Barley - an infectious eye disease with an acute inflammatory process. May be caused by pathogens entering the meibomian gland or eyelash hair follicle.
Styes on the eye, compared to other eye infections, are quite common. According to medical statistics, 8 out of 10 people have had stye at least once in their lives. The disease is characterized by an acute course and pronounced pain in the inflamed eye.
Usually, ophthalmologists quickly visually identify this eye pathology.
1
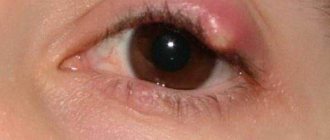
Stye on the eye
2 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
3 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
Don't underestimate barley! This is not a temporary cosmetic defect, but an infectious disease that must be treated. In some cases, barley can cause serious complications such as purulent-septic eye lesions.
Causes of stye on the eye
Barley on the eye occurs due to the entry of pathogenic flora (streptococci and Staphylococcus aureus) into the eyelash hair follicle or into the sebaceous gland of the eyelid (meibomian gland). When the gland becomes clogged, the disease intensifies, the walls of the follicle become inflamed, and pus is formed.
Under normal conditions, pathogenic flora is present in small quantities on the skin even in a healthy person. But for some reason, pathogenic organisms begin to multiply rapidly, capturing healthy neighboring tissues. The disease can also be caused by the demodex mite, which lives at the mouth of the hair follicles. But sometimes Demodex also settles in the meibomian sebaceous gland. With reduced immunity, a person develops allergic reactions to mite waste products, causing acne or stye on the eye.
A number of factors contribute to the appearance of stye on the eye:
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules (scratching the eyes with unwashed hands, wiping the face with a dirty towel, using someone else’s decorative cosmetics);
- decreased immunity due to a number of diseases, for example, due to HIV infection;
- stress;
- diabetes mellitus;
- conjunctivitis;
- gastrointestinal diseases;
- furunculosis, blepharitis, seborrheic dermatitis, acne vulgaris, etc.
1 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
2 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
3 Diagnosis and treatment of barley
How to speed up the maturation of an abscess
A lump has formed, but there is no white plug? The stye will ripen and burst faster if you apply dry heat to the eyelid. Suitable: boiled eggs; sea or table salt; buckwheat.
Chicken eggs are boiled hard, wrapped in a piece of soft cloth and applied to the problem area for 10-20 minutes. Heat buckwheat or salt in a frying pan, do not grease the bottom with oil. Pour the hot filler into a thick fabric bag. Cover the eyelid with a clean towel folded in several layers, apply salt or buckwheat on top.
An alternative to heat is compresses, which draw out the infection and accelerate the maturation of the abscess. Tea brewing is suitable, but it must be loose leaf, not from a bag. You can use black or green.
Place 2-3 tablespoons of dried tea leaves into a cup. Pour boiling water over it, just hot water is not suitable. Cover. Leave for 30 minutes. Wait until the tea becomes warm. You can't put sugar or honey. Moisten cotton swabs with liquid and apply to eyes. Lie for 15 minutes with lotions. After the procedure, avoid drafts.
Chamomile has antibacterial and soothing properties. For a cup of boiling water you will need 2 tbsp. l. dried flowers. Infuse under the lid, wrapping the container. The strained drink can be consumed instead of tea or used as an eye wash and anti-inflammatory compress.
The lotions should be applied to both eyes, because stye can spread to the second eyelid. Throw away cotton swabs after each procedure, because they remain infected and bacteria.
Compresses should be applied after 2-4 hours. Keep for 15 to 25 minutes to speed up recovery.
Symptoms of stye on the eyelid
There are 2 types of barley: external and internal .
External barley develops as a result of inflammation of the Zeiss glands located in the area of the roots of the eyelashes. These glands produce a special secretion to lubricate and protect the surface of the eye. Barley on the eye is formed as a result of clogging of the gland with its own secretion and the appearance of infection in this place.
Internal stye occurs when the meibomian sebaceous glands located in the inner eyelid become clogged. With internal barley, inflammation can also affect the cartilaginous plate of the eyelid. With frequent relapses, the disease becomes chronic and can develop into another, very unpleasant eye disease - chalazion.
Barley can be either single or multiple , affecting both eyes. Numerous and frequently recurring styes occur in people with weak immunity (with cancer, viral hepatitis, HIV diseases) or the elderly.
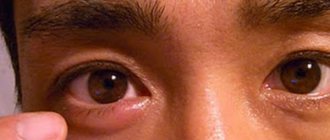
Barley disease is characterized by an acute course and rapid development of the pathological process. Initially, itching appears along the edge of the eyelids, accompanied by swelling and pain, which can increase when pressing on the inflamed area. Sometimes, with stye, the eye swells so much that a person cannot even open it.
When numerous styes appear on the eye, fever, headache, chills and body aches, enlarged lymph nodes near the ears and under the jaw are observed.
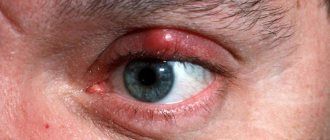
After some time, an abscess (pustule) appears on the stye, and the pain begins to subside. When the barley is opened independently, the purulent contents begin to come out, and the signs of the disease disappear. Sometimes inflammation can last up to 7 days.
Internal stye appears on the inside of the eyelid in the thickness of the cartilage. If you evert your eyelid, you may notice redness and swelling of the conjunctiva. Three days later, a yellow-green purulent ball appears under the skin of the eyelid. Spontaneous opening of the stye occurs in the conjunctival area. Later, leaf-shaped granulations appear in this place.
Stye on the eyelid of a child
Children have a fairly weak immune system, so they suffer from stye much more often than adults. With this disease, hyperemia and swelling of the eyelid occurs, as a result of which the palpebral fissure narrows and it is sometimes difficult for the child to open the eye. The appearance of stye on the eye is accompanied by chills, fever, headache and severe pain in the inflamed eye.
The following factors can provoke pathology: conjunctivitis, gastrointestinal diseases, helminthic infestation, allergies. Even hypothermia or overheating of a child’s body can cause barley, not to mention diseases such as otitis media, tonsillitis, and adenoids.
If stye on the eye is not treated, the child's vision may be severely damaged.
If stye appears on the eye, you should visit an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. He will identify the cause of the disease and prescribe adequate treatment.
You should not squeeze out the stye yourself! This can lead to complications such as phlegmon of the orbit, abscess on the eyelids, thrombophlebitis of the vessels of the orbital eyelids, meningitis and sepsis!
Why does it arise
It will not be wrong to say that barley, like conjunctivitis, is a disease of dirty hands. If you constantly rub your eyes on the street, work in a gassy or dusty room, use a dirty handkerchief or towel, or do not follow basic hygiene rules, then sooner or later you will definitely become familiar with stye.
Less commonly, the cause of the problem is diseases of the endocrine system, malfunctions of the gastrointestinal tract, and respiratory viral diseases. Weak immunity especially contributes to the development of the disease.
Factors against which barley often occurs are the following:
- past infectious acute or chronic diseases;
- impaired metabolism;
- disturbance of the bacterial flora in the intestines - dysbiosis or atony;
- improper diet - excess of sweet or starchy foods;
- high blood sugar;
- prolonged exposure to cold or draft.
When you see redness and swelling of the eye, you should never panic. It is urgent to see a specialist who will prescribe treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you are tormented by frequent relapses of the disease, you need to consult doctors such as a dermatologist, allergist-immunologist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist. You may need to take a test for glucose tolerance and capillary blood glucose levels.
Examining stool for parasite eggs and examining eyelashes under a microscope to identify demodex mites will help identify the nature of the disease. To determine bacteremia, it is necessary to take a blood test for sterility, and to identify a specific pathogenic pathogen, a bacteriological examination of secretions from the conjunctiva.
When did the white plug appear?
When the stye begins to look like a large pimple with a white head, the most important thing is not to even think about squeezing it out. It's good if you're lucky, but it's better not to take risks. And all because during squeezing, purulent masses can get on healthy tissues and infect them.
In addition, due to the close proximity of the network of small vessels, it is very easy to damage the vessel and cause infection. This can cause meningitis or other dangerous diseases. Therefore, if barley becomes noticeable, you need to use special medicinal ointments.
In this case, pharmacology has advantages over natural remedies. Firstly, it is more secure. Secondly, the ointment has a targeted and rapid effect on the source of inflammation. At the same time, most ointments have an antimicrobial and analgesic effect.
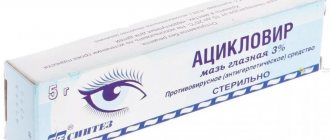
The most popular, effective ointments for the treatment of barley are: Levomecithin, Tetracycline, Floxal, Hydrocortisone. All preparations are applied locally before bed with light movements, exclusively with clean hands, on inflammation.
Later, the ointment will spread a little, which will affect vision, which is why ointments are used before bed, but this is temporary and safe. Drops can be used together or separately from ointments. The most popular drug is Albucid. Any of the drugs described is prescribed only by a doctor.
Treatment of stye on the eye
Since barley is caused by various cocci, with this disease preference is given to antibiotics - drops or ointments. For external stye on the eye, as a rule, conservative treatment is used, but for internal stye, surgical intervention may be necessary.
In case of recurrent stye, it is important to promptly carry out a course of eyelid massage from an ophthalmologist and other preventive measures.
Entrust the treatment of eye diseases to professional ophthalmologists at the MedicCity clinic. We have high-precision diagnostic equipment and the latest treatment methods in our arsenal!
The MedicCity Clinic is your faithful assistant in the diagnosis and treatment of ophthalmological diseases!
Removal methods
If removal is indicated, the patient can choose how to get rid of the stye. This procedure is not considered urgent; you can choose a day. Two methods are considered popular: classical surgery and laser. Both operations involve local anesthesia and then removal of the purulent capsule from the eyelid. The surgical operation takes place in stages:
Before the actual manipulation begins, the problem area is numbed.
- The patient lies down on the table, the head is secured with special belts.
- The surgical field is treated with an antiseptic.
- Anesthesia is administered and the patient waits 3-5 minutes for it to take effect.
- The eyelid is fixed with a clamp. This gives the surgeon direct access to the stye and reduces the risk of bleeding.
- The tubercle is opened and the entire capsule is removed.
- Treated with an antiseptic.
- Stitch the wound.
- Apply a sterile dressing.
The laser method is simpler and painless. During the operation, an incision and excision of the capsule are also made, but with the help of equipment. Thus, the procedure is carried out without contact, eliminating the possibility of bleeding. Disinfection is also carried out using the laser method. Ophthalmologists recommend using this method to remove internal stye. The duration of the operation is shorter than surgery, maximum 20 minutes. The risk of relapse is reduced to zero. The main disadvantage of laser surgery is its price, which significantly exceeds the cost of the traditional method.