Causes
The disease can develop under the influence of several factors:
- Bacterial infection. The cause may be opportunistic microorganisms, which include staphylococci and streptococci. The spread of pathogenic bacteria that are not part of the normal microflora is possible. These include gonorrhea, pneumococcus, chlamydia. Infection occurs through contact and household contact after interaction with a sick person.
- Viruses. These include adenovirus, herpes, and rubella. The disease is dangerous because it is transmitted by airborne droplets. A person can become infected even by talking. The virus affects not only the tissues of the eyeball and eyelids, but also the entire body. Therefore, the patient’s general well-being worsens and the body temperature rises.
- Allergy. More often, blepharoconjunctivitis is common in the form of hay fever. This is an allergic reaction that occurs under the influence of flowering plants. The disease is seasonal, manifesting itself in spring and summer. At any time of the year, the disease is formed as a result of exposure to animal hair, bird feathers, house or street dust, and chemicals.
- Demodex. These are mites that penetrate the eyelash bulbs, causing inflammation. Swelling of the sebaceous glands forms. If left untreated, the disease is complicated by inflammation of the cornea or the formation of benign growths on the inside of the eyelid.
- Mechanical damage. This is an injury accompanied by damage to the integrity of the mucous membranes. Infections and viruses penetrate inside the wound. Inflammation begins. The disease occurs instantly. A person begins to experience spasms of the eyelids, due to which he cannot open his eyes.
- Fungal infections. The causes may be fungi belonging to normal microflora or pathogenic microorganisms. Infection occurs as a result of decreased immune function, immunodeficiency, and prolonged use of antibiotics. Films, nodules, and inclusions may appear before the eyes. If there is no treatment, the fungi spread throughout the internal structures of the eyes.
Treatment for each type of disease is different. Therefore, the doctor is obliged to identify the root cause in order to eliminate the risk of relapse.
Blepharoconjunctivitis: causes, symptoms and treatment
The term “blepharoconjunctivitis” is a combined diagnosis, which is very common in ophthalmology and indicates an inflammatory process in both the eyelids and the conjunctiva.
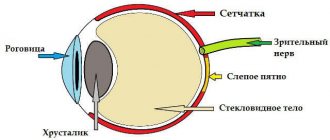
There is no need to explain what “eyelids” are: there is a mirror in every home. The conjunctiva is the thin transparent mucous membrane of the eyeball; the surfaces of the eyelids adjacent to the cornea are also lined with it. The conjunctiva produces a special liquid secretion, which, as part of the tear fluid, serves to moisturize, cleanse and lubricate the eyeball. The very high frequency of inflammation in this area - and conjunctivitis and blepharitis are the most common reasons for visiting an ophthalmologist - is explained by the complexity and compactness of the structure of the eye, and the close interconnectedness of all its components. Indeed, branched vascular networks of blood supply, outlets of various glands, places of contact or interface of various functional tissues are concentrated in a very limited area. Therefore, almost any pathological process sooner or later involves adjacent structures - which is what happens with blepharoconjunctivitis. The eyelids simply cannot remain healthy if their inner walls are inflamed, and vice versa: if superficial skin inflammation on the eyelids develops at the ciliary border and reaches the border of the inner mucous layer, the process spreads to the conjunctiva.
Depending on the location, blepharitis is divided into angular (angular), anterior marginal and posterior marginal. The first option means inflammation mainly in the corners of the palpebral fissure, the second – damage to the outer walls of the eyelids, the third – deeper inflammation involving the posterior, internal surfaces. It is the tendency to expansion of inflammation that allows the term “marginal blepharitis” to be used as a synonym for blepharoconjunctivitis: inflammation of the conjunctiva in this case is almost inevitable.
Risk group
The risk group includes the following categories of patients:
- persons with congenital immunodeficiency;
- patients infected with immunodeficiency during life;
- children and elderly people, since their immunity is weakened or does not function sufficiently;
- people who neglect hygiene rules;
- persons visiting public bodies of water (swimming pools, rivers, ponds), standing water is especially dangerous in the summer;
- patients who often suffer from viral and infectious diseases.
The above categories of patients should periodically visit an ophthalmologist to check the distance of the eyes. In case of any deviations, it is recommended to immediately begin treatment prescribed by your doctor.
Do you need effective treatment, but still have doubts?
“Neurodoctor” is today considered one of the most effective methods of treating diseases of very different etiologies. It goes well with traditional treatment methods and allows the body to recover faster. Today the Neurodoctor device is:
- Treatment method awarded the Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine
- The history of the device goes back more than 20 years.
- Neurodoctor takes part in medical exhibitions around the world.
- The press writes about the Neurodoctor device (publications such as KP and others).
- Neurodoctor is used by thousands of people in 26 countries around the world.
- Produced in Russia at enterprises of the military-industrial complex.
- Can be used effectively together with any medications, without any side effects.
- The device has no contraindications.
An equally dangerous disease is glaucoma, which if not treated correctly can lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms
For patients with blepharoconjunctivitis, the following clinical symptoms are most typical:
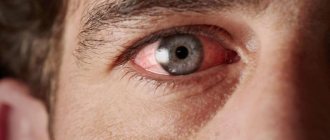
- pronounced redness of the eyes and eyelids;
- swelling and inflammation of the eyelids;
- purulent discharge from the eyes, which is present in the bacterial and less often in the fungal form (because of this, the patient cannot open his eyes in the morning, the pus dries out and sticks the eyelashes together);
- increased production of tear fluid;
- itching, burning, pain in the eyes;
- sensation of a foreign body under the eyelids;
- increased reaction of the eyes to the action of bright light, in which a spasm of the eyelids occurs and a person cannot open them;
- increased eye fatigue, detected in the absence of overstrain;
- decreased visual acuity if the disease becomes more complicated and spreads to the cornea;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes, especially in the viral form.
During illness, the patient cannot wear contact lenses. Their installation causes acute pain and spasm of the eyelids. If the disease is not caused by an infectious factor, the regional lymph nodes are not enlarged.
Forms and types
Blepharoconjunctivitis is divided into the following types:
- Viral: occurs during diseases caused by or after a virus.
- Demodectic mange: is a consequence of a tick bite.
- Meibomian: damage to the meibomian glands.
- Seborrheic: scaly formations on the eyelids.
- Bacterial: the disease is caused by bacteria (staphylococcus, streptococcus).
It has acute, chronic and subacute forms of the disease.
The acute form of the disease develops quickly and rapidly and has pronounced symptoms.
The subacute form is similar to the acute form, but progresses more slowly, and the symptoms are mild.
The chronic form is the most difficult to treat and is accompanied by phases of exacerbations and remissions.
Relapses occur under the influence of external factors or as a result of concomitant diseases.
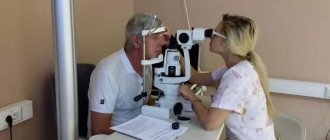
Diagnostics
To determine the root cause of inflammation of the eyelids and conjunctiva, the doctor prescribes several diagnostic tests:
- Collection of complaints from the patient. The doctor asks at what point in time the disease began, how much the eyes hurt, the presence or absence of pus, eyelash gluing, whether there was mechanical damage, the presence of allergic reactions in the medical history. On this basis, the doctor assumes a diagnosis and prescribes further diagnostic tests to confirm or refute it.
- General examination of the patient. The doctor determines severe swelling of the eyelids, due to which the patient often cannot open his eyes. Redness of the conjunctiva occurs. If the disease develops due to a bacterial factor, pus is formed. In the complicated stage of the fungal form, doctors detect a film, nodules, and grains.
- Bacteriological culture. A swab is taken from the patient's eyes and sent to the laboratory. Biological material is sown on different nutrient media. Once bacterial growth is detected, the exact pathogen is determined. Additionally, the antibiotic to which he is sensitive is determined. If the disease is not caused by a bacterial infection, the growth of pathogenic microflora will not be detected.
- PCR analysis. A swab is taken from the patient's eyes and sent to the laboratory. There it is examined using a semi-automatic analyzer, which determines the exact genotype of the pathogen. This method only detects viruses. The doctor identifies influenza, parainfluenza, adenovirus, herpes.
- Microscoping. The smear is examined under a microscope. Determine the number of bacteria, fungi and their spores. If the disease is caused by one of these factors, the entire smear will be completely covered with microorganisms, as they are actively multiplying.
- Allergen test. Such a study can only be carried out during a period when the patient has no clinical symptoms. The analysis is carried out in autumn or winter. Different types of allergens are sequentially applied to the patient's hand. Next, they determine in which area of the skin inflammation, redness, and itching have formed.
After determining the root cause, the doctor prescribes treatment that will completely eliminate the infectious-inflammatory condition.
Treatment
Complex therapy is used, which is aimed at completely eliminating the pathogen and preventing complications. Certain types of treatment are suitable for different types of disease. For example, for a fungal infection, antibiotics cannot be prescribed, which will further worsen the patient’s well-being. They are applicable only for bacterial blepharoconjunctivitis.
Antibacterial therapy
It is recommended to undergo a test to determine the type of pathogen before starting to use antibiotics. This will reduce the risk of developing resistance in opportunistic microflora. Most often, doctors do not resort to such research, identifying the disease by symptoms. This is due to the fact that the analysis takes 5-7 days, during which time the patient’s condition worsens.
Broad-spectrum antibiotics that are active against most pathogenic microorganisms are prescribed. Use topical preparations, which include drops:
- Vigamox;
- Tobrex;
- Ceftriaxone;
- Levomycetin.
Drops are used during the daytime. To prevent pathogenic microflora from multiplying overnight, it is recommended to apply antibacterial ointments under the eyelids before going to bed:
- Erythromycin;
- Tetracycline.
After 1-2 days, redness, inflammation, and purulent exudate will completely disappear. This is a sign of the initial stage of eliminating the disease. At this point, stopping treatment is prohibited. It is important to use the drugs for up to 7 days in order to completely destroy the bacteria and prevent the development of resistance of opportunistic microflora to the action of the drug.
Antiviral therapy
In the viral form of blepharoconjunctivitis, pathogens spread throughout the body, entering the lymph nodes. Therefore, the use of systemic agents that are taken orally (Acyclovir, Ingavirin) is recommended. If the inflammation is excessively severe, it is possible to use antiviral drugs in the form of drops for up to 2 weeks. They are used up to 10 times a day.
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
The drugs are indicated to eliminate swelling, inflammation, and redness. They suppress the immune system only in the eye area. Diclofenac drops are suitable, which has a small list of side effects and contraindications.
If non-steroidal drugs do not help, the doctor will prescribe glucocorticosteroids. They are also used for local therapy, but the list of side effects increases.
Antihistamines
Indicated for allergic nature of the disease. If a person suffers from seasonal allergies, it is recommended to start drug therapy in advance. The most commonly used are Cetrin, Zodak, Suprastin. Their use should be done before bedtime, as they lead to drowsiness.
Complex vitamins
If a patient develops chronic blepharoconjunctivitis, recurring in the autumn-winter period, this means that immune function is reduced. To correct it, it is not necessary to use immunomodulators. Multivitamins that increase metabolic rate are suitable. As a result, tissue regeneration increases and the cellular composition is renewed faster. Immune function increases.
How to cure blepharoconjunctivitis as quickly as possible?
We offer an innovative method of color pulse therapy, the discovery of which was awarded the Nobel Prize.
The answer is obvious: for the visual system to work well, it is necessary to debug the precise functioning of the brain centers responsible for its regulation. This is exactly the problem that the innovative Neurodoctor device solves.
The device is based on the pulse therapy method. This is one of the most progressive and effective treatment methods known to modern world medicine. Thanks to pulse therapy, certain parts of the visual system “awaken”, which ensures the elimination of malfunctions in its functioning. This occurs due to the impact on the control centers of the brain.
How it works?
Neurodoctor affects the control centers of the brain.
The brain begins to produce dozens of neurohormones and form “corrective” nerve impulses.
Neurohormones are many times more effective than the most powerful drugs in quickly curing the disease. Nerve impulses eliminate pathological processes at the cellular level and correct the functioning of other organs and systems of the body.
LEARN MORE ABOUT THE METHOD
Complications
In the absence of treatment for the disease or the presence of immunodeficiency, the patient develops complications:
- a change in the normal location of the eyelids, as a result of which they stretch and the eye does not close completely;
- chronic dry eyes, which appears as a result of deformation of the eyelids;
- inflammation of the cornea;
- spread of infection to the lacrimal sac;
- drying of the eyelid and conjunctiva;
- purulent inflammation of the retina, which can be complicated by fistulas (holes from which pus flows);
- thrombosis resulting from chronic inflammation.
Complications do not lead to the death of the patient, but greatly worsen his quality of life. To prevent their development, it is important to consult a doctor at the first symptoms of inflammation and undergo treatment.
What is the result?
You will strengthen your immunity. The inflammatory process is localized. The pain, itching and burning that tormented you will disappear. Redness and swelling will disappear. Metabolism in tissues, muscles and the cornea of the eyes will improve. Your body will begin a powerful process of regeneration and restoration. Immunity will increase. The risk of vision-threatening complications will be eliminated.
Powerful and effective treatment with the Neurodoctor device will quickly eliminate the clinical manifestations of the disease, localize the foci of pathology, and reduce the dose of medications. This will allow you to live a full life and forget about your illness forever.
Your body will quickly cope with the inflammatory process and return to its normal functioning. Unpleasant symptoms of inflammation will disappear, appearance will improve and cosmetic defects will be eliminated. And most importantly, you do not have to worry about the serious consequences of the disease associated with deterioration or loss of visual functions.
Prevention
To prevent the development of the disease, you should adhere to the following rules:
- compliance with hygiene rules in the area of hands, face, eyes;
- rules for wearing contact lenses, using a cleaning solution;
- eating food containing all the beneficial substances, minerals, trace elements, vitamins that contribute to the normal functioning of the immune system;
- an annual visit to an ophthalmologist for timely detection of abnormalities and treatment in the early stages of the disease;
- timely treatment of systemic diseases, especially viral and infectious ones;
- lack of swimming in public bodies of water, especially in standing water.
If you follow the rules of prevention, it is impossible to completely eliminate the risk of infection. The disease is easily transmitted from other people with viral or bacterial forms of blepharoconjunctivitis. It is important to carry out treatment on time, which will completely eliminate the risk of complications.
Chronic demodectic blepharoconjunctivitis
Many reports have been published that from 40% to 85% of cases of blepharoconjunctivitis are initially demodectic, and only then, depending on the nature of the secondary pathogenic factors, infectious-inflammatory or infectious-allergic symptoms are added. As is known, Demodex is found in the vast majority of people (over 95%) and does not manifest itself in any way until the onset of favorable conditions for it - which, in general, are reflected in the above list of provoking factors. When the mite is activated, the skin epidermis and eyelash follicles (where the parasite mainly lives) are intensively injured, toxic and allergenic waste products accumulate - which creates the ground for the development of one of the three main forms of blepharoconjunctivitis (or a combination thereof).