Childhood astigmatism
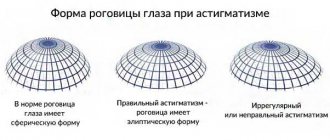
, caused by improper refraction of the cornea is called corneal, lens - lenticular. Normally, the cornea of the eye has an almost even spherical shape; with astigmatism, it becomes elongated and oblong.
The amount of astigmatism is measured in diopters. There are three degrees:
- up to 3 diopters – weak degree;
- from 3 to 6 diopters – average;
- over 6 diopters – high.
Astigmatism up to 0.5 diopters occurs in most patients, both in childhood and in adulthood, is a physiological norm and does not require any treatment.
Often astigmatism is accompanied by myopia and is called myopic, and farsightedness is called hypermetropic.
Pediatric ophthalmologists distinguish three types:
- simple astigmatism
- in one of the planes the refraction of rays is normal, and in the opposite plane there is a deviation with a myopic or hypermetropic component; - complex
– in both planes there is a disorder with a myopic or hypermetropic component; - mixed
- myopic in one plane, hypermetropic in the opposite.
It is quite difficult to recognize astigmatism on your own. It is rare for children to complain of blurred vision, especially very young ones. In this case, parents should pay attention to indirect signs: the child gets tired quickly, rubs his eyes, blinks frequently, and peers for a long time at distant objects.
Astigmatism in children is primarily a hereditary disease. Therefore, those children whose parents have a history of this pathology are at risk. If there is no identified eye pathology at birth and the parents do not have additional reasons, then the pediatric ophthalmologist should be visited for the first time at approximately 4-6 months. The sooner it is possible to detect astigmatism in a child, the easier it will be to cope with it. In addition to congenital astigmatism, children may have acquired astigmatism: due to various types of injuries, burns, eye surgeries, and peculiarities of the eye structures.
Hypermetropic astigmatism in children
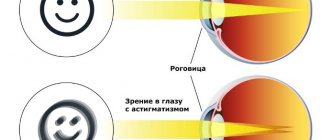
What is hypermetropic astigmatism? It is astigmatism that is combined with farsightedness. Normally, a beam of light passes through the cornea and lens and is focused on the retina at one point. Under the influence of various factors, the surface of the optical medium is distorted and the image is projected onto the retina at two points at once.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is normal in children. As the baby grows, his eyes also improve, and farsighted astigmatism disappears. But this again is the norm. Unfortunately, there are exceptions when the disorder remains with the child.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is an ophthalmological disease in which there is a violation of the shape of the lens or cornea, as a result of which refracted light is formed at two or more points behind the retina.
As for children over 10 years of age, the disease manifests itself in them in the same way as in adults, causing vision problems. At the same time, the child’s complaints may be vague: fatigue, burning eyes, pain in the frontal region, reluctance to read, draw, or write.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is sometimes called hypertrophic astigmatism, since they are the same disease. Causes visual impairment and farsightedness in the child.
Prevention
Astigmatism in children most often has a congenital form, so it is impossible to prevent it. The task of parents is to identify the deviation in time and do everything possible to ensure that the disease does not progress . Already at six months, the baby can be shown to an ophthalmologist - at this stage it is possible to diagnose strabismus and detect refractive errors.
If the disease is nevertheless diagnosed, you must strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations, do not miss scheduled visits and do not forget to change your optics.
You cannot overload the visual apparatus of a child with astigmatism and neglect the principle of alternating load and rest. Children should receive adequate nutrition, spend more time in the fresh air, do morning exercises and perform visual exercises.
Why does astigmatism occur?
There are two main causes of the disease: changes in the shape of the cornea; lens deformation.
Today it has not been reliably established why the lens and cornea change their shape. There are several assumptions on this matter: It is believed that lens deformation is a congenital developmental anomaly and rarely develops during life. Changes in the shape of the cornea can occur due to its scar changes: after surgical interventions, injuries.
In pediatric practice, mild astigmatism is most often encountered. A similar disorder is detected in approximately 50% of schoolchildren.
Kinds
Astigmatism is distinguished:
- corneal (anomaly of corneal curvature) – most common;
- lenticular (defect in the shape of the lens).
Types of anomaly:
- myopic (combination with myopia);
- hypermetropic (farsightedness).
By form:
- simple (with hypermetropia, one meridian focuses the light beam behind, and the other on the retina);
- complex (the combination of farsightedness or myopia has different severity indicators);
- mixed (rays are focused behind or in front of the retina).
By origin:
- physiological – up to 0.5 diopters, does not require correction and does not affect visual acuity;
- congenital - if indicators are above 1, treatment is required;
- acquired – cicatricial changes in the cornea due to trauma, burns, injuries, operations.
Classification according to picture perception:
- straight;
- back;
- along oblique axes.
Useful video
What is astigmatism:
Features of the development of hypermetropic astigmatism
Concomitant pathologies influence the development of the underlying disease. A characteristic feature of the course of the disease is the appearance of signs of farsightedness, which indicates that light rays are focused at several points behind the retina. This leads to the development of the hyperopic form.
The light beam is refracted in such a way that, in addition to ghosting, a blurred image also occurs. The syndrome affects the corneas of both eyes. Rarely only one eye is affected.
Due to damage to the cornea, changes in its shape, under the influence of pathology, a person begins to see poorly both at close distances and at a distance. In most cases, the disease is inherited and is rarely accompanied by pain or irritation. This is due to genetic factors.
If one parent is astigmatic or has difficulty seeing close up, the child is also at risk of developing the condition.
Causes
According to doctors, the disease has a genetic basis and can be transmitted to a child from one or both parents . Therefore, when farsighted astigmatism is detected in childhood, there is every reason to assume that the baby does not perceive visual information well from birth. And if hyperopia within 0.5 diopters can be considered a conditional norm, then violations of 1 diopter and above will signal that the disease is out of control and is capable of progressing.
In rare cases, farsighted type astigmatism is acquired . The following factors may contribute to its development :
- previous injuries to the eyeball;
- infectious and inflammatory diseases of the eye structures;
- pathologies of the dental system, deforming the walls of the orbit;
- subluxation of the lens.
Often the disease is diagnosed after undergoing ophthalmological operations. Various types of surgical interventions lead to the formation of a scar on the membranes of the eye, which negatively affects the operation of the optical system.
Pathological manifestations
External factors that can push the development of the disease are currently unknown. In most cases, it is diagnosed in childhood. The main symptoms are: farsightedness; presence of double vision of objects before the eyes; blurry image; headache.
It is easier to recognize the disease in a teenager than in children of primary school age. The baby does not yet understand that he has vision problems and does not make any complaints. In addition, not all parents can notice this disorder in a timely manner. Parents with a predisposition to astigmatism should carefully monitor their child.
Only then can they notice the following symptoms: difficulty reading; inability to examine a nearby object; lack of focus on an object; dizziness.
Due to the discomfort, the baby tilts his head slightly and squints his eye to look at the object of interest. If parents notice one of the symptoms in their child, they should immediately go to the ophthalmologist.
Poor health during the development of the disease often entails unpleasant symptoms that worsen the general condition. If you do not seek medical help in a timely manner, it can lead to rapid visual fatigue and strabismus.
Farsighted astigmatism in children under 10 years of age is considered normal. But if the child has not outgrown the pathology, treatment measures must be taken immediately.
Features of treatment
Correction is necessary if visual acuity is reduced by more than 2 diopters. According to Dr. E. O. Komarovsky, children can outgrow mild farsighted astigmatism by the age of 5-6 years. Other experts believe that the curvature of the lens does not disappear on its own.
The hypermetropic form of moderate and severe astigmatism requires mandatory correction. In children, it is carried out only using conservative methods. The operation is contraindicated before the age of 18, since the formation of the organ of vision is finally completed only by this age.
Correction with glasses or contact lenses does not correct the curvature of the lens. It is used to provide children with normal vision. Until the age of 10–12, glasses are prescribed; after this age, contact lenses can be used. To correct hypermetropic disorders, special spherocylindrical glasses are used.
Surgical intervention before the age of 18 is prescribed only for extremely severe changes in the lens. The following techniques are used:
- laser correction;
- placement of an intraocular lens (IOL).
Corneal pathology can be corrected surgically. If the disease is caused by deformation of the eyeball, surgical methods are powerless.
Additionally, visual exercises, eye massage, and vitamin supplements are prescribed.
We invite you to watch a program about methods of treating astigmatism in children:
How is the diagnosis made?
To determine the diagnosis and assess the extent of damage to the visual organs, clinical examinations of both eyes are performed. The main diagnostic methods are:
- Visometry - determination of visual acuity. During the examination, the child’s one eye is covered, and lenses of varying strengths are put on the other;
- Skiascopy;
- Biomicroscopy;
- Refractometry;
- Ophthalmoscopy;
- Ultrasound of the eyeball.
In difficult cases, computed keratotopography is prescribed.
Most often, ophthalmologists make the diagnosis of “hypermetropic astigmatism” in children in the second year of life.
The disease can be recognized at home using schematic tests. It’s easy to make a drawing for the test yourself; you can also get ready-made samples on the Internet.
The Siemens Star test allows parents to monitor their child’s visual acuity and monitor its changes. To do this, you need to turn on full lighting and close one of the baby’s eyes with your palm. Next, you need to ask the child to look at the lines and determine if they are all the same. A similar test is performed on the other eye, then the results are compared.
The “Dark Lines” test is similar in execution technique to the “Siemens Star” test. Take a white sheet of paper and draw 5-10 intersecting lines on it. The task for the child is the same: determine whether all the lines are identical.
If all the lines seem equally dark to the baby, then there are no problems with vision. But if even one line appears gray or blurry, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist for further examination.
If a disease is diagnosed - hypermetropic astigmatism, treatment and preventive measures are required. Early diagnosis of the disease in children is the key to a complete cure.
Characteristics of the disease
There are simple and complex variants of the course of the disease. Both types are characterized by the presence of corneal pathology, in which its shape changes to non-spherical. The main factors that formed the basis of the classification are meridional disturbances.
Simple hypermetropic astigmatism of both eyes is diagnosed if farsightedness is present in one of the main meridians, and emmetropia, that is, normal vision, is present in the other. In the early stages there are no signs at all; it is diagnosed during examination. The cause is injury and surgery. Almost always purchased.
Complex hyperopic astigmatism is diagnosed if farsightedness is present in both main meridians, and of different magnitudes. The focal point is located behind the retina, so a person sees a blurred image up close and at long distances.
Depending on the degree of farsightedness, visual acuity varies. If the pathology is at an early stage of development, then the image in the distance is clearer than the image near. When farsightedness progresses, the child sees equally poorly at all distances from the object.
Degree of development of pathology
In medicine, hyperopic astigmatism is divided into several degrees of severity. This indicator allows you to determine the refractive index of light rays in the main meridians of the visual apparatus. Ophthalmologists distinguish the following degrees of pathology:
- weak degree up to 3 diopters - the most common disease, responds well to treatment;
- moderate hyperopia with astigmatism up to 6 diopters is a less common disorder;
- high degree hypermetropia with astigmatism of more than 6 diopters - develops against the background of serious disorders in the cornea.
The higher the degree of the disease, the more difficult it is to treat. At the first signs, it is important to consult a doctor. The specialist will prescribe a series of examinations, make an accurate diagnosis, and select a course of treatment. The patient should fully follow all the doctor’s recommendations and then vision will be restored.
Vision correction for hypermetropic astigmatism
Mild forms of the disease do not require special correction. Usually doctors select special exercises for the eyes and register the child at the dispensary.
More pronounced forms require mandatory correction, which is achieved by wearing glasses or contact lenses. The correct selection of glasses can only be carried out by an experienced ophthalmologist. For correction, lenses with varying degrees of refraction are used, which are made individually to order.
As for contact lenses, they are best used by children starting from middle school age. This is due to the fact that it is difficult for a small child to use lenses and properly care for them.
Laser correction can be performed only after reaching 18 years of age, when the eyeball is fully formed and stops growing.
To prevent the occurrence of childhood astigmatism, it is necessary to accustom the child to a healthy lifestyle and proper distribution of eye strain from a very early age.
Symptoms
A mild form of the disease is indicated by only a slight deterioration in vision. The child may not even pay attention to it. Pathology is diagnosed only in an ophthalmology office using special instruments.
The following symptoms indicate a complex and severe form of the disease:
- Regardless of the distance, all objects are perceived by the child in a blurry form;
- their contours are distorted;
- objects split into two;
- the baby often complains of headaches and pain in the eyes;
- he gets teary every now and then.
Due to the manifestation of all the above symptoms, a fidget may become nervous, irritable, and unsure of himself. He may develop complexes about his vision. There may also be learning difficulties. With an advanced form of the disease, he may develop strabismus.
If a child constantly bumps into any objects, falls, or gets tired quickly, then this is a serious reason to visit an ophthalmologist with him.
A pain that is dangerous to endure is ocular migraine.
Significant visual impairment
The causes of eyelash loss in women are described in detail in the article.