Mezaton is a vasoconstrictor with a wide spectrum of action. The medicine in the form of drops is used to lower the pressure inside the eyeball and enlarge the pupil. Mezaton eye drops should be used only after consultation with a doctor and under his direct supervision.
Used in the form of ampoules, the drug increases heart contractions and increases blood pressure, slows down peristalsis and dilates the bronchi. Instructions for using Mezaton in ampoules suggest various ways of introducing the drug into the patient’s body.
Pharmacological authorities
Pharmacodynamics.
The drug effect has a stimulating effect on the postsynaptic α-adrenergic receptors, while the effect on the β-adrenergic receptors of the heart may not have any effect. The drug exhibits a vasoconstrictor effect similar to that of norepinephrine, but in which it has almost daily chronotropic and inotropic effects on the heart. The vasopressor effect of the drug is less pronounced than that of norepinephrine, but is significantly more trivial. When taken at primary doses, it does not exhibit a significant stimulating effect on the central nervous system. After instillation, phenylephrine acts as a dilator of the conjunctiva, thereby causing dilation and smooth swelling of the arterioles of the conjunctiva. Daily infusion on the ciliary muscle, which causes mydriasis without cycloplegia.
Pharmacokinetics.
Phenylephrine easily penetrates the eye tissue, dilatation occurs over a period of 10–60 weeks after a single instillation. Mydriasis persists for 4–6 years. Inheritance of a significant shortening of the dilator of the ovary, after 30–45 weeks after instilation, particles of pigment from the pigment layer of the iris may appear in the hair of the anterior chamber of the eye. This phenomenon must be differentiated from the manifestations of anterior uveitis or from the presence of blood cells in the anterior chamber.
Showing
- Iridocyclitis, anterior uveitis (through treatment and prevention of posterior synechiae and changes in exudation from the iris of the eye).
- Diagnostic extension of the area under the hour of ophthalmoscopy and other diagnostic procedures necessary for determining the status of the posterior eye).
- Conducting a provocative test in patients with a narrow profile of the anterior chamber and suspected of closed-cuta glaucoma.
- Differential diagnosis of the type of eyeball injection.
- Expanded range when performing laser treatments on an on-site basis and in vitreoretinal surgery.
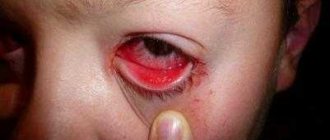
- “Red eye” syndrome (changes in hyperemia and changes in the membranes of the eye).
- Complex therapy for accommodative spasm in school-age children.
- Treatment and prevention of asthenopia.
Contraindicated
- Sensitivity has been extended to any component of the medical specialty.
- Vuzkokutova or zakritokutova glaucoma.
- Significant damage to the side of the cardiovascular system (heart disease, arterial hypertension, aneurysm, tachycardia), especially in patients of late age.
- Insulin-dependent cerebrovascular diabetes.
- Thyrotoxicosis.
- Hyperthyroidism.
- Immediate treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAO) and for 2 days after treatment with MAO inhibitors.
- Additional expansion of the area during surgical intervention in patients with impaired integrity of the eyeball or impaired function of the tear duct.
- Immediate treatment with tricyclic antidepressants, antihypertensive drugs (including beta-blockers).
- Congenital deficiency of glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.
- Pechinkova porphyria.
It is contraindicated for zastosovuvati:
- newborns with low body weight;
- newborns and babies with cardio- or cerebrovascular disorders;
- summer age patients with important arteriosclerotic, cardiovascular or cerebrovascular diseases.
Contraindications and side effects
Patients are not allowed to use the product:
- with pheochromocytoma;
- with ventricular fibrillation;
- in case of hypersensitivity to the components;
- with glaucoma in closed-angle or narrow-angle form;
- with disturbances in the functioning of the cardiovascular system;
- with diabetes mellitus in an insulin-dependent form;
- with hyperthyroidism, thyrotoxicosis;
- with fundus disorders;
- with impaired lacrimal function.
Interactions with other medicinal drugs and other types of interactions
The mydriatic effect of phenylephrine is enhanced by local administration of atropine, and weakened by local administration of other ophthalmic drugs that counteract miotic effects. The drug may suppress the production of mitotic functions and change the internal pressure.
The mydriatic effect of phenylephrine is enhanced by locally administered atropine.
Antihypertensive drugs
(including β-blockers) it is contraindicated to take one hour with phenylephrine for mucosal congestion, as there may be a reversal of many antihypertensive drugs, which may have lethal effects, possibly arterial Hypertension.
MAO inhibitors.
Phenylephrine administration is contraindicated before administration of MAO inhibitors and for 2 days after administration of MAO inhibitors. Acute treatment with MAO inhibitors for 21 days after completion of treatment should be used with caution, as systemic adrenergic effects may develop.
Tricyclic antidepressants
It is contraindicated to take one hour with phenylephrine. The vasopressor effect of adrenergic agents can be potentiated by tricyclic antidepressants (an important risk of causing cardiac arrhythmias, including for several days after taking them), propranolol, reserpine, guanethidine, methyldopa and m-cholinergic blockers.
Inhalation anesthesia
. The drug may potentiate the suppression of cardiovascular activity during inhalation anesthesia. Due to the increased risk of fibrillation of the sac, the drug, with care for the traces, should be combined for an hour of general anesthesia with anesthetics such as halothane (fluorothane), which causes an increase in the sensitivity of the myocardium to sympathomimetics .
Cardiac glycosides and quinidine
. Movement risk and arrhythmia.
Other forms of release of Mezaton
In addition to ophthalmology, the drug is used to treat disorders associated with the circulatory system. For this purpose, a high concentration of phenylephrine is used. The product is available in injection ampoules, tablets and powder for preparing a solution. Mezaton in solution format is used to treat:
- arterial hypotension;
- vascular insufficiency;
- rhinitis of allergic and vasomotor origin;
- toxic or traumatic shock.
In addition, the medicine is used as an auxiliary drug when administering local anesthesia. It helps to narrow the blood vessels and reduce blood flow in them, and this allows for more effective pain relief for the patient. Thus, phenylephrine has a wide range of uses in various fields of medicine.
Features of good stagnation
Phenylephrine hydrochloride is a medicinal drug that produces an adrenergic effect and is used in ophthalmology as a mainstay to achieve a mydriatic effect. The drug has a minor effect on the ciliary muscle of the eye, so there is no significant effect on accommodation, although the expanded zone can change the depth of sharpness and cause a decrease in the volume.
Systemic infusion can be minimized by pressing the inner cut of the eye with a finger for 1 length after instillation of droplets (this blocks the passage of droplets through the nasolacrimal duct to the mucous membrane of the nose and pharynx, especially recommended for children and children who are unable to speak This century).
The effect of dilated vision may last for 1–3 years, patients may develop photophobia, so until the vision is restored, it is necessary to protect the eye(s) from the bright sleepy light la, including vikoristannya suntsezakhisnyh eyepieces. It is necessary to turn off stress (reading, watching TV shows) until excessive manifestations of mydriasis subside.
With conjunctival hyperemia and damage to the corneal epithelium, it is possible to promote swelling and enhance unimportant systemic effects.
For the treatment of acute glaucoma, it is necessary to evaluate the cut of the anterior chamber before treatment is prescribed. To prevent unpleasant reactions from infused phenylephrine, you can infuse the drops with the anesthetic a few minutes before instilation.
Summer age patients.
Pozhlive viniknennya reactive myosis. Reactive miosis was observed in patients of the summer age a day after stagnation of phenylephrine, and repeated application led to a decrease in the dilatation of the region. Use caution in patients with cerebral atherosclerosis, diseases of the cardiovascular system, chronic bronchial asthma, arterial hypertension or insulin-controlled diabetes.
In connection with the infusion of the drug into the dilated zones, there may be a temporary appearance of floating pigmented spots in the internal eye area in patients with summer age for a period of 30–45 weeks after instilation stabbing phenylephrine in the eye.
Children's age.
Next, take the lowest dose necessary to stop the effect. Fathers should be aware of the need to avoid applying the drug to the child’s mouth and cheeks, as well as the need to wash their hands and the child’s cheeks after administration. Fawning children, and especially unborn babies, who have low vagus during pregnancy and premature newborns may be at risk for the development of systemic adverse reactions, including temporary shifting of the arterial pressure, which precipitates the risk of intraventricular bloody. It is necessary to watch out for inconveniences after instilation and ensure, if necessary, that adequate ritual actions are carried out.
Suspension during pregnancy or breastfeeding.
It didn’t work out. Stagnation is possible, if measles is predicted for the mother and there is a risk for the fetus or child. At the hour of treatment with the preparation, apply the chest to the chest.
This is due to the fluidity of the reaction during treatment with vehicles or other mechanisms.
Before using a car or robots with mechanisms, it is necessary to check until the sharpness of the vision returns.
Mode of application
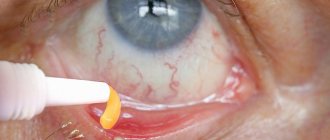
The method of use and dosage depend on the task at hand. If eye drops are used for diagnostic purposes to dilate the pupil, then it is enough to administer one drop of the drug into each eye. During a long-term examination, the instillation is repeated after an hour.
For ease of use, the drug is available in small dropper bottles of 5 ml each.
For therapeutic purposes, the drug should be dripped according to the following scheme:
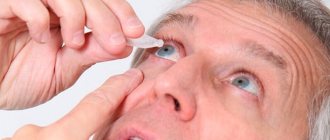
- Wash your hands with soap and wipe dry.
- Prepare eye drops, clean warm water, cotton swabs or cotton swabs, and napkins.
- Take a sitting position with your head thrown back or lying down.
- Remove decorative cosmetics from eyelids and eyelashes, remove contact lenses if the patient uses them. It is allowed to put on contact lenses again a quarter of an hour after the administration of the drug.
- If necessary, clean the eye from discharge, and the eyelids from dried crusts.
- Open the ampoule bottle, gently pull down the lower eyelid and inject one drop into each affected eye.
- Lower your eyelids for a few seconds and press the corners of your eyes with your fingertips so that the drug penetrates where it should and does not leak out.
Repeat the procedure three times a day until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear and recover. The course of treatment can only be stopped or extended by the attending physician. It is not recommended to change the dosage, frequency of administration of eye drops and duration of treatment on your own.
Important: Mezaton eye drops are intended for topical use only; apply them only to the conjunctival sac of the affected eye or eyes according to the instructions or recommendation of the attending ophthalmologist.
Method of congestion and dosage
During ophthalmoscopy
Use a one-time instillation of 2.5% dose. As a rule, to achieve mydriasis, add 1 drop of 2.5% dose of the drug to the conjunctival sac. Maximum midriasis is achieved after 15–30 weeks and is maintained at a sufficient level for 1–3 years. If there is a need to maintain mydriasis for at least three hours, re-instillation is possible after 1 year.
To carry out diagnostic procedures, a one-time instillation of 2.5% is used:
- as a provocative test in patients with a narrow profile of the anterior chamber and suspected of closed-cuta glaucoma
. If the difference between the values of the internal clamp before instillation and after expansion of the zone becomes 3 to 5 mm Hg. Art., a provocative test is considered positive; - for differential diagnosis of the type of injection of the eyeball:
if after 5 weeks after instilation, sounding of the veins of the eyeball is detected, the injection is classified as superficial; when saving the red eye, it is necessary to carefully monitor the patient for the presence of iridocyclitis or scleritis, in order to be aware of the dilation of the blood vessels in the deeper tissues of the eye; - in case of iridocyclitis, the anterior uvea is treated with vicorista to treat and prevent the development of posterior synechiae;
to reduce exudation in the anterior chamber of the eye . This method involves instilling 1 drop of the drug into the conjunctival sac of the diseased eye(s) 2-3 times per dose.
Complex therapy for accommodative spasm and asthenopia in school-age children.
For mild cases of short-sightedness, take 1 drop of 2.5% dose of the drug before going to bed on the day of high health; in the middle stage of short-sightedness - 1 drop of 2.5% dose 3 times a day before bedtime, and in cases of emetropia (myopia present) - every day, regardless of vision.
For patients with farsightedness, who have a tendency to develop a spasm, take 2.5% doses of the drug in a combination with 1 drop of 1% cyclopentolate before bedtime during important health care periods, and at extreme times, stop 3 times per week.
Treatment for patients of the summer age.
There is no need to adjust the dose for summer age patients. Repeated instillations may produce less mydriasis.
When performing instillation, it is necessary to adhere to the sanitary and hygienic rules, shake your hands gently, and do not touch the nozzle with your fingers.
Children.
In pediatric practice, for carrying out diagnostic procedures (ophthalmoscopy, retinography), it is possible to provide medical treatment to children from the first days of life. Premature babies can be treated with caution after the doctor has assessed the relationship between risk and measles: no more than 1 drop in the skin.
Special instructions for use and interactions with other drugs
Mezaton drops have a dilating effect on the pupils. In this regard, you should avoid activities that require high speed or are associated with increased load on the visual organs. For example, you should stop driving a car, working at a computer, using complex equipment, etc.
Schoolchildren and students should not read or write much, only listen to the teacher in class. In summer and winter, when the sun is bright, you should take care of sunglasses. Sunlight with dilated pupils can cause retinal burns.
Enlarged pupils lead to changes in blood pressure. When using drops, you need to remember its effect not only on intraocular pressure, but also on blood pressure. If there is a surge in blood pressure or cardiac dysfunction, you should immediately stop instilling Mezaton.
If you use Atropine and Mezaton at the same time, the effect will be much stronger. Therefore, combining medications is highly undesirable.
If you are taking medications for high blood pressure, be careful, because mezaton weakens their effect as it increases blood pressure. The effect of mecamylamine, guanadrel, methyldopa, guanethidine may disappear.
It is recommended to remove contact lenses before instillation. You can put them on 20 minutes after the procedure.
With repeated use of the drops, the effect of pupil dilation will be less pronounced. If the medicine enters the bloodstream, weakness in the body may occur. To prevent the drug from spoiling, it should be stored in the refrigerator for no more than 2 weeks.
Side effects
On the side of the immune system: hypersensitivity, allergic conjunctivitis.
From the side of the organs
: pain in the eyes, in some cases there is a liver problem (congestion), reactive hyperemia, blurred vision, teasing, allergic reactions due to discomfort, lacrimation, increased internal pressure in patients with narrow-cuta or closed-cuta glaucoma, reactive miosis (the day after stagnation ; with which repeated instilation may produce fewer expressions of mydriasis, lower than anterior; the effect is more often manifested in patients with summer age). Premature newborns may experience periorbital pallor.
On the side of the cardiovascular system:
tachycardia, cardiac arrhythmias, including cardiac arrhythmias, arterial hypertension, reflex bradycardia, coronary artery occlusion, pulmonary artery embolism, myocardial infarction.
On the side of the central nervous system:
headache, restlessness, confusion, tremor, paresthesia, insomnia.
Inshi:
pale skin, weakness, buttocks, dyspeptic symptoms.
Information about suspected adverse reactions.
Following drug registration, reporting suspected adverse reactions is an important procedure. This makes it possible to monitor the “measles/risk” relationship when the drug is frozen. Healthcare professionals can report any suspected adverse reactions through the national pharmacovigilance system.