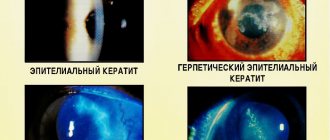
Sjogren's syndrome is a chronic systemic autoimmune disease with insufficiency of the functions of the external secretion glands - lacrimal, salivary. This syndrome occurs more often in women during menopause, menopause or ovarian failure, in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus, systemic scleroderma, rheumatoid arthritis.
Dry eye syndrome is a disease that occurs due to a decrease in the volume and quality of tear fluid, which forms a tear film on the surface of the eye, which is responsible for several important functions, such as nutritional, optical and protective.
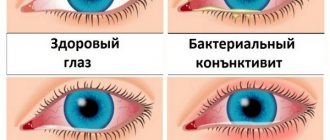
Purulent discharge (yellow, brown)
Purulent discharge appears as a result of the formation of a yellowish or brown thick inflammatory substrate - pus - in the eye (eyes). This is the “merit” of the large number of leukocytes (white blood cells) present here, which the body mobilized to fight bacteria, and in addition, the result of the vital activity of microorganisms. The discharge that sticks together in your eyes is a natural reaction of the body to progressive conjunctivitis - an acute lesion of the transparent spherical membrane covering the human eyeball.
Classification of vitreous destruction
Destructions of the vitreous body can be of various origins and characterized by various signs.
Grainy
With granular pathology, there is diffuse damage to the vitreous substance with small, grain-like inclusions. With timely treatment, the clouding process is completely controllable and reversible. Crystalline inclusions
If such changes are present, the patient, when moving the eyeball, pays attention to the movement of shiny crystals. The latter can flicker, and therefore resemble silver or gold sparkles. The exact structure of these crystals has not yet been established, but one of the substances that may form the basis of these inclusions is cholesterol.
Such changes in the vitreous are more common in older people who suffer from diabetes. However, a decrease in visual acuity is observed only in the later stages of the disease.
Wrinkling
With wrinkling, a decrease in the volume of the vitreous body is noted. More often this occurs as a result of injury or surgery, during which part of the gel had to be removed. Inflammation of the uveal tract and retina. Such changes are considered the most common, and also the most dangerous in terms of the development of complications.
Parasitic infestation
Penetration of parasites into the vitreous region is not common. In this case, the most appropriate surgical treatment strategy for the patient. If for some reason the operation could not be performed, then the interfering threads or worms will be accompanied by a pronounced decrease in visual acuity. To accurately determine the location of the parasite, it is necessary to use ophthalmoscopy and a professional examination by a doctor.
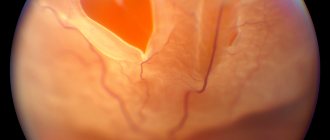
Damage to the vitreous can be noticed already during a visual examination, when the red background of the pupil is examined.
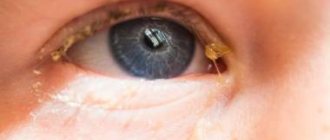
Discharge from the eyes of a child
In children, in addition to these eye diseases, the cause of discharge from the eyes is often inflammation of the lacrimal ducts (dacryocystitis). This disease is especially common in newborns - this is due to the peculiarities of the anatomical structure of the lacrimal organs.
This problem is no longer the responsibility of an ophthalmologist - it is dealt with by an otorhinolaryngologist (ENT doctor). For diagnosis and treatment in this case, probing and lavage of the lacrimal canals are used, and sometimes surgical treatment is required in a children's ENT department.
Dry eye syndrome
Signs
The first symptoms of dry eye syndrome are a feeling of sand in the eyes and watery eyes. Later, a feeling of dry eye appears. With the further development of the disease, the patient feels a burning sensation and pain in the eyes, photophobia begins, in the evening vision deteriorates noticeably, discomfort is felt in the eyes, they turn red. It becomes difficult for a person to work on a computer or watch TV. These symptoms are especially aggravated when exposed to air conditioners, fan heaters, wind or smoke. The discharge from the eye becomes viscous and is pulled out in threads, causing discomfort.
Description
The liquid that moisturizes the cornea has a complex composition. It comes from the meibomian glands, the glands of Zeiss, Moll and Manz, Krause and Wolfring, from the large and small lacrimal glands. And each of these glands produces a certain secret. The main lacrimal gland secretes a secretion in various emotional states, pain or mechanical injury to the cornea. She is responsible for reflex lacrimation. Per day, if you do not cry, these glands normally secrete about 2 ml of fluid. And if you cry, then up to 30 ml.
In the conjunctival cavity (the slit-like space between the eyelids and the eyeball) there is constantly about 7 microliters of tear fluid, which is distributed in a thin film over the front surface of the eye. This tear film is 6-12 micrometers thick. It consists of three layers:
- mucin (mucous), which is distributed over the surface of the epithelium and retains the moisture of the aqueous layer, preventing it from draining;
- watery, consisting of a solution of salts and organic substances;
- lipid, preventing excessive evaporation of liquid and preventing heat transfer from the surface of the epithelium and cornea.
Normally, the aqueous layer of the tear film is formed by the glands of Krause and Wolfring. They secrete a small amount of mucus. Manz's glands also produce mucus. Lipids are secreted by the meibomian glands, as well as the glands of Zeiss and Moll.
The tear film performs protective, metabolic and optical functions.
All three layers play an important role in the implementation of the protective function:
- The lipid layer prevents aerosols from penetrating the eye, prevents excess evaporation, and also protects against overheating and hypothermia.
- The aqueous layer washes away foreign particles from the surface of the eye, restores pH if it is disturbed, and has a bactericidal and antiviral effect.
- The mucus coats foreign bodies, thereby reducing the likelihood of eye damage.
The metabolic function is to transport nutrients to the cells of the corneal epithelium, moisturize it and remove dead cells. All this occurs due to electrolytes and organic substances in the aqueous layer.
The optical function is to smooth out irregularities in the outer surface of the cornea, providing it with shine and mirror properties. All layers of the tear film take part in this.
With every movement of the eyelid, the eye is moistened by the tear film.
Dry eye syndrome develops when the stability of the tear film is disrupted. Moreover, this may be associated both with a reduction in the production of its components, and with a direct violation of its integrity by exogenous factors (dust, exhaust gases, dry air, tobacco smoke) or its thinning due to strong evaporation.
There are many reasons for the development of dry eye syndrome. This:
- malnutrition of the cornea;
- lacrimal gland defects;
- facial paralysis;
- eye surgeries;
- taking certain medications (oral contraceptives, some antihypertensives, migraine medications, some antidepressants);
- working at the computer, watching TV;
- menopause;
- old age;
- eye injuries;
- low-quality cosmetics;
- environmental effects (exhaust gases, cigarette smoke);
- poor nutrition.
As a result of these causes, breaks appear in the tear film. Moreover, there are so many gaps that blinking cannot restore the integrity of the tear film. Dry areas form in places where there are ruptures.
Dry eye syndrome can be mild, moderate, severe, or particularly severe.
In young people, dry eye syndrome most often develops as a result of prolonged work at the computer (monitor syndrome), wearing contact lenses, as well as after injuries and eye surgeries. Dry eye syndrome can also be caused by a very low fat diet. It is thanks to young people that the number of visits to the doctor with this disease has now increased so much.
In people over 50 years of age, age is most often to blame for the development of dry eye syndrome. The fact is that in old age the body produces 60% less fat than in youth. Dry eye syndrome can develop as a consequence of glaucoma due to long-term use of eye drops containing beta-blockers, Sjogren's syndrome and Steven-Johnson syndrome.
Diagnostics
The doctor makes the diagnosis of “dry eye syndrome” based on the patient’s complaints, biomicroscopy of the cornea, conjunctiva and free edges of the eyelids, identifying changes in areas of the conjunctiva and cornea using special drops. The rate of tear production, the rate of tear evaporation, and the quality of the tear film are also measured.
The most characteristic picture of dry eye syndrome is the absence of tear menisci (thickening of the tear film along the posterior edge of the lower eyelid). In their place there is usually a swollen, dull conjunctiva. Also, during examination, foreign inclusions can be detected in the tear film - epithelial threads, air bubbles, mucus clots.
Treatment
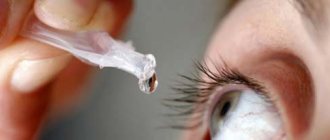
The main task in the treatment of dry eye syndrome is to restore sufficient moisture to the conjunctival cavity and cornea of the eye. Most often this is achieved by instilling artificial tears. It forms a stable film on the surface of the eye. It should be used 3 to 8 times a day, depending on the severity of the disease.
Surgery for dry eye syndrome is rarely used and is only used in patients with a marked decrease in tear production or severe corneal changes. If the patient has a hole in the tear duct, it is plugged with a special silicone plug. This helps avoid loss of tear fluid.
Prevention
If you spend more than 4 hours a day at the computer, take care to prevent dry eye syndrome. To do this, drink more fluid, take a break from the monitor once an hour for 10 minutes, watch the distance to the monitor, it should be at arm's length from your face, and its center should be 10 cm below the vision line (straight line connecting the fixed gaze point with the center of rotation of the eyeball). Blink more often; with concentration, the frequency of blinking decreases, and this leads to dry eyes.
In summer, wear a hat with a brim or a cap with a visor. And don't forget about sunglasses. In the sun, moisture evaporates very quickly.
If you are in a hot, dry climate, wash your eyes with water more often.
Severe frost is also harmful to the eyes. In the cold, try to blink more often, renewing the protective film.
Smog, exhaust fumes, cigarette smoke - all this irritates the eyes. Try to be less likely to be in such conditions. And if this is not possible, use protective drops.
Eat right. Excess fat in food is, of course, bad, but it’s also impossible to avoid it completely.
Use high-quality cosmetics. Keep an eye on its expiration dates. Remove makeup thoroughly at night, using special products for this. It is advisable that these products do not contain alcohol, as it dries out the eyes.
Don’t forget to do eye exercises several times a day:
- Close your eyes and relax.
- Rotate your eyes first clockwise, then counterclockwise. Do 10 laps in each direction.
- Move your eyes left and right, up and down.
- Blink, squeezing your eyelids tightly. Do the exercise 8-10 times.
- Now blink lightly and quickly. 100 times.
- Go to the window, select a point on the glass, or, if you are at work and the organization of your workplace allows it, then on the upper edge of the monitor. Concentrate your gaze on her. Now turn your gaze to something outside the window, located at approximately the same level as the previously selected point, or to the wall behind the monitor. Concentrate your gaze on the selected item. Now concentrate your gaze on the first point. Repeat the exercise several times.
© Dr. Peter
What to do if there is discharge from the eyes
The best thing to do if you find yourself in the situation described above is to wash your face with warm boiled water and immediately visit an ophthalmologist. Only a specialist can determine the cause that caused this pathology, and then prescribe adequate treatment.
If you find any kind of discharge from your eyes, you should not tempt fate and wait until the disease becomes chronic. Treating an advanced disease is always more difficult and expensive than acting in hot pursuit. It is urgent to see an ophthalmologist so that the doctor can make a diagnosis and prescribe appropriate treatment.
For any vision complaints, you can contact specialized ophthalmological clinics: doctors will quickly conduct a thorough eye examination using modern diagnostic equipment and, based on the results, prescribe the most effective treatment.