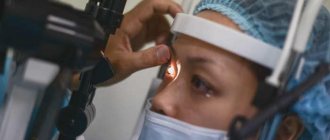
The importance of vision in the life of any person is difficult to underestimate. In the daily bustle, we sometimes forget that our eyes sometimes need rest, special gymnastics and “life-giving” nutrition in the form of vitamins, microelements and various vitamin complexes.
Due to various circumstances, some of us encounter eye diseases such as glaucoma, which, with the right approach, can be prevented and cured with existing procedures and medications.
In the fight against this disease, vitamins and microelements necessary for the eyes to fully resist glaucoma play an important role.
The variety of vitamins for glaucoma and vitamin complexes that are currently available allows for high-quality prevention of the disease and are of great importance in treatment at different stages of its development.
Glaucoma and its forms
Vitamins for glaucoma for treatment and prevention Source: vizhuchetko.com
Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease. It is characterized by increased blood pressure inside the eye, as a result of which the optic nerve atrophies. This term is very broad, it includes about 60 different diseases with similar features.
From Greek “glaucoma” means the green color of sea water. In the last, most severe stages of the disease, the pupil becomes green.
Hippocrates used this word as a name for a disease as early as 500 BC.
The flow and flow of fluid inside our healthy eye is balanced. In the case of glaucoma, fluid circulation is disrupted and the accumulated fluid begins to put pressure on the optic nerve.
It atrophies, and nerve impulses from the eye stop flowing to the brain. First, peripheral vision disappears, then the person stops seeing completely.
There is open-angle glaucoma and closed-angle form of this disease. The vast majority of patients complain about angle closure. They differ from each other in that with an open-angle eye, the functions of the eye responsible for the outflow of fluid are impaired, and with a closed-angle eye, the path for the outflow of fluid is closed.
In addition to blurred vision and narrowing of its field, a person with glaucoma experiences a number of other unpleasant symptoms. The eyes begin to hurt and there is a pain. “Rainbow circles” appear when you look at a bright light.
Glaucoma can be congenital and occur at any age. But still, most often it affects older people.
A little about the disease
Glaucoma is an ophthalmological disease, the main manifestation is a persistent increase in intraocular pressure. Gradual atrophy of the optic nerve leads to damage or loss of function of the eye, including blindness. The level of development of medicine still does not allow to cure the disease completely, but it can keep its development under control.
In a healthy eye, there is a constant flow and flow of fluid. If there is a discrepancy between the volume of fluid produced and drained, the pressure inside the eye increases. As a result of its action, the nerve at the back of the eye is damaged. Due to atrophy of the optic nerve, visual signals stop reaching the brain and the person loses the ability to see.
Open angle. Violation of the function of the natural drainage system, although access to moisture is open. The visual field narrows over several years; this process occurs unnoticed and painlessly. Patients find it difficult to answer the question about the presence of complaints.
Closed angle. The intraocular fluid does not have access to the drainage system due to the iris blocking the angle of the anterior chamber. The pressure inside the eye increases quickly and an acute attack of glaucoma occurs, which can lead to sudden loss of vision.
A serious excuse for visiting an ophthalmologist is the appearance of complaints:
- Black spots or veils before the eyes;
- Deterioration of lateral vision and image distortion;
- Pain in the eye sockets;
- Blurred vision at dusk, in the evening, at night;
- Redness of the sclera;
- Decreased vision;
- Dark spots in the field of vision.
Sharp pain in the eye and obvious visual impairment, the appearance of rainbow circles when looking at a light source, swelling and redness, nausea and vomiting are symptoms of an acute attack; you should consult a doctor immediately.
Treatment of pathology
Diagnosis of glaucoma includes measuring intraocular pressure, examining visual fields, measuring refraction, and examining the anterior chamber of the eye and lens.
Treatment is medicinal, using drops that increase the outflow of fluid or inhibit its production. They help reduce pressure on the optic nerve and retina. Vascular medications are prescribed to improve blood supply. Drops and other medications are prescribed only by a doctor. Self-treatment with traditional medicine is not acceptable.
Surgical and laser treatment of glaucoma involves the creation of an artificial channel for the outflow of fluid - a fistula, which provides drainage for some time, the period varies from a year to 10-15 years. The choice of treatment methods depends on the degree of development of the disease, the effectiveness of therapeutic treatment, the characteristics of the patient’s body and concomitant diseases.
Proper nutrition prevents eye diseases and influences the effect of therapeutic measures. An unreasonable approach to food choices can reduce the effect of treatment. After surgery to restore the outflow of moisture, the fistula is perceived by the body as a wound that needs to be healed.
The rate of scarring depends on the characteristics of the body, including the presence or absence of nutrients. Fluid retention in the body as a result of excess drinking or due to excess salt directly affects the production of moisture in the eyeball.
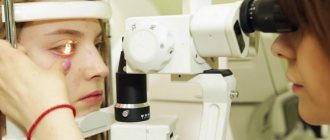
Diagnosis of open and angle-closure glaucoma
Diagnosis of open and closed-angle glaucoma Source: klinikaglaz.ru
The main problem in diagnosing glaucoma, primarily open-angle glaucoma, is the absence of typical symptoms in the early stages.
Many people who have this disease are unaware of it. Therefore, it is very important, especially in old age, to undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist. There are several methods for diagnosing glaucoma.
Eye pressure is measured using tonometry. Checking eye pressure is an important part of diagnosing glaucoma. High intraocular pressure is often the first sign of the disease.
Gonioscopy (examination of the anterior chamber angle) allows you to get a clear picture of the condition of the anterior chamber angle of the eye to determine the type of glaucoma. This is difficult to do during a routine examination.
Using a mirror lens makes it possible to examine the anterior chamber angle and determine the presence of open-angle (if the anterior chamber angle does not function effectively enough) or closed-angle (if the anterior chamber angle is at least partially closed) glaucoma or a dangerous narrowing of the anterior chamber angle (when the iris is located so close to the drainage system eyes, which can block it).
Ophthalmoscopy
Ophthalmoscopy (examination of the optic disc for signs of damage) is performed using an ophthalmoscope, an instrument that allows you to view the internal structure of the eye under magnification.
The pupil is dilated using special drops. Glaucoma damages the optic nerve, causing the death of its fibers. As a result, its appearance changes, it begins to resemble a bowl. If its size increases, “dark” spots appear in the field of vision.
Perimetry (read more) reveals “dark” spots in the field of view. The test results will show their presence and location. The patient may not even notice some of them.
The test is performed using a cup-shaped instrument called a perimeter. Only one eye can be tested at a time, so the other eye is covered with a bandage during the test.
The patient must look directly at the mark. The computer gives a signal and luminous points flash inside the device in a random order.
The patient must press the button when he sees them. Not every sound signal is accompanied by the appearance of a dot. Perimetry is usually performed every 6-12 months to monitor changes.
Pachymetry
Pachymetry is the measurement of corneal thickness. This indicator may affect the accuracy of IOP measurement.
If the cornea is very thick, then the intraocular pressure will actually be lower than what is measured by tonometry. Conversely, with a very thin cornea, the true intraocular pressure is higher than the measurement result indicates.
Glaucoma treatment
Treatment of glaucoma is mainly divided into three main areas - medication, laser and surgery.
Drug (conservative) treatment of primary glaucoma
Currently, drug treatment of glaucoma is carried out in three main areas:
- therapy aimed at reducing intraocular pressure (ophthalmic hypotensive therapy);
- therapy that helps improve blood supply to the inner membranes of the eye and the intraocular part of the optic nerve;
- therapy aimed at normalizing metabolic processes (metabolism) in the tissues of the eye in order to influence the degenerative processes characteristic of glaucoma.
It is necessary to immediately stipulate that the key point in the treatment of glaucoma is the normalization of the level of intraocular pressure (IOP), and techniques aimed at improving blood circulation and influencing metabolic processes in the eye are only auxiliary.
The correct mode of work and life of a patient with glaucoma has a known therapeutic value. When prescribing a regimen of instillation of anti-glaucoma drops, the patient should be dynamically observed by a doctor for at least 2-3 weeks.
Subsequently, monitoring of the effectiveness of treatment is carried out at least once every 3 months. Regular replacement of drugs after 1-2 years with appropriate re-monitoring is recommended to prevent the development of resistance to them.
Medicines used in the treatment of glaucoma are divided into two large groups: drugs that improve the outflow of intraocular fluid (IOH) from the eye and drugs that inhibit the production of aqueous humor.
Laser treatment
Laser surgery for glaucoma is aimed at eliminating intraocular blocks that occur in the outflow tract of intraocular fluid (IOH) in the eye (see section “Anatomy and physiology of the outflow tract of intraocular fluid”).
Laser radiation has been widely used in glaucoma surgery since the 70s of the last century. Currently, argon lasers (wavelength 488 and 514 nm), neodymium YAG lasers (wavelength 1060 nm) and semiconductor (diode) lasers (wavelength 810 nm) are most often used for this purpose.
Laser therapy
The action of lasers is based either on the application of a local burn to the trabecular area, followed by atrophy and scarring of its tissue (coagulator lasers), or on a microexplosion, which is accompanied by tissue rupture and a shock wave (destructor lasers).
Many types of laser operations have been proposed, of which laser iridotomy (iridectomy) and laser trabeculoplasty are the most widespread.
Laser iridectomy (iridotomy) involves creating a small hole in the peripheral part of the iris. The operation is indicated for functional pupillary block and leads to equalization of pressure in the posterior and anterior chambers of the eye and opening of the anterior chamber angle.
It is used for primary and secondary angle-closure glaucoma, as well as for mixed forms of glaucoma.
Laser trabeculoplasty involves applying a series of burns to the inner surface of the trabecula. This effect improves the permeability of the trabecular diaphragm for aqueous humor and reduces the risk of blockade of Schlemm's canal.
The operation is indicated for primary open-angle glaucoma, which cannot be compensated by drug therapy.
Surgery
The issue of surgical treatment of open-angle glaucoma is decided individually, taking into account the form of glaucoma, the level of intraocular pressure (IOP), the coefficient of ease of outflow, the state of the anterior chamber angle, the field of view and the general condition of the patient.
Currently, the question of indications for surgical treatment of glaucoma remains open.
Among ophthalmologists, there are sometimes opposing points of view: from recommendations for surgical treatment already in the early stages of the glaucomatous process (immediately after diagnosis of the disease), to complete refusal of surgery. However, only a small number of specialists adhere to such extreme points of view.
The main goal of antiglaucomatous operations is to reduce and normalize increased intraocular pressure (IOP), create conditions for the most favorable microcirculation in the optic nerve, relieve the phenomena and consequences of its hypoxia, improve its nutrition and tissue metabolism.
Any antiglaucomatous operation can be considered successful if, in the long term after the operation (6-12 months), the achieved level of intraocular pressure (IOP) is consistently maintained at the lower limit of normal.
Glaucoma of the eye: definition, etiology and types
According to the ICD, glaucoma is defined as a chronic pathology of the organs of vision, which is characterized by periodic or constant increased intraocular pressure, provoking optical neuropathy and dysfunction of the visual system.
The classification of glaucoma is determined according to:
- Origin: primary and secondary
- Mechanism of occurrence: closed-angle, open-angle
- IOP level: normotensive or hypertensive with a moderate increase or high tonometric pressure.
- Currents: stabilized and unstabilized
- Time of occurrence: congenital, acquired (infantile, juvenile, adult).
The etiology of glaucoma is determined by the inability to maintain a natural balance between the volumes of produced and drained intraocular fluid in the visual organs.
The main factors that provoke an increase in intraocular pressure include:
- Increased volume of intraocular fluid
- Pathological changes in the drainage system of the eyes, leading to changes in fluid excretion
- The use of mydriatics for eye drops
- History of injury or contusion of the visual organs
- Burdened heredity
- Chronic ophthalmological pathologies
- Hypertonic disease
- Diabetes mellitus and obesity of any type
- Sclerotic dysfunction of blood vessels
- Atherosclerosis
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, provoking the development of innervation of the eyeballs.
As a result of such pathological conditions, the channel that drains fluid from the orbit becomes blocked.
Physical limitations for different types of glaucoma
Physical limitations for different types of glaucoma Source: fitnesru.com
If glaucoma is diagnosed, then you need to slightly reconsider your lifestyle. You will have to avoid actions that may cause an increase in intraocular pressure.
These include: washing floors in an inclined position; handwash; any work that requires significant physical effort.
When performing general strengthening physical exercises, you should avoid sudden bends and jumps. It is advisable to increase physical activity through long walks in the fresh air.
Recommendations for the prevention of glaucoma
An annual visit to an ophthalmologist, following his recommendations for taking medications, physiotherapy, special exercises and diet, vitamins and spa treatment - all these measures can curb the development of glaucoma. However, glaucoma cannot be completely cured.
In case of impending blindness, surgical intervention must be resorted to.
At home, a patient with glaucoma should, if possible, avoid situations that cause a rush of blood to the head:
- physical labor associated with bending the head and torso while washing floors
- weeding work on a personal plot
- washing clothes
- picking mushrooms and berries
- lifting weights
- “upside down” pose when doing gymnastics or yoga in some sports (for example, weightlifting)
If you drive a car, here are a few precautions:
- use glasses when driving;
- in bright sunshine, wear special protective green glasses for patients with glaucoma;
- try not to drive a car at dusk or at night;
- be alert, watch the road in front of you and to the sides;
Remember that your self-care plays a key role in the fight against glaucoma.
Nutrition for glaucoma
Nutrition for glaucoma Source: uglaznogo.ru
Nutrition for glaucoma should be balanced, you need to know which foods can be consumed and which should be excluded. Long breaks in eating are not recommended.
You should eat at least four times a day, spreading your meals evenly throughout the day. The last meal should be no later than two hours before bedtime.
Healthy diet
It is necessary to exclude from the diet foods and drinks that stimulate the nervous system: natural coffee, strong tea, smoked foods, fried meat, pickles. The consumption of alcoholic beverages is completely contraindicated. Meat can be consumed 3-4 times a week, boiled or baked.
- Wheat and rye bread.
- Vegetarian vegetable soups.
- Lean varieties of beef, veal, chicken, rabbit (boiled).
- Low-fat fish: pike, carp, pike perch, cod, navaga (boiled).
- A variety of dishes and side dishes made from vegetables.
- Dishes and side dishes from cereals, pasta, noodles, noodles.
- Sweet dishes, fruits, berries in all types.
- Milk, kefir, yogurt, cottage cheese.
- Butter, vegetable oil (ghee is limited).
- Sauces with milk, vegetable broth, fruit.
Excessive fluid intake increases the intraocular pressure of patients with glaucoma, so they should limit fluid intake to 1.5 liters per day. It is not recommended to drink more than one glass at a time.
Baking, coffee and strong tea, spices, alcohol and fatty foods are completely excluded from the diet. Vitamins are introduced into the diet in the form of a medicinal complex, since the diet for glaucoma is not rich in foods that contain them in the required volume.
Products are contraindicated for patients
The following foods should be avoided if you have glaucoma:
- Fresh baked goods (complex, difficult-to-digest carbohydrates);
- Concentrated vegetable and meat broths (it is better to use the second or third broth, drain the first);
- Spices and hot spices (increase blood flow to the head);
- Salty foods (increase blood pressure, and therefore intraocular pressure);
- Tea and coffee (coffee can be replaced with chicory, and tea is best consumed in a weak form);
- Alcohol.
These products contribute to an increase in blood pressure, which leads to the development of hydrocele or increased symptoms. It is very important to completely remove alcohol from your diet!
Firstly, it contributes to the worsening of the disease, and secondly, most drugs for the treatment of glaucoma are strictly contraindicated in combination with alcohol.
It is advisable to limit:
- easily digestible carbohydrates (sugar, jam, sweets, honey);
- butter, sour cream;
At least 30% of all fats should be vegetable fats.
Variety of vitamins in food
A variety of vitamins in food Source: etodavlenie.ru
Diet is considered an important factor in the treatment of glaucoma. Proper nutrition, as well as additional intake of a complex of vitamins and minerals, have a beneficial effect on the condition of the optic nerve and improve metabolic processes in it.
The diet should preferably be dairy-vegetable, rich in vitamins and microelements.
To maintain and restore cells and tissues of the eye and the whole body, vitamins must first be included in the diet.
The importance of vitamins A, E and C in the treatment of glaucoma
Among all groups of vitamins, the most important for patients with glaucoma are vitamins A (beta-carotene), E and C. They have high antioxidant properties, significantly preventing the progression of the disease.
Valuable food sources of vitamin C include beets, red peppers, all types of cabbage, strawberries, asparagus, spinach, and tomatoes.
Natural sources of vitamin A are extremely diverse. Most of it is found in raw carrots and potatoes, least of all in apples.
Beta-carotene is found in moderate amounts in beets, red peppers, apricots, cabbage, green salad, citrus fruits and bananas.
Vitamin E is rich in vegetable oils (corn, sunflower, peanut, olive), fresh herbs, raw leafy vegetables, poultry, and sea fish.
Glaucoma patients are recommended to eat blueberries, blueberries and red grapes in the summer.
In addition to antioxidants, a patient with glaucoma should take B vitamins (B1, B2, B6, B12). They control oxidative reactions that regulate cell growth and carbohydrate metabolism.
B vitamins are found in large quantities in brewer's yeast, sprouted cereals, dairy products, nuts, meat and fish.
In addition to vitamins, the diet should include microelements in sufficient quantities, which actively influence all biochemical processes in the body (including the retina and optic nerve).
Mineral compounds enter the body with drinking water and food. Important food sources of microelements include fruits, green vegetables, cereals, meat, and fish.
Vitamins
Essential vitamins for glaucoma:
- Vitamin B - peanuts, egg yolk, walnuts, cheese, brown rice, leafy vegetables, buckwheat, whole grain bread.
- Zinc - oranges, currants, rice, beans, potatoes, ginger, squid, meat, beets.
- Omega 3 - tuna, salmon, trout, mackerel, nuts.
- Vitamin C - broccoli, orange, lemon, onion, tomato, potato.
- Tocopherol - corn, sunflower and soybean oil. Contained in hazelnuts and walnuts, sunflower seeds.
- Vitamin A - peach, melon, cod liver, milk, eggs, butter.
- Vitamin P - blackberries, lettuce, tomatoes, rowan and black currants.
Basic vitamins and microelements for glaucoma eyes
Basic vitamins and microelements for glaucoma Source: glazexpert.ru
For the normal functioning of the organs of the optical system, several groups of microelements and vitamins are required.
Vitamins
Let's consider the necessary vitamins for glaucoma, which are used to treat other eye diseases.
Vitamin A
Vitamin A and its importance in the treatment of glaucoma are very important. Retinol is a precursor to a substance that is part of the photosensitive layer of the retina. The retinal rods contain the protein rhodopsin, in which retinal plays the role of the active center.
With each impact of a light wave on the retina, this substance is gradually destroyed, as a result of which the human body must constantly renew its reserves of vitamin A.
With hypovitaminosis (lack of vitamin A), twilight vision decreases and the clarity and brightness of the image decreases.
This component is found in large quantities in blueberries, apricots, carrots, and bell peppers.
Vitamin B2
Riboflavin is a precursor of flavin coenzymes, which take part in redox processes.
Together with retinol, vitamin B2 leads to increased image clarity and brightness, and also reduces eye fatigue. A lot of riboflavin is found in dairy products, beef, and eggs.
Vitamin B6
Pyridoxine is responsible for the conduction of nerve impulses and is involved in the synthesis of nucleic acids. There is a lot of this vitamin in meat, liver, eggs, leafy greens, and dairy products.
Vitamin C
Ascorbic acid helps make the vascular wall strong and elastic; it is a powerful antioxidant.
Effects of vitamin C deficiency
With a lack of vitamin C, the nutrition of the eyes decreases, and the risk of developing hemorrhage in the vitreous or retina increases.
Long-term hypovitaminosis can provoke the development of glaucoma.
There is a lot of ascorbic acid in blueberries, citrus fruits, potatoes, rose hips, and sauerkraut. Vitamin C helps form the enzyme cholinesterase, which lowers intraocular pressure. Provides strength and elasticity to the blood vessels of the eye, relaxes the muscles of the eye.
Helps cope with improper outflow of fluid inside the eye.
Vitamin D
Calciferol helps muscle fibers absorb calcium, meaning it is responsible for muscle contraction.
With a lack of vitamin D, the eyes quickly tire and accommodative ability decreases.
Vitamin D is found in sea fish, especially in fish oil, and in milk.
Vitamin E
Tocopherol is an antioxidant that protects the eye from the harmful effects of free radicals and active oxygen. With its deficiency, cataracts can develop. There is a lot of vitamin E in liver, vegetable oil, sea buckthorn, liver, and nuts.
Vitamin PP
Niacin takes part in redox processes. With its deficiency, eye nutrition suffers. Vitamin PP is found in large quantities in legumes.
Microelements
Let's look at the necessary microelements for glaucoma.
Calcium
This microelement takes part in the contraction of muscle fibers. If few calcium ions enter the body, the accommodation process is disrupted, myopia occurs, fatigue increases and early farsightedness develops.
Zinc
One of the important elements for human eyes with glaucoma is zinc, which is involved in the reaction of converting vitamin A into the substance retinal.
With zinc deficiency, color vision is impaired and cataracts develop.
Thus, zinc restores the perception of colors by the eyes and affects the clarity of vision. To increase the level of zinc in the blood, you need to eat more fish, brain, liver and pumpkin.
Selenium
Selenium takes an active part in converting a light signal into a nerve impulse. This microelement also has an antioxidant effect.
Low selenium levels may lead to the development of cataracts and decreased visual acuity.
There is a lot of selenium in coconut, peanuts, lard and mushrooms. Also, the vitamin complex Complivit Selenium is excellent for eliminating selenium deficiency.
Lutein
Lutein, which is a yellow pigment related to carotenoids, should be included in a separate group.
Effects of lutein on the human body
The main function of this substance is to protect the retina from the effects of ultraviolet and intense radiation. There is a lot of lutein in yellow fruits and vegetables, chicken yolk.
For the optical system to work properly, it is necessary that all of the listed substances be present in sufficient quantities in human food.
At the same time, it is not always possible to eat a balanced diet, so multivitamin complexes come to the rescue, which enrich the body with the necessary drugs.
What vitamins are needed for cataracts and glaucoma
Vitamin deficiency often leads to eye diseases. For example, a lack of magnesium, zinc and selenium can trigger the development of cataracts. Regular intake of nutrients slows down the pathological process and stops the progression of eye diseases.
We recommend reading: Why does the body need zinc, where it is found, daily requirement
The following nutrients are necessary for the visual organs:
- Tocopherol (vitamin E). The antioxidant is able to protect the eyes from adverse environmental influences.
- Retinol (vitamin A). The component helps preserve vision and prevents the development of pathologies associated with the eyes.
- Riboflavin (vitamin B2). The substance restores the eyes after fatigue, and also eliminates the harmful effects of ultraviolet radiation, supporting the lens.
- Ascorbic acid (vitamin C). The useful component helps strengthen the retina and blood vessels.
- Zinc. The nutrient improves color perception, which is impaired with cataracts.
- Calcium. The element normalizes the functioning of nerve fibers.
Important! Vitamins produce a general strengthening effect, affecting the lens and cornea. Their regular intake is considered to prevent the appearance of cataracts.
Multivitamin complexes for the treatment and prevention of glaucoma
Typically, vitamins for eye health include various active components focused on a particular pathology.
In particular, there are complexes that were developed specifically for the prevention and treatment of age-related organ degeneration (cataracts, age-related degeneration of the corpus luteum, glaucoma).
Another group of medications are vitamins for patients with myopia and twilight vision impairment. You can buy these complexes at almost any pharmacy.
Vitamins that are prescribed by highly specialized specialists stand apart. These include drugs with a high content of B vitamins, which are used by pilots in aviation (flight fatigue).
Below are the most popular multivitamin complexes prescribed for eye health.
Strix Forte
"Strix Forte" is a dietary supplement containing:
Beta-carotene, aimed at normalizing color and twilight vision and helps maintain vision despite prolonged stress.
Vitamins C and E help stabilize the capillary membrane and improve blood flow through the vessels of the eye.
Lutein is a component of the macula because it plays the role of a light filter and protects the retina from the harmful effects of short-wave radiation. Selenium and zinc are classified as stabilizers of the activity of nerve and muscle fibers.
Blueberry anthocyanins help reduce the effects of hypoxia, are antioxidant agents and prevent the development of vascular disorders and cataracts.
The area of application of Strix Forte is myopia, glaucoma, diabetic retinopathy, intense visual loads, including long-term driving.
Blueberry Forte
This dietary supplement contains mainly blueberry fruit extract, the pigments of which are powerful anthocyanins. These substances perform angioprotective and antioxidant functions and normalize metabolic processes.
Elements included in 'Blueberry Forte'
For additional protection, the drug contains zinc, rutin and vitamin C. There are also B vitamins that support the functioning of the optic nerve.
“Blueberry Forte” is useful for eye fatigue due to long-term work and driving. These vitamins are also used in the complex treatment of eye diseases (cataracts and glaucoma), myopia.
Lutein complex
This multivitamin mainly consists of lutein, which provides protection against age-related changes. Lutein is found in the structures of the macula, and with regular replenishment of its reserves by the body, it helps to cope with age-related macular degeneration.
The complex also contains blueberry extract, vitamins C, E and A, zinc, selenium, copper, taurine. All these substances normalize metabolic processes in the structures of the eye, protect retinal cells from the negative effects of blue radiation and free active radicals.
Vitamin A also increases the concentration of photosensitive pigment.
This complex is used for severe eye fatigue, computer syndrome, long-term driving, as well as for the treatment and prevention of age-related changes.
Vitrum Vision
This vitamin complex consists of plant microelements and pigments:
- Vitamins C and E have an antioxidant effect and improve blood flow through the vessels;
- The pigments zeaxanthin and lutein are light filters that neutralize the effects of ultraviolet radiation on retinal cells;
- Copper and zinc regulate metabolic processes in the organs of the optical system.
"Vitrum Vision" is recommended for the prevention and treatment of myopia, for the correction of twilight vision and reducing the risk of age-related changes (cataracts, macular degeneration).
Doppelhertz asset
This dietary supplement contains Lutein, which has an antioxidant effect. It also contains vitamins A, E, C, zeaxanthin and zinc.
Doppelhertz Active should be taken by people who work with a computer and have visual impairments. It can also be used to prevent age-related pathologies of the organs of vision.
Complivit Oftalmo
This drug compares favorably with many other vitamin complexes, since the composition of “Complivit Oftalmo” is very rich: vitamins B1, B6, B2, B12, B9, E, A, C, selenium, zinc, lutein, zeaxanthin, rutin, copper.
Vitamins and rutin improve metabolism in eye tissues, zeaxanthin and lutein, as well as trace elements (zinc, selenium, copper) protect the retina from active radicals and oxidation by active oxygen.
In addition, these substances protect against the damaging effects of ultraviolet radiation and help transmit photosignal to the central brain structures.
"Complivit Oftalmo" is used for the prevention of age-related pathologies (glaucoma, macular degeneration, cataracts).
In addition, the drug helps eliminate inflammation and eye fatigue during prolonged work, and eliminates dryness in patients who use contact lenses.
The composition of the drug allows you to fill the daily need for these microelements and vitamins, and it was created to prevent eye diseases.
Tianshi
This dietary supplement is recommended for use by patients with increased visual stress. It helps eliminate fatigue and prevents a decrease in visual acuity. Tiansha includes:
- Blueberry extract;
- Vitamin A, which accelerates the regeneration of retinal structures and improves dark adaptation of the eye;
- B vitamins have a neuroprotective effect and eliminate symptoms of eye fatigue;
- Lutein provides eye protection from active oxygen and free radicals.
This drug is prescribed for the prevention of eye diseases in elderly patients and people who work with computers.
Basic drugs
There are many vitamin preparations. They vary in composition, some have restrictions on indications. Here are some of them:
- Strix. In addition to the main set of vitamins, the composition contains the microelements selenium and zinc. They are used by the body in many metabolic processes as stabilizers and enzymes that accelerate reactions. It has a pronounced retinoprotective property, significantly slows down the natural aging process and normalizes microcirculation of aqueous humor. Several forms of release allow the drug to be used even in children over 6 years old. It has many positive reviews from both doctors and patients.
- Vitrum Vision. The drug is based on blueberry extract and contains daily dosages of essential vitamins, microelements, as well as lutein, a pigment that has a protective effect against ultraviolet rays. It is successfully used in the postoperative period as the main adaptogenic drug that helps restore and protect the retina.
- Tianshi. It has a wide range of effects on all structures of the eye: they participate in the regenerative processes of the cornea, stabilize intraocular pressure by normalizing vascular tone and microcirculation, and slow down the processes of atrophy of the optic nerve head.
- Complivit Oftalmo. Thanks to its composition, it allows for adequate prevention of both glaucoma itself and its complications. It has affordable prices, which makes it accessible to various segments of the population. The course of use of the drug is at least three months.
You may be interested in: Can I wear sunglasses if I have glaucoma?