Barley - an infectious eye disease with an acute inflammatory process. May be caused by pathogens entering the meibomian gland or eyelash hair follicle.
Styes on the eye, compared to other eye infections, are quite common. According to medical statistics, 8 out of 10 people have had stye at least once in their lives. The disease is characterized by an acute course and pronounced pain in the inflamed eye.
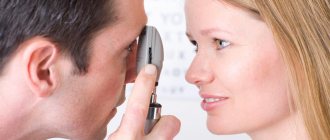
Usually, ophthalmologists quickly visually identify this eye pathology.
1
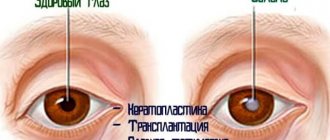
Stye on the eye
2 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
3 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
Don't underestimate barley! This is not a temporary cosmetic defect, but an infectious disease that must be treated. In some cases, barley can cause serious complications such as purulent-septic eye lesions.
Causes of stye
As a rule, the inflammatory agent of the disease is a staphylococcal or streptococcal infection. Frequent styes often indicate a decrease in immunity (general and local). Gastrointestinal diseases, parasitic infestations, as well as diabetes mellitus and persistent foci of infection (chronic sinusitis, untreated teeth, etc.) increase the risk of purulent inflammation, including barley. The disease can recur, with styes appearing repeatedly throughout the year.
Barley is a non-contagious disease, it cannot be transmitted from person to person through communication, however, if barley occurs, towels and scarves must be used strictly individually.
2. Symptoms of the disease
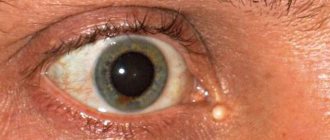
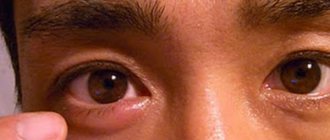
A stye on the eye usually appears as a red bump along the edge of the eyelid, similar to a pimple. As the stye grows, the eyelid becomes swollen and painful, and the eyes may water. It usually takes about three days for a stye to grow and swell before it ruptures and releases fluid. Barley usually goes away within a week.
A chalazion looks similar to a stye, especially in the early stages of the disease. But unlike styes, they often don't rupture and simply disappear gradually over a few months without treatment. A chalazion grows more slowly than a stye. If a chalazion grows large enough, it can negatively affect your vision. In addition, inflammation and swelling may spread to the area around the eyes.
Visit our Therapy page
Clinical manifestations
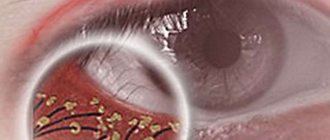
The disease begins with the appearance of swelling and then redness in a limited area of the eyelid. There is pain on palpation, as well as eyelid movement and blinking. Swelling, redness, and soreness may increase over several days. When examined with a slit lamp, it is clearly visible that the center of inflammation is the eyelash. After two or three days, an abscess forms at the top of the inflammatory focus, which looks like a yellowish vesicle. Afterwards it opens, releasing pus. When it is opened, the pain subsides and the condition improves.
What is stye and its symptoms
A disease characterized by inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash with suppuration, as well as the sebaceous gland from the edge of the eyelid or the meibomian gland located in the depths, is called hordeolum or, more simply, barley.
Depending on the location, the pathology can be:
- External, when the hair follicle and sebaceous glands nearby become inflamed due to infection.
- Internally, the inflammatory process develops in the duct and meibomian gland.
- Barley can be unilateral or bilateral, single or with many abscesses. There are acute purulent inflammation and chalazion, which is characterized by a slow course and inflammation in a chronic form.
The disease occurs in several stages, each with its own symptoms:
- Infiltration. Characterized by thickening of the upper or lower eyelid. There are complaints of redness, itching and foreign body sensation.
- Purulent melting. After 2-4 days, the eyelid becomes increasingly swollen, the center thickens and becomes painful, and a yellow-white head in the center is noticeable. Pus accumulates and it can be difficult to open the eye.
- Resolution when the abscess opens. The result is a reduction in inflammation, pain and swelling. The stage of pus discharge lasts several days.
The most common in practice is external unilateral barley. The disease should not be left untreated, as there is a risk of developing an abscess with inflammation of the lymph nodes and fever.
If the focus is located internally, then the abscess will not be visible; it can only be detected when the eyelid is everted by a specialist. A sign of this pathology is pain when turning the eyeball, pressing on the eyelid and blinking.
Treatment of stye on the eyelid
As a rule, barley is treated conservatively (using medications and physiotherapy), surgical intervention (opening the barley) may be required only in severe cases or complications.
In the initial stages of the disease, even before the formation of suppuration of the head, you need to use dry heat and UHF. A good therapeutic effect is obtained by treating the area of barley with alcohol solutions (brilliant greens, 70% ethyl alcohol, calendula tincture). When an abscess has formed, it is strictly forbidden to heat the area of the stye - this can lead to the spread of the process of suppuration and cause an abscess of the eyelid.
Drops with antibiotics or sulfonamides (Tobrex, Floxal, Tsipromed, etc.) are additionally prescribed to be instilled into the affected eye, and the edges of the eyelids are lubricated with antibacterial ointments (Floxal, Tobrex ointments, Tetracycline eye ointment).
Recovery, in most cases, occurs quickly, no complications are observed.
For recurrent styes, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system - multivitamins are prescribed, and autohemotherapy is effective. Consultations with a dentist or ENT doctor are recommended to identify chronic foci of infection and eliminate them.
Do not squeeze out the barley under any circumstances. Mechanical impact causes microtraumas - through damaged skin, pus can enter the vascular bed, which can cause serious complications - abscess, phlegmon of the eyelid, even purulent meningitis and sepsis. Better consult a doctor. He will recommend medications and, if possible (no abscess), prescribe physical therapy, which will collectively speed up recovery.
4.Prevention
A few simple tips will help prevent stye in most cases:
- Don't rub your eyes. This can irritate the eye and allow bacteria to enter the eye. If you must touch your eyes, wash your hands first.
- Protect your eyes from dust and dirty air if possible. For example, wear safety glasses during very dusty household tasks.
- Regularly (at least every 6 months) renew your eye makeup, especially mascara. This is a very favorable environment for bacterial growth.
- If you tend to get styes and chalazions frequently, wash your eyelids regularly with warm water. You can add a small amount of baby shampoo to it.
- See a doctor immediately and treat any inflammation or infection of the eyes or eyelids.
Our achievements
"Moscow Eye Clinic" offers comprehensive diagnostics and effective treatment of all types of inflammation of the eyelids: styes, chalazions, meibomites. We provide not only medication, but also, if necessary, surgical treatment. The use of the most modern equipment and the high professional level of specialists working in the clinic eliminate the possibility of diagnostic errors.
Based on the results of the examination, each visitor will be given recommendations on choosing the most effective methods of treating the eye pathologies identified in them. You will receive a quick and accurate diagnosis of barley and its effective treatment.
3.Diagnostics and treatment
Diagnosis of stye and chalazion
The doctor diagnoses this problem by carefully examining the eyelid. It can be difficult to distinguish a stye from a chalazion. But if there is a hard lump inside the eyelid, the doctor will likely diagnose a chalazion.
Treatment of stye and chalazion
Stye and chalazion can be treated at home without any complex medications. It is usually sufficient to follow these recommendations:
- Apply warm wet compresses for 5-10 minutes 3-6 times a day. This usually helps with faster healing and can also help open a blocked pore to allow its contents to come out;
- You can try special ointments, washing the eyes with solutions recommended by your doctor;
- Do not put pressure on the stye or chalazion and do not deliberately open it. Let the stye or chalazion break open on its own.
- Do not wear contact lenses or apply eye makeup until the affected area is completely healed.
If home treatment for stye on the eye does not help, consult your doctor. He may recommend antibiotic ointments or eye drops. If the infection has spread to the eyelid or eye, you may need to take antibiotic tablets.
If a stye or chalazion becomes very large, your doctor may try opening it and flushing the area. But it is strictly not recommended to perform this procedure yourself.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Prices for treatment for barley
The cost of barley treatment at MGK is calculated individually and will depend on the volume of therapeutic and diagnostic procedures performed. You can find out the cost of a particular procedure by calling (499) 322-36-36 or online using the appropriate form on the website; you can also familiarize yourself with the “Prices” section.
Go to the "Prices" section
Mironova Irina Sergeevna
Prevention
The main principle of preventing eye diseases, especially infectious ones, is the rule - first of all, maintain personal hygiene. Do not touch your face and eyes with dirty hands, use only your personal hygiene items (face towel, handkerchief) and accessories for applying cosmetics to your eyelids.
Since barley often occurs against the background of existing diseases and weakened immunity, it is necessary to diagnose and treat the underlying disease and take measures to maintain and strengthen the immunity of the entire body.
When stye appears on the eye and until the end of its treatment, it is necessary to take preventive measures to prevent possible complications and the spread of infection to other elements of the eye, as well as to the second eye.
What not to do, especially after the appearance of pus, the contact of which with healthy neighboring tissues can cause unpleasant consequences and complications:
- touch and comb the stye with your hands;
- squeeze or pierce;
- warm up barley with a purulent head.
All treatment procedures should be carried out with clean hands, and hands should be washed both before and after procedures. Barley is not a very dangerous pathology, but, as with other diseases, prevention and timely treatment will avoid many troubles.
Clinical picture
The onset of the disease is usually characterized by discomfort when a person feels pressure in the eye or its surroundings. There may be a sensation of the presence of a foreign body in the eye, which cannot be eliminated even by intense blinking. After this, a feeling of pain appears on the eyelid or around the eye, pain and burning in the eyes, painful perception of light.
Attention! Sometimes it is not the stye as such that itches, but the eyelid itself, where the inflammatory process has not yet begun, but the infection is already present. Itching is the first sign indicating the approach of the disease.
At first, stye on the eye manifests itself as swelling and redness of the entire affected eyelid, later – pain and redness of the skin, concentrated in one small place on the edge of the eyelid. Subsequently, a lump (tubercle) forms in this place, gradually filling with pus.
Symptoms and causes of stye in children
The child behaves restlessly, constantly scratches the eye, complains of pain or “specks in the eye”; very soon (in the next few hours) the eyelid turns red, swells, and a characteristic painful volcanic-looking tubercle with a yellowish center appears; The temperature may rise (up to 38°C and above), headaches, and increased lacrimation. Then the festering stye spontaneously opens - and in a couple of days everything goes away without a trace... until next time. This is a typical algorithm for the development of a child's hordeolum.
Symptoms
This eye pathology is perhaps the most recognizable, since its characteristic symptoms are easy to recognize even by the average person, not to mention a qualified specialist. The disease may also be accompanied by headaches and pressure in the eye area. In some cases, an increase in body temperature may occur. The first “bell” is a feeling of itching at the outer edge of the eyelid. Soon a slight swelling appears, increasing every day, and after it a yellowish head appears. If you open it yourself, pus will flow out of it and you will be able to see particles of dead tissue. In most cases, a person develops only one stye, but in some situations there may be several of them, including in both eyes at the same time.
What's really going on?
Barley is an acute, purulent clinical, infectious inflammatory process in origin. From this exhaustive definition, the reasons for its appearance, patterns of development, and the choice of adequate treatment and preventive measures clearly follow.
In the vast majority of cases, hordeolum is caused by the introduction of a bacterial (more precisely, Staphylococcal aureus) infection with subsequent rapid proliferation of the pathogen in the hair follicles, glands of Moll and/or Zeiss, less often in the meibomian glands (in this case, the “internal” barley is turned by the fistula canal towards the conjunctiva ).
Constant, often recurrent styes in a child always indicate the presence of some hidden or obvious systemic pathology. Usually this is a decrease in immunity due to an incorrect, unnatural lifestyle for children (physical inactivity, lack of sunlight, fresh air, etc.), hypovitaminosis, endocrine or gastroenterological disorders, recent diseases or operations, and the presence of worms.
Hypothermia and overheating, untreated or undertreated infectious foci, for example, in the oral cavity or nasopharynx (caries, tonsillitis, etc.) contribute to the development of stye.
But the main factor that makes styes a global problem and an almost inevitable companion to childhood is children's curiosity, combined with unwashed hands and a lack of strong sanitation and hygiene skills.
The crowding of children's preschool and school groups, the use of common towels or pillows, the habit of examining everything, so to speak, by palpation, the reflexive impulse to intensively rub the eyes in case of any discomfort - all this creates extremely favorable conditions for the spread of staphylococcal infection.
In addition, adults make a significant contribution to increasing the adaptability and survival of staphylococcus: uncontrolled and inadequate use of antibiotics leads to mutations and the formation of drug-resistant bacterial strains.