It puts pressure on the eyes, there is a feeling of fullness in the eyeballs, heaviness on the eyelids, dizziness and headache - all these are symptoms of overwork, stress or ophthalmological, vascular, neurological diseases. Unpleasant sensations have different intensity and frequency, which depend on the pathological processes in the body.
To determine why there is pressure on the eyes, you need to contact a specialist who will conduct an examination.
Why does it put pressure on the eye?
In a situation where the eyes hurt as if they were pressing, it is necessary to study the regularity of this manifestation and the circumstances of its occurrence. For isolated attacks in people working at a computer or with papers, there is no need to worry too much. It is necessary to contact a specialist if the patient develops additional symptoms. A condition when there is constant pressure on the eyes is considered a dangerous signal, so this most often indicates various diseases.
Migraine
With a pathology such as migraine, pain localizes to one side of the head. In addition, there is a pulsation in the temple, which spreads to the ear and organs of vision. If your eyes are closed, colored circles are formed, which are complemented by flashes. In addition, there is pronounced pulsation in the eyelid area.
A migraine attack can last from several hours to 2-3 days, and during this period the patient becomes too irritable. In addition, there is a feeling of weakness and constant fatigue. With loud noise and bright light, there is an increase in pain.
Overwork
Working at a computer for too long and reading small print texts increases the likelihood of eye discomfort. In addition, the cause of severe pain can be any activity that requires increased attention and strong visual strain.
With severe overwork, a person suffers from pain in the organ of vision, a sensation of cutting and burning. It feels as if sand has been poured into the eyes, and there is a disturbing feeling of pressure and heaviness.
Glaucoma
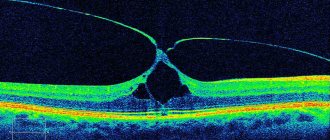
A pathology such as glaucoma, caused by an increase in pressure inside the organ of vision, does not always provoke pain. Usually there is a dull or aching pain, which is complemented by various visual changes. Fogging of the cornea, the appearance of rainbow circles and photophobia are observed.
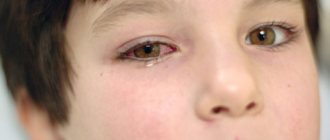
During an acute attack of glaucoma, the patient experiences sudden pain in the organ of vision, which radiates to the temples, the back of the head and sometimes along the trigeminal nerve. Attacks of nausea and dizziness, as well as significant changes in the eyes, may occur. When examining the patient's face, it becomes noticeable that the cornea and eyelids swell greatly, and the pupil dilates significantly.
With glaucoma, the patient may experience severe discomfort. It should be remembered that pain cannot be relieved with painkillers. Only drugs that lower blood pressure help alleviate the patient’s condition.
Increase in pressure
The situation with pain from inside the eyes may indicate surges in intracranial pressure. The cause of the pathological condition lies in a concussion, stroke and impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid. In addition, a rapid increase in the size of a cyst or malignant neoplasm localized in the skull can cause pain.
The patient complains not only of pressure, but also of increasing pain, pain and pulsation behind the organ of vision. When coughing, blowing your nose and other sudden movements, an even greater increase in pain is noted. In addition, symptoms such as nausea, spots before the eyes, hallucinations and increased drowsiness may appear.
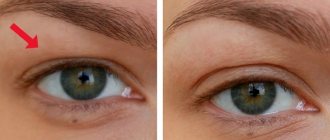
In some cases, pressure from inside the eyelids and the appearance of a feeling of fullness inside the organ of vision indicate surges in intraocular pressure. The patient experiences severe redness of the sclera and a feeling of heaviness in the eyelids.
If the increase in pressure inside the eyes is chronic, then there is a high probability of degeneration of the optic nerve and the appearance of glaucoma. With this pathological condition, the patient experiences a gradual narrowing of the field of vision and, in the worst case scenario, the patient may become completely blind.
Other reasons
Experts identify some reasons that cause increased pressure in the eye and pain:
- Increased psycho-emotional stress. In this condition, any increased stress can cause severe pain in the forehead and eyes.
- Osteochondrosis of the neck. The cause of damage to the organ of vision is frequent headaches and curvature of the spine.
- Various visual impairments. Various infections inside the organ of vision, inflammatory processes, barley and injuries to the corneal layer of the eye can provoke an unpleasant symptom.
- Problems with blood supply to the brain. This condition causes headaches, which can result in a stroke.
- Injuries and damage to the skull. Pressure in the eye in this pathological condition can be accompanied by weakness, nausea, double vision, and a constant desire to sleep.
- Changes in hormone levels in the female body. Most often, expectant mothers experience a feeling of pressure in the eye during pregnancy.
In addition, pain and increased pressure in the eye can be observed with diabetes, a decrease in the body's defenses and bad habits. An unpleasant symptom often occurs when the body is poisoned, has allergic reactions, or wears glasses that were chosen independently without consulting a doctor.
Prevention
Prevention consists of normalizing sleep and work patterns. Watching TV or using the computer should be kept to a minimum. Every 40 minutes of reading or sitting at the monitor, you need to take a break and light exercises.
Proper lighting is of great importance. The room should not have bright light contrasts, but at the same time the light should not be too dim. Sedentary work should be combined with physical exercise.
If you have dry eye syndrome, it is recommended to use special drops. The drug and dosage should be selected by a doctor.
To preserve your eyesight you need to eat right. You should choose foods with vitamin A. It protects the retina and improves vision. Sources of vitamin A:
- spinach;
- eggs;
- broccoli;
- carrot;
- rash;
- milk;
- dark green leafy vegetables.
It is recommended to drink freshly squeezed carrot juice with a small amount of vegetable oil. It is recommended to season carrot salads with sour cream and vegetable oil.
B vitamins help normalize photosensitivity and get rid of the feeling of heaviness. It is present in beans, peas, liver and milk and porridge. Omega-3 fatty acids reduce the risk of developing dry eye syndrome.
You should stop smoking and drinking alcohol. Smoking increases the risk of developing cataracts and other eye diseases. People who smoke have a worse absorption of vitamins and other beneficial substances. This negatively affects the condition of the optic nerve. When drinking alcohol, blood circulation is impaired.
You need to monitor your child’s behavior especially carefully. Symptoms of heaviness in the eyes and vision problems:
- headache;
- complaints of rapid eye fatigue;
- closing one eye when reading or watching TV;
- squinting.
Important! Children of preschool and primary school age need to limit the amount of time they watch TV or play on the computer. It is necessary to ensure that the child maintains a normal plant from the eyes to the notebook or book.
You should regularly undergo preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist. Timely diagnosis will help begin treatment at an early stage of the development of the pathological condition. The sooner therapy is started, the more effective it will be. If necessary, the doctor selects means for vision correction. Lenses or glasses need to be purchased only with a doctor's prescription from an optician. The quality of materials is of great importance.
In what cases should you consult a doctor?
Most often, eye pain can be dealt with at home on your own. However, in some situations the patient requires urgent assistance from a specialist. You should consult a doctor as soon as possible if:
- pain does not disappear after taking medications with an analgesic effect and performing various procedures aimed at alleviating the condition;
- pain syndrome torments the patient constantly, regardless of the duration of treatment;
- pressure in the eyes is complemented by severe discomfort;
- pressure and pain in the eyes are combined with temperature fluctuations.
With pain in the eyes, nausea and severe discomfort in any part of the skull, dangerous pathologies can be suspected. Often this sign indicates meningitis, cancer or stroke.
Associated symptoms
The feeling of “heavy” eyelids may be accompanied by accompanying symptoms:
- feeling of a foreign object or sand in the eye socket;
- decreased clarity of vision, photophobia;
- increased tearfulness or, on the contrary, dryness of the cornea;
- blurred vision, diplopia, headaches;
- in case of allergic reactions, itching and burning of the conjunctiva may occur;
- cervical osteochondrosis is manifested by pain in the upper spine, back, shoulders;
- In case of infectious diseases, there may be an increase in body temperature, aching sensations in the joints, sweating, chills;
- when the eyes are overstrained, general fatigue of the body occurs;
- Inflammatory eye diseases are characterized by swelling of the eyelids and purulent discharge from the organs of vision;
- Migraine is accompanied by throbbing pain in the temples.
If heaviness in the eyeballs bothers you for a long time, you need to contact an ophthalmologist for a diagnosis. In some cases, consultation with specialized specialists – a neurologist, endocrinologist, cardiologist, ENT specialist, etc. – will be required.
Diagnostics
It is necessary to find out why there is pressure on the eyes from an ophthalmologist. Using a special device, intraocular pressure is measured and the result is evaluated. In addition, an ophthalmological examination is carried out aimed at studying the condition of the optic nerve.
To confirm the diagnosis, the following types of studies may be prescribed:
- MRI. Using this procedure, it is possible to determine which pathologies caused the unpleasant symptom. MRI helps identify strokes, cystic formations, tumors and hydrocephalus.
- Ultrasound. This diagnostic method determines the presence or absence of vascular damage, thrombosis and the speed of blood flow.
- CT. The procedure determines the presence of an inflammatory process affecting the bone structure of the head. In addition, CT scans can detect the presence of pathologies such as sinusitis and frontal sinusitis.
If indications are present, the ophthalmologist may refer the patient for consultation to other specialists.
How to deal with the problem
After determining the cause of this condition, when there is pressure from inside the eye, a specific treatment is selected.
Drugs
Drug therapy includes taking painkillers such as Analgin and Pentalgin. The condition can be alleviated with the help of non-steroidal drugs with an anti-inflammatory effect, among which Diclofenac and Ibuprofen are considered the most effective. To improve the removal of fluid from the body, it is possible to prescribe drugs such as Furosemide and Diacarb.
Patients whose cause of pain in the eyes is a bacterial infection are prescribed antibacterial drugs. To treat the eyes, it is recommended to use Erythromycin ointment, and oral medications in tablets, for example, Cephalexin and Amoxicillin.
When pain in the eyes occurs as a result of stress or nervous tension, various antidepressants, tranquilizers and sedatives can be prescribed. For increased intraocular pressure, drops such as Azopt, Travatn, Bitoptik and Pilocarpine are usually prescribed.
Exercise for the eyes
You can relieve pain caused by fatigue with the following exercises:
- you need to look left and right, up and down;
- move your eyeballs clockwise and back;
- draw a square in the air clockwise and back;
- Draw several figure eights in the air in a horizontal and vertical position.
You need to do the exercises up to 10 times during the day, adhering to the specified sequence.
Alternative medicine
Non-traditional treatment methods help alleviate the patient's condition, but they are unable to completely cure the disease. At home, it is recommended to wash your eyes with chamomile or aloe decoctions. To do this, moisten a cotton pad in the prepared liquid and wipe your eyes with it so that the product is slightly squeezed onto the mucous membrane.
It is allowed to take decoctions of mint or lemon balm, which will relieve unpleasant sensations inside the organ of vision. Clover infusion helps to cope with discomfort due to pressure surges inside the eye.