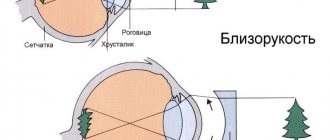
Refractive error - myopia, farsightedness, astigmatism - in most cases is caused by incorrect geometric proportions in the structure of the eyeball. Most often, the horizontal distance from the outer transparent corneal layer to the photosensitive zone of the retina is abnormal (too short or excessive). So, it is for this reason that almost all children are born farsighted, i.e. They see at a distance much better than at close range, however, as they grow and develop, the optical-geometric relationships are normalized and vision acquires its “calculated” acuity. In some cases, however, this process, for one reason or another, does not stop in time, and infantile farsightedness turns into its equally abnormal opposite - myopia, or myopia, develops.
Myopia in children: how does the disease manifest?
Myopia, or myopia, is a refractive disorder of visual ability in which the image of distant objects is focused not on the central zone of the retina, as happens under normal conditions, but in front of it. As a result, a person sees blurry outlines of distant objects. The described phenomena can occur in the visual system due to the irregular shape of the eyeball - its anteroposterior axis is elongated - or due to strong refraction of light rays.
It is important to know that almost all babies are born with farsightedness. Their optical vision index is approximately +3-3.5 diopters. This is explained by the fact that newborns have very small eyeballs. As it develops, vision stabilizes. If after birth the baby does not have a reserve of +3-3.5 diopters, then by a certain age the child develops myopia.
Heredity
It is reliably known that heredity has a huge impact on our health. Thus, the risk of myopia in a newborn is up to 50% if both of his parents had low vision. It does not matter whether their myopia is congenital or acquired, or what specific “minus” their parents have. However, even if you have good vision, the risk of having a child with congenital myopia is 8% due to the presence of external factors.
Congenital glaucoma, as well as abnormalities of the eyeball, lens or cornea can affect the appearance of myopia.
Features of myopia manifestation in preschool children
If a child does not yet know how to speak, then detecting the presence of a visual anomaly is extremely problematic. That is why already in the first years of the baby’s life it is necessary to show it to an ophthalmologist. The child’s first vision diagnosis is done at three months of age, then at six months and a year. The procedures allow the doctor to find out whether the baby has myopia or whether vision is developing normally.
In children under one year of age, myopia is extremely rare (as mentioned above, due to the reserve of farsightedness). However, in ophthalmological practice there are cases when myopia is congenital.
Therefore, the child should be regularly monitored by a specialist.
One of the characteristic signs of congenital pathology is divergent strabismus.
In children aged 3 to 6 years, identifying a visual abnormality becomes much easier because they can already speak and can easily communicate that they have trouble seeing. Parents will also be able to detect the problem by the child’s characteristic behavior: he will come close to objects to examine them, squint while looking into the distance, and may have poor orientation in space.
Myopia in school-age children and adolescents
Myopia in children reaching school age is a common occurrence. This is due to the fact that already from the age of 6-7 years a child begins to learn, and his visual organs are subjected to high loads when writing, reading, using a computer, gadgets, watching TV, etc. The result is elongation of the eyeball and progression of myopia.
Is it possible to restore vision in school-aged children with myopia? It depends on the pathology. Experts can give a positive answer if myopia is false, since this is a temporary phenomenon that is caused by a spasm of accommodation and occurs with severe eye fatigue. False myopia can occur not only in children, but also in adults at different ages. If the spasm is eliminated in a timely manner, vision is completely restored.
Types of Myopia
Myopia in children has a different nature and varies in type:
- False - as mentioned earlier, is caused by overstrain of the ciliary (eyelash) muscle, which as a result takes on an incorrect position and contracts. Therefore, the child sees poorly not only in the distance, but also, possibly, near. Such myopia in school-age children is curable. If the spasm is removed in time and prevention is started, the anomaly will not develop into true myopia, and the child will return to normal vision.
- Progressive is a form of true myopia in which there is a rapid decline in visual ability. Over the course of several years, myopia can go from mild to severe. However, children also experience temporary visual impairment. Having reached a certain value of the optical index, the progression stops, myopia takes on a stationary form.
- Physiological - occurs due to an insufficient reserve of farsightedness from birth. As soon as the growth of the eyeball stops, signs of myopia appear. The disease reaches a certain level (each child individually).
- Lenticular - the disease is typical for children who suffer from diabetes or central cataracts.
In addition, there are three degrees of severity of myopia:
- Weak - from -3 diopters;
- Medium - from -3 to -6 diopters;
- High - more than -6 diopters.
Clinical picture of progressive myopia
The main problem of myopia is its progressive potential against the background of increasing load near. Children prefer to spend time on computers or tablets instead of walking in the fresh air. As a result, there is a lack of oxygen and a lack of relaxation of distance vision.
For timely diagnosis of pathology, it is necessary to regularly visit a pediatric ophthalmologist. With progressive myopia, parents can independently notice changes, which are characterized by:
- the child squints his eyes, strains his facial muscles, trying to look at the object;
- there is an increase in anxiety, habits such as chewing pencils and pens appear;
- upon examination, the doctor observes a wide palpebral fissure, the increase of which is associated with the growth of the eyeball;
- the frequency of inflammatory reactions of the eye mucosa increases (conjunctivitis, iritis, iridocyclitis);
- narrowing of the field of angular space visible with a fixed gaze.
Many parents notice that their child has become worse in school, gets lower grades, and hangs his head as low as possible when trying to read a book.
How does myopia occur in a child?
In ophthalmology, there are risk factors for myopia in children. These include:
- Genetics - a child may exhibit myopia inherited from the parents;
- Premature birth - premature babies are predisposed to refractive pathology in 40% of cases;
- Incorrect sitting position when writing and reading, poor lighting;
- Regular high eye strain;
- Unbalanced nutrition - deficiency of vitamins and beneficial microelements in the diet;
- Infectious pathologies.
Past illnesses
Doctors recommend that expectant mothers see an ophthalmologist monthly, starting from 1 month of pregnancy, since the changes that occur in the body during this period can affect the sensitive optical system of both mother and child. In particular, the development of myopia in a newborn is influenced by diseases suffered by the mother during the period from conception to three months of pregnancy. Also, various visual defects, including myopia, can be a consequence of prematurity, acute respiratory viral infections, influenza or pneumonia.
Symptoms of myopia in a child
Clear signs of myopia in a child can be detected at 2-3 years of age. Experts include:
- Headache;
- Frequent blinking and rubbing of the eyes;
- Approaching objects close to the face in order to examine them;
- Squinting when looking at distant objects.
If the eye disease progresses, then vision begins to decline, the child sees worse and worse. Schoolchildren need to move to desks as close as possible to the board. If the above symptoms are detected, parents should take the child to an ophthalmologist for a comprehensive diagnosis and take appropriate measures.
Diagnosis of myopia
Methods for examining a child’s visual system vary depending on his age. Children under three years of age are diagnosed exclusively with the help of specialized instruments. Older children are studied using tables that show pictures or letters.
In addition, the vision diagnostic procedure may include:
- Fundus examination;
- Ultrasound of the visual organs;
- Refractometry;
- Skiascopy;
- Ophthalmoscopy.
After the examination, the ophthalmologist will make a diagnosis and prescribe therapy that can correct visual impairment.
Surgical treatment methods
In children, due to their early age and actively growing body and, accordingly, the eye, it is not recommended to undergo laser vision correction, replacement of their own lens, or implantation of phakic lenses, since the risk of complications and undercorrection is too great.
However, in some cases there are exceptions, and the choice of one or another method of surgical treatment is decided by the ophthalmic surgeon after an in-depth examination.
Laser vision correction
Depending on the characteristics of the operation, there are several types of laser vision correction: LASEK, LASIK, PRK. The surgical effect is achieved by reducing the thickness of the cornea by evaporating tissue with a laser with a certain wavelength.
Modern equipment makes it possible to accurately determine the size of the layer being removed. The method is not recommended until adulthood, since the length of the eye may change, and the optical power of the cornea achieved by the operation may be insufficient.
Replacing your own lens with an intraocular lens
The principle of the method is similar to the surgical method for treating cataracts. It is based on the removal of the native lens through a small incision with implantation of a lens into the lens bag.
It is worth noting that the bag of its own lens does not contain vessels, being a fairly dense connective tissue formation, so rejection is not observed. In young people, unlike older patients, ultrasonic crushing is not used, since the lens substance is quite soft.
Modern small incision surgery allows this operation to be done on an outpatient basis. In young people, it should be performed by an ophthalmic surgeon with extensive experience, since a number of complications occur.
Phakic lens implantation
A special lens of a certain shape and strength is placed in front of the lens in the anterior chamber of the eye, having previously carried out all the necessary studies. The method also applies to small incision surgery. Use before the age of 18 is not recommended, as undercorrection may occur.
Laser photocoagulation of the retina
Peripheral preventive laser coagulation is used in case of degenerative changes in the retina that occur against the background of high myopia. In the zone of dystrophy, the retina is thinned; any sudden movement, blow, or lifting of a heavy object can lead to its rupture, and subsequently to detachment.
Laser coagulation allows you to delimit this place like a barrier. Its implementation has virtually no effect on visual acuity, since problem areas are located on the periphery.
Scleroplasty
Used for staphylomas (protrusions) of the sclera. Allows you to both eliminate a cosmetic defect and strengthen the sclera.
Vitrectomy
Removal of the vitreous body, combined with laser coagulation and retinal tamponade with certain substances. Performed in case of retinal detachment. In children, tamponade of the vitreal cavity is used with silicone oil rather than gas, since children are more active and are unable to fix the head in the proper position for a long time. Unlike the use of gas, vision with silicone tamponade is quite good if corrected.
Silicone oil can cause the development of cataracts. In this case, an operation to replace the lens will be offered, with the selection of an exact calculated value taking into account age.
In case of strabismus, there are a number of operations aimed at eliminating it. In this case, the earlier surgical treatment is performed, the higher the effect. Before surgical treatment for strabismus, a thorough history is collected and an examination is performed.
Remember, treatment of myopia in children is compliance with a certain lifestyle, aimed at stabilizing the process and inhibiting the development of complications.
How to cure myopia in a child?
Treatment of myopia in children is aimed at restoring visual ability and stopping the disease. In the first case, as a rule, it is possible to correct myopia with the help of vision-correcting means - glasses or contact lenses. In the second case, an integrated approach is required.
How to cure myopia that is progressing? The complex may include the following methods:
- Drug therapy;
- Surgical intervention;
- Hardware therapy;
- Phytotherapeutic procedures.
Based on the data obtained after diagnosis and the individual characteristics of the patient, the specialist determines the necessary treatment method. As a rule, he gives recommendations to parents on selecting a child’s diet to improve his vision.
Establishing diagnosis
Myopia is the most common reason why we see distant objects blurry. Vision problems may be a sign of more serious eye problems, such as cataracts, or medical problems, such as diabetes.
Myopia is diagnosed by determining the clarity of a child's vision and is confirmed by an ophthalmologist using various methods.
The type and degree of myopia can be determined through additional testing, which includes assessing the child's binocular vision, eye movements, ability to focus on objects, etc. To identify associated complications (diabetes, degenerative myopia, etc.), the doctor uses a method such as dilatation (dilation of the pupil).
Optics for correcting myopia in children
One of the most common problems when choosing glasses for a child is his reluctance to wear them. In this case, you can choose a beautiful, stylish frame that your child or schoolchild will like, and choose contact lenses for him. The advantage of lenses over glasses is that they are not visible on the face, do not hinder movement, provide a wide viewing angle and do not fog up when the temperature changes. Not all parents know at what age children can wear contact lenses.
Ophthalmologists say that if the child is sufficiently independent and careful, lenses can be used from the age of eight. However, they are more often prescribed to schoolchildren over 12 years of age.
The second question that parents are often interested in is how to correct their vision with glasses, that is, is it worth wearing them all the time? Experts note that this will depend on the severity of the pathology. So, if a child has a mild degree of myopia, then glasses should be worn only when it is necessary to examine objects at distant distances. For example, in a lesson while using a blackboard. When moderate or high degrees of myopia are detected, wearing glasses becomes a constant necessity.
One of the most effective lenses for glasses are considered perifocal; they evenly distribute the light load throughout the retina and block the process of decline in visual function.
Development of medically induced myopia
A high degree of myopia can be associated with various syndromes: Ehlers-Danlos, Marfan, Down and Stickler.
Myopia is often observed with retinopathy, a serious eye disease that develops mainly in very premature infants, accompanied by changes in the retina and vitreous body.
Retinopathy occurs in 68% of low birth weight babies, and more than 80% of babies born with retinopathy will be nearsighted. Myopia associated with retinopathy progresses by age 5, after which it stabilizes.
How to cure myopia with medication?
It is important to understand that drug treatment for myopia is only auxiliary and is prescribed in combination with other treatment methods.
Medicines that help improve vision in children include:
- Vitamin complexes for the eyes - “Vitrum Vision”, “Okuwait”;
- Eye drops that relieve tension and improve the condition of the tissues of the visual organs - “Taufon”, “Systane”;
- Eye drops containing atropine, which eliminate spasm of accommodation;
- Medicines containing nicotinic acid - "Trental";
- Drugs that strengthen the walls of blood vessels in the visual system - “Ascorutin”.
The selection of medications, their dosage and frequency of administration should be determined by a specialist.
Vitamin preparations and dietary supplements
In the autumn-winter period, when there are few nutrients and sunshine, the use of vitamin preparations is indicated, the main effect of which is aimed at improving visual functions through the supply of active components involved in the mechanisms of vision from the outside.
For prophylactic purposes, almost all drugs are used 1 capsule 1 time per day for up to 1 month, after which it is recommended to take a break of 1 month and repeat the course. With the appearance of fresh vegetables and fruits, the intake is stopped until the onset of cold weather.
Modern vitamin complexes and eye supplements also contain components necessary for the central vision area - lutein and zeaxanthin, as well as omega-3 fatty acids in the dose required by the body. The drugs are used in complex therapy.
How can myopia be cured using hardware techniques?
Hardware therapy is one of the most effective and safe procedures for restoring vision in children. The following treatment methods are used in ophthalmology:
- Electrical stimulation - the currents of the device have certain effects on the eyes, restoring conductivity if a child has abnormalities in the functioning of the optic nerve.
- Laser therapy - the device activates the retinal receptors, affecting it;
- Vacuum massage - increases blood flow and promotes relaxation of the visual organs.
- "Amblyocor" - stimulation of the work of visual neurons using a device.
Surgical intervention
Today, the most effective surgical method for restoring vision for myopia is laser correction. However, it is not recommended for children under 18 years of age, since the visual system is still developing until this age. In severe cases of pathology, the child may require scleroplasty (an operation aimed at strengthening the scleral membrane of the eye). The procedure is necessary for the patient in case of progression of the pathology. Experts say that it is possible to completely get rid of myopia surgically only after reaching adulthood.
Prevention of myopia in children
To prevent your children’s vision from deteriorating during school and adolescence, you should adhere to the following recommendations:
- Provide your child with proper balanced nutrition, rich in beneficial microelements and vitamins;
- Equip his workplace with a comfortable chair and proper lighting;
- Teach him to read at a distance of 30 cm from his face;
- Show some simple eye-relaxing exercises;
- Limit the time you use your computer and gadgets.