Allergic reactions are an unpleasant problem that worsens the quality of life, requiring many restrictions and medications. However, there are acute conditions that pose a threat to life. These include angioedema and anaphylactic shock2.
Everyone should be able to recognize the symptoms, know the causes, and be able to provide first aid to people with allergic swelling. It is important to quickly recognize the problem, call medical staff, and follow a clear algorithm of actions to reduce risks and improve the person’s condition.
Signs and diagnosis
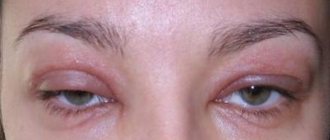
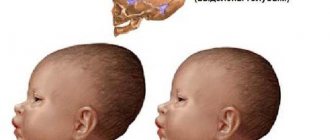
Quincke's edema in the eyes is characterized by a sudden appearance and the same unexpected disappearance, and more often it affects children of school and primary school age.
In adults it appears much less frequently. The eyelids of one eye or both can swell at the same time. In addition, there is also a separate lesion of the upper or lower eyelid. Sometimes the face also increases in volume, and if Quincke's edema occurs in only one eye, then it is that side of the face that will differ in size from the other. This allergic manifestation occurs in the eyes within a few minutes, a maximum of half an hour after the allergen enters the body (for example, after drinking a cup of chocolate or walking through a flowering garden). The patient develops a feeling of anxiety, his eyes narrow to slits and begin to water. Then swelling occurs, its size varies from patient to patient. Some people are luckier and the changes in appearance during Quincke's edema are insignificant before the eyes, but for others it's the other way around.
The swelling is usually not too painful, but may be accompanied by itching. When you touch the eyelids at normal temperature, there is a feeling of heaviness in the eyes.
The skin is pale or takes on a bluish tint. If you touch the affected eyelid, there will be no hole left. This distinguishes this type from the inflammatory type, in which the eyelids are bright red, hot and there is pain when touched.
These symptoms are also similar to Meige's disease (trophedema), which is characterized by prolonged swelling of the subcutaneous fatty tissue of the lower eyelids. It is also dense to the touch, there is no trace when pressed. But, unlike Quincke's edema, when trophedematous edema occurs, the patient's temperature rises, general weakness sets in, and a headache appears.
Diagnostic principles
Diagnosis of the disease is complex and includes the following studies:
1. Collecting anamnesis, interviewing the patient. The doctor asks how often the patient experiences such attacks, whether he has allergies, which organs and tissues swell most often, and whether the patient has previously complained of abdominal pain of unknown etiology.
In addition, the doctor asks whether the patient’s immediate relatives have had similar cases, whether the patient takes any medications on an ongoing basis, and finds out whether the appearance of signs of Quincke’s edema is associated with food intake and stress.
2. General inspection. The doctor examines the swelling, assesses its color, consistency, location and extent of spread.
3. In the allergic form: blood test - an excess of eosinophils is detected; allergy tests (carried out to identify the allergen after the symptoms of Quincke's edema have been relieved); determination of the level of immunoglobulins class E.
REFERENCE! Quincke's edema of the eye occurs suddenly and goes away just as quickly. Children of preschool institutions and schoolchildren often suffer. Quincke's edema in the eyes can manifest itself as swelling of one or both eyes. Sometimes with this pathology only one eyelid suffers. The face changes, and this is visible to the naked eye.
Who to contact?
Angioedema is treated by an allergist, with the possibility of involving a dermatologist and an ENT specialist.
Why does angioedema occur in the eyes?
During the first attacks, angioedema in the eyes lasts from 12 hours to several days, and when it disappears, it leaves no trace.
But if relapses occur, they can leave noticeable effects of swelling and the eyelids increase in size. Description of the signs of Quincke's edema in the eyes usually makes it easy to make the correct diagnosis due to the typical clinical picture. But determining the cause of Quincke's edema in a particular patient is much more difficult. In addition, the inheritance of a tendency to swelling in the eyes is excluded, that is, the factors are reduced either to the consequences of an infectious disease (helminthic infestation) or to allergens.
The causes of the disease include certain foods (whole milk, citrus fruits, fish and seafood, chocolate, strawberries, etc.), pollen, cosmetics, medications, animal fluff and hair, dust, and other irritants. In fact, the list can be very long, since different people have completely different factors that cause puffy eyes, and there are countless of them. And if it is easier for adults to understand what triggered the swelling, then in children it is more difficult to determine the reasons for the appearance of angioedema in the eyes.
Treatment
- refractive error correction;
- removal of irritating factors;
- mechanical removal of scabs by wiping with a swab;
- wiping the edge of the eyelid with a 3% AgNO3 solution;
- massage with corticosteroid ointments in combination with antibiotics - sulfonamides;
- in severe forms of the disease - general treatment with antibiotics.
Viral
The situation changes if the swelling of the eyelids is viral, induced by viruses. Usually these are processes caused by herpes viruses, primarily herpes simplex palpabrae. First, swelling of the eyelids occurs, then typical vesicles begin to form on the eyelid. As a rule, the disease affects one eye and often recurs, especially with any other diseases, stress, etc.
Often the disease resolves spontaneously, without treatment. The doctor intervenes only in case of frequent relapses: the medications Herpesin or Zovirax and other therapeutic methods are used. An increased intake of B vitamins and vitamin C may have a positive effect.
Herpes zoster ophthalmicus can also be the causative agent. We are talking about the ophthalmic form of herpes zoster (the first branch of the trigeminal nerve). The patient experiences a headache and blisters appear on the eyelid, forehead and scalp. Therapy is carried out with Acyclovir.
Treatment of edema caused by viruses:
- acyclovir;
- vitamins B and C;
- locally indifferent powders, liquid powders, gentian violet;
- analgesics as needed.
First aid
In this part of the article, we will describe step by step the steps to provide first aid to a victim of Quincke's edema in the eyes. So what to do:
- If you know what caused the swelling, you need to remove the irritant away from the patient.
- The patient needs to be laid down, reassured, and fresh air supplied (open doors and windows if the person feels ill in the room). Then you need to free your neck and chest from tight clothing and jewelry. It is better to take the child in your arms.
- It is necessary to give the patient an antihistamine in the dose indicated in the instructions according to the age of the victim. If you don’t have allergy medicine on hand, drop a couple of drops of regular naphthyzine into the patient’s mouth or nose.
- Apply a cool compress to your eyes.
- Another important point: in order to help the victim’s body independently remove the largest amount of allergen, you need to persuade the patient to drink as much liquid as possible (preferably at room temperature).
Treatment and prevention of swelling in the eyes
Treatment of Quincke's edema in the eyes of adults and children must be carried out by a good ophthalmologist and allergist. First, be sure to eliminate the cause that led to the swelling of the eyes. Then the doctor prescribes desensitizing medications for oral administration, as well as antihistamines and hormonal ointments and eye drops.
In addition to passing the necessary tests, the doctor will offer to check the digestive organs, ENT organs, and eliminate all sources of infections in the body, including caries. The victim may also be prescribed an individual hypoallergenic diet, taking into account all the products necessary for life.
Thus, to prevent swelling in the eyes, it is advisable to reduce the amount of household and food allergens, maintain a rational work and rest schedule, and avoid excessive medications. At the first manifestations of an allergic reaction in the eyes, you should definitely contact an allergist.
Causes of swelling
Following the information in the section above, the main cause of angioedema is an allergic reaction that arose as a response of the immune system to an irritant from the external environment. Allergies occur due to eating foods or when the skin comes into contact with an allergen. Let's consider the main sources of the body's response:
- a specific product - meat, fish, citrus fruit, chocolate or various nuts;
- down or bird feathers;
- pet hair—mostly cat or dog hair;
- pollen from indoor and outdoor plants;
- insect bites - mosquitoes and bees;
- poisonous saliva of animals and insects;
- preservatives and harmful dyes contained in sausage and cheese products;
- accumulation of dust and debris at home.
Below is a list of other causes of angioedema in adults and children:
- Viral and parasitic infections. Edema appears in diseases such as hepatitis and giardiasis.
- Hereditary syndrome. Quincke's disease is inherited. The baby's body is deprived of enzymes such as inhibitors of the complementary system. Therefore, the state of the immune system deteriorates due to the inability to process certain substances, which causes damage to the internal and external tissues of the body. The syndrome is in most cases transmitted to the male sex. In adulthood, the cause of the appearance of Quincke's edema lies in a previous injury or as a psychosomatic disorder develops.
- Tumors and neoplasms, blood stagnation.
- Disturbed functioning of the endocrine system. Swelling provokes a malfunction of the thyroid gland.
- Pseudo-allergic mood of the human body. This condition can occur due to nervousness, which leads to depletion of the somatic system. As a result, disturbances in the digestive organs may develop.
- Chemicals entering the body or environmental influences. The main factors and causes of edema in this case are medications, increased body temperature, pressure and vibration waves. Among the medications, there are medications to which the human immune system reacts ambiguously: analgesics and antibiotics from the penicillin group.
When the etiology of Quincke's edema is not identified, the pathology is diagnosed as idiopathic. But in 70% of cases, doctors find the cause of the disease. In addition, do not confuse the usual swelling that appears after drinking alcohol with the above syndrome.
Symptoms and Treatment
Angioedema (Quincke's edema) is an allergic disease characterized by the appearance of severe swelling of the mucous epithelium, skin and subcutaneous tissue. Most often, this pathology develops on the neck, face, feet, hands and upper body. Much less often, swelling is observed on the membranes of the brain, internal organs and joints.
Angioedema can develop in any person, but people with allergies are most susceptible to this disease. Children and young women experience this pathology much more often than older people and young men.
Depending on the causes of occurrence, there are two forms of Quincke's edema:
A factor contributing to the occurrence of allergic Quincke's edema is a hypersensitivity reaction that develops when a specific allergen penetrates the patient's body. Pseudoallergic angioedema can be observed in people with congenital disorders of the complement system - a complex of complex proteins present in the human blood and involved in the development of allergic and immune reactions. Under normal conditions, activation of the described proteins occurs only at the moment when antigens enter the human body. In the presence of pathology, the complement system is activated spontaneously, thereby provoking the occurrence of a pronounced allergic reaction.
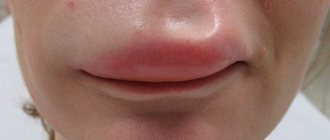
The first symptom indicating the development of angioedema is the rapid swelling of the mucous epithelium, skin and subcutaneous tissue in the affected area. The skin color remains natural, and instead of itching, the patient experiences burning and pain. Large swellings usually appear on the cheeks, eyelids, lips, genital mucosa, mouth and other places with loose tissue. Under normal conditions, all manifestations of pathology disappear on their own within a few days.
Classification
The classification of Quincke's edema syndrome is as follows:
- Allergic nature:
This case is the most common. Typically, this pathology affects people who are diagnosed with food allergies. In addition, there are also frequent cases of allergic reactions to mosquito and bee bites, contact with latex and medications, usually penicillin and aspirin. When an allergic person’s body reacts sharply to an external irritant, the throat area: tonsils and tongue may swell.
This type of angioedema provokes anaphylaxis and is not chronic. Doctors recommend refusing to eat certain foods, and also replacing medications with aspirin with others.
- Idiopathic type.
The essence of this classification is that doctors cannot identify the true cause that caused the swelling. It could be anything: alcohol, caffeinated drinks, energy drinks, stressful situations, overheating in the sun, anxiety, infection in the body or frostbite. But, basically, idiopathic angioedema is diagnosed together with thyroid disease, when the body has insufficient folic acid. It is especially important to “keep” the thyroid gland in order when planning a pregnancy, since a difficult situation may arise with possible bad consequences for the unborn baby.
- The culprits are medications.
Tumors and edema can be caused by medications that doctors prescribe for high blood pressure. An example of this is Angiotensin, which converts the enzyme ACE. In this case, the symptoms may bother the patient for 2-3 months from the moment the medication is stopped.
- Passed on by inheritance.
This is one of the rare cases. Unlike acquired edema, hereditary edema is diagnosed when a defective gene is inherited. At the same time, the level of C1-esterase inhibitor protein in a blood test is low. Gradually, as the child grows older, he begins to feel uneasy—symptoms associated with the disease appear. This is especially noticeable during puberty. If a girl is pregnant, this can also trigger the appearance of edema due to hereditary pathology. In most cases, the patient is prescribed drug therapy. In addition, those with hereditary angioedema are recruited into the army after careful treatment.
First aid for Quincke's edema
If you notice the first signs of angioedema, you should call a doctor. This should be done even if the patient feels quite well. Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- protect the patient from interaction with the allergen;
- help the victim calm down;
- ensure that clean air enters the room in which the patient is located;
- remove the patient’s belt and tie, unbutton the collar of his clothes;
- apply a cold compress to the affected area;
- try to remove the maximum amount of allergen from the victim’s body by giving him a little activated charcoal and making him drink as much liquid as possible;
- if angioedema appears after an insect bite or administration of a drug, apply a cold compress to the injection or bite site and, if possible, apply a tourniquet slightly above it;
- drip any vasoconstrictor drops into the patient’s nose;
- Give the victim a suitable antihistamine.
Emergency care for Quincke's edema
Emergency care for angioedema involves the following measures:
- hormone therapy (intravenous or intramuscular administration of prednisolone (60-90 mg), intravenous administration of dexazone (8-12 mg);
- detoxification therapy (enterosorption, hemosorption);
- use of diuretics (Lasix);
- desensitizing therapy (intramuscular administration of suprastin 2%);
- use of protease inhibitors (contrical, epsilon-aminocaproic acid).
In addition, the patient is hospitalized in the allergy department as soon as possible.
The treatment program for angioedema involves several successive stages. First of all, doctors determine the cause of the development of the pathology and recommend that the patient eliminate all potential contacts with the allergen from his life. In addition, a person who has suffered from angioedema is advised to avoid eating foods containing natural salicylates (raspberries, strawberries, cherries, strawberries, peaches, apples, grapes, apricots, plums, tomatoes, carrots, cucumbers and potatoes) for the duration of treatment, and also from the use of certain medications (paracetamol, analgin, ibuprofen, baralgin, citramon, pentalgin, askofen, indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid, butadione and others).
Drug therapy for the treatment of angioedema involves the prescription of corticosteroids and antihistamines. In addition, the patient is advised to take vitamin supplements and medications that normalize the activity of the nervous system (ascorbic acid, ephedrine).
Persons who have suffered severe angioedema are advised to always have an individual syringe with adrenaline solution on hand. In order to prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary not only to avoid contact with the allergen, but also to stop drinking alcohol, and also to protect yourself from hypothermia, overheating and stressful situations.
At the end of the article, we offer you a TV show about Quincke's edema and its dangers.
Information about similar diseases:
Thanks for the information about Quincke's edema. No one in my family has allergies. And my young daughter-in-law suffers from allergies. Yesterday her face was swollen, she was shy, she hid it behind her hair, I couldn’t understand why she let her hair down like that. And when I saw her face, I was scared. An ambulance was called and she was hospitalized. And I began to “enlighten myself” via the Internet. Many thanks to Elena Malysheva for the broadcast about Quincke's edema.
Natalya Alexandrovna, visit our resource more often, we have a lot of interesting information.
Thank you for the article. Last night my daughter had swelling and they called an ambulance. Now I decided to read about him. Everything is clearly explained. Thank you!
Hello everyone. I don't know who can help anymore. My husband first had one foot swell on the second day and the other became painful to swallow, but it wasn’t hard to breathe, they called an ambulance, they put on something harmonious and suprastin, my husband slept for almost a day but got up with new swelling on his face, the right side of his face was swollen, starting from his forehead and including to the lip and the next day the same system only on the other side, then the eyes, one by one. In short, something new swells every day. During all this time, we had a bunch of tests done by both an allergologist (she said that it didn’t look like an allergy) and a therapist (he explained this by saying that supposedly there is some kind of bacterium in the liver that may react either to water or to some product). In just 1.5 weeks I’ve changed my mind, the thing is that 1 year ago we moved from Central Asia to Kaliningrad and I’m thinking that maybe it’s not the climate that’s causing swelling, because after 26 years my husband has I wasn’t allergic to anything, but then it appeared out of the blue. But it seems very similar to Quincke's edema, but then why does the allergist deny this?
I bought paint and painted it, it started to itch, I didn’t pay attention. I went to work, then the pimples on my head began to ooze, I applied a herbal lotion, and after a while my face began to swell, at night I woke up because I felt discomfort, one eye was already swollen and my face was twice as big, they called an ambulance, they injected me with dexamethasone, we drove on to the hospital and there they told me to give 4 more injections, I’m very afraid of injections into a vein and I didn’t want to do them and left, in the morning I went to another hospital with the hope that I didn’t need injections into a vein, I was prescribed 3 intramuscular injections, they gave me injections, and at home for the evening For some reason, my second eye is also swelling, is it bad to do this or is it supposed to be like this?
First aid for Quincke's edema
If you notice the first signs of angioedema, you should call a doctor. This should be done even if the patient feels quite well. Before the ambulance arrives, you must:
- protect the patient from interaction with the allergen;
- help the victim calm down;
- ensure that clean air enters the room in which the patient is located;
- remove the patient’s belt and tie, unbutton the collar of his clothes;
- apply a cold compress to the affected area;
- try to remove the maximum amount of allergen from the victim’s body by giving him a little activated charcoal and making him drink as much liquid as possible;
- if angioedema appears after an insect bite or administration of a drug, apply a cold compress to the injection or bite site and, if possible, apply a tourniquet slightly above it;
- drip any vasoconstrictor drops into the patient’s nose;
- Give the victim a suitable antihistamine.
Emergency care for Quincke's edema
Emergency care for angioedema involves the following measures:
- hormone therapy (intravenous or intramuscular administration of prednisolone (60-90 mg), intravenous administration of dexazone (8-12 mg);
- detoxification therapy (enterosorption, hemosorption);
- use of diuretics (Lasix);
- desensitizing therapy (intramuscular administration of suprastin 2%);
- use of protease inhibitors (contrical, epsilon-aminocaproic acid).
In addition, the patient is hospitalized in the allergy department as soon as possible.
The treatment program for angioedema involves several successive stages. First of all, doctors determine the cause of the development of the pathology and recommend that the patient eliminate all potential contacts with the allergen from his life. In addition, a person who has suffered from angioedema is advised to avoid eating foods containing natural salicylates (raspberries, strawberries, cherries, strawberries, peaches, apples, grapes, apricots, plums, tomatoes, carrots, cucumbers and potatoes) for the duration of treatment, and also from the use of certain medications (paracetamol, analgin, ibuprofen, baralgin, citramon, pentalgin, askofen, indomethacin, acetylsalicylic acid, butadione and others).
Drug therapy for the treatment of angioedema involves the prescription of corticosteroids and antihistamines. In addition, the patient is advised to take vitamin supplements and medications that normalize the activity of the nervous system (ascorbic acid, ephedrine).
Persons who have suffered severe angioedema are advised to always have an individual syringe with adrenaline solution on hand. In order to prevent the development of pathology, it is necessary not only to avoid contact with the allergen, but also to stop drinking alcohol, and also to protect yourself from hypothermia, overheating and stressful situations.
At the end of the article, we offer you a TV show about Quincke's edema and its dangers.
Information about similar diseases:
Thanks for the information about Quincke's edema. No one in my family has allergies. And my young daughter-in-law suffers from allergies. Yesterday her face was swollen, she was shy, she hid it behind her hair, I couldn’t understand why she let her hair down like that. And when I saw her face, I was scared. An ambulance was called and she was hospitalized. And I began to “enlighten myself” via the Internet. Many thanks to Elena Malysheva for the broadcast about Quincke's edema.
Natalya Alexandrovna, visit our resource more often, we have a lot of interesting information.
Thank you for the article. Last night my daughter had swelling and they called an ambulance. Now I decided to read about him. Everything is clearly explained. Thank you!
Hello everyone. I don't know who can help anymore. My husband first had one foot swell on the second day and the other became painful to swallow, but it wasn’t hard to breathe, they called an ambulance, they put on something harmonious and suprastin, my husband slept for almost a day but got up with new swelling on his face, the right side of his face was swollen, starting from his forehead and including to the lip and the next day the same system only on the other side, then the eyes, one by one. In short, something new swells every day. During all this time, we had a bunch of tests done by both an allergologist (she said that it didn’t look like an allergy) and a therapist (he explained this by saying that supposedly there is some kind of bacterium in the liver that may react either to water or to some product). In just 1.5 weeks I’ve changed my mind, the thing is that 1 year ago we moved from Central Asia to Kaliningrad and I’m thinking that maybe it’s not the climate that’s causing swelling, because after 26 years my husband has I wasn’t allergic to anything, but then it appeared out of the blue. But it seems very similar to Quincke's edema, but then why does the allergist deny this?
Why is angioedema dangerous?
An assistant at the Department of Clinical Immunology and Allergology at the Institute of Clinical Medicine of the First Moscow State Medical University tells the story I. M. Sechenova, Candidate of Medical Sciences Assel Nurtazina:
— There are two types of angioedema (another name is Quincke's edema, named after the German doctor Heinrich Quincke , who first described it in 1882). The first is, as a rule, allergic in nature, the second develops as a hereditary disease. More common is angioedema (or histamine) edema, which occurs with allergies to food, cosmetics, chemicals, animal hair, and pollen. In approximately 50% of cases, angioedema occurs together with urticaria. For example, a person ate a fruit cake with jelly filling, just fruits, nuts, drank cold medicine, and developed skin rashes and swelling. This reaction can happen to any product. Most often, the eyelids, lips, soft tissues with loose subcutaneous tissue, and face swell. Sometimes arms, legs, even internal organs may swell. In children, viral diseases can cause urticaria and angioedema.
Article on the topic Blooming epidemic. How can allergy sufferers avoid hay fever?
The development of acute edema is often observed when using cosmetics. For example, a woman applied a new cream to her eyelids and got swelling. I have had patients who developed swelling of the eyelids after eyelash extensions or gluing false eyelashes (the reaction was provoked by the glue).
Chronic swelling can be a sign of other diseases. For example, these are autoimmune diseases and reactions, kidney disease with protein loss.
What to do if swelling develops for the first time? You need to take any non-sedating antihistamines. This could be cetirizine, loratadine, desloratadine, fexofenadine, etc. Within a few hours after taking the medicine, in some people even faster, literally before our eyes, the swelling goes away. The most dangerous situations are when the face, tongue, mouth, neck, and therefore throat swell, which can lead to asphyxia (suffocation). With such swelling, especially if a person feels difficulty breathing, you need to call an ambulance, because swelling can develop quickly and there is a high risk of suffocation.
Hereditary angioedema is also found (albeit less frequently). With them, the hands and face may also swell. However, such edema has significant differences from histamine edema. The latter develops quickly, from a few minutes to 4 hours. For example, a person ate something and got swelling. However, such swelling goes away just as quickly. For some, even without treatment for 24 hours.
Question answer
Why is the level of uric acid in the blood increased after angioedema?
As a rule, hereditary angioedema develops slowly and increases within 12 hours, in some patients - up to 24 hours. And then they don’t go away for a long time (several days or a week). An important difference: hereditary angioedema is painful, pale, firm and cold to the touch, while histamine edema is usually hot and red. Doctors have a method to determine hereditary edema. Usually, if you press on the site of the edema, a hole remains on it, but hereditary edema is so dense that there is no hole left after pressing. In this case, antihistamines do not help. The swelling will continue to develop. In such a situation, you should definitely contact an allergist-immunologist, especially if it is recurrent swelling. Swelling of the throat poses a danger; hoarseness can indicate this. Swelling in the abdominal area (belly area) is accompanied by severe pain. Any internal organs can swell: the liver, spleen, urinary tract (then the person stops urinating, which is extremely dangerous). For some people, the pain may be so severe that they have to call an ambulance. Sometimes they undergo several operations for an “acute abdomen,” but in fact the cause is not surgical pathology, but swelling, and they need to contact an allergist-immunologist to undergo an examination, confirm the diagnosis and receive specific therapy. Hereditary edema debuts before the age of 30 and is classified as a primary immunodeficiency disease.
Quincke's edema
Quincke's edema (or angioedema) is an allergic disease in which sudden swelling of the subcutaneous tissues and mucous membranes occurs.
Most often, Quincke's edema affects the face, mouth, respiratory tract and gastrointestinal tract. But it can also affect joints and internal organs. Damage to the larynx (due to the risk of difficulty breathing) and the brain (can lead to serious neurological disorders) is considered especially dangerous. Pathology of this type can develop in almost any person, since there are many predisposing factors: from food allergies to acute infectious diseases.
In half of the cases it accompanies urticaria, and in 11% of cases it develops in isolation. Sometimes the cause of sudden swelling cannot be found, and then it is called idiopathic. It is noteworthy that Quincke's edema is a kind of family disease, and is often transmitted, for example, from parents to children. “Inherited” a person receives a deficiency of certain enzymes that should fight substances responsible for edema.
Edema can develop, pass or recur 1.
4.Treatment
The key is to reduce and, if possible, completely eliminate the likelihood of contact with the allergen. To relieve acute symptoms, antihistamines, desensitizing, decongestants, anti-inflammatory drugs are used, incl. hormone-containing. In most cases, the patient is hospitalized, mainly due to the risk of asphyxia.
Methods for drug correction of immune failure (immunotherapy) are being actively developed, but at the moment such treatment is very expensive.
Sign up for a consultation
Symptoms of Quincke's edema
Symptoms depend on location and are especially acute at the onset of the disease, developing at high speed - from a few minutes. External manifestations of the pathology are severe swelling of the nasolabial triangle, tongue and tonsils.
It is believed that the form of the disease becomes most dangerous at the moment when the trachea, larynx and pharynx are exposed to an allergic reaction. In this case, the following may be observed:
- hoarseness of voice;
- difficulty breathing up to suffocation;
- "barking" cough.
If medical attention is not provided promptly and further swelling is not prevented, the outcome can be fatal 2 .
Less commonly, with Quincke's edema, loose stools, vomiting and painful attacks appear, localized in the abdominal area. Symptoms of an “acute abdomen” indicate the spread of the disease to the gastrointestinal tract.
If the brain is “affected” during an allergic reaction, the symptoms will resemble nervous system dysfunction:
- aphasia;
- hemiplegia;
- nausea, vomiting and severe dizziness;
- frequent seizures.
If the reactions go further, then the urinary system will come under the influence of the disease. Acute cystitis develops, accompanied by prolonged urinary retention. Swelling of the genital organs is possible.
Complications
With Quincke's edema affecting any organ, especially if it is accompanied by intense manifestations of urticaria, anaphylactic shock can develop at lightning speed. This is an extremely life-threatening allergic reaction that spreads throughout the body. Manifests itself in the following symptoms:
- generalized (widespread) itching;
- swelling of the tissues of the pharynx, tongue, larynx;
- nausea, vomiting, cramping abdominal pain, diarrhea;
- convulsions, respiratory arrest, coma;
- the appearance of urticaria (swelling and itchy red-pink spots, blisters);
- lacrimation, sneezing, bronchospasm with excessive mucus production, blocking the flow of oxygen;
- increased heart rate, drop in blood pressure, cardiac arrhythmia, increase in acute cardiovascular failure.
Incorrect treatment of hereditary angioedema also leads to fatal consequences for the patient.
Quincke's edema in children
Quite often, young children suffer from laryngeal edema. The following factors influence this:
- feeding an infant with artificial food;
- frequent use of medications;
- allergic reaction of a household type (to shampoo, bed linen conditioner or powder);
- abuse of multivitamins and potent antibiotics.
For children under 3 years of age, non-allergic Quincke's edema is typical. This is due to heredity and often manifests itself in combination with bronchial asthma or urticaria. The narrowing of the pharynx occurs quickly.
- the first stage manifests itself almost imperceptibly, without shortness of breath;
- the second causes pale skin, the nasolabial triangle turns blue, and the heart rate increases;
- at the third stage, respiratory failure occurs. Severe sweating appears, the child has difficulty breathing;
- the fourth stage is the most difficult. It is accompanied by a slow heartbeat, shallow breathing and loss of consciousness.
At the first manifestations of swelling of the larynx, it is necessary to consult a specialist, since the lack of qualified assistance in this case can be fatal.
Diagnosis of Quincke's edema
Diagnosis includes examination of the patient and collection of anamnesis (predisposing factors).
During the examination, the specialist pays attention to:
- location, its size, density and color, temperature of the edema and surrounding tissues, the presence of itching or burning, time of development;
- the condition of the respiratory tract, voice, swallowing process to eliminate danger to life;
- blood pressure and pulse rate, body temperature, etc.
At the second stage, predisposing factors are assessed. These include:
- cases of edema in the family;
- the presence of blows, injections, injuries in the patient in the last few hours;
- taking estrogen-containing drugs during pregnancy;
- nutritional and medicinal factors;
- frequent hospitalizations with signs of an “acute abdomen” (may indicate internal edema).
You should also find out whether the patient suffered from oncology or autoimmune diseases. Only after analyzing all the complaints and information will it be possible to determine the nature of the edema - whether it is acquired or hereditary.
Emergency care for Quincke's edema
Given the speed at which swelling develops, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before the ambulance arrives, you need to act as follows:
- calm the patient and sit him in the most comfortable position;
- It is necessary to remove everything unnecessary from the patient. It is necessary to ensure a flow of fresh air;
- limit direct contact with the irritant. If the swelling is caused by an insect bite, you need to get rid of the sting;
- administer antihistamines. In this case, injections will be the most effective. But if it is not possible to get an injection, you need to take the drug. This is the only way to reduce the intensity of the reaction. Among the latest generation of antihistamines, Cetrin® stands out. Its action is aimed at blocking histamine, a substance responsible for the occurrence of an allergic reaction. Therefore, the drug works regardless of the cause that caused Quincke's edema and can help in stopping the attack 3.
Treatment of Quincke's edema
Direct treatment of the disease takes place in the inpatient allergy department. In order to begin treatment, it is necessary to determine the cause of the allergic reaction. The patient is prescribed a mandatory diet that excludes foods containing honey and chocolate, berries and citrus fruits and other strong allergens; Prescribe drugs with an antihistamine effect in combination with hormonal drugs - dexamethasone or, for example, prednisolone ointment. To remove the allergen, treatment is accompanied by the prescription of polysorbs.
The above complex of medications is supplemented with agents that normalize the functioning of the body’s nervous system, for example, calcium or ascorbic acid.
Self-treatment of Quincke's edema, without consultation and supervision of a qualified specialist, is impossible.
Treatment of allergic eye swelling
Before you begin treatment for allergic eye swelling, the allergen should be identified. This is why a thorough diagnosis is necessary. Only after this will the doctor prescribe medications
It is very important to exclude the patient from contact with the allergen in order to completely get rid of allergies.
Symptomatic drug treatment of allergic eye edema is based on the use of drugs that eliminate the disease:
- antihistamine eye drops to relieve swelling and itching;
- hormonal eye ointments to relieve inflammation and swelling;
- antihistamines to relieve symptoms associated with the disease;
- medications with a vasoconstrictor effect to eliminate red eyes.
Any medicine can be taken only as prescribed by an ophthalmologist. The doctor will create an individual program for you to treat and prevent the disease.
In case of deep and severe damage to the lower and/or upper eyelid, the doctor may prescribe local or general antimicrobial drugs. They prevent infection and relieve inflammation.
Only a doctor knows how to relieve allergic swelling of the eyelids. Strengthening the patient's immune system when an allergen is injected under the skin in small doses is today an effective treatment method. Over time, the patient’s immunity ceases to recognize the allergen as an irritant, and any negative reactions soon disappear from the body.