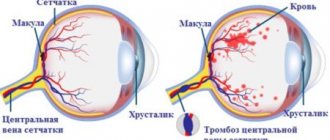
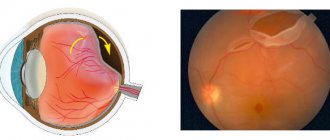
Occlusion of the central retinal vein (CRV) and its branches develops as a result of thrombosis with subsequent circulatory disorders and is manifested by a sharp decrease in vision. This disease is prone to acute onset and rapid progression.
The risk group includes people who have concomitant diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis, varicose veins, glaucoma, etc. In most cases, occlusion of the central retinal vein develops acutely. Patients note a marked decrease in vision in one eye without pain. In rare cases, vision is reduced in both eyes. The degree of loss can range from moderate to complete loss of vision. It is extremely important to identify signs of occlusion of the central vein in a timely manner, because the further prognosis will depend on the timeliness of seeking medical help. Maximum effectiveness of treatment can be achieved in cases where the patient consults an ophthalmologist on the first day after the appearance of characteristic symptoms.
What is the danger of vascular occlusions?
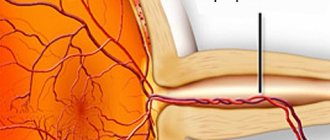
Occlusion is the obstruction of blood vessels, which causes circulatory problems. Impaired patency of the central retinal artery is one of the most dangerous and severe conditions. Due to the fact that blood cannot flow to the retina, its tissues no longer receive enough oxygen and nutrients, causing ischemia to develop. Occlusion of the central nervous system can quite quickly lead to irreversible (partial or complete) vision loss. When the central vein is blocked, the outflow of blood from the retina is disrupted. This causes swelling and can also lead to damage to the retinal tissue, which can lead to decreased vision and loss of vision. Venous occlusions are characterized by loss of visual fields in the area of the damaged vessel or a uniform decrease in vision throughout the entire field. With arterial obstruction, there is a risk that, in addition to blindness, the patient will begin a pathological process in the brain. Often, blockage of blood vessels does not occur gradually, but abruptly, and even a minute of delay can cost a person his sight. At the first signs of occlusion, you should immediately consult a doctor for qualified help.
Possible complications
If detected untimely and without proper treatment, central retinal vein thrombosis can be accompanied by a number of complications, among which it is worth noting optic nerve atrophy, central retinal dystrophy, the development of secondary glaucoma, the appearance of hemophthalmos (bleeding in the eye), and repeated retinal vein thrombosis.
To detect retinal vascular pathology in a timely manner, you should not ignore visits to the doctor and undergo regular diagnostic eye examinations, especially if you are at risk.
What causes obstruction of retinal vessels?
The patency of venous vessels in most cases is impaired due to thrombi - blood clots that appear in the vascular lumen. Retinal vein thrombosis usually occurs as a complication of diabetes mellitus, heart and vascular diseases, hypertension, and atherosclerosis. Alcohol abuse and smoking are also risk factors. Occlusion of arterial vessels can be caused by blood clots and emboli (“plugs” in the form of gas bubbles, foreign particles), as well as arterial spasms. Blockage of the arterial vessels of the retina can be caused by endocrine diseases, hormonal disorders, diseases of the autonomic nervous system, cardiovascular pathologies, heart defects and a number of other disorders in the body. Another possible cause of retinal vascular obstruction may be an inflammatory process that causes a narrowing of the vascular lumen or a slowdown in blood flow.
What it is?
Thrombosis
is a pathological condition in which dense blood clots (thrombi) form in the vessels, slowing down or completely stopping the normal flow of blood. As a result, a lack of organ nutrition (ischemia) may occur, which in turn can lead to tissue death (necrosis, infarction) and death. There are two types of thrombosis: venous and arterial. From the names it is clear where the formation of blood clots occurs. In the first case - in the veins, in the second - in the arteries. The disease can occur in acute and chronic form. Arterial thrombosis is the most dangerous.
What symptoms require immediate medical attention?
With occlusions, irreversible vision loss can occur very quickly, so it is important not to miss the first symptoms and see an ophthalmologist as early as possible. Blockage of the arteries and veins of the retina is painless and is most often expressed only by deterioration or loss of vision. The following clinical signs should be the reason to consult a doctor:
- loss of areas of the visual field;
- decreased visual acuity in the center or periphery;
- sudden loss of vision.
Acute occlusions of the central retinal artery are the most dangerous because they lead to ischemic tissue disease, and it is often impossible to restore lost visual functions.
MagazinLinz.ru team
Central retinal vein occlusion
The diagnosis of central retinal vein occlusion is made by an ophthalmologist taking into account medical history, physical and instrumental examination, and advisory opinions of a cardiologist, endocrinologist, rheumatologist, and hematologist.
Methods for objective diagnosis of central retinal vein occlusion include: testing visual acuity, perimetry, tonometry, biomicroscopy, ophthalmoscopy, angiography of retinal vessels, electrophysiological studies.
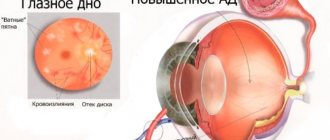
In the stage of prethrombosis, as well as with occlusion of the second and third order branches of the central vein, visual acuity decreases slightly or does not change at all. With non-ischemic occlusion of the central retinal vein and its branches, visometry reveals visual acuity above 0.1. Ischemic thrombosis of the central vein and temporal veins is accompanied by a decrease in visual acuity below 0.1. Visual field examination reveals central or paracentral scotomas in the quadrants of the retina corresponding to the lesion, concentric narrowing of the visual fields.
Tonometry can detect ocular hypertension; Using 24-hour tonometry, IOP is assessed over time. Changes detected by biomicroscopy can be different: neovascularization of the iris; relative afferent pupillary defect; the presence of a suspension of blood elements, exudate, floating blood clots in the vitreous body, etc.
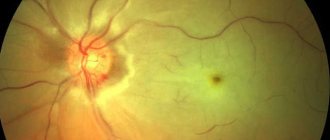
Signs typical of central retinal vein occlusion are detected using ophthalmoscopy. Characterized by swelling of the optic disc and macula, hemorrhages in the form of “tongues of flame”, tortuosity and moderate dilatation of the veins, their uneven caliber and microaneurysms, cotton wool-like foci. The ophthalmoscopic picture of lesions of various branches of the central vein has its own characteristics.
Vascular fluorescein angiography reflects delayed retinal contrast enhancement, uneven contrast enhancement of veins, prolongation of the venous perfusion phase, and granularity of blood flow. Based on the results of angiograms, the duration of thrombosis, the localization and degree of occlusion of the central retinal vein, the development of neovascularization, the condition of the macula and optic disc are judged.
Electroretinography, which reflects the degree of retinal ischemia, allows you to monitor the dynamics and make a prognosis regarding visual function.
Of the laboratory methods for occlusion of the central retinal vein, a significant role is played by the study of blood sugar, coagulograms, determination of cholesterol and lipoproteins, and coagulation factors.
Differential diagnosis of central retinal vein occlusion is carried out with secondary retinopathy (hypertensive, atherosclerotic, diabetic, etc.).
Epiretinal fibrosis
This is a thin film that forms in the vitreous cavity in close proximity to the macula. It is usually a slowly progressive disease that impairs central vision, causing blurred and distorted images. As it progresses, the membrane begins to pull the macula towards itself, which causes its swelling, the formation of a hole in it and detachment. Epiretinal fibrosis can lead to the development of vitreomacular traction syndrome
Treatment of epiretinal fibrosis
Microinvasive vitrectomy.
Treatment
Treatment of the disease is carried out with the help of medications. Doctors prescribe medications that lower blood pressure (Nifedipine, Phenigidine, Dibazol - intravenously and Lasix - intramuscularly). These drugs reduce swelling. Timonol in the form of eye drops is used to lower intraocular pressure.
In order to restore normal blood flow in the affected vessel, medications from the group of fibrinolytics (Plasminogen) are used under the eye. To prevent relapses, antiplatelet agents (acetylsalicylic acid or Plavix) are prescribed. You can use Dexon under the eye to relieve inflammation.
If blood circulation in the capillaries is impaired, then Reopoliglyukin and Trental are prescribed. Doctors use Dicynon and Emoxipine. Antispasmodics such as No-Shpa or Papaverine are actively used. It is recommended to drink B vitamins and ascorbic acid to support the body's immune system.
Subsequently, depending on the severity of the disease, laser coagulation of the retina is used. This procedure involves injecting an anesthetic into the patient's eye, and before performing the operation, the doctor injects atropine to dilate the pupil. Then you need to put a lens on the sore eye to prevent its involuntary movements.
Laser coagulation of the retina
Tissue coagulation is carried out using a laser. After this, the doctor removes the lens. The postoperative period is characterized by the presence of complications:
- swelling and redness of the eye, which disappears after 14 days,
- inflammation of the conjunctiva,
- deterioration of vision during intervention in both eyes,
- dry eye syndrome, i.e. insufficient amount of tear fluid secreted.
After the operation, doctors recommend that the patient avoid physical activity and heavy lifting. You should not drink alcohol. If your vision is impaired, you should not drive a vehicle. Working at a computer is also contraindicated.
Care should be taken when treating with certain medications, because the patient may develop allergies. Before starting therapy, you need to find out whether there have been any allergic reactions to foods or medications. Treatment with folk remedies is not used because it does not bring the desired effect. To improve the quality of vision and the general condition of the body, you can eat fresh vegetables and fruits, especially carrots.
Symptoms of thrombosis
The following signs are characteristic of arterial thrombosis:
- Sharp pain that occurs in one place and spreads to adjacent areas in the form of a pulsating stream
- A feeling of numbness in the extremities depending on the location of the blood clot, causing them to lose sensation and become cold
- Shortness of breath, irregular heart rhythm, chest tightness (due to blockage of the pulmonary artery)
- Dizziness, speech disorder (due to blockage of cerebral arteries)
With venous thrombosis the following is observed:
- Increasing pain in the affected area
- Swelling and hardening of the veins at the location of the blood clot
- The skin color in this area takes on a blue tint.
- Swelling and bulging of superficial veins.
Prevention
Preventive actions:
- Using elastic bandages and compression garments
- To give up smoking
- Rational and proper nutrition
- Vitamin therapy
- Physical activity
- Timely treatment of concomitant diseases
- Monitor cholesterol and blood glucose levels
- Reducing body weight.
If symptoms of the disease appear, you can seek advice and examination in Moscow from specialists from the Central Clinical Hospital of the Russian Academy of Sciences. Registration is made by phone...
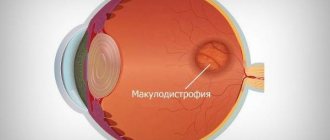
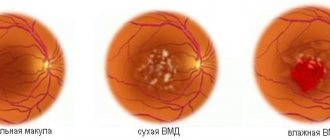
Age-related macular degeneration AMD (macular degeneration)
This is a degenerative disease of the central part of the retina - the macula, which is responsible for central, clear vision. Therefore, in AMD there is loss of central vision. In the initial stages, the disease occurs unnoticed by the patient and can only be detected during an appointment with an ophthalmologist. As AMD progresses and passes into the so-called neovascular (wet) form, the patient may notice decreased vision, a sensation of curved lines, blurred and disappearing areas.
In the wet form of AMD, due to a lack of oxygen in the retina, the growth of new defective blood vessels (neovascularization) occurs. The walls of these new vessels are much thinner than the walls of ordinary vessels, so they can rupture very easily, leading to hemorrhage and the formation of retinal edema.
Treatment of age-related macular degeneration (AMD)
Currently, the most effective treatment for AMD (wet form) is anti-VEGF therapy - this is a therapy aimed at blocking angiogenesis (the formation of new blood vessels) in the eye. It is carried out by intravitreal administration of drugs. The clinic "Eye Surgery Combs" uses
Intravitreal administration of the drug Aflibercept (Eylea).
Diagnostics
In the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic, a diagnostic complex is used to identify pathologies of the retina and fundus of the eye, including the following studies:
- optical coherence tomography (OCT);
- slit lamp examination of the anterior part of the eye;
- autorefractometry;
- visometry;
- examination of the fundus with pupil dilation;
- tonometry;
- Ultrasound (B-scan);
- fluorescein angiography of the retina;
- optical coherence tomography of the macular zone in angio mode.
The most informative research method for retinal diseases is optical coherence tomography, which allows you to obtain ultra-thin images of the layers of the retina with a resolution of 8-10 microns
The cost of a diagnostic complex for retinal diseases is 2500 rubles.
To study the vessels of the retina, optic nerve and choroid, the clinic uses one of the most effective diagnostic methods - fundus fluorescein angiography (FAG), which is carried out using the latest equipment - the FF 450 Visupac Zeiss fundus camera.
FA makes it possible to diagnose a number of diseases that are characterized by pathological changes in the blood flow of retinal vessels and which cannot be detected using traditional diagnostic methods.
Early diagnosis of a number of retinal diseases and timely treatment are the main principles that will prevent vision loss, minimize damage to the eyes and significantly increase the chance of cure, as well as avoid blindness!
Each case of the disease is individual; only a specialist can decide which method or combination of treatment methods is most preferable for each individual patient.
The specialists of the Rascheskov Eye Surgery clinic have extensive experience in managing patients with pathologies of the retina and fundus of the eye. For each patient who comes to the clinic, after a thorough diagnosis, an optimal individual treatment program is selected using all possible modern techniques to achieve maximum effect in the treatment of complex retinal diseases.