The eyes are auxiliary organs of the brain that help us perceive information visually.
Humans have eye whites that other primates do not.
At the same time, they are designed to control the movements of the eyeballs and the direction of gaze.
More and more evidence suggests that men and women are completely different not only visually. They differ in character and anatomical structure of the body. There is even a difference in the structure of the eyes, which makes the phrase “different outlook on life” relevant. Also gaining relevance is the phrase “eyes in the back of the head,” which should not be taken literally. This is due to the wider horizons of women's eyes compared to men.
Structure of vision
The organs of vision have not only different anatomical features, but also psychological ones. There is also a difference in how the brain perceives a picture. At the back of the visual organs are photoreceptor cells, which provide black and white images, and photoreceptors, which are designed to convert everything into a color image. The field of vision of a man and a woman has been different since ancient times.
We must not forget about the ancient population, in which men hunted and saw animals at great distances. The field of vision of men at this moment narrows as much as possible, concentrating attention on the desired object.
This process contributes to the development of tunnel vision, which made it possible to see long distances without problems, but only straight ahead. Now this difference is clearly noticeable in the rapid fatigue of the eyes when working at a computer, because it is much easier for men to look at objects at a distance.
Women took care of the house and children. At the same time, they needed to see the kids, control the fire and perform many other actions at the same time. Based on this, the female brain perceives information received from the eyes differently, which means there is an urgent need for a broad outlook.
Women's eyes do not have a visual field limitation, since it was necessary to recognize danger from a distance. Thus, in the weaker sex, the visual organs are in constant tension, due to which lateral vision develops. Such eye capabilities allow women to easily work with small objects that require visual concentration.
Structure of the human eye: photo/diagram/drawing with description
In order to understand what the human eye is, it is best to compare the organ with a camera. The anatomical structure is presented:
- Pupil;
- Cornea (colorless, transparent part of the eye);
- Iris (it determines the visual color of the eyes);
- Lens (responsible for visual acuity);
- Ciliary body;
- Retina.
The following structures of the ocular apparatus also help ensure vision:
- Choroid;
- Optic nerve;
- The blood supply is carried out by nerves and capillaries;
- Motor functions are carried out by the eye muscles;
- Sclera;
- Vitreous body (main defense system).
Accordingly, elements such as the cornea, lens and pupil act as the “lens”. The light or sun rays that hit them are refracted and then focused on the retina.
The lens is “autofocus”, since its main function is to change the curvature, due to which visual acuity is maintained at normal levels - the eyes are able to clearly see surrounding objects at different distances.
The retina acts as a kind of “photo film”. The image seen remains on it, which is then transmitted in the form of signals via the optic nerve to the brain, where processing and analysis takes place.
Knowing the general features of the structure of the human eye is necessary to understand the principles of operation, methods of prevention and treatment of diseases. It is no secret that the human body and each of its organs is constantly improving, which is why the eyes, in evolutionary terms, managed to achieve a complex structure.
Due to this, structures of different biology are closely interconnected in it - vessels, capillaries and nerves, pigment cells, and connective tissue also takes an active part in the structure of the eye. All these elements help the harmonious functioning of the organ of vision.
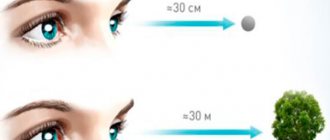
A person's visual angle is the ability to capture visible information while fixating the eye. For example, while reading. The wider this scope, the faster a person can read. This means that a person can also receive more visual information.
The width of the visual angle is different for each person. It depends on the size of the object on which the gaze is focused and on the distance of this object from the eyes.
An interesting fact is that when viewing objects of different sizes, but distant at the same distance, the angle of view changes. But if these objects, regardless of their size, are at different distances, the angle of view will not change.
human vision photo Following from this, the closer the object is in relation to the eye, the wider the angle of view becomes. This explains why, in order to examine an object in detail, we bring it closer to the eye. Thus, we see this object from a wide angle.
Scientific research confirms that the eyes of a healthy person distinguish two points only when he sees them at a viewing angle of at least 1 minute. It is also known that the eye is able to distinguish each point separately only in the case when the “legs” of the light beam do not fall on both nerve elements at once, but when there is at least one nerve element between them, for example, a rod or cone.
Since the amount of information perceived depends on the angle of view, it makes sense to expand it. Thanks to this, you can learn to read quickly without losing the meaning of the text and remembering it.
How to expand your perspective?
It's not difficult to do this at all. It is necessary to regularly train the eyes using the method of representation. Representation is the ability to correctly organize the reading process. For example, you can read by changing the distance of the text from your eyes. Additionally, you can include music that suits the meaning of the text. This will allow you to remember what you read faster and for a longer time.
Thus, regular practice will expand the angle of vision and thereby increase the amount of perceived visual information.
Genetic difference
The visual organs of men and women differ at the genetic level. Everything that is contained at the gene level is collected in the X chromosomes. Men have one chromosome in their genes, while women have two. In this regard, women distinguish more colors and their shades, while men distinguish only the main bright colors.
Every second, the eyes perceive millions of different background light rays, which contain and transmit certain information. Because everything the eyes see is processed by the brain, the structure of the visual organs has limitations that help focus attention on specific objects and tasks. A striking example of this is the search for a needle that has fallen to the floor, when a sharp narrowing of the visual field occurs.
Car driving
The fact that the vision of men and women is different is documented by scientific data. Road accident statistics show that men are more likely to be involved in accidents. This is due to the fact that women’s lateral vision is more developed, which makes it possible to prevent side impacts in cases of sudden interference. It has also been noted that women's vision at night is better than men's. Women tend to see small objects in large areas, but only when they are close.
Men see objects well at long distances, but only if they are located on the same line. Therefore, men are considered the best drivers at night. This fact allows you to clearly see cars not only from the front, but also from the back. In turn, the lack of such skill in women makes them practically blind when driving at night.
There are problems with recognizing the line for the movement of cars heading towards a meeting. And, conversely, men do not have problems with this. Based on these data, it is recommended that women drive only during the day, and men at night if necessary, which will ensure a safe trip.
The main causes of such disorders.
Most pathologies occur after 40-45 years, when the first signs of age-related changes in the organ of vision appear (clouding of the lens, deviations from the norm in the parameters of the eyeball).
Work associated with prolonged visual stress and poor lighting of the workplace.
Poor nutrition, lack of vitamins and nutrients in the diet necessary for the full functioning of the visual system.
If even minor symptoms of vision changes appear, especially if they are periodic, you should pay attention to them.
Color perception
Few people think about it, but women cannot be colorblind. As mentioned earlier, the X chromosomes are responsible for color perception at the gene level. Color blindness is a hereditary disease that occurs due to a mutation on the X chromosome. As a result of the lesion, this disease can develop in men.
If the X chromosome is damaged, a woman still has one more. In medicine, there is no data on the mutation of two X chromosomes at once and a woman who is colorblind. All this makes it incomprehensible for women how it is possible not to distinguish shades of colors, while men may not even distinguish colors, without realizing it.
In everyday life, biological differences in the structure of the visual organs of men and women help determine important features that will make life easier. Many women are needlessly angry with men because they do not understand that their helplessness in everyday matters is inherent in nature. You need to understand that men's eyes have a structure in which they can easily observe one point, but they get tired much faster.
Also, you should not try to change this, since such features of the visual organs are congenital. At the same time, if any unusual changes appear, they should not be considered a sign of gender differences, because they may indicate acquired disorders.
Photoreceptors
Type of neurons that make up the retina of the eye. They provide processing of the light signal in such a way that it is converted into electrical impulses. This triggers biological processes leading to the formation of visual images. In practice, photoreceptor proteins absorb photons, which saturates the cell with the appropriate potential.
Photosensitive formations are peculiar rods and cones. Their functionality contributes to the correct perception of objects in the outside world. As a result, we can talk about the formation of a corresponding effect - vision. A person is able to see due to biological processes occurring in such parts of the photoreceptors as the outer lobes of their membranes.
There are also light-sensitive cells known as the eyes of Hesse. They are located inside a pigment cell that has a cup-shaped shape. The work of these formations is to capture the direction of light rays and determine its intensity. With their help, the light signal is processed when electrical impulses are obtained at the output.
The next class of photoreceptors became known in the 1990s. It refers to the light-sensitive cells of the ganglion layer of the retina. They support the visual process, but in an indirect form. This refers to biological rhythms during the day and the pupillary reflex.
The so-called rods and cones differ significantly from each other in terms of functionality. For example, the former are characterized by high sensitivity. If the lighting is low, then they guarantee the formation of at least some kind of visual image. This fact makes it clear why colors are poorly distinguished in low light conditions. In this case, only one type of photoreceptor is active - rods.
The cones require brighter light to function to allow the appropriate biological signals to pass through. The structure of the retina requires the presence of different types of cones. There are three of them in total. Each defines photoreceptors tuned to a specific wavelength of light.
The parts of the cortex oriented towards processing visual information are responsible for the perception of pictures in color, which involves recognizing impulses in the RGB format. Cones are capable of distinguishing light flux by wavelength, characterizing them as short, medium and long.
Depending on how many photons the cone is capable of absorbing, corresponding biological reactions are formed. The different responses of these formations are based on the specific number of absorbed photons of one or another length.
In particular, L-cone photoreceptor proteins absorb the conventional red color associated with long wavelengths. Light rays of shorter length can produce the same answer if they are bright enough.
The reaction of the same photoreceptor can be provoked by light waves of different lengths, when differences are also observed at the level of light intensity. As a result, the brain does not always determine the light and the resulting picture.
Through visual receptors, the selection and selection of the brightest rays occurs. Then biosignals are formed that enter those parts of the brain where this type of information is processed.
A subjective perception of an optical image in color is created.
The human retina consists of 6 million cones and 120 million rods. In animals, their number and ratio are different. The main influence is lifestyle. In owls, the retina contains a very significant number of rods. The human visual system is made up of almost 1.5 million ganglion cells. Among them there are cells with photosensitivity.