Types of pain
Headache in the forehead and eyes has a different character. It happens:
- acute. Patients describe it as “strong” or “strongest”. It appears suddenly. The duration of sensations depends on the type and stage of the disease. Acute pain occurs with migraine, meningitis, sinusitis;
- pulsating. Occurs in cluster conditions, paroxysmal hemicrania, as well as in diseases that are accompanied by an inflammatory process in the body;
- piercing. Characteristic of neuritis and neuralgia, especially with inflammation of the optic nerves. The pain permeates the entire head, extends to the eye sockets and the bridge of the nose;
- pressing. Appears due to psychogenic factors or changes in atmospheric pressure. A pressing feeling is characteristic of infectious diseases and tumor processes.
Pain resulting from overwork
Most often, the cause of such sensations in absolutely healthy people is banal overwork. This condition usually develops after stressful situations or prolonged work at a computer monitor.
- Children's eye drops V.Rohto for Kids Moisturize and support visual health;
- Safe for children;
- Prevents the development of inflammatory and infectious diseases;
Unpleasant sensations in this case are provoked by spasms of blood vessels responsible for feeding the muscles located in the shoulder girdle, neck and face. Spasms disrupt the normal blood supply to the muscles, which leads to the accumulation of histamines in them - elements released during the development of inflammatory processes.
These headaches are characterized by one unpleasant feature, which is the duration of the sensations, which do not subside even after the elimination of the provoking causes. Therefore, for many people who are engaged in heavy mental work every day, pain in the forehead and eyes is a frequent occurrence. As a result, this condition can provoke the development of neuroses and depression.
Features of pain in the frontal region
Pain in the frontal part of the head and eyes often appears with cerebrovascular diseases. In this case, accompanying symptoms are observed: pallor, weakness, vomiting or nausea. The same can happen when the cervical vertebrae are displaced, injured or physically overloaded.
Information: Pain in the eyes can occur due to poor posture in childhood.
From the left side
If unpleasant sensations occur on the left side, they can be provoked by:
- tumor processes;
- migraine;
- weather sensitivity;
- stroke;
- injuries.
On the right side
If the frontal part of the head on the right hurts, this indicates the following signs:
- Costen's syndrome;
- osteochondrosis;
- oncology;
- inflammation of the tonsils;
- hemicrania.
Migraine
Migraine
is a form of headache that manifests itself in a varied combination of autonomic, neurological, and gastrointestinal manifestations. Migraine occupies the first section in the classification of headaches, which was developed in 1991 by the International Headache Society.
Migraine symptoms
Migraine symptoms are manifested by paroxysmal headaches, which are accompanied by a number of typical symptoms and some other manifestations. The main characteristics of a migraine headache attack are:
duration of pain (usually expressed in hours);
frequency of pain (number of attacks per month);
pain intensity (usually assessed on a visual analogue scale from 0 to 10 and expressed as a percentage).
A neurologist, in order to diagnose migraine, will have to take into account the following aspects, along with the symptoms mentioned above:
- hereditary predisposition;
- time, nature and location of headache;
- the nature of provocateurs, precursors of an attack, as well as factors that relieve pain;
- accompanying symptoms, including atypical ones;
- the nature of concomitant conditions and diseases;
- the state of a person in the interictal period;
- also quality of life in general.
Most research studies examine only a few of these parameters. Today, doctors study not only the nature and presence of all these important clinical and psychological criteria, but also evaluate their relationship and the degree of their impact on the course of migraine and the quality of life of patients, leaving aside generally known information about the clinical manifestations of migraine.
Most scientists argue that migraine patients rarely exhibit organic neurological symptoms. In patients with severe frequent migraine attacks with aura, a neurological examination may reveal a number of organic symptoms (pyramidal signs, unilateral weakness of the facial muscles, asymmetry of reflexes). The detection of the above organic neurological symptoms is an indication for a thorough examination of the patient in order to exclude a more serious disease (mass formation of the brain, vascular malformation, etc.). When examining a person with migraine, a doctor can often detect symptoms of autonomic dysfunction (Chvostek’s sign, temperature changes, hyperhidrosis and discoloration of the fingers, etc.).
As a rule, patients feel “satisfactory” outside of migraine attacks. Among the most common disorders detected in people with migraine outside of attacks are emotional, as well as permanent and paroxysmal autonomic disorders, pain syndromes of other localization, sleep disorders and other symptoms.
The authors of one study stated that the ability to predict migraines could alleviate or even prevent headaches [1].
Causes of headaches in the forehead and eyes
Why does my head hurt and what is it connected with? There are a number of diseases for which headaches are typical. They vary in nature and are accompanied by a number of symptoms.
Migraine
This disease is often inherited. It affects women from 20 to 50 years old. Sometimes found in men. A migraine attack is accompanied by severe pain in one half of the head (right or left side). They pulsate and radiate to the temples and forehead. In the acute period of the condition, patients become dizzy, feel nauseous, and are afraid of bright light.
Migraine is preceded by an aura. This is a precursor condition that is always observed shortly before an attack. Patients' vision becomes dark, the skin on their face becomes numb, and they have difficulty hearing. The condition lasts from several hours to a day.
Important! During an attack, it is necessary to provide the patient with maximum rest. Sometimes regular analgesics help. Recently, doctors have advised taking special medications against migraines.
Cluster pain
This condition occurs for no reason. The headache begins to hurt so much that patients think about suicide. The pain seems to pierce the head, radiating to the eyeball, temples and back of the head. Unlike migraine, cluster pathologies more often affect men. All signs disappear as quickly and suddenly as they appear. The duration of attacks ranges from several minutes to several hours.
Cluster pain is characterized by seasonality. Spring and autumn are the time for their appearance. During the periods between attacks, the person feels absolutely healthy.
Increased intracranial pressure
One of the causes of increased ICP is the pressure of cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) on the brain. This is the cause of pain syndrome. Also, ICP may increase due to vascular spasms, intoxication and lack of oxygen. The following symptoms are observed: increasing severity, pain in the eyes, visual disturbances. Swelling may appear on the face and eyelids.
Information! Intracranial pressure usually increases in the morning.
Sinusitis
This is an inflammation of the maxillary sinuses. It manifests itself:
- pain in the nose and eyes;
- pressing sensations in the forehead and superciliary area;
- nasal congestion;
- temperature rise to 38C;
- nasal discharge.
The mucous secretion may be transparent or yellow. When a person tries to tilt his head forward, the pain becomes stronger.
Frontit
This is an inflammation of the sinuses in the forehead. Frontal sinusitis is often a complication of influenza and other colds. Also contribute to its appearance:
- chronic rhinitis;
- adenoiditis;
- infections of the mucous membranes;
- deviated nasal septum.
Pain occurs in the forehead and above the eyebrows, radiating to the ears and jaw. Patients also experience fever and runny nose with purulent discharge. The face swells, the nose is stuffy, the sense of smell and taste deteriorate.
Meningitis
Meningitis is a dangerous infectious disease. At first, its symptoms resemble the flu or a cold: weakness, high fever, difficulty breathing, lack of appetite. If a patient is constantly thirsty, has aching joints, feels dizzy and vomits, this should alert others. A typical sign of meningeal infection is that a person cannot tilt their head forward. This is due to the inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain.
Attention! Meningitis occurs quickly. If the patient does not receive medical attention in time, he may die. If you suspect meningitis, you should urgently call a doctor at home.
Osteochondrosis and myositis
With osteochondrosis, blood circulation in the vessels is impaired. Vertebrae deformed by the process can compress the vertebral artery. As a result, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. Severe pain can radiate to the frontal and occipital parts of the head.
Often osteochondrosis is accompanied by myositis. This is an inflammation of the muscles that are located close to the affected part of the spine. The muscles hurt when touched and become swollen. If it is the neck muscles, the pain also affects the head.
Trigeminal neuritis
The characteristic symptoms of this disease are painful tics and unilateral muscle spasms. Pain occurs in the eyes, “shoots” in the temples and ears, in the jaw and the back of the head. The face becomes red and swollen on one side and is painful to touch. Sometimes a runny nose and watery eyes occur.
Oncology
Tumor formations in the brain prevent the free outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. As a result, intracranial pressure increases. This is fraught with the appearance of pain. Tumor processes in the brain are characterized by pain in the morning. Symptoms such as weakness and nausea are often associated.
Foods that trigger headaches
Headaches can also be triggered by eating certain foods, for example:
- nitrates, which can be found in significant quantities in meat products that have undergone various types of processing;
- histamine, a significant amount of which is found in alcoholic beverages, namely red wine and beer; in small amounts, histamine has a beneficial effect on human immunity, otherwise it can cause the development of migraines;
- monosodium glutamate, which is a fairly common food additive, the accumulation site of which is often raw seafood;
- tyramine, found in chocolates, nuts and some types of cheese;
- caffeine, a small dose of which has a stimulating effect on the functioning of the brain, and the result of abuse is intense headaches.
But not only the foods consumed play an important role, but also the nutrition system itself, which involves following a certain eating regimen.
Where to go for help
First you need to go to your local therapist. He will help you find out the causes of the condition and, if necessary, give a referral to another doctor. Before referring a patient to an ENT specialist, oncologist or neurologist, the therapist must prescribe a number of studies:
- urine and blood tests;
- Doppler scanning of the vessels of the brain and neck;
- MRI;
- X-ray.
To assess the condition of the nasal sinuses and septum, the ENT doctor performs a video endoscopic examination. Depending on what disease is causing the headaches, a psychotherapist or neurologist can help a person.
Eye strain
Eye strain can also lead to headaches. Eye strain headaches are usually caused by uncorrected vision or astigmatism in one or both eyes.
Causes of eye strain
Eye strain can have a number of causes:
- prolonged reading or computer use;
- long periods of concentration;
- stress;
- bad posture.
People with headaches caused by eye strain should see an ophthalmologist (eye doctor) for an eye exam. If the cause is visual impairment, the person may need glasses or contact lenses.
For headaches with eye strain, the following may help:
- taking regular breaks when reading or using the computer;
- good posture;
- stretching of the neck, arms and back;
- using an anti-glare filter for computer screens.
Prevention
No one is immune from injuries and malignant neoplasms, but it is always possible to improve health. Often advanced cases of frontal sinusitis, sinusitis and other diseases arise due to a person’s frivolous attitude towards his body. Healthy and sound sleep, regular walks, and healthy physical and mental work will help you avoid many consequences. It won’t hurt to give up addictions (smoking and alcohol).
Recommendation: Regular preventive examinations help to identify the causes of headaches in a timely manner.
Carrying out diagnostics
To make a correct diagnosis, you need to undergo an examination.
It includes:
- general blood and urine analysis to exclude infectious damage to the body;
- EEG to determine epileptic activity, exclude migraine;
- ECG to check the condition of the heart and blood vessels;
- blood pressure measurement;
- analysis of thyroid hormone levels to exclude endocrinological pathologies;
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the neck, head, thyroid gland;
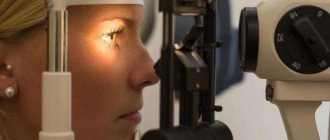
- measuring eye pressure to exclude eye diseases;
- tomography of the head to detect tumors, hematomas, disorders of the structure of the brain;
- X-ray of the cranial sinuses to identify ENT pathologies.
A comprehensive examination does not always reveal the cause of pain. But it helps determine the presence or absence of serious diseases.
Groups of reasons
The causes of headaches radiating to the forehead or eyes can be classified into 4 groups, namely:
- Increased load on the head and neck muscles. Prolonged activity in the same position, stress on the same muscle day after day makes itself felt. The pain that appears over time turns into serious diseases, for example, osteochondrosis.
- Pathologies with blood vessels of the brain. In this case, the brain, for one reason or another, does not receive sufficient nutrition through the vessels and sends “alarming” impulses along the nerves, which are identified as pain.
- Viral diseases or diseases associated with bacteria. Here the headache works as a side effect, that is, it is simply a concomitant phenomenon of the main problem.
- Injuries. Damage to the brain can have a serious impact on its functionality and can also cause severe headaches.
If the pain does not bother you much, then first you can try to “drown out” it with the help of special tablets or other medications. But prolonged pain that does not go away for several days or even more so weeks should make a person worry about his health.