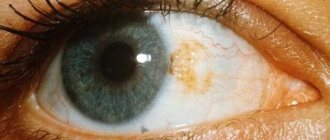
Why does a tumor appear?
The mosquito is a typical blood-sucking insect, often choosing animals and humans as its prey. At the same time, blood is necessary exclusively for female insects - the biological fluid contains elements for the full cultivation and laying of eggs. Males consume flower nectar as food, since their mouthparts are not developed enough to pierce the skin.
The ectoparasite finds its victim at a great distance. To do this, it has two dozen receptors that record the release of lactic acid, carbon dioxide and sweat, and the intensity of movement of warm-blooded organisms. Insects attack outdoors and indoors, preferentially targeting sedentary creatures. After landing on the epithelium, they search for nearby capillaries, puncture the skin and inject saliva containing anticoagulants to prevent blood clotting. This biological natural fluid of insects provokes local unpleasant symptoms.
If mosquito bites on the skin of the torso, upper and lower extremities in the absence of an allergic reaction appear insignificantly, then the corresponding damage to the skin of the face and eye area has more characteristic signs due to the lack of a full fat layer and less thickness of the epithelium.
Consequences of an insect bite
What happens after a mosquito or midge bites a child: (we recommend reading: a child was bitten by a midge: photos of external manifestations, first aid)
- the damaged area becomes red, inflamed and swollen;
- the bite itches and itches (the main thing is to try not to let the baby scratch the wound);
- scratching even small wounds injures the delicate baby skin, which can lead to infection and scars;
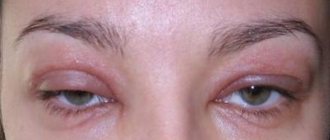
- The thin and delicate skin around the eyes (upper or lower eyelid) becomes severely inflamed after a bite and increases significantly in size.
The main consequences of an insect bite are unbearable itching and burning, redness, swelling and a visible wound. Without following the rules of hygiene and first aid, complications are possible. You should also not forget about the allergic reaction that many children suffer from.
Why does the eyelid swell?
At night after a bite, the child is in a lying position, which contributes to a significant accumulation of fluid at the site of the lesion. However, if the baby is not in bed the next day, the fluid drains and the eye returns to its normal size.
The second cause of swelling is an allergic reaction. An allergy to insect bites is called culicidosis (we recommend reading: allergy to mosquito bites in children: photos, symptoms and treatment). This is a pathological response of the immune system to a specific stimulus. In most cases, the reaction is caused by the chemical composition of the insect's saliva. It contains poison, to which many children react acutely.
What complications may arise?
The main complication that occurs most often is infection of the bite site. It is difficult for a child to resist scratching. When he scratches the bite, small scratches, cracks or abrasions appear on the epithelium. Injured areas become infected, which can be very dangerous.
The baby is at risk of infection with various bacteria (staphylococci, streptococci, rod-shaped microorganisms, etc.) or fungi. The most common complication is conjunctivitis. When infected, the damage and unpleasant symptoms usually spread to the second eye.
Warning signs of infection:
- pain and burning (one or both eyes);
- redness (from bright pink to red);
- tearfulness;
- formation and discharge of pus;
- temperature increase;
- signs of general intoxication.
In some severe cases, allergies also have complications (difficulty breathing, rhinitis). This depends on the child’s individual predisposition and the state of his immune system. In this case, the child requires emergency medical care and specialist consultation.
Signs of an allergic reaction:
- manifestation of asthma symptoms (suffocation, shortness of breath, etc.);
- dizziness;
- allergic rhinitis;
- abdominal pain.
The most severe manifestations of allergies are anaphylactic shock and Quincke's edema. Anaphylactic shock involves a significant decrease in blood pressure, tachycardia, and dizziness. With Quincke's edema, swelling and several-fold increase in the soft tissues of the face and neck are observed. Gradually, the swelling spreads to the mucous membranes (tongue, larynx), which can lead to difficulty breathing and its complete blockage.
Symptoms
Main symptoms of the pathological process:
- Edema. Volumetric, occupies a significant part of the outer surface of the eyelid or other nearby areas.
- Itching. Regular and painful, worsens with blinking, forced opening or closing of the eye.
- Hyperemia. At the site of the bite, the temperature rises locally and the skin turns red.
Many people experience an allergic reaction. It develops as a consequence of penetration of mosquito saliva into the epithelium. The symptoms described above intensify, swelling spreads to the entire eye and part of the face, and the skin becomes covered with a small rash.
Patients who have hypersensitivity to individual components of insect biological fluid have a significantly increased risk of systemic allergic manifestations, including the development of pathologies of the autoimmune spectrum. Their signs include a general rise in body temperature, Quincke's edema, intoxication of the body - anaphylactic shock. If the patient exhibits the indicated symptoms, it is necessary to urgently call an ambulance to the scene.
Folk remedies
Traditional recipes for mosquito bites
In order to reduce itching, swelling and other consequences of mosquito attacks, infants or older children can use proven “grandmother’s” methods:
- make a soda solution from 3 tsp of powder and 1 liter of water, put the resulting slurry on the bite site until it dries;
- use the juice of medicinal plants (dandelion, plantain, mint, parsley), from which a lotion is made using a moistened cotton pad on the eye area;
- Shredded cabbage leaves should be placed on the bitten area;
- wipe the eyelid with an ice cube, repeat several times;
- put a cold lotion on the bite site for 15 minutes, repeat every hour;
- make lotions with aloe juice, making sure that the liquid does not get on the mucous membrane;
- vinegar solution with water - used to wipe the affected area, relieve swelling and reduce itching;
- The use of essential oils (tea tree, etc.) is possible only when diluted with water. When applying, be careful not to get into the eye.
Important!
Some herbal remedies and essential oils may cause allergies in young children. Therefore, it is imperative to check for skin sensitivity: drop the product onto an undamaged area and check the reaction; if there is no redness, then you can use it.
How to get rid of a tumor?
The treatment procedure for pathological problems in the absence of a systemic allergic reaction is carried out at home. Medicines are used, supplemented with traditional medicine recipes.
Drug therapy
The priority is the use of local agents that do not have a systemic effect on the body. In some cases, they are supplemented with medications in tablet form or injections as specifically prescribed by a doctor as part of outpatient therapy.
Effective drugs:
- Antiseptics. Used to reduce the risk of developing local secondary bacterial infections. Safe for the organs of vision - hydrogen peroxide (outer epidermis), chlorhexidine and miramistin (skin and mucous membranes). The bite site and nearby skin are washed with these liquids 3-4 times a day for a week.
- Antihistamines. Used for the development of local allergic manifestations. Apply to the outer skin at the site of swelling (excluding the surface of the eye itself). A typical representative is fenistil gel. As a supplement, it is possible to use antihistamines in tablet form (diazolin, loratadine).
- Anti-inflammatory ointments. Reduce pain and swelling. The first choice drugs are non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Typical representatives are flamidez gel, diclofenac ointment. If necessary, treatment is supplemented with tablets - paracetamol, ibuprofen, analgin. In the presence of extensive edema that has formed against the background of an allergic reaction, the use of corticosteroid ointments is rational. Typical representatives are dexamethasone, prednisolone. In oral or injectable form, steroids are allowed to be used only after a doctor's prescription.
- Recovery sprays. After the partial disappearance of acute symptoms of the pathology, skin-regenerating sprays based on dexpanthenol are used. Typical representatives are panthenol, depanthenol.
- Antibiotics. They are prescribed exclusively by a doctor, regardless of the form of release of the drugs for a confirmed bacterial infection. Typical options are tetracycline and chloramphenicol ointment, baneocin, chitosan.
ethnoscience
Any folk remedies for swollen eyes after a mosquito bite should be used with great caution. Many recipes contain alcohol, various aggressive components, herbs, which themselves can cause allergies if they come into contact with mucous membranes and irritated skin. Before using procedures, consult your doctor.
- Soda. The outer skin in the area of the bite and swelling is regularly wiped with a solution based on this substance. Recipe: one teaspoon of soda per 700 milliliters of water. The liquid is thoroughly stirred until the substance is completely dissolved, cooled to room temperature and used 3-4 times a day for 4-5 days.
- Potato. One medium-sized potato is peeled and thoroughly washed under running water, after which it is cut lengthwise into thin slices (2-4 millimeters). The latter are applied to the swollen eye for 30 minutes 4-5 times a day. Treatment is designed for one week.
- Chamomile and calendula. The two components have a soothing, wound-healing and antiseptic effect on all types of skin. Buy ready-made products in packages at the pharmacy. Take one teaspoon of each of the dried and variable herbs, then pour 500 milliliters of boiling water over them and let it brew for 10 minutes. Strain through several layers of gauze. Use the liquid to rinse the affected eye 5-6 times a day for 1 week.
Consequences of a mosquito bite
Try not to scratch the bite area
What consequences do an adult or child expect after a mosquito bite on the eyelid?
- The bite causes a desire to scratch the injured epithelium.
- Scratching barely visible wounds can cause infection to get under the skin. Adults can control the healing process, distract the child from scratching and explain to him why he should not disturb the bite site, which is quite difficult.
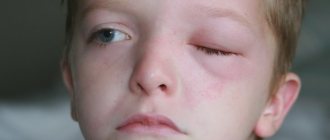
- If a mosquito bites you in the eye, the damaged eyelid will increase in size several times.
When a baby rubs an injured eye with dirty hands, there is a chance of infection, such as conjunctivitis.
Why does the eyelid swell?
Since the skin around the eyeball is quite elastic, it can swell to unprecedented proportions after a bite. Having slept all night with a “bitten” eye, the eyelid accumulates fluid, therefore, having assumed a sitting or standing position, the eye that does not open in the morning takes on a normal appearance by lunchtime.
Sometimes a small red dot remains at the site of the bite. The color of the swollen epithelium may vary from light pink to pale red. It depends on the accumulated fluid and the person’s immunity. How can you determine if there is an infection?
Possible complications in children
If an insect bites a child
If a bloodsucker bites a child in the eye, the parents may be frightened by the swollen eyelid. Such a phenomenon should not become a cause for concern. Most often, the swelling will subside after the baby spends several hours of active time.
Enlargement of the area injured by the mosquito, burning under the eyelid, rhinitis, difficulty breathing - such symptoms are a manifestation of allergic reactions of the body.
With such a course of the disease, it is recommended to seek advice from a specialist in order to avoid serious consequences.
Pharmacy drugs
If there is a severe allergic reaction, antihistamine tablets are prescribed. The dose is selected depending on age. Children under 1 year of age are given ¼ part of Elcet, Eden, 1 tablet of Diazolin, 1/2 part of Suprastin. It is recommended to give the drugs to the child before bedtime. The course of therapy depends on the complexity of the situation, but no more than 10 days. Antihistamines relieve swelling, redness, resist complications, and have antiallergic properties.
You should definitely put Albucid drops into your eyes. Broad-spectrum antibiotic at an affordable price. Prescribed for the treatment of infectious diseases, for prevention. The active ingredient is sulfacetamide with an antimicrobial effect. Place 1-2 drops into the eye up to 6 times a day on the first day. The dosage is reduced as symptoms disappear. The maximum course of therapy is 7 days. The cost of the drug is within 100 rubles. Separately, products are produced for children and adults.
Carefully treat the bite site with an antihistamine - Fenistil gel, Soventol, Nezulin. The drug should be applied pointwise up to 2 times a day. Use for no more than a week.
Important!
If there are obvious symptoms of a severe allergic reaction, hormonal drugs are used, but their use should be supervised by a specialist. Akriderm is often prescribed. The addition of a secondary infection involves the use of antibiotics. The doctor determines which drug to buy and how long to treat. This is especially true for mosquito bite remedies for children.
Complications in children with a mosquito bite in the eye
Complications after a mosquito bite
All folk remedies and medicines are highly effective in treating swelling and changes in the skin of a child within 24 hours after an attack by “bloodsuckers”. However, complications are also possible that occur due to an allergic reaction of the child’s body.
Symptoms that require you to see a doctor:
- the size of the edema exceeds 10 cm;
- persistent itching and severe redness;
- fever after a mosquito bite;
- heart rhythm disturbance, tachycardia;
- signs of drowsiness, pain and dizziness;
- choking or breathing problems.
Products for the treatment of mosquito bites should always be present in a home medicine cabinet in order to provide assistance to the injured child quickly and effectively, helping to relieve swelling, reduce itching and prevent scratching of the bitten area.
After a mosquito bite, there is always redness and itching on the skin, and sometimes there is slight swelling. Over time, these symptoms disappear. This is not the case with allergies - the swelling becomes painful and pronounced.
Why are bites dangerous?
Swelling and swelling from a mosquito bite is a common occurrence in the summer. A short-term swelling appears on the affected area, which you always want to scratch. The consequences are not always harmless.
Human blood is a vital substance for mosquitoes to survive. Why does the bite of this insect itch? The thing is that during a mosquito bite, anticoagulants penetrate into the blood, preventing it from clotting. Otherwise, the microscopic wound would quickly close, and the mosquito would not get enough. This is why the affected area itches and swells.
Anticoagulants act as an irritant for the human body and provoke an allergic reaction. Depending on the location of the mosquito bite, various complications can develop. For example, a mosquito bite on the eyelid can cause a person to lose visual ability due to swelling and swelling. The tumor does not disappear from this area of the body for a long time, since the skin around the eyes is thin and delicate. In rare cases, a mosquito bite can lead to the development of eye diseases.
Due to the individual structure of the body, people have different effects on stimuli from the external environment. Swelling is especially pronounced in a small child, causing severe itching and redness.
Allergy
Swelling and redness after a mosquito bite is a common cause of allergies. If the substances that penetrated the human blood did not cause allergies, then the swelling will quickly pass and will not leave a trace.
Let's consider the main manifestations of histamine release into the bloodstream:
- Allergic swelling of the face, characterized by massive rashes like urticaria.
- A sudden attack of suffocation that resembles bronchial asthma.
- Increasing body temperature.
- Periodic itching in the affected area that does not go away for several hours.
- Accumulation of a large amount of viscous fluid in the nasal cavity.
- Rash on other parts of the body.
It is necessary to visit a doctor if a person has these symptoms. In extreme cases, angioedema may develop. This situation rarely happens in medicine. As a rule, an ambulance is called for the patient.
Mosquitoes as carriers of diseases
Health problems arise from a mosquito bite if the insect was a carrier of the following diseases:
- Encephalitis.
- Tularemia.
- Setariasis.
- Fever.
- Malaria.
- Dirophyllariasis.
- Brugioz.
- Wuhereosis.
Infections with the listed diseases are often recorded in tropical countries and Central Asian countries. In the Russian Federation, similar cases have been recorded in the south, rarely in the central part and Siberia.
The following changes in the human body indicate infection:
- Detection of eye infections.
- Low blood pressure.
- Modification of the subcutaneous layer.
- Disturbed functioning of the central nervous system.
- The presence of urge to vomit and nausea.
- The work of the lymphatic system is being restructured.
In rare cases, a person may faint. It is noted that the types of mosquito bites and symptoms after them may differ. If you are planning a vacation to tropical countries, you must be vaccinated against the above-mentioned diseases in the hospital.
Hyperemia
Hyperemia after a bite is swelling, due to which blood flow to the affected area of the body increases, and, as a result, redness develops. The name of the pathology comes from two Greek words “over” and “blood”. The disease is not transmitted to other people.
If such a symptom is present, consult a doctor for treatment. Hyperemia is divided into 2 types. In the first type, arterial, the patient’s blood flow in the arteries increases, so the tone of the vasoconstrictor or vasoconstrictor nerves decreases. Venous congestion is characterized by swelling at the site of blood accumulation.
Parents' actions
Rules of conduct and treatment of swelling after mosquito bites:
- Wash the affected eye thoroughly with water and soap to remove germs.
- The area where the mosquito bite was made in the form of a red dot must be carefully disinfected with an alcohol solution, without touching the eyeball itself.
- Parents need to ensure that children do not scratch the itchy eye, so as not to infect the mucous membrane.
- Take an antihistamine drug that will help prevent an allergic reaction and reduce unpleasant symptoms: Suprastin, Claritin, Loratadine, Erius.
- Use folk and medical remedies to treat the consequences of mosquito bites.
- Drink plenty of fluids to remove toxins from the body.