The appearance of flashes, sparks, circles of fire, lightning and other similar light optical effects in the eyes in medical language is called photopsia (Greek phōtos light + opsis vision). If such phenomena begin to occur regularly, this indicates eye pathologies, neurological diseases, or abnormalities in brain function.
Light flashes can occur due to severe fatigue and eye strain. If they begin to recur with clear regularity, then this is a sure sign of developing pathologies of a different nature. Let's take a closer look at what could be causing this.
Kinds
Based on the nature of the observed phenomena, photopsies are divided into:
- Lightning, which includes the appearance in the field of view of bright light lines, zigzags, rings and other similar shapes. May differ in brightness and location.
- Sparks - rapid movement of bright points of light in the field of view.
- Flashes that are short and sharp, reminiscent of the sensations that occur when you hit your head hard.
- Veil. This visual distortion is expressed in the blurring of objects of visual perception due to a bright and dense veil.
- Floaters that look like various combinations of small dots and stripes accompanied by floating opacities (the opacities move with the eyeball).
With mechanical (for example, finger pressure on the corner of the eye) or electrical stimulation of any part of the visual analyzer, phosphenes occur - artificially caused photopsia.
What it is
Photopsia refers to visual entopic phenomena. The reasons lie in internal disorders of the nervous system. Therefore, the symptom often develops in one or both eyes. Moreover, such a phenomenon can manifest itself both in complete darkness and in light, in both sighted and blind people.
The concept of photopsia includes many manifestations, which may include:
- Flying flies;
- Flashes in the eyes;
- Veil before the eyes;
- Lightning.
Accordingly, each photopsia has its own localization, shape, duration of manifestation and brightness.
Types and reasons
There are many reasons for photopsia. Almost every disease can cause different light phenomena, or even several types of them... here is the main list of pathologies with this symptom:
- Diseases of the vascular system (VSD, arterial blockage, choroiditis, and so on). But this information will help you understand what retinal vascular angiopathy looks like and what can be done about this problem.
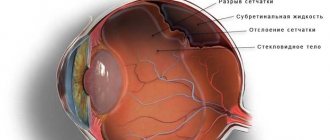
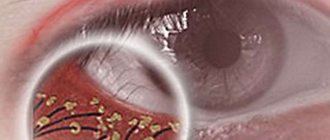
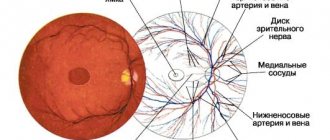
- Disruption of the retina due to retinitis, detachments, ruptures;
- Diseases of the cornea. But what are the consequences of corneal erosion and what can be done about such a problem is indicated here.
- Cataract;
- Progression of glaucoma;
- Hemorrhages in the retinal area;
- Inflammation of the optic nerve or neuritis;
- Eye and head injuries. You can also use pain-relieving eye drops;
- Infectious lesions of the vitreous body and retina;
- Detachment, destruction of the vitreous body of the eye;
- Contact with a foreign body on the conjunctiva;
- Migraine. But how such a problem is treated is indicated here;
- Poisoning with strong poisons;
- Diabetic retinopathy;
- Oncological pathologies;
- Macular edema. You can read here what causes swelling of the upper eyelid of the right eye.
- Hypertension.
The video shows a description of the disease:
Accordingly, from this list it turns out that most of these deviations in vision are either vascular or neurological causes (that is, we are talking about neurological photopsia). Accordingly, it will not be possible to eliminate the problem without eliminating the primary pathology.
With such manifestations, people often find themselves in dangerous situations, for example, while driving a vehicle or operating machinery. Therefore, if the manifestations of the light phenomenon are quite intense, you need to change your type of activity.
Symptoms
As mentioned earlier, photopsia can manifest itself in the form of various light phenomena, including:
- Flashes;
- Lightning;
- Front sights;
- Veil. But how to treat veils before the eyes and which remedies are the most effective, the information at the link will help you understand.
Outbreaks are transient. They appear suddenly and disappear just as quickly. In its manifestation, this light phenomenon resembles a strong blow to the head. Lightning can have different localization and brightness. They can take various forms - lines, rings, zigzags and other types.
Veil refers rather to visual distortion, which manifests itself in the form of clouding of the picture. The curtain can have different densities and brightness. Accordingly, flies appear as small marks or dots, which can have various combinations and layers. These are floating opacities that move with the eyeball (depending on where the gaze is directed).
In the video there are flashes in the eyes:
In addition, the patient often experiences other manifestations of symptoms:
- Eye fatigue;
- Blurred vision;
- Dizziness;
- Pain in the eyes;
- Migraine;
- Irritability due to loud noises;
- General fatigue. It is worth using eye drops for fatigue and redness.
With such manifestations, the patient constantly experiences discomfort. In some cases, a vicious circle results, as, for example, with migraines. It provokes the development of photopsia, which in turn intensifies migraines.
Some conditions are dangerous for humans, since even short outbreaks can disorient the patient, which is fraught with consequences when driving, carrying out daily activities, and performing work.
Reasons for development
Photopsia can be a main or indirect symptom:
- Diseases of the vascular system. Occurs with choroiditis (inflammation of the choroid), blockage of arteries and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Inflammation (retinitis, chorioretinitis), ruptures and detachments of the retina of the eye.
- Diseases of the cornea (keratitis, Fuchs' dystrophy, etc.).
- Progressive glaucoma (occurs when the optic nerve is damaged as a result of increased eye pressure).
- Cataracts (manifested by clouding of the lens of the eye). Manifestations of photopsia intensify as the disease progresses.
- Neuritis (inflammation) of the optic nerve. It can be retrobulbar (without involving the optic nerve head in the pathological process) and intrabulbar. The nature of neuritis can be autoimmune, infectious or demyelinating. Retrobulbar neuritis is often observed in multiple sclerosis, but manifestations of photopsia do not always accompany this type of neuritis. With intrabulbar neuritis, flashes are observed in the periphery of the visual field.
- Retinal hemorrhages. Occurs with mechanical injuries, hypertension, elevated blood sugar levels and excessive physical exertion.
- Various injuries to the eye (foreign body, etc.) or brain (primarily injuries affecting the cortical fields of the occipital lobes and other parts affecting the functioning of the visual centers).
- Destruction of the vitreous body, which occurs due to vascular disorders, endocrine and metabolic changes in the body, injuries, etc.
- Vitreous detachment.
- Exposure to certain toxic substances (organophosphorus compounds, etc.).
- Migraine. The duration of the observed flares ranges from 5 to 45 minutes. Classic migraine is characterized by the presence of bilateral photopsia, and retinal (retinal) photopsia is characterized by unilateral photopsia.
- Atrial scotoma (ocular migraine). Accompanied by loss of image in certain areas of the visual field and photopsia on the periphery of these areas.
- Diabetic retinopathy, which is a complication of diabetes mellitus and is accompanied by damage to the vessels of the retina.
- Various tumor lesions.
- Hypertension. Photopsia is caused by spasms of the retinal arterioles.
- Macular edema (Irvine-Gass syndrome), which occurs as a postoperative complication during cataract removal or as a consequence of chronic uveitis and other eye diseases.
- Vertebral artery syndrome. This diagnosis is made to patients whose clinical symptoms are associated with developmental anomalies or degenerative processes in the cervical spine. Most often, photopsia occurs with osteochondrosis (usually appearing in the form of flies and spots, but lightning and flashes are also possible).
The most common causes of photopsia include pathology of the retina or vitreous, and photopsia of cortical origin are quite rare.
Prevention
Completing a course of treatment for photopsia is not a 100% guarantee of the absence of floaters in front of your eyes. To get rid of the recurrence of symptoms, it is important to adhere to the right lifestyle, namely:
- Healthy eating. Proteins, fats and carbohydrates must be balanced, vitamins and microelements must be present. As for sweets, fatty foods and other treats for the stomach, they can be, but to a minimum. Overeating leads to an imbalance in the body and, as a result, excess weight, then diabetes, which is accompanied by photopsia.
- Absence of bad habits: smoking (not only cigarettes, but also hookah and all other products of the tobacco industry), drinking alcoholic beverages even of low strength.
- Strong physical activity. If you have never exercised in your life and immediately decide to run 20 km a day, then it is not surprising that the body will stop working as it should and will begin to send signals to its owner that he is feeling unwell.
- Regular walks. Lack of fresh air negatively affects blood circulation in the brain and the activity of this organ as a whole. Go to the park or at least to the street near your house at least 2-3 times a week.
In addition, it is necessary to make an appointment with an ophthalmologist once a year, or better yet, more often; as a rule, it is diseases of the organs of vision (retina and vitreous body) that cause photopsia.
Symptoms
Symptoms of photopsia, regardless of its origin, are the appearance of light images of various shapes.
Photopsia, depending on the cause of its origin, may be accompanied by:
- increased eye fatigue;
- headaches;
- pain in the eyes;
- dizziness;
- general increased fatigue, intolerance to intense stimuli (loud sound, etc.);
- vascular dystonia, cardialgia and autonomic dysfunctions;
- increased intracranial pressure;
- pharyngeal and laryngeal symptoms.
Diagnostics
In the presence of photopsia, the diagnostic methods used are aimed primarily at studying various aspects of the visual system. Diagnostics include:
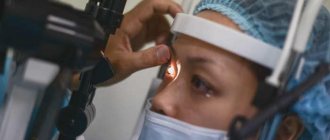
- General examination performed by an ophthalmologist. During the examination, it is important to clarify whether photopsia occurs during movements of the eyes and head, or in the dark (light phenomena during eye movements are characteristic of retinal pathologies).
- Ophthalmoscopy, in which the fundus of the eye is examined using a slit lamp.
- Computed tomography of the eye.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball.
- Intraocular pressure measurements using the indirect method of determining IOP (non-contact tonometry, tonometry using ICare, Goldmann, Pascal tonometers).
- Fluorescein angiography of the retina (FA).
- Perimetry, which allows you to examine the visual field.
- Visometry, which determines visual acuity (table with Russian letters by Sivtsev-Golovin, etc.).
- Optical coherence tomography (OCT), which allows to identify pathological changes in the structure of the retina.
If the ophthalmologist does not identify any pathology, the patient is referred to a neurologist for:
- EEG, which allows to identify pathological rhythms;
- MRI, which allows you to identify pathologies of parts of the brain.
If vertebral artery syndrome is suspected, Doppler ultrasound is performed.
Treatment
Treatment of photopsia consists of eliminating the causes of its occurrence.
In the presence of massive retinal lesions or extensive hemorrhages, vitrectomy is performed - an operation during which blood clots, clouded areas of the vitreous body and fibrovascular cords are removed.
For cataracts, the clouded lens is removed (it is replaced with an artificial intraocular lens).
For choroiditis, symptomatic treatment and antibiotic therapy are carried out (inpatient treatment).
Treatment of macular edema includes a conservative method (anti-inflammatory drugs (Kenalog, etc.) are used), surgical and laser methods.
Treatment of photopsia for migraine involves stopping attacks with the help of serotonin receptor agonists, and for atrial scotoma, sedatives and drugs that improve blood flow in the vessels of the brain (Cavinton, etc.) are prescribed.
For vertebral artery syndrome, drugs that eliminate venous edema (ginkgo biloba, troxerutin, nimesulide, etc.), drugs that normalize blood flow (vinpocetine, cinnarizine, nicergoline, etc.), actovegin and ceraxon are prescribed to prevent the development of chronic ischemia of brain tissue, muscle relaxants (tolperisone), vitamin B.
Treatment of photopsia
As such, this phenomenon itself cannot be treated, because it is only a symptom of another ongoing disease. It can only be eliminated by dealing with the primary cause. If this is caused by retinal detachment, then laser coagulation will help. In the case of cataracts, phacoemulsification surgery, which replaces the damaged lens with an IOL, will also eliminate photopsia. Surgery will also help with other eye diseases. In case of diabetes, neurology, hypertension, their treatment is carried out by specialized specialists.