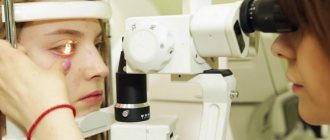
Ophthalmotonus (increased pressure inside the eye chamber) causes glaucoma. To prevent the development of complications, ophthalmologists prescribe eye drops for glaucoma. Let's consider what medications are recommended to be taken to normalize intraocular pressure, and how to prevent the development of a dangerous pathology with timely treatment.
Symptoms of the disease
Drops for glaucoma Source: nikafarm.ru The name “glaucoma” indicates the first and most noticeable sign of the disease, namely blueness and clouding of the pupil (translated from Greek, this term means “sea of green”).
With this disease, the patient experiences an increase in intraocular pressure for various reasons, resulting in excessive stress on the optic nerve. Since the nerve is the connecting link that transmits the “picture” from the retina to the brain, vision loss occurs, which may be irreversible if the disease is in an advanced stage.
The danger of this pathology is that in most cases it develops without noticeable signs, and even the person himself cannot suspect the presence of such an illness. In the best case, signs such as:
- causeless decrease in visual acuity;
- narrowing of the field of view (peripheral vision disappears);
- when looking at light sources, rainbow stains and spots appear before your eyes; headache;
- decreased quality of vision in the dark or in poor lighting;
- pain and burning in the eyes.
If such symptoms are detected, persons over 40 years of age are recommended to undergo examination by an ophthalmologist to confirm or exclude the diagnosis of glaucoma.
Signs of illness
Glaucoma develops unnoticed and is chronic. If pathology is not detected in a timely manner and measures are not taken to normalize intraocular pressure, the optic nerve may die. Therefore, it is very important not to ignore suspicious symptoms that may indicate the onset of the development of this dangerous disease.
You can suspect glaucoma based on the following symptoms:
- Feeling of discomfort associated with blurred vision.
- Decreased ability to distinguish objects in poor lighting.
- Narrowing of visual fields.
- Heaviness, pain, stinging, redness of the eyes.
- Headache.
- The appearance of rainbow circles before the eyes when a person looks at the light.
With glaucoma, attacks may occur, accompanied by nausea, weakness, and sometimes vomiting. Often, attacks occur due to severe stress, overwork, physical activity, drinking large amounts of liquid or working in an inclined position.
When examining a patient, the ophthalmologist identifies the following signs of pathology:
- Damage to the optic nerve.
- Increased IOP, which is observed constantly or periodically.
- The patient complains of an unusually narrow field of vision.
Eye drops for glaucoma
In most cases, it is impossible to completely get rid of glaucoma - this disease is chronic and leads to complete loss of vision. However, there are treatment programs to slow down this process. The most radical way is surgery, but it is not always possible.
Therefore, eye drops occupy a leading place. This dosage form allows you to deliver the active substance directly to the affected area, to the diseased eye, without causing systemic side effects. The use of drops is quite safe and most effective for primary glaucoma.
If increased intraocular pressure is a consequence of another pathology, drops become an excellent adjuvant. In case of an acute attack of glaucoma, this dosage form allows you to most quickly alleviate the patient’s condition.
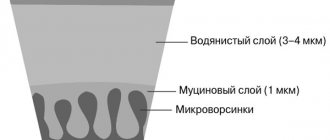
Management of patients with dry eye syndrome in glaucoma practice
The management of patients with glaucoma in case of detection of dry eye syndrome has some peculiarities: adjustment of the regimen of antiglaucoma drugs is required in order to reduce the toxic load.
Minimizing the frequency of instillation (use of combination drugs, long-acting forms)
Switching from BAC to alternative preservatives with minimal toxicity or preservative-free forms
In case of severe symptoms of dry eye syndrome and damage to the ocular surface, laser and surgical treatment options can also be considered2.
Indications for use
Indications for the use of eye drops for glaucoma are based on the therapeutic properties of the drugs. Eye drops for glaucoma are one of the most important methods of conservative treatment. Drops allow you to reduce and maintain intraocular pressure at a normal level.
Increased pressure of a chronic nature can lead to atrophy of the optic nerves and complete loss of vision.
- Drops for glaucoma are prescribed to treat atrophy of the optic nerve, which is responsible for normal vision. With atrophy of the optic nerves, peripheral vision appears, the picture becomes narrow or tunnel-like. After this, complete blindness occurs.
- The optic nerve contains more than a thousand fibers, some of which die due to increased intraocular pressure. The use of drops helps reduce pressure in glaucoma in the initial stages. But you need to use the drops only according to the schedule drawn up by your doctor.
It is necessary to start treatment and use medications at the first symptoms of glaucoma. Due to procrastination or forgetfulness of patients, the disease begins to progress, which leads to rapid death of optic nerve fibers.
It is necessary to use drops only after consultation with an ophthalmologist, strictly according to the instructions of the drug and with regular examination and measurement of intraocular pressure. This will allow you to maintain clear vision for many years.
Contraindications
Contraindications to the use of eye drops for glaucoma are based on the composition of the drug and the effect of its active components. Drops are contraindicated for use in case of hypersensitivity to the components of the drug, during exacerbations of bronchial asthma, after ophthalmic surgery and in cases of high risk of retinal detachment.
Eye drops for glaucoma are contraindicated for use in chronic lung diseases, heart failure, cardiogenic shock, and sinus bradycardia. Many drugs are not recommended for use during pregnancy, lactation and for the treatment of glaucoma in pediatric patients.
Possible side effects
Side effects of eye drops for glaucoma occur due to non-compliance with the rules of use and dosage of the drug. Most often, drops cause headaches in the periorbital and temporal areas, spasms, blurred vision, lacrimation, eyelid dermatitis and more.
If the drug is ingested, it causes sweating, nausea, chills, abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, increased blood pressure and increased urination.
- Despite the side effects described above, the drops are well tolerated. The drug causes symptoms of local irritation: conjunctivitis, decreased sensitivity of the cornea, visual disturbances, keratitis, blepharitis.
- In some patients, eye drops cause adverse cardiovascular reactions: cerebrovascular accidents, bradycardia, arrhythmia, heart failure and others.
- Eye drops also cause side effects from the respiratory system. The drug can cause bronchospasms, shortness of breath and respiratory failure.
- With long-term use, the drops cause fatigue, chest pain, localized rash and urticaria, and increase the symptoms of myasthenia gravis. Many groups of drugs adversely affect the digestive system, causing nausea and gastrointestinal problems.
Pregnant women and children
When choosing medications for the treatment of glaucoma in pregnant women and children, special care must be taken. The vast majority of eye drops should not be used during the first trimester. The exceptions are Brimonidine, Dipivefrin and some other drugs, but they cannot be used in the final stages and during breastfeeding.
The choice of antiglaucoma drops for children should be made by a pediatrician, taking into account the presence of contraindications and side effects.
Using eye drops during pregnancy
The use of eye drops for glaucoma during pregnancy is possible only with the permission of the attending physician. After instillation into the eyes, some of the ingredients of the drug penetrate into the bloodstream. The active substances can enter the fetus’s body through the placenta, and through milk during lactation.
All this suggests that glaucoma during pregnancy is a very dangerous disease, the treatment of which should be carried out under the supervision of a doctor. But fortunately, glaucoma does not often occur in women of childbearing age. If the disease appears, then drops are used for treatment.
The main danger is that today there is no reliable data on the effect of drops on the intrauterine development of the fetus. Let's look at the most common glaucoma medications that are unsafe during pregnancy:
- Beta blockers - eye drops from this group are dangerous in the early stages of intrauterine development, therefore they are strictly prohibited for use in the first trimester of pregnancy.
If a woman uses drops with beta blockers in the second and third semester of pregnancy or during lactation, this may cause a decrease in heart rate and a decrease in blood sugar levels in the child. In addition, the drops can cause disruption of the natural contractions of the uterus, which is very dangerous during pregnancy. - Miotics – lead to intrauterine development disorders in the first trimester of pregnancy. During lactation they cause weakness and increased body temperature in the child, and in rare cases cause muscle weakness.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors - drops with this substance are considered safe for the unborn child. But if the expectant mother uses tablets with carbonic anhydrase inhibitors for glaucoma, this leads to the development of congenital disorders in the baby.
- Prostaglandins can cause premature birth. If the drops are used during lactation, they are excreted in breast milk and cause adverse reactions in the child.
For glaucoma during pregnancy and lactation, it is recommended to avoid any medications. The doctor must select the safest methods for the health of the expectant mother and her child to reduce intraocular pressure.
If drops are still used, it is recommended to instill low doses to avoid possible side effects. Glaucoma does not affect conception and pregnancy, but the drops used for treatment, if they enter the mother’s body, can lead to unwanted side effects.
Preservative-free forms
Studies have shown a relationship between the frequency of dry eye syndrome and the presence of a preservative in the medications used by the patient. For example, according to a multicenter cross-sectional epidemiological study in 4 European countries involving 9658 patients with glaucoma, switching to a preservative-free form of the drug can reduce undesirable symptoms10:
Today, there are drugs produced in preservative-free form - disposable dropper tubes (monodoses), or multi-dose vials with a special anti-contamination system (special membrane or valve). However, the release of the drug in monodose form increases its cost, and the list of antiglaucoma drugs in multi-dose vials without a preservative is still limited.
Application area
Glaucoma is a disease that can lead to complete blindness if left untreated. Glaucoma can be a chronic form, which is characterized by a constant increase in intraocular pressure (ophthalmotonus) and impaired outflow of intraocular secretions. This contributes to the development of optic nerve atrophy.
The main causes of the disease
Glaucoma occurs due to increased pressure affecting the walls of the vessels of the visual organ. So when treating pathology, the most important thing is to reduce this very pressure. If nothing is done, the patient risks remaining blind.
Eye drops used for glaucoma reduce pressure and inhibit the destruction of the optic nerve. Drops for glaucoma can be prescribed when the optic nerve, which is responsible for normal vision, is destroyed. If optic nerve atrophy is present, peripheral vision develops.
Because of this, the image becomes narrow and tunnel-like. Then complete blindness occurs. The optic nerve contains many fibers. Some of them die due to ophthalmotonus. Using eye drops, it is possible to lower blood pressure in glaucoma at the initial stage of development.
The use of any drops for glaucoma is allowed only after consulting a doctor. Features of drugs Eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma can be divided into several groups:
- Carbanhydrase inhibitors. The action of these drugs is aimed at the production of intraocular fluid. When using them, side symptoms are possible. This includes burning, redness of the eyes, and a bitter taste in the mouth.
- Prostaglandins. Due to them, the outflow of intraocular fluid increases. Side symptoms include darkening of the iris and lengthening of the eyelashes.
- Beta blocker. These medications reduce the production of intraocular secretions. Most often prescribed together with prostaglandins. These pressure drops affect the heart rate. Their use may cause unpleasant side effects in people suffering from diabetes and lung diseases.
List of drugs:
- Timolol.
The main component is thymol. Its action is to purposefully exert a therapeutic effect directly on the site of the pathological process. The medication helps reduce the level of fluid inside the eye, which increases blood pressure. Timolol for glaucoma should be used before going to bed. Adults and children use the medicine 1 drop, sending it into the conjunctival sac. Such events are carried out 2 times a day. If the expected therapeutic effect is absent, then adults can switch to a 0.5% solution. The cost of these drops is 25-30 rubles. - Betoptik. The drug is based on a component such as betaxolol. Due to it, the medicine quickly relieves the symptoms of glaucoma. The drug creates an obstacle to the concentration of fluid in the tissues of the visual organ.
As a result of using Betoptik, visual ability improves and the contraction of tissues of the organ of vision stops. The drug is prescribed for the treatment of mild glaucoma, and a positive effect is expected within a few hours after use.Betoptik should only be used under the supervision of a doctor, since such treatment often leads to the development of side symptoms. This should include:
- tearfulness;
allergy;
- discomfort and burning;
- corneal hyperemia;
- photophobia.
- Xalatan. This remedy belongs to prostaglandins. The active component is lataprost. Use the medication effectively to reduce intraocular pressure that occurs against the background of open-angle glaucoma.
Drops are classified as safe and effective drugs against high blood pressure. And this is due to the gentle effect, because after using the drops, side symptoms rarely develop.
Positive dynamics can be seen after a few hours, and they last throughout the day. Drop 0.5 ml of the product before going to bed. The cost of the drug is 650 rubles.
- Travatan.
The therapeutic effect achieved from these drops is associated with the action of the main component travoprost. The drops have found their use in the treatment of glaucoma and ophthalmic hypertension. Due to the action of the active components of the drug, it is possible to enhance the outflow of fluid, which is concentrated between the lens and the cornea. Travatan should be used for glaucoma once a day, 0.5-1 ml. It is best to carry out such manipulations before going to bed. You can notice the positive effect of the medication within a few hours. You can buy drops for 550-600 rubles. - Trusopt. Trusopt's action is aimed at blocking a special enzyme of the ciliary body - carbonic anhydrase. It is responsible for the production of intraocular fluid. The peculiarity of this drug is that it does not lead to addiction. At the same time, the effectiveness of therapy does not decrease with prolonged use of drops.
- Azopt. The active ingredient is brinzolamide. This component helps reduce the production of intraocular fluid. When using drops, the following side symptoms may develop: burning sensation, excessive release of tear fluid, photophobia, dizziness, headache.
Rarely does the drug leave a mark on the state of the nervous system. This manifests itself in the form of short-term depression or disturbed sleep. It is necessary to use drops of 0.5 ml twice a day. The cost of Betoptik is 350 rubles.
Bottom line
Glaucoma cannot be completely eliminated. Treatment with eye drops aims to preserve visual function and prevent blindness. The therapeutic regimen is aimed at correcting ophthalmotonus, optimizing metabolic processes in the visual apparatus, and activating the blood supply to the internal structures of the eye. Treatment is carried out with medication and surgery (iridectomy). The choice of treatment method is determined by the condition of the patient’s visual system and the duration of the disease.
Under certain circumstances, the ophthalmologist prescribes drops to activate the outflow of excess moisture from the chambers of the eye; in other cases, control over the production of intraocular fluid is necessary. In difficult cases, combination drugs are prescribed to solve several therapeutic problems.
It is important to understand that one of the reasons for the appearance of excess intraocular pressure is a deficiency of vitamins B6 and C. If there is a predisposition to glaucoma, it is necessary to take vitamin complexes daily, agreed upon with an ophthalmologist.
Sources used:
- Eye diseases. Atlas. Guide to practical training / E.I. Kovalevsky. - M.: Medicine, 1985.
- Taking care of your eyes. Vision problems from dry eye syndrome to macular degeneration. - M.: Art-Rodnik, 2011.
- Perfect vision without glasses. Treatment of imperfect vision without glasses: monograph. / William Bates. - M.: Book on Demand, 2013.
- The University of Chicago's Department of Ophthalmology and Visual Science
Types of drops to reduce intraocular pressure
The main goal of glaucoma treatment is to reduce intraocular pressure to prevent damage and preserve optic nerve function. As a rule, treatment of glaucoma begins with the prescription of drops that reduce intraocular pressure. These drops must be dripped constantly, strictly according to the doctor’s instructions.
The regularity of their instillation is, to a certain extent, a guarantee of the success of treatment. If some drops are ineffective in maintaining normal intraocular pressure, the doctor may strengthen your regimen by prescribing additional drops of another chemical group, especially since some drops can enhance the effect of others.
All eye drops are absorbed through the superficial vessels into the ocular bloodstream and, albeit in small quantities, still enter the systemic circulation. If the patient, due to his general condition or some other reason, is not able to regularly instill glaucoma drops, then it is better to offer him other treatment methods.
The active chemicals in some glaucoma drops have undesirable side effects on the body's cardiovascular and respiratory systems, so it is very important for your ophthalmologist to know your common chronic diseases.
Today, there are many different drugs for the treatment of glaucoma in the form of eye drops, which are classified:
- by active chemical substance: prostaglandins, beta blockers, cholinomimetics, etc.
- by the mechanism of reducing intraocular pressure: reducing the production of intraocular fluid, improving the outflow of intraocular fluid and drugs with a combined mechanism of action.
The main course of treatment for glaucoma is aimed at reducing intraocular pressure and normalizing the production of fluid, the accumulation of which inside the eyeball leads to such disorders. Complex treatment is used, in which the following types of drops are used:
- Beta blockers. They block the operation of systems responsible for the production of intraocular fluid (betoptik, timoptik and similar drugs).
- Prostaglandins. Hormonal drugs that lower IOP levels. Despite the large number of possible side effects, sometimes only such drugs can help restore the level of pressure inside the eye.
- Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors. These drugs also inhibit the glands that produce intraocular fluid (the most commonly prescribed of these drugs are Azopt or Trusopt).
- Alpha adrenergic receptor agonists. Combined-action drugs that not only provoke the outflow of fluid from the body of the eyeball, but also reduce the level of its formation.
Prostaglandin analogues
Prostaglandins are highly effective and safe drugs for glaucoma. Intraocular pressure decreases 2 hours after instillation, the maximum effect is achieved after 12 hours. These drugs: Travatan (Alcon), Xalatan (Pfizer), Tafluprost, etc., appeared relatively recently.
However, due to their high efficiency and duration of action (they need to be instilled only once a day), they have established themselves as the drug of choice in the treatment of glaucoma. Their mechanism of action is based on improving the outflow of intraocular fluid through an additional outflow pathway.
But prostaglandin group drugs have a number of side effects: transient redness of the eyes (due to dilated superficial vessels), changes in the color of the iris (it becomes darker) and increased eyelash growth (they become thicker, longer and darker).
The latest side effect of prostaglandins, which pleases some patients, has also found its way into cosmetics companies.
Beta blockers
This group of drugs reduces the production of intraocular fluid. They begin to act 30 minutes after application with maximum effect after 2 hours, so the frequency of instillation is usually 2 times a day. They are often prescribed in combination with prostaglandins to enhance the effect.
Timolol, Arutimol, Okumol, Okupress, Okumed - this is an incomplete list of existing beta blockers used in the treatment of glaucoma. As a rule, they have the same active chemical substance, so they are interchangeable. But these drugs have a number of side effects: decreased heart rate, bronchospasm, etc.
Therefore, these drugs are contraindicated for people with certain heart diseases, bronchial asthma, and emphysema. There are highly selective beta blockers Betoptik and Betoptik S (Alcon), their side effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems are less pronounced than other drugs in this group.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Azopt (Alcon), Trusopt, reduce the production of intraocular fluid. These are highly effective and safe drugs that have no side effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, but should be used with caution in people with certain kidney diseases.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors are usually given twice a day and can be given in combination with other drops, such as beta blockers or prostaglandins, if necessary. The tablet drug Diacarb has the same active ingredient as Azopt and can also be used in the treatment of glaucoma, especially in acute and subacute attacks of glaucoma.
Cholinomimetics
These drugs (Pilocarpine, Carbocholine) improve the outflow of intraocular fluid by constricting the pupil and contracting certain groups of intraocular muscles, which leads to easier passage of intraocular fluid through the angle of the anterior chamber.
Pilocarpine, as the main representative of this group, is most often prescribed for narrow-angle or closed-angle glaucoma in order to open the drainage network from the root of the iris. Prescribed on average 1-2 times a day.
If necessary, pilocarpine is prescribed in combination with other drugs, for example, beta blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, prostaglandin analogues. Side effects of pilocarpine are caused by a narrow pupil, which can limit the field of vision and cause unpleasant pain in the forehead, eyebrows, and temple.
Neuroprotectors
Neuroprotective treatment, i.e. Treatment aimed at improving nutrition and blood supply to the optic nerve plays an important role in the prognosis and course of glaucoma. Studies examining changes in the optic nerve during glaucoma prove the feasibility and necessity of neuroprotective treatment for any form of glaucoma, especially in advanced and advanced stages.
It is important to note that there are studies proving some neuroprotective effect of antiglaucoma drops: prostaglandin analogues, beta blockers, etc. But this, as a rule, is not enough.
Today, many drugs are known, of different origins and chemical compositions, that have certain neuroprotective properties. Main groups of neuroprotectors:
- Medicines that improve blood circulation: ginkgo biloba, trental, dicinone, etc.
- Agents that improve the regeneration of nervous tissue: picamelon, cinnarizine, nootropil, fezam, etc.
- Agents that activate the nutrition of nervous tissue: retinalamin, cortexin, Semax, Cerebrolysin, Noben, etc.
- Antioxidants and vitamins: emoxipin, mexidol, aevit, rutin, ascorbic acid, vitamin E, B vitamins, riboxin, lutein complex, mertilen forte, histochrome, erisod, etc.
Causes
There are several main causes of the disease. The first option is the occurrence of increased pressure inside the eye. In this condition, the eye is subject to severe stress for a long period of time.
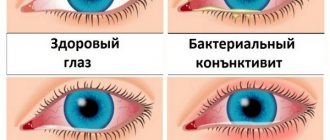
In addition, it impairs blood flow and the normal condition of the eye. Visually, this symptom becomes noticeable due to constantly red eyes and inflamed eyelids.
The second cause of the disease is fluid accumulation. With poor blood circulation, lymph can linger and accumulate in the eye area. For the patient, it will feel like a foreign body getting into the eyelid, for example, like sand in the eyes or something like that.
Glaucoma may be accompanied by the occurrence of other, mainly infectious diseases. The cause of infections is stagnation of fluid in the eyeball area.
The cause may also be an incorrect lifestyle or prolonged work in dark rooms, which can provoke a structural deviation in the structure of the retina. But congenital defects of the retina are not uncommon.
Destruction in the functioning (dystrophy) of the optic nerve. If cataracts occur for this reason, treatment should be carried out immediately, since there is no way to predict the further functioning of the nerve.
Delays in treatment can cause vision loss. And these are only the main causes of the disease, and there are about five dozen other causes that can cause glaucoma.
Drops that improve the outflow of aqueous humor
Source: magicworld.su These are drugs containing active substances, cholinomimetics, which change the physiology of the eye in such a way that the channels through which fluid flows expand.
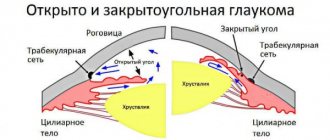
All of them cause constriction of the pupil, as a result - tension of the iris and opening of the angle of the anterior chamber of the eye. At the same time, both the venous sinus and trabeculae - thin channels through which fluid flows out - expand. Drops of this action are suitable for the treatment of angle-closure glaucoma, which occurs in 40% of patients, when the outflow of fluid from the posterior chamber of the eye is blocked.
- Pilocarpine.
Belongs to the group of cholinomimetics. The drug significantly improves the outflow of intraocular fluid. A decrease in intraocular pressure occurs 20 minutes after instillation. In addition, pilocarpine constricts the pupil, which is why ophthalmologists use this drug for diagnostic purposes. Like all anticholinergics, pilocarpine causes a narrowing of the bronchial lumen, and therefore its use is strictly contraindicated in bronchial asthma. - Xalatan (glauprost). Indicated for continuous long-term use. The undoubted advantage of Xalatan is that it needs to be instilled into the eyes only once a day, before bedtime. The drops are well tolerated by patients. Rarely, nausea, headache, and dry mouth may occur.
- Travatan (travaprost). The mechanism of action is similar to xalatan. The maximum effect of the drug develops over 12-14 days of continuous use. To prevent addiction to Travatan, it is recommended to replace it after a year.
- Tosmilen (demekarium bromide) – 0.013% solution, causes pupil constriction after 10 minutes, lasts more than 24 hours. Apply 1 time per day, 1-2 drops.
- Phosphacol (paraoxon) – has a fast and strong effect, pupil constriction lasts up to 3 days. Apply 1-2 drops 1 time per day.
- Armin - 0.005% and 0.01% solution, causes constriction of the pupil after 15 minutes, it also lasts up to several days.
Prescribed 1-2 drops 1 time per day. Side effects of these drugs include short-term pain in the eyes, “fog” before the eyes, and redness of the sclera. Xaltan has gained the greatest popularity among the entire group, combining long-lasting action and a minimum of side effects.
Contraindications
It is difficult to find drugs on the pharmacological market without side effects and contraindications. As a rule, absolutely safe drugs have a low therapeutic effect and only have a supportive effect. Many medications used to treat glaucoma have a number of serious contraindications.
For example, beta-blockers based on timolol are prohibited from being used for bronchial asthma, allergic rhinitis, pulmonary pathologies, pregnancy and breastfeeding, and corneal dystrophy. Cholinomimetics based on isoptocarbachol are contraindicated in persons with acute iritis, iridocyclitis, asthma, and angina.
Prostaglandin analogues are contraindicated only in patients with hypersensitivity to their ingredients, and antienzymes should not be used in cases of renal failure, pregnancy or breastfeeding.
Some antiglaucoma drops should not be administered if there are injuries or wounds in the eye area. Therefore, before using this or that medicine, it is recommended to study the instructions attached to it with information regarding contraindications.
Drops that reduce the production of intraocular fluid
Drugs that affect the formation of intraocular fluid include beta-blockers, carbonic anhydrase inhibitors and sympathomimetics. The mechanism of their action is to lower the osmotic pressure in the capillaries and, as a result, slow down and reduce the flow of fluid from the vascular bed into the eye.
The most widely used in practice are beta-blockers, which have a long-lasting effect and do not lead to impairment of accommodation (visual acuity). Depending on the type of glaucoma, they can be used alone or in combination with cholinomimetics.
- Timolol (Ocumed). The drug blocks the receptors that are responsible for the production of aqueous humor. Okumed reduces intraocular pressure by 25% of the initial level. Contraindicated in case of heart rhythm disturbances, diabetes mellitus and chronic obstructive diseases of the respiratory system (bronchitis, bronchial asthma).
- Betaxolol (betoptik).
The mechanism of action is the same as that of timolol. However, betaxolol acts more selectively (directed towards the organ of vision), so it can be used in the initial stages of bronchial asthma and compensated type 2 diabetes mellitus. But this is only possible as a last resort, when the patient needs betaxolol for health reasons, and with strict adherence to all medical recommendations. - Trusopt (dorzolamide, dorzopt). Trusopt blocks carbonic anhydrase, a special enzyme of the ciliary body that is responsible for the production of intraocular fluid. The advantage of trusopt is that it does not become addictive and, thus, the effectiveness of treatment does not decrease with long-term use.
- Azopt. The active ingredient of the drug, brinzolamide, can reduce the production of intraocular fluid. May cause a number of adverse reactions: burning during instillation, excessive lacrimation, increased sensitivity to bright light, dizziness, headache.
- Proxodolol is a drug from the group of beta blockers, which has proven itself in practice, with a duration of action of 12 hours. Recommended for the treatment of open-angle glaucoma, apply 1-2 drops 2-3 times a day.
- Betoptik S is a 0.25% suspension solution from the group of beta-blockers, often causing dry and itchy eyes, a feeling of discomfort, and lacrimation. Prescribed 1-2 drops 2 times a day.
- Brinzolamide is a drug from the group of carbonic anhydrase inhibitors, also used for open-angle glaucoma as an independent treatment or as part of combined drops. Contraindicated for kidney disease and allergies. Apply 1 drop 2-3 times a day.
The leader in this group of drugs is the long-acting beta-blocker Timolol - more than a day, with a minimum of side effects.
Drops with a combined effect
Combined eye drops for the treatment of glaucoma are designed to more effectively reduce intraocular pressure, improve the quality of life of patients and more convenient use of drugs (1 bottle instead of several). In addition, there is a mutual enhancement of the action of the drugs - an additive effect, which makes it possible to reduce their dose.
Most often, a combination of cholinomimetics and beta-blockers is used in one bottle. Such combinations are well suited for any type of glaucoma and provide a more stable and long-lasting hypotensive effect.
- Fotil.
This is the most popular and effective remedy against glaucoma, which can reduce intraocular pressure by 32% of the original figures. The drug combines two substances: pilocarpine (accelerates the outflow of aqueous humor) and timolol (reduces the production of intraocular fluid by the ciliary body). The simultaneous presence in the drug of two substances with different mechanisms of action increases the number of contraindications to photyl. The dosage and frequency of instillation are selected individually for each patient. - Cosopt. It consists of two components that reduce the production of aqueous humor - timolol and trusopt. A noticeable effect occurs 15-20 minutes after instillation (instillation).
- Proxofeline. Consists of two components: proxodolol and clonidine. Clonidine improves the output of intraocular fluid and also reduces its production. Proxodolol acts on the receptors of the ciliary body, which helps reduce the secretion of intraocular fluid. Proxodolol has virtually no effect on its outflow.
- Azarga. Used only for open-angle glaucoma. The action of the drops is aimed at reducing the pressure inside the eye chamber.
- Fotil forte - includes timolol maleate and pilocarpine hydrochloride, available in 5 ml polyethylene dropper bottles. It is used for both open-angle and closed-angle glaucoma, in its secondary form, after surgical eye interventions. Prescribe 1 drop 2 times a day. The drug is contraindicated in heart failure, bradycardia, bronchitis, asthma.
- Xalacom - consists of prostaglandin (hormone-like substance), latanoprost and timolol (beta blocker), is a very successful combination. Does not contain cholinomimetics and has a minimum of side effects. But the use of eye drops is limited only to the treatment of open-angle glaucoma.
Among various combinations of ingredients, one is selected that is suitable for treatment in a particular case (individually).