even be poisoning with certain types of chemicals.
Symptoms
Symptoms of eye pressure will depend on the intensity of the increase in this indicator. If the changes are minor, then external signs may be absent altogether.
When the deviation from the norm grows, the patient may notice the presence of headaches, often in the temporal region, pain when moving the eyeball and increased fatigue in general.
Often, discomfort becomes especially noticeable when working in front of a computer monitor or when reading printed materials written in small print.
In especially severe cases, all of the above symptoms may be accompanied by visual disturbances or redness of the eyes. Although redness may indicate other diseases of the visual system.
Treatment
Treatment of eye pressure directly depends on the causes that provoked it. Often, drops come to the rescue that can increase the outflow of fluid and provide the eye tissue with additional nutrition. If the cause of high blood pressure is the development of a disease, then only by curing it can the pressure inside the eyeball be normalized.
If drug therapy cannot solve this problem and shows its complete failure, then the patient may be prescribed laser pressure correction. Sometimes microsurgical intervention is quite effective.
Traditional treatment
Traditional treatment of eye pressure has in its arsenal a lot of effective and inexpensive means of solving the problem.
A decoction of meadow clover is quite effective in reducing pressure inside the eyes. In order to prepare a healing infusion, the wonderful herb is brewed instead of tea, infused for two hours and taken one hundred grams before going to bed. The vodka tincture of the golden mustache has proven itself very well. To prepare it, seventeen purple knees of the plant (pre-crushed) are poured with half a liter of vodka and infused in a dark place for twelve days. By the way, during the preparation process, you need to lightly shake the container with the wonderful drink every three days. Take a dessert spoon of alcohol tincture early in the morning, thirty minutes before meals.
Another proven remedy for blood pressure is ordinary kefir. Taking one glass of delicious fermented milk product daily will help normalize blood pressure and maintain it at normal levels constantly, and adding a pinch of cinnamon to the drink will enhance the healing effect.
Drops
Drops for eye pressure
Eye pressure drops are quite popular in this area.
Currently, pharmacies offer a fairly large assortment of products of this nature, for every taste and budget.
Due to its properties to increase the outflow of excess fluid from the eyeball area and effectively nourish the tissues of all parts of the visual apparatus, this remedy can very successfully and quickly normalize high blood pressure.
Eye pressure standards
Normal eye pressure may vary slightly depending on the age and certain physical characteristics of the patient. But most often the norm for an adult is considered to be in the range from twenty-two to twenty-three millimeters.
Remember, regular eye pressure checks can warn you in time about negative changes in the visual system, which means it will help maintain the strength and health of your eyes for many years.
Deterioration of vision due to hypertension
In blood pressure without the use of antihypertensive drugs, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed periventricular changes. Subsequently, a J-shaped relationship was shown between the incidence of silent brain damage and the magnitude of the nocturnal decrease in blood pressure: multiple lacunae on MRI were found in 56% of over-dippers, 38% of non-dippers, and only in 6% of patients with a preserved circadian blood pressure rhythm. Signs of periventricular edema were found in 44% of over-dippers, 22% of non-dippers and 18% of patients with normal blood pressure reduction.
The effect of arterial hypertension on vision
In recent years, studies have been conducted that have shown a relationship between an excessive decrease in blood pressure at night and the progression of visual impairment in patients over 50 years of age due to ischemic neuropathy of the anterior branch of the optic nerve. The cause of this complication is considered to be a decrease in blood flow in the posterior ciliary artery, which can lead to infarction of the optic nerve nipple, manifested by its swelling. According to Hayreh et al. patients who developed this complication were characterized by a significantly more pronounced nocturnal decrease in blood pressure (25.3% for SBP and 31.2% for DBP) compared to normal values (10-20%). Moreover, patients whose vision loss progressed also had a significantly greater decrease in blood pressure at night than those whose visual impairment was stable (respectively 35.3% versus 26.8% for SBP and 30.5% versus 19. 6% for DBP). The data from this study supported the hypothesis that an excessive nocturnal decrease in blood pressure may be a factor provoking the development of ischemic optic neuropathy. Subsequently, the authors came to the conclusion that relative hypotension at night and in the morning may be important for the development of this complication.
Blood pressure studies
Studies conducted using ABPM have confirmed the importance of pulse pressure as an independent risk factor for the development of cardiovascular complications. At the same time, an abrupt increase in risk is observed when the average daily pulse blood pressure is >53 mm Hg. Art. while the critical level for clinical pulse pressure is considered to be 60 mmHg. Art.
The results of the Syst-Eur study made it possible to establish that the main factors determining daily fluctuations in blood pressure in elderly patients with ISAH are gender, age, smoking, and alcohol intake. Thus, the average daily values of SBP and DBP tended to be higher in men (150 ± 15/82 ± 9 mm Hg) than in women (147 ± 17/79 ± 10 mm Hg), however, the differences between sexes were significant. differences were only for diastolic blood pressure.
It is known that blood pressure increases acutely with smoking, possibly due to sympathetic stimulation. Population studies have shown that in smokers blood pressure in traditional measurements increases by 1-2 mm Hg. Art. higher than non-smokers. The Syst-Eur study did not reveal significant differences in the level of clinical blood pressure between smokers and non-smokers, while the average daily systolic blood pressure increased by 3 mm Hg. Art. for every 10-year increase in age, it was significantly higher in smokers.
Changes in blood pressure depending on age
The same study demonstrated clear dynamics of average daily blood pressure values depending on age. The average daily DBP in men was 2 mm Hg. Art. higher than in women and decreased by 1.5 mm Hg. Art. for every 10 years of increase in age. The day-night difference increased by 2 mm Hg. Art. for every 10 mm Hg. Art. increase in blood pressure measured by the traditional method and decreased by 5 mm Hg. Art. for every 10 years as age increased, it was 2 mmHg. Art. higher in women than in men by 6 mm Hg. Art. more in smokers.
In addition, the degree of nocturnal BP reduction was closely correlated with gamma-glutamyl transferase levels, used as an index of alcohol intake.
In elderly patients, the morning rise in blood pressure also has its own characteristics, which plays an important role in the complex of unfavorable neurohumoral and hemodynamic changes that determine a significantly higher frequency of cardiovascular and cerebrovascular accidents during this period of the day. Thus, according to Carmona J. et al., when comparing the magnitude and rate of rise in blood pressure during 6 morning hours (3 hours before the patient gets up and 3 hours after), in patients over 60 years of age, a sudden jump in blood pressure is recorded much more often, than in young and middle-aged patients. According to these data, more than 75% of cardiovascular events in elderly patients are recorded during these hours.
Blood pressure variability is an independent risk factor for the development of cardiovascular accidents and tends to increase with increasing age.
Symptoms of increased intraocular pressure
Increased eye pressure can lead to the development of various eye diseases, such as glaucoma. As a rule, at the initial stage of development of this disease, the symptoms of increased intraocular pressure are not pronounced. But it is at the initial stage that glaucoma can be treated non-operatively.
Therefore, in order to promptly detect increased intraocular pressure, you need to undergo a scheduled examination by an ophthalmologist at least once a year. As a rule, increased intraocular pressure is more common in people over forty years of age. Inside the eyes there is a special fluid that nourishes the cornea and other components of the eye. It circulates inside the eye, but it happens that the outflow of this fluid is disrupted, and it begins to gradually accumulate inside the eye. This leads to an increase in intraocular pressure in humans.
Various factors contribute to the accumulation of fluid inside the eye. One of them is obesity. Bad habits, a sedentary lifestyle and other factors can lead to this phenomenon. After all, our body is a single whole and all organs and systems in it are closely interconnected. A disruption in the functioning of one system inevitably leads to a disruption in the functioning of the entire organism.
- Symptoms of glaucoma include narrowing of the visual field. This can be checked by undergoing a special diagnosis in the ophthalmologist's office.
- And with glaucoma, a grid may appear in front of the eyes, which blurs vision.
- The above symptoms may be accompanied by pain in the eyes or constant waterlogging of the conjunctiva of the eye.
- The eyes may become red and watery. Pain may occur in or around the eyes.
All these symptoms should alert and prompt a person to contact an ophthalmologist for examination and diagnosis.
Treatment of vision problems caused by hypertension
If a person manages to start treatment in a timely manner and normalize blood pressure, then most retinal problems can be avoided. This requires regular ophthalmoscopic examinations at your eye doctor's office to evaluate the effects of high blood pressure on your vision. The condition of the arteries and arterioles is assessed only by examining the fundus. As a rule, normalizing pressure to normal levels is sufficient to eliminate the signs and consequences of hypertensive retinopathy. To do this, the patient undergoes a course of drug treatment aimed at taking vasodilators. Sometimes systematic medication is required to maintain normal blood pressure (often after 40 years).
If pathological processes are detected in the organs of vision (with advanced hypertension), an additional course of ophthalmological treatment is necessary. The sooner eye pathology is detected and the sooner a course of rehabilitation is selected, the more favorable the outcome. Ophthalmologists say that people with hypertension have every chance of maintaining 100% vision, subject to systematic examination and compliance with recommendations.
First signs
How to recognize the first signs of increased eye pressure?
One of the first symptoms is eye fatigue. Due to the fact that many people experience increased intraocular pressure after forty, they begin to attribute such fatigue to age and aging. But it's not worth the risk. If you feel that something is wrong with your vision, consult an ophthalmologist. Another symptom is decreased vision. It could also be headaches. They can easily be attributed to migraines, but they may well be caused by increased pressure inside the eyes. Typically, these symptoms may come and go, but never completely go away. This should alarm a person, because the first signs of increased eye pressure will help identify the disease at an early stage and prevent its severe course.
It is important to understand that it is better to play it safe and have your eyes checked at the first suspicion of increased eye pressure. Than subsequently undergoing a long course of treatment or undergoing surgery on the organs of vision.
What to do if you have symptoms?
So, first of all, if you suspect that you may have increased intraocular pressure, you need to consult a doctor.
During the examination, you will be asked to measure your eye pressure. It is important to understand that when measuring it, special drops will be dropped into your eyes. This could be Atropine - drops to dilate the pupil. You will have blurred vision for some time after this procedure, so it is important not to drive to the doctor or go alone. What to do if you have symptoms of high eye pressure if your suspicions are confirmed? An integrated approach to your health is important here. It is important to identify what led to the increase in pressure inside the eyes. If this is poor nutrition, obesity and a sedentary lifestyle, then drug treatment should be supplemented with exercise, diet and getting rid of bad habits.
As a rule, doctors prescribe medications that additionally nourish the eyes. For example, your doctor may prescribe Xalatan drops. These drops help improve the drainage of fluid from the eyes. These drops only need to be applied once a day. In this case, the dosage should not exceed one drop per eye. The drug can be administered to adults and elderly people. This medicine is not recommended for children, as no clinical trials have been conducted for children.
Xaltana also has contraindications. There are two types of glaucoma. These drops cannot be used for angle-closure glaucoma. Children's age is also among the contraindications to the use of this drug. It also cannot be used to treat glaucoma if the patient has an intolerance or allergy to one of the components of the drug.
Another drug that may be prescribed for the drug treatment of glaucoma is Travatan. This drug, like Xaltan, belongs to prostaglandins, that is, drugs that help fluid circulate better in the eyes and prevent its stagnation. This means they help reduce intraocular pressure. Travatan also needs to be instilled only once a day, one drop in each eye.
Side effects can occur if you overdose the medicine. They manifest themselves in the form of redness of the eyes and irritation of the eye mucosa. Contraindications to the use of this drug include pregnancy and childhood. If there is an allergic reaction to one of the components of the drug, it also cannot be used to treat glaucoma.
The next group of drugs that are used to treat glaucoma without surgery are cholinomimetics. These drugs narrow the pupil of the eye. Carbohol is one of these drugs. This drug should be used up to 4 times a day. In this case, 2 drops should be instilled into each eye at a time. These drops cannot be used if there are abnormalities in the cornea of the eye. Side effects include burning and pain after instillation.
Another group of drugs for the drug treatment of glaucoma are sympathomimetics. These drugs act on the nervous system cells in the eye and help improve the outflow of aqueous fluid. One such drug is adrenaline hydrochloride. For treatment, 2 percent rasters of the drug are used. Typically, side effects from this treatment may occur one or more months after you start using it. Instill this solution 2 times a day. Contraindications for use include hypertension.
Together with the above-mentioned drug treatment of glaucoma, it is advisable to maintain an active lifestyle. It can enhance the effect of such treatment and improve its results. Another treatment option is eye surgery. But sometimes it is possible to get by with laser eye treatment. Therefore, the sooner you consult a doctor, the lower the risk of surgical intervention.
Understanding the essence of the problem and knowing the symptoms will help you avoid serious consequences for your vision. If you know what the symptoms of high eye pressure are, you can get checked by a doctor promptly, treat the problem and maintain your eye health.
Myths about hypertension
QUIET-QUIET
Headache, increased irritability, and nausea bother most hypertensive patients only in the initial stages of the disease.
Then “not good” happens only during hypertensive crises. And since nothing hurts, they don’t pay attention to hypertension. But in vain. The leading cause of death in the world is cardiovascular diseases. According to the American Heart Association, they cause more deaths than cancer, Alzheimer's, and accidents combined. And hypertension, in turn, provokes these diseases. According to recent studies, hypertensive patients are 3-4 times more likely to develop coronary heart disease, and strokes occur 7 times more often than those whose blood pressure is normal. The fact is that high blood pressure injures the vascular wall, and cholesterol begins to deposit in it. This leads to rapid aging of blood vessels, and, consequently, early heart attacks and strokes. From the point of view of biological age, hypertensive patients are older than their peers with normal and especially low blood pressure. It’s not for nothing that hypertension is called the “silent killer.” 40% rule
40% of hypertensive patients know about their disease. Of these, 40% take medications. 40% of those who take medications take them correctly and in the right doses. That is, only 6.4% of hypertensive patients receive adequate therapy!
A WORD ABOUT GENDER
Every year there are more and more hypertensive patients. Moreover, interestingly, until recently it was believed that gender did not play a special role in the development of hypertension. Moreover, up to 80% of participants in hypertension research are men. However, it turns out that there are still differences. And a woman’s life, from the point of view of the risks of hypertension, is clearly divided into 2 stages. The first is before menopause. During this period, female hormones reliably protect the heart and blood vessels, so the chances of getting sick in women are generally lower than in men (provided that there is no metabolic syndrome). The second stage is menopause. At this time, in a matter of months, due to a decrease in estrogen production and an increase in androgens in the blood, gender advantages are lost. Moreover, by the age of 59, there are even more women with hypertension than men. By the way, it is estimated that by 2025, 793 million women in the world will suffer from hypertension. Very often, during menopause, high blood pressure is combined with excess weight and prediabetes. This condition is called menopausal metabolic syndrome. It further increases the risk of cardiovascular disease.
WHO IS GUILTY
Hypertension, or arterial hypertension, is an increase in blood pressure from 139/89 mmHg. Art. and higher, recorded at least twice in a patient at rest. In 95% of cases, this is essential hypertension, or, as it is called in our country, hypertension. It is impossible to name a clear cause of the disease; usually there is a whole complex of reasons related to heredity, lifestyle, bad habits, hormonal changes and constitution.
In 5% of cases the cause can be identified and (often, but not always) eliminated. These hypertensions are called symptomatic. The main organ involved in blood pressure regulation is the kidney. Problems with the blood vessels of the kidneys, the kidneys themselves, or the adrenal glands are the main cause of symptomatic hypertension. The disease can also be caused by changes in the thyroid gland, congenital and acquired abnormalities of blood vessels and the heart. Ideally, the diagnosis of hypertension should be made only after all symptomatic hypertension has been excluded. However, if your relatives have been diagnosed with hypertension, you are over 30, there are no kidney problems, there are no sudden increases in blood pressure, most likely you have hypertension. The doctor decides whether or not to prescribe additional examinations in this case.
Degrees of hypertension:
• I degree: 140–159/90–99 mm Hg. Art.
• II degree 160–179/100–109 mmHg. Art.
• III degree >180/110 mmHg. Art.
PEOPLE IN WHITE COATS
False-positive results occur with “white coat” hypertension. When you see a doctor, your subconscious mind remembers how, as a child, a person dressed like that gave you a very painful injection in your butt. This is stressful for you and your blood pressure naturally increases. Come home, measure your blood pressure, and it is completely normal. In this case, the solution is daily blood pressure monitoring. A device is attached to the body that measures blood pressure every 20-40 minutes throughout the day. This is the “gold standard” for diagnosing hypertension.
MYTHS ABOUT HYPERTENSION
- Hypertension causes headaches. Headache occurs in the same percentage of cases in people with normal, high and low blood pressure. Most often, headaches are not related to blood pressure. Most often, oddly enough, they are provoked by diseases of the cervical spine. Most people, even with systolic pressure over 200, do not have a headache. The only way to determine blood pressure is to measure it at least occasionally.
- You need to monitor your blood pressure very carefully. The other extreme is excessive attention to pressure indicators. It is usually not necessary to measure blood pressure more than 3 times a day. Moreover, this must be done in a state of physical and emotional peace, having sat quietly before the measurement for 10 minutes, in a warm room. There is no point in measuring blood pressure immediately after training in the gym, or when you are nervous, drink coffee or smoke - any person’s blood pressure increases in these situations. If a person starts measuring blood pressure every hour or more often, this will more likely lead to neurosis than help cope with hypertension.
- Electronic blood pressure monitors lie . This conclusion can be made if you measure the pressure with an electronic tonometer several times in a row. We will get indicators that differ by 5-10 mmHg. With. But the point here is that the device is quite accurate and detects the slightest fluctuations in blood pressure. You just need to measure the pressure 3 times in a row with an interval of 2 minutes and calculate the average. The readings of tonometers worn on the forearm may be inaccurate. Or if the width of the shoulder cuff does not match the circumference of the shoulder.
- The pressure needs to be reduced . The use of short-acting antihypertensive drugs for a quick but short-term reduction in blood pressure leads to a “swing effect” when blood pressure jumps up and down during the day. This therapy does not reduce the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- If your blood pressure is normal, you do not need to take the medicine. Normal blood pressure is maintained by a certain concentration of the drug in the blood. Therefore, the drug prescribed by the doctor must be taken constantly, even if the blood pressure is normal or low. Low blood pressure, by the way, is not a reason to stop taking the drug on your own; you need to see a doctor to adjust the dose.
- As soon as the pressure returns to normal, your health will improve. If a hypertensive person has lived with high blood pressure for many years, then reducing the pressure to normal levels can lead to dizziness, weakness and drowsiness. This is due to the fact that the vascular system has adapted to high pressure, and normal is not enough for “good” health. This, by the way, is the most common reason for refusing therapy. It must be borne in mind that the body needs 2-3 weeks to adapt to the new operating mode. Sometimes, if the pressure is too high, it is reduced in several stages. First, up to 140 by 90, after a few weeks, when the person gets used to it a little, up to 120 by 80.
- If the doctor prescribed a drug, but it does not help, you need to look for another doctor. Taking into account the individual characteristics of the body, the reaction to the same drug in different people can be completely different. Therefore, drugs and dosage are usually selected 2-3 times. The patient is prescribed a drug, he takes it and at the same time keeps a diary of “pressure, pulse, well-being.” After 2 weeks, a second consultation is usually scheduled to adjust the dose, if necessary, or add drugs from another group.
- I took the course and am healthy . There are no courses in the treatment of hypertension. This is a chronic disease, which is most often based on a genetic defect in the regulation of salt excretion from the body. Each molecule of sodium chloride retains at least 10 molecules of water in the body, the volume of circulating blood increases, which leads to an increase in pressure. It seems to our body that a pressure of 160 over 90 is “normal” for it. To convince him, you need to constantly take medications. If you stop doing this, the pressure will rise again. Accordingly, the risk of heart attacks and strokes will sharply increase, and life expectancy will decrease.
- There is "working pressure" and it may be higher than normal. According to the Framingham study, with a blood pressure of 130-139 over 85-89 (considered normal high blood pressure), the risk of cardiovascular disease increases by 2 times. There is no "work" pressure. This term arose due to confusion in cause and effect relationships. Many people believe that if a pressure of 130 over 85 often causes headaches, then this is hypertension, that is, “high blood pressure.” And if someone’s blood pressure is 160 over 100 and nothing hurts, then this is “working pressure.” Only in the first case, the person does not have hypertension, and he will live for a hundred years. But the second case is real hypertension, with all the ensuing consequences.
- The lower one is renal. There is a strong belief that an increase in lower diastolic pressure is associated with the kidneys, or rather with kidney diseases. Where? - here I am at a loss. Let's figure out what systolic (upper) pressure is and what diastolic (lower) pressure is. If you connect a pump to an inflated bicycle chamber and imagine that the pump is the heart and the chamber is the vessels, then the pressure in the chamber, which will be at the moment of pumping, will be systolic. And diastolic pressure is the pressure with which air presses on the walls of the chamber (blood presses on the walls of blood vessels) while the pump is not operating. The level of diastolic pressure will depend on the elasticity of the chamber walls. As a rule, diastolic pressure increases more in overweight people and people leading a sedentary lifestyle.
- If hypertension is a hereditary disease, then the pressure should be increased at a young age, and not just after 40. Until a certain age, the genetic defect in the regulation of the excretion of sodium chloride from the body can be compensated for by other regulatory systems. But these systems can fail, especially if a person leads an unhealthy lifestyle, is nervous a lot, does not watch his weight, or eats too much salt.
- If you lead a healthy lifestyle and lose weight, you can get rid of hypertension without pills. Lifestyle changes are the basis of antihypertensive therapy. It is worth giving up salt, walking 10-15 thousand steps daily, monitoring your waist size (less than 102 cm for men and 88 cm for women), giving up smoking and stopping abusing alcohol. However, in isolation, without the addition of pills, all this will help only at the very early stage of the disease. In other cases, it is imperative to immediately prescribe antihypertensive therapy.
IN NUMBERS:
- Increase in systolic pressure by 1 mm Hg. increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases by 3.3%.
- Losing just 5% of your weight can significantly reduce your blood pressure.
- Each additional gram of sodium increases blood pressure by 5 mm Hg. Art.
Author: Alexey Utin Published: September 7, 2016