During pregnancy, a woman's body, under the influence of hormonal changes, is completely rebuilt in a new way. Metabolism is activated, a utero-placental circulation is created - all this affects the vital functions of the body, including the organs of vision.
The fact is that the blood flow in the eyeball is connected to the rest of the circulatory system in the body. From the second trimester of pregnancy, a woman feels a systematic change in pressure - it usually decreases. Due to the decrease in pressure, the amount of blood flowing to the eyes decreases. If pregnancy is accompanied by late toxicosis or gestosis, then circulatory disorders become even more noticeable. A woman can feel them as early as 28–32 weeks of pregnancy.
What is myopia?
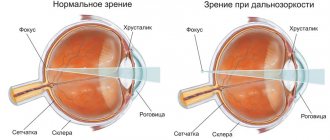
Myopia (myopia) is an eye disease in which the image is focused not on the retina, as it should be normally, but in front of it. That is, a person blurrily sees those small and large objects that are located far from him. Whereas when looking at objects located close to the eyes, there are no difficulties, they seem clear.
It is precisely because people with myopia can see everything close to them perfectly that the familiar Russian-language designation for the disease appeared - myopia.
As a result of the disease, the size and shape of the organs of vision may change, taking on a more oval and elongated shape. Due to the deformation of the eyeball, the image does not focus correctly on the retina.
With myopia, not only does visual acuity decrease (this is the most harmless symptom of all possible), in addition to this, pathologies of the retina arise, since due to the increase in the size of the organ of vision, it becomes stretched and strained.
Myopia can be congenital, hereditary, acquired and mixed. Congenital is characterized by an abnormal structure of the eyeball. It is often caused by infectious diseases suffered by the mother during pregnancy. This type cannot be cured completely, but you can at least stop the decrease in visual acuity.
The hereditary variant does not immediately manifest itself; it is usually transmitted from both parents, and not from one. In this case, only partial improvement of the condition is also possible; complete recovery remains unavailable. The acquired disease develops over the years as a result of excessive loads on the visual apparatus; it is most typical for schoolchildren and students who incorrectly distribute visual activity and do not follow a daily routine.
Myopia reduces a person’s quality of life and interferes with the full realization of the individual in society.
Prevention
To avoid vision problems, do not overstrain your eyes and take a break from working at the computer and reading every couple of hours. Do not forget about the importance of rational and nutritious nutrition. Especially during pregnancy, a woman needs to eat fresh vegetables, fruits, and vitamin complexes.
It is also recommended to follow a daily routine and get enough sleep. Protect yourself from emotional and physical stress.
If there are any vision problems, perform special eye exercises. Visit your ophthalmologist regularly and wear contact lenses and glasses if necessary.
Myopia is not an indication for cesarean section. However, if the disease is severe or degenerative changes are observed in the retina, natural delivery is risky. Childbirth can cause hemorrhage and complete loss of vision.
Myopia and pregnancy:
See also:
- Characteristics, symptoms and treatment of eye myopia
- Eye diseases in children
- Glaucoma of the eye - causes and symptoms
- Treatment of “lazy eye” in adults: ways to cure the disease
- Complex hypermetropic astigmatism: causes, symptoms and treatment methods
- Drugs for the treatment of anemia during pregnancy
- Treatment of retinal hemorrhage
- Corneal clouding: treatment of eye pathology
- How to get rid of strabismus: traditional or folk medicine
(No Ratings Yet)
About the author: Natalya MirBodrosti
« Previous entry
Degrees of the disease
The higher the degree of the disease, the worse the person sees. There are 3 degrees of this disease:
- Weak (myopia I degree; up to 3.0 diopters). The main symptom observed in people with this degree of pathology is squinting of the eyes. This happens when a person tries to focus on an object. Also in this case, rapid fatigue due to stress on the visual organs and frequent blinking are characteristic. Often there is increased sensitivity to light and discomfort in the eyes. It happens that a weak degree develops over several years without causing severe discomfort. However, you should still consult an ophthalmologist, since myopia is often accompanied by astigmatism (deformation of the cornea or lens body), and this is a more serious pathology, due to which you can completely lose visual acuity. If you notice the problem in time, it will not be so difficult to cure.
- Moderate (second degree myopia; 3.25-6.0 diopters). The quality of visualization deteriorates already from a distance of 2-3 meters; a person does not clearly differentiate objects located at a small distance from himself. The disease develops rapidly, the retina, blood vessels and tissues of the visual organs are deformed. If treatment is not started in a timely manner, visualization will deteriorate even at a distance of half a meter. At this level, doctors prescribe wearing glasses or contact lenses. If myopia is accompanied by additional pathological changes in the optical apparatus, it is advisable to perform laser correction or ophthalmic surgery.
- High (III degree myopia; more than 6.0 diopters). In this case, the blood supply to the visual apparatus is disrupted, as a result of which the retina is severely affected, and the eyeball increases in size. A person distinguishes objects no more than at arm's length from himself. To examine, he brings objects close to his eyes. This pathology can only be eliminated through surgery. In severe cases, the lens is replaced.
Symptoms of myopia during pregnancy
The clearest and most striking symptom of the development of myopia is deterioration of vision when trying to see objects located in the distance. If a woman knows about her illness, then she also knows about its characteristic symptoms, which will be present throughout pregnancy.
However, it happens that for the first time they can be experienced while carrying a child, so it is worth paying attention to the following signs and diagnosing them correctly:
- Flashing before my eyes.
- The appearance of outbreaks.
- Clouding of visible objects, distortion of their shape.
- Rapid eye fatigue.
- Loss of objects in the field of vision, which is characterized by its narrowing.
- Feeling of discomfort in the eyes.
- Headaches and pain in the forehead and eye sockets.
Since while carrying a child, a woman experiences changes in all systems and organs, even if there are no vision problems before, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist at least once.
Reasons for the development of the initial stage of pathology
One of the presented causes or a combination of them can lead to the initial development of the disease.
Heredity
It is not myopia itself that is inherited, but the predisposition to it, the size of the visual organs, and the refractive properties of the lens. If both parents have any degree of the disease, then their child is automatically at risk. In the case where the pathology is observed only in the mother or father, the risk of difficulties in the child is reduced by 30%. Still, it’s worth worrying about prevention.
Lack of microelements
Due to improper nutrition, the body does not receive the necessary microelements, it is weakened, which leads to a decrease in visual function. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully ensure that the foods you eat are filled with beneficial microelements.
It is recommended to take additional vitamins (before this, it is advisable to consult a doctor). Eating should be monitored before illnesses occur in order to reduce possible risks.
Violation of hygiene requirements
To preserve vision, there are hygienic requirements. If they are not followed, problems will arise in the visual apparatus. What can't you do?
- overstrain the eyes, giving them excessive stress;
- read in a moving vehicle, in a dark room, in a supine position (both on your back and on your side);
- spend many hours on the computer, telephone, TV and other gadgets;
- leave a distance of less than 30 centimeters between yourself and a book, screen or monitor;
- do not allow your eyes to rest while working (at least once every 40 minutes);
- work with small objects for a long time;
- Do not protect your eyes from ultraviolet radiation.
Important! It is recommended to comply with hygiene requirements not only to improve the condition of the visual organs, but also to prevent the occurrence of disorders. If these rules are neglected, visual acuity can decrease by up to 3 diopters per year.
Past infections
A number of diseases that weaken the body can lead to decreased visual acuity. These include the following:
- damage to the musculoskeletal system (scoliosis, flat feet, etc.);
- allergies;
- infectious diseases (measles, diphtheria, scarlet fever, etc.) suffered by both the child and the mother during pregnancy;
- rickets;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- tuberculosis;
- infectious hepatitis;
- reduced immunity.
Hormonal imbalances
Hormonal imbalances occur as a result of improper functioning of the endocrine system. They disrupt the normal functioning of other body systems: cardiovascular, digestive, and also lead to diabetes and vision impairment, among other things. Hormonal imbalances are difficult to recognize, they rarely have specific symptoms, and they are similar to other ailments. At the slightest suspicion, you should consult an endocrinologist.
Hormonal changes are caused not only by disturbances in the endocrine system, but also by pregnancy. Every third pregnant woman experiences mild myopia. A slight decrease in visual acuity is not considered critical; it is only a response to hormonal changes in the body. If the process of gestation and childbirth goes well, visual functions are restored.
Birth injuries
Birth injuries in newborns, which are accompanied by damage to the visual areas, can lead to myopia in the child. Often the cause is damage to the cervical spine, because it is next to it that the visual centers of the brain are located. Injuries cause disruption of blood supply and lead to vascular spasms - this already has a high probability of eye diseases.
Causes of myopia during pregnancy
The main reason for the development of the disease is its inheritance from parents to children. In addition, myopia can be acquired as a consequence of the negative impact of prolonged stress on vision, with frequent illnesses, due to traumatic brain injuries, etc.
However, during pregnancy there are additional risks of developing myopia due to the fact that:
- During pregnancy, especially in the third trimester, tissue elasticity increases, so pre-existing low myopia can cause serious problems, including retinal detachment.
- If a woman suffers from toxicosis, then myopia can worsen significantly, and vision can decrease to 5 diopters. The reason for this is the increased permeability of the lens capsule to water, its swelling and curvature, which will lead to increased refractive power.
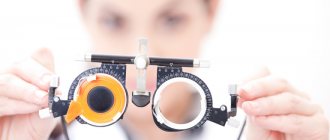
How is diagnosis carried out?
An adult often notices a decrease in visual acuity, but the child does not realize that he has begun to see worse than before. It is recommended that both adults and children undergo regular examinations, even if there seems to be no problem. Vision diagnostics is carried out by a doctor such as an ophthalmologist.
First of all, the patient is asked to perform a test, which is a table with letters of different sizes (the top row is the largest letters; the lower, the smaller they become). This method allows you to clarify the clarity of vision and select the optimal lenses. However, the diagnosis does not end with the tables, since this procedure is subjective.
If the doctor notes any deviations, then he will then use an ophthalmoscope to examine the fundus of the eye and the degree of refraction of the rays. Thanks to this method, pathological changes in optical structures are detected. An ultrasound examination can be performed when it is necessary to find out the size of the ocular axis and lens, the degree of retinal detachment, and the homogeneity of the vitreous body.
Expert opinion
Nosova Yulia Vladimirovna
Ophthalmologist of the highest category. Candidate of Medical Sciences.
Even parents can notice congenital myopia if they carefully observe their baby. A child with reduced vision will not react to the movement of objects far from him, but will notice only those that are directly in front of him. At the slightest suspicion, you should visit an ophthalmologist. If it is possible to detect pathology in the first 3 years of the baby’s life, then only special exercises will be enough to correct the problem.
Myopia and retinal detachment
Retinal detachment occurs due to its rupture, for example, due to thinning or dystrophy. After rupture, the intraocular fluid penetrates under the retina and peels it away from the choroid, with which they are in close contact in the healthy eye.
The process of retinal detachment is accompanied by characteristic clinical manifestations. Here are the main complaints that should alert the patient:
- periodic blurred vision, a veil before the eyes, which cannot be eliminated independently by rinsing;
- the appearance of light sensations before the eyes (flickering, sparks);
- curvature of the objects in question.
If such complaints occur, you should immediately consult a doctor. Treatment must be carried out immediately. The viability of the retina persists for 7-10 days. And if you do not have surgery during this time, you can lose your vision. This disease cannot be treated with medication.
What are the risks for the expectant mother?
Myopia usually appears even before pregnancy, at a younger age. During pregnancy, it is possible that the disease will only get worse. Even in situations where a woman’s vision was normal, there is no guarantee that it will not deteriorate. Often problems still arise. First of all, it includes low myopia. It often develops into a moderate degree, especially if left untreated.
What is the reason?
Despite the fact that pregnancy is a natural process for the female body, it leads to physiological changes that affect not only the reproductive system.
During pregnancy, the expectant mother's intraocular pressure increases (an additional circulatory system is formed for the embryo). An absolutely healthy mother’s body is able to cope with these difficulties, and the pathology of the visual structures causes the retina to exfoliate and become deformed, and in severe cases, exfoliate. It is possible that the deformed fragments will simply rupture during labor during childbirth.
There are several other reasons, in addition to increased intraocular pressure and hormonal changes:
- due to the fact that fluid is retained in the body, the corneal layer changes its shape;
- body tissues, including visual organs, become elastic and do not retain their previous shape;
- intraocular metabolic processes are disrupted;
- changes appear in the vessels, which leads to insufficient nutrition of the eye structures.
Treatment
If during pregnancy a woman is diagnosed with visual impairment of 3 or more diopters, a mandatory repeated ophthalmological examination is prescribed. Treatment of myopia is not dangerous and does not affect the development of the fetus.
Mild myopia in pregnant women is treated using the following methods:
- Wearing glasses and contact lenses to correct and prevent vision deterioration.
- Laser coagulation to eliminate retinal dystrophy and detachment. The procedure is absolutely safe, but it is not recommended to do it later than 30 weeks of pregnancy.
- Surgical correction of retinal detachment.
If you want to give birth on your own, be sure to undergo treatment and vision correction. Indeed, with second and third degree myopia, a cesarean section is often prescribed.
Treatment of myopia during pregnancy
Laser coagulation of the retina is considered a completely safe and painless method of treating myopia. Thanks to this procedure, the retina is strengthened and, relatively speaking, sealed. In the future it will not peel off.
After laser coagulation, the expectant mother is required to visit an ophthalmologist every month. When there is a month left before the birth, the doctor gives indications on how to manage it. If there are no problems, natural childbirth is allowed. If the retina re-ruptures, another laser treatment is performed. Surgical intervention is used in situations where the retina is detached.
The only contraindication for exposure is signs of gestosis (it causes spasms in the blood vessels).
In addition to laser coagulation, vision correction with contact lenses or glasses is not prohibited. You can wear them throughout the entire process of bearing a child. Even to the maternity hospital you are allowed to take disposable lenses with you. They do not require special care and can be worn for up to 12 hours.
Possible complications
All pregnant women are examined by an ophthalmologist between the tenth and fourteenth week. An ophthalmoscopy is required to analyze the condition of the fundus. If pathological processes are identified, the doctor recommends laser coagulation or surgery (for retinal detachment).
| With moderate to severe myopia, a woman should be examined every trimester. The last visit to the ophthalmologist is at the thirty-sixth week, where the final decision on the method of delivery is made. |
One of the complications of anemia is gestosis; it is dangerous because it can cause a malfunction in the central circulation and aggravate deviations in the functioning of the organ of vision. In case of retinal detachment and swelling of the optic nerve, hospitalization is recommended. If therapy for gestosis in the first trimester does not produce results, and pathological processes in the fundus intensify, the pregnancy will have to be terminated.
How does pathology affect the way childbirth is managed?
Pathology affects the process of labor and can lead to complications. The method of labor management depends on its presence.
Is it possible to give birth through natural means?
With a mild degree of the disease, ophthalmologists do not give contraindications for natural childbirth, since the internal structures of the eye are minimally changed. A woman will be able to give birth on her own without any problems. A healed retinal tear or laser vision correction performed before pregnancy are not considered an obstacle to natural childbirth.
With an average degree of pathology, the situation becomes more complicated. When myopia does not progress, natural childbirth is allowed. During the entire pregnancy, the expectant mother will have to visit the ophthalmologist at least 3 times to identify all possible risks.
Reference. If a pregnant woman is diagnosed with moderate or severe myopia, and there is also a threat of retinal detachment, then a caesarean section is recommended. Natural childbirth significantly increases the load on the body and the visual apparatus in particular. There are high risks of serious injury or even blindness. Under such circumstances, doctors recommend a caesarean section.
Pregnant women with visual impairments especially need to take courses in preparation for childbirth. You can learn to breathe properly and relax between contractions. If you push incorrectly, it will only make your eye problems worse. Severe tension contributes to retinal detachment. With competent behavior during labor, the load on the visual organs is significantly reduced, and the risk of vascular injury is reduced.
Useful video
Myopia and pregnancy, what are the consequences?
Indications for surgical delivery
There are a number of indications for surgical intervention during childbirth:
- myopia progresses (i.e. visual acuity worsens by at least 2 diopters per year);
- moderate or high degree of pathology, accompanied by significant changes in the fundus;
- the retina of the eye is torn during pregnancy;
- severe degenerative changes occur in the retina;
- retinal detachment was operated on (it does not matter at what point in life the operation was performed, even if long before pregnancy; the sutures and scars made may come apart);
- they did scleroplasty and keratotomy (also does not depend on the time of the intervention);
- a combination of visual impairment with diabetes mellitus (it leads to impaired blood circulation and hemorrhages in the retina, which can cause it to detach during natural childbirth).
Problem of poor vision
In women of reproductive age, the diagnosis of myopia (myopia) occurs in approximately 30% of cases. With this pathology, the refractive systems of the eye cannot align the fundus with the focal point. As a result, the focusing of visual information does not fall on the retina, as in normal vision, but occurs in front of it. Because of this, objects located in the distance appear fuzzy and blurry.
The reasons for this type of poor vision can be different:
- Genetic predisposition. It has been proven that there are forms of myopia that are transmitted through the female line.
- Traumatic brain injuries. Affect the regulation of vision by the central nervous system.
- Infectious eye diseases. May lead to changes in the refractive media of the eye.
- Diabetes. Against this background, retinal anomalies are often found.
- Injuries to the eye itself. Blunt injuries can cause changes in the geometry of the eyeball and lead to myopia.
According to modern data, increased load (reading, watching TV) does not have an effect on visual acuity if there are no predisposing factors indicated in the list.
Not so much pregnancy as childbirth can cause a decrease in visual acuity. When examined by an ophthalmologist, a pregnant woman should tell about all the problems she has had with her vision. If your mother or grandmother wore glasses to look into the distance, this should also be mentioned.
Degrees of severity and types
Visual acuity is a key criterion for determining the degree of myopia. Expressed in how “strong” lenses are required to achieve 100% vision. Ophthalmologists distinguish the following degrees of myopia:
- Weak degree, when corrective lenses up to 3 diopters are enough.
- Average. The required refraction value is from 3 to 6 diopters.
- High. In this case, a correction of more than 6 diopters is needed.
With myopia, the parameters of the eyeball are increased in length, which indirectly thins and stretches the retina. Considering the changes in the body with the onset of pregnancy in tissues, blood vessels, and hemodynamics, the thinned retina may suffer: there is a risk of ruptures and detachment.
In addition to determining the severity, the type of myopia is also important. There are only two of them:
- Axial, in which the eyeball is elongated and the retina recedes slightly from the focal point. For example, genetic weakness of connective tissue.
- Refractive. We talk about it when everything is anatomically in order, but the refractive system of the eye works excessively. An option is a spasm of accommodation.
During childbirth, the first type is more dangerous. Since it is often hereditary, complications may develop with pushing and increased intraocular pressure. Most often, there is a sharp progression and transition of myopia from low to moderate or even high.
However, mild myopia during pregnancy, like moderate myopia, is not a threatening factor for the decision about the method of childbirth, if there is no progressive deterioration in the visual organs.
Therefore, consultation with an ophthalmologist is required at the beginning of pregnancy and shortly before birth. If vision deterioration progresses, it is easy to notice during a repeat ophthalmological examination.
Increased risk during childbirth
In the normal course of pregnancy and the absence of complications in the visual organs, natural childbirth is practiced without the risk of worsening the condition. A mild degree can become more severe if pronounced gestosis in the second half of pregnancy is observed in the later stages.
Labor pushing poses a particular danger in terms of the progression of myopia. Against this background, the following may occur:
- Hemorrhage into the retina and vitreous body.
- Retinal detachment and tears.
- Increased intracranial pressure and papilledema.
Even grade 1 myopia during pregnancy does not guarantee childbirth without deterioration of vision, which may be a reason to choose a cesarean section.
All women with any type of myopia should undergo preventive examinations by an ophthalmologist. If the disease progresses, the specialist will prescribe the necessary treatment or laser correction of the retina. By carrying out these measures before birth, you can significantly reduce existing risks and give birth naturally.
Danger during pregnancy
It happens that myopia appears only with the onset of pregnancy. The expectant mother should be wary of the following phenomena:
- Blurred image and distortion of visible objects.
- Light spots with closed eyelids, flickering “flies”.
- Eye fatigue.
- Narrowing of visual fields.
- Headaches, pain in the forehead and eye area.
If such signs appear during pregnancy, an unscheduled consultation with an ophthalmologist is required.
The risk of progression of myopia during pregnancy is associated with changes in the body. Women with gestosis require increased attention.
If already at the first scheduled examination of the ophthalmologist at 10–14 weeks, the doctor discovered breaks in the fundus, gross degenerative changes or retinal detachment, laser coagulation is performed and the patient is monitored every month. If foci of dystrophy and detachment reappear, another laser correction or surgery is recommended.
The degree of myopia is not a determining factor for deciding on the birth technique. Changes in the fundus and retina are more important. As a result of physiological changes in the body, pathological effects of toxicosis and other complications, retinal detachment or rupture may occur, which threatens reduction or loss of vision.
Previously, myopia was an important criterion for choosing tactics for managing pregnancy and childbirth. Nowadays, the attitude towards this has changed. Women diagnosed with myopia are seen by an ophthalmologist, treated, and the prognosis is often favorable.
How is moderate, mild, and severe myopia diagnosed?
Often a woman knows about the pathological condition of her vision organs even before registering with the antenatal clinic during pregnancy. The doctor will need to assess the severity of the disease and send the patient for a vision test by an ophthalmologist. He will assess the health of the visual organs using several diagnostic techniques:
- Ophthalmoscopy is a process that will allow you to assess the condition of the retina, blood vessels, nerves, and fundus of the eye;
- Analysis of visual acuity – allows you to assess the severity of myopia;
- The study of refraction is carried out using special equipment that allows you to check the refractive ability of the living optical system of the eye;
- Ultrasound of the eyeballs is a process that will allow you to evaluate the characteristics of blood flow in the organ.
Other diagnostic methods can be used, including biomicroscopy, when a Goldmann lens is also connected to the process. The technique will allow you to find out everything about the condition of the retina, etc.
Often, one examination by an ophthalmologist is not enough to give a conclusion about the need to allow a woman to have a natural birth or to send her for a caesarean section. To obtain a final conclusion, three visits to the ophthalmologist will be required, the last of which is planned for 35–36 weeks.