The vision of any person is formed gradually. Eyes grow just like other organs. Therefore, babies see quite poorly. Gradually their vision will improve and reach the coveted “one”, which is considered the norm. However, astigmatism most often appears in childhood. So it is important to detect this deviation as early as possible to avoid serious complications.
Share
Tweet
Share
Cool
Send
What it is?
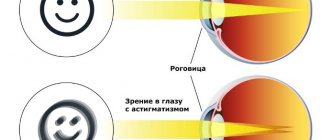
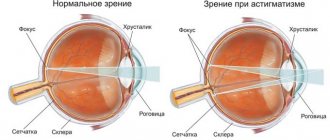
Astigmatism is a form of refractive error, the focusing of rays within the eye. With astigmatism, the lens (or cornea) has an irregular shape, which prevents the eye from forming a single point for focusing.
In most clinical cases, it is the cornea that is to blame for the appearance of astigmatism, but there are 2-3% of patients whose pathology appeared due to a change in the shape of the lens. In both cases, light rays passing through the optical surfaces of the eye are refracted in different forms, so that there can be several focal points in different zones (behind or in front of the retina). Because of this, any image “entering” the optical organ is distorted and loses sharpness.
Description of the disease
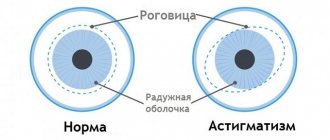
Astigmatism refers to the pathology of refraction together with farsightedness and myopia, sometimes astigmatism is combined with one of these diseases. If, with myopia, a person has difficulty seeing objects far away from him, and with farsightedness, he does not clearly visualize nearby objects, then astigmatism is characterized by a distortion of the shape of the objects themselves.
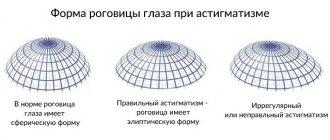
A person sees distorted objects due to the deformed shape of the lens or corneal layer. Ideally, the cornea should have a spherical shape. Thanks to the correct structure of the corneal layer, light rays are focused on the retina of the eye, and a person sees clear outlines of objects. If the cornea takes on a convex or cone-shaped shape, then the focus shifts: the person sees distorted shapes.
Note! Congenital astigmatism is characteristic of both eyes; acquired astigmatism often affects only one visual organ.
Ophthalmologists diagnose a congenital form of astigmatism with a deviation of 1 diopter in almost every person. This is not a pathology, but is an absolute norm. However, deviations of more than one diopter already indicate pathology and are subject to correction.
The congenital form of astigmatism is characteristic of every newborn baby, and by the age of three it goes away on its own. If the refractive error worsens and deviates in the pathological direction, measures must be taken. The situation is complicated by the absence of pronounced symptoms at the stage of slight refractive error; the disease becomes noticeable only at the middle stage of its development.
Causes of the disease
There may be several reasons for changes in the shape of the cornea or lens. They are usually divided into two groups depending on the etiology: congenital and acquired.
In most cases, astigmatism is congenital in children. Genetics or improper fetal development are to blame here. If one or both parents had vision problems, then the likelihood that the child will somehow develop similar problems in the future is quite high.
The risk of developing the disease also increases for the following reasons:
- maternal consumption of alcohol-containing products during pregnancy;
- congenital diseases, for example, albinism, retinitis pigmentosa, keratoconus;
- congenital deformities of the walls of the orbit or pathology of jaw development;
- In premature babies, the risk of developing astigmatism is slightly higher than in those born on time.
Acquired astigmatism can appear after injuries, surgical interventions, or severe eye infections.
In newborn children, astigmatism is normal (their vision is just developing), so the diagnosis can be made only after a year of life.
Surgical techniques
Laser correction is the most effective method, but it can only be used upon reaching adulthood, when the structures of the visual organ have already been formed. Depending on the cause of astigmatism, the cornea or lens of the eye is subject to correction.
Laser vision correction belongs to the category of surgical operations, but it is quite simple to perform, although it is performed using high-tech medical equipment. The entire procedure takes on average about 15 minutes, after which the patient is sent home.
Using a special instrument - a microkeratome - the doctor separates the upper flap of the cornea, after which the desired part of the corneal layer is evaporated with a laser. Thus, its curvature is corrected, acquiring sphericity.
The next method, astigmatomy, involves applying arcuate incisions to the peripheral zones of the cornea. It also aims to correct the shape of the cornea, although it is considered a less alternative method.
Surgery on the lens to replace it with an artificial lens. It is used for abnormalities in the structure of the lens, an excessively thin cornea with a high degree of deformation.
Treatment
The earlier the pathology is detected, the easier it is to correct. Hypermetropic astigmatism subsequently leads to advanced forms of pathology.
It is important to contact an ophthalmologist in time. The consequences can be serious:
- development of amblyopia (“lazy eye”) – the brain does not merge pictures, both eyes see differently, the “lazy eye” practically does not participate in visual processes, its function is suppressed;
- strabismus - when looking directly, deviation of one or two eyes is manifested (binocular image); danger - strabismus becomes fixed over time, and surgery is no longer possible.
Important: correction is required in early childhood (1-3 years); After 12 years, it is difficult to correct the pathology.
Optical correction
The leading way to correct a defect is correction. Correcting the optical system is first and urgent aid. Based on the diagnostic results, the doctor determines the severity of the anomaly and recommends the optimal treatment method.
Treatment of hyperopic astigmatism
The disease is corrected in two ways - with glasses or contact lenses or surgically.
Spectacle correction
This correction does not eliminate the defect itself, but forcibly changes the refraction, restoring visual acuity. Children under 3 years of age cannot wear glasses carefully. Therefore, correction is possible with specially shaped hard contact lenses. If the degree of the disease is weak, then the cornea can be given the correct shape in this way.
Children over 3 years old are prescribed glasses to prevent further development of the disease.
Surgery
Farsighted astigmatism can be completely eliminated only by surgical methods. There are different types of interventions that restore vision:
- Infrared coagulation (thermokeratocoagulation) is carried out using a heated needle. This needle is used to make pinpoint burns on the cornea. After this, coagulation (folding) of collagen occurs in the center of the cornea, due to which the central part becomes more convex, and flat on the periphery. As a result, refraction is restored throughout the entire cornea.
- Laser coagulation is the effect of a laser beam on the center of the cornea to correct its shape.
- Hypermetropic laser keratomileusis - small incisions are made on the cornea using a laser beam to gain access to the middle layers of the cornea. Corrections are made on them. This is one of the most advanced operations with good results.
The operation is recommended after 18 years of age. At an earlier age, surgical intervention is indicated only for a high degree of farsighted astigmatism.
After the operation, within a few days the child sees well and his vision is completely restored.
Types and degrees of pathology
Childhood astigmatism can be divided into several types:
- Myopic (myopic ) . This type of astigmatism is characterized by normal refraction of one main meridian and increased refraction of the other. Unlike normal myopia, there is no single point of focus in the eye.
- Farsighted (hypermetropic ). The situation is the opposite of myopic astigmatism: the refractive power of one meridian is weakened, while the second is normal.
- Mixed. Combines the properties of the first and second types of refractive error.
If astigmatism is observed in only one eye, then it is called simple, and if it is observed in both eyes, it is called complex. There are also direct, reverse and axial types of astigmatism, which depend on the main meridian.
According to severity, astigmatism is divided into:
- weak (up to 3 diopters);
- medium (from 3 to 6 diopters);
- heavy (more than 6 diopters).
Causes
The most common causes of astigmatism are heredity and intrauterine developmental anomalies. Children who have close relatives with astigmatism require especially close attention. The likelihood of inheriting the disease is quite high.
The action of negative factors during intrauterine development can also cause abnormalities in the visual system.
It is necessary to distinguish physiological astigmatism in newborns from true pathology. In the first year of life, astigmatism up to 0.5 diopters is considered normal. It manifests itself especially often in premature and low-birth-weight babies. Normally, by the age of one year, visual acuity should approach healthy levels. If the dynamics of the first months indicate a worsening of functional disorders, it should be assumed that non-physiological (pathological) astigmatism occurs.
Adviсe
Evgeny Komarovsky gave recommendations on how to properly form the baby’s vision. It is important to follow simple tips to keep everything in order.
Recommendations:
- You should not hang beautiful and richly colored toys in front of a newborn’s face. Up to 3 months he will not be able to see them, and then low-hanging objects can provoke the development of astigmatism and strabismus. Toys can be hung at a distance of at least 50 cm from the face.
- The color of things is important for the development of visual function. In the first six months after birth, it is better to purchase green and yellow toys. After this, the eyes will be able to distinguish other colors, so you can add variety.
- The light should be normal in the child's room. There is no need to dim the lighting, because this will negatively affect visual function.
Otherwise, parents can be advised to ensure that the child does not damage his vision. If any alarming signs appear, you should immediately consult a doctor. Even with head and eye injuries, as well as frequent headaches, you should see an ophthalmologist. The doctor will diagnose and, if necessary, prescribe treatment.
Prices
| Name of service (price list incomplete) | Price |
| Appointment with an ophthalmologist, therapeutic and diagnostic, primary, outpatient | 1750 rub. |
| Consultation (interpretation) with analyzes from third parties | 2250 rub. |
| Consultation with prescription of a treatment regimen (for up to 1 month) | 1800 rub. |
| Consultation with prescription of a treatment regimen (for a period of more than 1 month) | 2700 rub. |
| Consultation with a candidate of medical sciences | 2500 rub. |
| Biomicroscopy of the anterior segment of the eye | 500 rub. |
| Selection of glasses with plain lenses | 600 rub. |
| Subconjunctival injection (1 eye) | 500 rub. |
| Removal of a foreign body from the conjunctiva, from the eyelids | 800 rub. |
Diagnostics
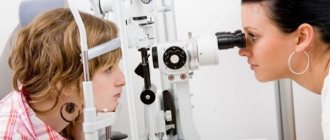
When contacting an ophthalmologist with suspected astigmatism, a detailed diagnosis will be carried out, which includes not only a conversation with the baby and parents (collection of complaints), but the use of hardware research methods.
For children one year old and younger, two diagnostic methods are used: skiascopy and ophthalmoscopy. For older children (3-4 years and older), you can use a vision test method with tables (symbols) and cylindrical lenses. Sometimes the doctor uses a slit lamp.
Diagnostic methods
After a physical examination, the pediatric ophthalmologist may order the following tests:
- Visometry – determination of visual acuity using a table.
- Ultrasound of the eyeball - contact ultrasound.
- Biomicroscopy is a visual examination of the tissues and optical media of the eye. Based on the contrast between illuminated and unlit areas. Allows you to examine in detail the iris, cornea, lens, anterior chamber of the eye, central areas of the fundus, and vitreous body.
- Skiascopy - the eye is illuminated by a beam of light that is reflected from the mirror, and the doctor observes the movement of shadows in the pupil area.
- Ophthalmoscopy – examination of the fundus of the eye.
- Computer keratotopography - prescribed in difficult cases, involves obtaining a color map of the ocular surface, a hardware-based technique, non-contact and painless.
Treatment Options
Therapy can be carried out in two ways: conservative and surgical. The operation will not be performed on a child under 18 years of age (or will be performed, but only in extreme desperate cases), since the eye continues to grow and develop. Until this age, conservative methods of treating astigmatism are used.
Optical correction
Optical correction includes two types of instruments: glasses and contact lenses. They are most often used in cases of mild to moderate forms of the disease.
Glasses
Glasses are made individually for each patient, taking into account the characteristics of his visual system. They cannot eliminate astigmatism, but they will significantly improve the quality of the picture that the child sees.
In cases of severe astigmatism, such instruments are not used, as they can cause headaches, dizziness and eye strain.
Contact lenses
To correct astigmatism, special lenses are used - spherocylindrical. But recently, the use of so-called hard night lenses, which the child puts on at night, and in the morning can walk freely without glasses, has become increasingly practiced.
Contact lenses have many advantages over glasses:
- minimal distortion of objects located to the side of the viewer;
- possibility of correction of moderate astigmatism;
- optimal conditions for seeing with both eyes at the same time;
- optical distortions are at a minimum level.
But this tool also has quite significant disadvantages:
- often children with astigmatism (even minimal) cannot get used to this type of correction and complain of headaches and eye fatigue;
- the risk of developing keratoconus increases (degenerative changes in the cornea that change its shape to a cone-shaped one and thin the tissue).
Surgical treatment of mixed astigmatism
Mixed astigmatism can only be completely cured through surgical correction. Modern ophthalmology uses the following types for this:
- Laser vision correction. The technique allows you to simulate the curvature of the cornea in the desired meridians, achieving optimal optical power in all planes.
- Astigmatic keratotomy. During the operation, micro-incisions are applied to the surface of the cornea to change the curvature and eliminate refractive errors.
Today, laser correction is the best treatment method. But this method cannot be used in all patients. Contraindications for laser correction include:
- Children under 18 years of age, surgery is performed only for individual indications.
- Inflammatory processes in the eye.
- Dystrophic changes and thinning of the cornea.
- Cataract. Glaucoma. Iridocyclitis.
- Fundus changes.
- Pregnancy.
- Diabetes.
If there are contraindications, specialists select other treatment and correction options: glasses, lenses, hardware treatment, and other surgical methods. That is, there is always a choice, the main thing is not to start the disease.
How to recognize symptoms of astigmatism in children?
In a child under three years of age, vision problems can be suspected or identified by performing a simple test. One adult takes the child in his arms and alternately closes one or the other eye. The second adult sits opposite and attracts the baby’s attention with the help of bright toys. A sharply negative reaction - crying, lifting your hand from a closed eye - may indicate that the open eye sees worse than the closed eye.
Parents can also pay attention to other symptoms of vision loss. For example, if a baby fails to pick up a toy, he misses the target with his hand - after all, one-year-old children with normal vision can complete such a task the first time.
At an older age, parents may suspect astigmatism if they notice that their son or daughter tilts his head or squints his eyes when looking at an image. Often stumbles or stumbles when walking, has difficulty focusing on printed text, and pulls the outer corner of the eye with a finger. It is worth paying attention to the child’s reluctance to look at pictures, draw, study letters, or read books, because it is difficult for him to fix his gaze on an object or text.
Children may also complain of poor vision near or far, distortion of visible objects, visual fatigue, eye fatigue and irritation, headache after visual stress, double vision.
But since babies adapt well to deteriorating vision, there may be no subjective signs of refractive error. Therefore, examinations by a pediatric ophthalmologist play an important role in identifying astigmatism.
Is it worth correcting children?
Only an ophthalmologist can correctly answer the question about the need to correct childhood astigmatism. But it is clear that timely diagnosis and correctly prescribed treatment for visual impairment reduces the risks of complications:
- amblyopia, when visual acuity decreases - it is difficult to treat;
- strabismus;
- delayed development of both visual and general.
Treatment of astigmatism in children is carried out using more conservative methods. After 18 years, provided the visual organs are formed, laser correction or surgical intervention can be used.
The simplest method for effectively correcting complex astigmatism in children is glasses with spherocylindrical lenses. At the beginning of wearing them, the patient may experience discomfort, pressure, headache, and irritation. If discomfort persists for more than a week, you should consult a doctor - perhaps the lenses were chosen incorrectly. It is also very important to choose a comfortable frame size.
Cons of glasses:
- limitation of binocular vision;
- inconvenience in adverse weather conditions;
- the child cannot engage in active sports;
- Often children refuse to wear them.
During adolescence, it is better to wear toric contact lenses. They create a natural image of objects on the retina. A child can actively engage in sports, since they are more comfortable than glasses, and due to their natural appearance, they do not negatively affect his self-esteem. Among the disadvantages of this method of correction are: the need to constantly take off for sleep and careful care. But here is the option when the lesser of “two evils” is chosen.
Eye exercises
Treatment of astigmatism in children includes the use of special eye exercises. Depending on the degree of the disorder, this can be either an independent manipulation or an addition to the main therapy. Exercises are prescribed to strengthen the eye muscles and relieve tension.
A child needs to do eye exercises:
- regularly;
- in a well-lit room;
- in the morning, when the eyes are not yet tired;
- You need to take short breaks between exercises.
Approximate set of exercises
- Look away at a distant object and hold it for 1 minute. Then focus on a close object for about a minute. It is necessary to repeat about 5-6 times for each eye.
- Close your eyes for 1-2 seconds, then open your eyes wide. Repeat for 1 minute.
- Direct your gaze to the lower right corner, then move it diagonally to the upper left. Then, on the contrary, from the lower left to the right corner. Repeat 5 times for each side.
- Frequent soft blinking.
- Rotate the eyes clockwise and counterclockwise, left to right, up and down, moving towards the bridge of the nose. Each exercise must be repeated 5 times.
- Hold your gaze upward for about 10 seconds. In this case, you need to look as high as possible. Then you need to repeat, look down, right, left.
- Stretch your hand forward, focus your gaze on the finger of this hand, gradually bring it closer, then move away.
Astigmatism in children is a serious vision problem, so parents should be attentive to their children and recognize the first signs of refractive error. With timely diagnosis and correction, treatment of astigmatism has favorable prognoses.
Possible complications
Parents should always closely monitor their child's condition. If he squints more and more often or tries to open his eyes wide, hunches over while doing homework, or tries to carefully examine what is written in a notebook or textbook, then it is quite possible that he has vision problems.
Possible complications of childhood astigmatism include:
- progressive farsightedness or nearsightedness (vision will begin to rapidly deteriorate, so there is a high probability that by adolescence the child’s vision will become very poor);
- strabismus (manifests itself when a child has poor vision in only one eye; over time, one eye will deviate towards the bridge of the nose or temple);
- amblyopia (otherwise called the exclusion of one eye from the vision process or a lazy eye, precedes strabismus, is formed when the brain is not able to put together a single picture of what it sees).
Most often, these complications appear when the main problem, astigmatism, is not eliminated. So it is better to undergo regular examinations with an ophthalmologist.
Useful video
Astigmatism: correct treatment:
Why is it dangerous?
As a result of prolonged astigmatism, lack of treatment (or incorrectly prescribed treatment), the child may experience serious complications, such as:
- Amblyopia is a persistent disorder of the visual analyzer. As a result, visual acuity decreases. This process becomes irreversible, and even after the astigmatism is cured, the child’s vision is not restored.
- Strabismus. As is known, with astigmatism, a child experiences problems with focusing vision, and in order to help himself establish a more or less clear image, he resorts to various techniques: squinting, tilting his head, stretching the corners of his eyes, changing the position of the pupils. Over time, this can lead to the development of strabismus, which does not go away even after the underlying problem is eliminated.
- Recurrence of astigmatism after surgical treatment. During surgery, special incisions are made on the cornea of the eye in order to normalize the degree of its curvature. However, body tissues, including corneal tissue, have the ability to self-regenerate, therefore, over time, there is a risk that the cornea will return to its original state.
How to prevent the development of the disease
The form of refraction is of two types: hereditary and acquired. The hereditary type cannot be prevented, but acquired astigmatism can be prevented by good eye care, which reduces the chances of pathology occurring.
Do not allow your baby to put dirty hands into his eyes or rub them too hard if his eyes itch. This way, you will prevent any damage and injury that causes the disease.
By following these tips you can avoid developing the disease in children:
- the child should eat healthy foods;
- fruits and vegetables that improve vision should be present in the daily diet;
- do not allow your child to watch TV close to him, sit at the computer for a long time, or read books;
- lighting should be good to avoid stress; too bright light is also harmful.
If you follow the advice of doctors and lead a healthy lifestyle, you can completely restore your vision. If everything is fine with your eyes, do not forget about preventive measures. If you do special five-minute exercises, your visual acuity will improve.
Prevention
Unfortunately, it is impossible to prevent the appearance of astigmatism. So most often preventive measures are aimed at inhibiting its development. As practice shows, regardless of the age of diagnosis, astigmatism will still develop further and affect vision. You can completely get rid of it only with the help of surgery, but it does not provide any guarantees confirming the restoration of vision for the rest of your life.
So, all parents and children can do is follow some recommendations that will help slow down the development of pathology:
- It is necessary to properly arrange the child’s working environment. There should be enough light, the table should be at the right height, it is advisable to choose an orthopedic chair.
- Give your eyes regular rest, especially if you work at the computer for a long time or do homework. Master the 20:20:20 rule.
- Regularly perform eye exercises prescribed by your doctor.
Astigmatism in a 1 Year Old Child What to Do Komarovsky
Every mother undergoes an annual preventive examination with her child from specialists. At an appointment with an ophthalmologist, the child may be diagnosed with astigmatism. What kind of disease is this? It causes concern for many. Should parents worry? Let's find out whether astigmatism in children can be treated or not. Dr. Komarovsky gives good information on this matter.
Kids and their problems
Source: https://imother.su/medicamenty/astigmatizm-u-rebenka-1-god-chto-delat-komarovskij.html