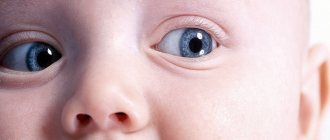
Conjunctivitis is one of the most common diseases in preschool age. Often bacterial and viral forms of conjunctivitis take an epidemic course. Parents should be attentive and take their child to the doctor in time so that he can prescribe effective treatment. By what signs can you identify conjunctivitis in a child?
Conjunctivitis is an ophthalmological disease characterized by inflammation of the outer layer of the eye.
In this article
- Allergic conjunctivitis
- Bacterial conjunctivitis
- Viral conjunctivitis
- Herpetic conjunctivitis
- Prevention of conjunctivitis
This can happen for several reasons: due to allergies, bacterial or viral infection. Each type has its own characteristics, in addition to the general symptoms. Using them, you can determine what type of conjunctivitis began in the child. However, it is unacceptable to prescribe treatment on your own - you must take the baby to a specialist who will make an accurate diagnosis and write a prescription for medications. To understand how conjunctivitis begins in children, you need to know the main signs characteristic of different types.
Viral conjunctivitis
This type of disease develops when various viruses enter the child’s body. The most common of them are adenoviruses, which are the causative agents of many ailments: influenza, ARVI, acute respiratory infections and others. When infected with adenoviruses 3, 4 and 7 serotypes, acute pharyngoconjunctivitis develops. Viruses 8 and 10 serotypes cause epidemic keratoconjunctivitis. Many adenoviruses cause the development of upper respiratory tract infections: tonsillitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis and other diseases. Adenoviruses are very tenacious. They can remain active on various surfaces for up to 7-10 days. As soon as a child picks up a dusty or dirty object and then touches the mucous membrane, the virus enters the body, provoking the development of the disease. Children under 6-7 years of age are especially susceptible to the effects of adenoviruses. Their immune system is still very weak and cannot resist infections to the same extent as an adult body. According to statistics, adenovirus infection in children under six years of age accounts for up to 30% of cases of all viral illnesses.
Viral conjunctivitis in a child can occur as an independent pathology or develop against the background of illnesses caused by viruses: influenza, acute respiratory viral infections, acute respiratory infections, nasopharyngitis and other diseases of the upper respiratory tract. In such cases, complex treatment is prescribed.
Complications of non-purulent conjunctivitis
If non-purulent conjunctivitis is not treated, complications may occur. Inflammation can become bacterial. In this case, purulent discharge will be added to all other signs. The occurrence of conjunctivitis without treatment will contribute to the penetration of infection into healthy tissues and deep layers of the organs of vision.
Treatment should be continued for several more days after the signs of the disease disappear. Otherwise, the disease may subside only for a while and after some period become chronic.
Sometimes non-purulent conjunctivitis provokes dry eye syndrome. Keratitis (damage to the cornea of the eye) and blepharitis (chronic inflammation of the eyelids) may also develop. However, complications can really be avoided if, if symptoms of conjunctivitis arise, you immediately consult a specialist.
Herpetic conjunctivitis
The herpes simplex virus is also a common cause of inflammation of the conjunctiva. It can provoke various types of herpetic conjunctivitis:
- catarrhal, which is characterized by mucous or purulent discharge from the eyes;
- follicular, in which vesicles with liquid content appear on the conjunctiva and eyelids - follicles;
- The vesicular-ulcerative type of the disease occurs with the formation of erosions or ulcers covered with films, often accompanied by the formation of dense nodules.
The herpes virus, once entering the body, is integrated into the DNA of the trigeminal ganglion, and a person lives with it all his life. From 60 to 90% of all people are carriers of the herpes simplex virus. However, in the normal state of the body, it does not bother the owner. But in certain situations, for example, a weakened immune system, hypothermia, vitamin deficiency, or after previous infections, the herpes virus is activated, provoking the development of inflammatory diseases: the well-known “cold” on the lips or conjunctivitis.
Causes
If the eye shell ceases to cope with its protective functions, a disease occurs.
Main reasons:
- infections (bacterial, viral, fungal);
- allergic;
- endogenous.
The immune system of newborn children is still immature. The conjunctiva cannot protect the eye from external irritants, as a result of which in a young child the disease is almost always of infectious origin.
The main causes of illness in newborns are maternal genital infections. Infection of newborns occurs during childbirth. The incubation period lasts from 2 to 15 days.
The infectious agent of infection of newborns can be chlamydial infection, gonococci, staphylococci, streptococci, fungal flora. Conjunctivitis is dangerous for newborn children, so they are hospitalized at the first signs of the disease. Conjunctivitis in a one-month-old (infant) baby occurs due to poor hygiene.
If a child has a respiratory disease, an infection from the nasopharynx can enter the eyes and cause conjunctivitis. Conjunctivitis along with a cold usually occurs in a one-year-old child and older (children under one year of age are less likely to suffer from acute respiratory infections and acute respiratory viral infections).
Infectious conjunctivitis is contagious, so children after one year can become infected from each other.
Allergic conjunctivitis in newborns and children under one year of age is rare. But it happens often in older children. This form is usually caused by drugs, plant pollen, and other agents.
Viral conjunctivitis in a child: symptoms
After the virus begins to act, the sick child shows signs of illness:
- lacrimation, swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids;
- feeling of “sand” in the eyes, pain, dryness, rejection of bright light;
- mucous discharge;
- weakness and lethargy in the muscles;
- deterioration of sleep and appetite.
If such symptoms appear, parents should call a doctor at home to examine the child. The sooner treatment begins, the faster the body will cope with the disease. In addition, sometimes bacterial conjunctivitis can be accompanied by viral conjunctivitis, accompanied by purulent discharge from the eyes, swollen lymph nodes and other unpleasant manifestations. It will be more difficult to cure the disease in this situation.
Diagnosis of the disease
To establish a diagnosis, a specialist conducts a visual examination and interviews parents regarding the appearance of the first signs of pathology, the nature of the discharge, changes in the area of redness and general condition.
In addition, the secreted fluid is collected for analysis. All these procedures will help determine the type of pathology.
Sometimes an ophthalmologist may prescribe additional examination by other specialists:
- allergist;
- dermatologist;
- virologist.
Based on the results of all examinations and tests, the doctor makes a diagnosis and prescribes appropriate treatment.
Treatment of viral conjunctivitis in children
To eliminate the symptoms of viral pathologies, drugs with interferon are used. They fight viruses, alleviate the symptoms of the disease and improve their general condition. Antiviral ointments complement the main course of therapy well. It is important that the prescribed drug affects exactly the pathogen that provoked the disease. In this case, the choice of medications depends on the age of the child. The standard method of treating conjunctivitis of viral etiology is drops and ointments. To eliminate symptoms, the drugs “Actipol”, “Oftan Idu”, “Oftalmoferon”, “Oftan”, “Sodium Sulfacyl”, “Vitabakt”, “Levomycetin”, “Tobrex”, “Floxal” and others can be prescribed. For the herpetic form of the disease, Florenal, Zovirax, Virolex and others drops are used.
If the virus has also affected the skin around the eyes, then Acyclovir and Valtrex ointments may be additionally prescribed. To avoid the addition of a bacterial infection, tetracycline or erythromycin ointments and antibiotic eye drops are additionally used.
What is
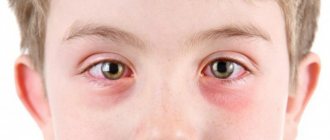
Often, mothers of children have to deal with the fact that in the morning the child’s eyes are swollen, the eyelids stick together and there is redness of the mucous membrane, and the baby becomes capricious and whiny for no apparent reason. In most cases, these signs indicate the presence of a disease.
The occurrence and further development of conjunctivitis does not depend on the age of the children; the disease can equally manifest itself in both infants and older children. The danger of the disease is that it has the ability to spread quickly. If at least one child in a class or kindergarten group gets sick, then conjunctivitis will soon spread to other children.
With proper treatment, already on the second day, further development of conjunctivitis is reduced, improvement is observed, and in the presence of good immunity, the inflammation goes away without a trace after just a few days. In very rare cases, the disease can acquire a chronic form, which is expressed as a sluggish process of development, but with the right course of treatment it does not reach this point. The emergence of a chronic variety occurs against the background of the presence of concomitant diseases of the ENT organs.
Conjunctivitis itself does not have any serious consequences for the body, but can significantly reduce the quality of life throughout the entire period of development.
When the diagnosis is made at the initial stage of inflammation, with effective therapy, most of the unpleasant symptoms of the disease can be relieved during the first day.
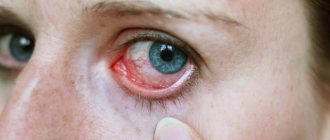
Bacterial conjunctivitis in a child
This form of the disease is caused by various pathogenic microorganisms: staphylococci, streptococci, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, etc. Young children have poor personal hygiene: they rub their eyes with dirty hands, eat unwashed fruits or vegetables that may have germs on them. Infection often occurs when swimming in ponds or pools, or using shared towels or bed linen. Conjunctivitis can develop with diseases of the nasopharynx (sinusitis, rhinitis, tonsillitis). When you sneeze, bacteria from your nose and throat enter your eyes, causing inflammation. It is not for nothing that it is recommended to wear protective masks for diseases of the upper respiratory tract. Even a newborn baby can suffer from bacterial conjunctivitis if it becomes infected through a woman’s birth canal. A particularly severe course of the disease in an infant is caused by gonococci and chlamydia.
Where does conjunctivitis occur in childhood?
The disease can occur on its own or against the background of a concomitant disease due to decreased immunity. Most often, the cause of the inflammatory process is harmful viruses, infections and fungi. They can get into your eyes when you rub your hands, or when you sneeze when you have a cold or flu.
The incubation period of conjunctivitis is about 5-10 days, so inflammation cannot be detected immediately. The disease can also be allergic in nature. In this case, it occurs as a result of the child’s body’s reaction to an external stimulus (pollen, food). In this case, there is no incubation period and symptoms appear immediately. In addition, chlamydial conjunctivitis may occur in children. This is a special form of bacterial conjunctivitis, which is accompanied by increased photosensitivity. As a rule, the disease manifests itself within 2-3 days after parasites enter the eyelids. They swell noticeably and purulent discharge appears. Parents often wonder where conjunctivitis comes from in their babies. At 8-10 days after birth, some children may experience such a characteristic form of the disease as dacryocystitis. This is a pathology that occurs as a result of stagnation of tears due to clogging of the lacrimal canal with elements of embryonic tissue during the birth process.
Conjunctivitis appears in children due to:
- exposure to viruses, infections, fungi or bacteria (including chlamydia);
- the occurrence of an allergic reaction;
- due to obstruction of the tear ducts (dacryocystitis).
Symptoms of bacterial conjunctivitis
A characteristic sign of this pathology, in addition to swelling and hyperemia of the eyelids, is profuse purulent discharge from the eyes, which sticks the child’s eyelashes together after sleep. Corneal ulceration, increased body temperature, and deterioration in vision clarity may also occur. Before administering drops or ointments when treating bacterial conjunctivitis, it is necessary to pre-wash the child's eyes. To do this, you can use a weak solution of boric acid, furatsilin tablets dissolved in clean water, or a special preparation “Blefarolion” from the Russian one.
Before starting the procedures, you need to wash your hands well so as not to get dirt into your eyes. It is advisable to rinse several times a day to eliminate traces of purulent discharge. To treat bacterial conjunctivitis, medications with antibiotics are prescribed, which are not absorbed into the blood, but act only on the eye structures, and therefore are safe for children. This therapy helps to quickly eliminate the symptoms of the disease. In this situation, the following drugs can be used: Sulfacyl sodium, Vitabact, Levomycetin, Tobrex, Floxal and others. If after 2-3 days there is no improvement, then you need to contact an ophthalmologist - he will prescribe another medicine.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed by a doctor after identifying the type and form of the disease. It usually involves the use of medications, eye treatments and herbal lotions.
Drug therapy
Treatment is carried out using topical medications - ointments and eye drops.
If the disease is caused by a bacterial infection, antibacterial drugs are prescribed and used to treat the child's eyes. When a viral form is detected, the use of ointments and drops with an antiviral effect is indicated.
Treatment of the affected organ
Along with drops and ointments, it is recommended to treat the eyes several times a day with disinfectants: furatsilin or boric acid solutions. It is necessary to wash the baby's eyes at least 4-8 times a day using sterile cotton swabs. During the procedure, eye cleansing is performed in the direction from the outer corner to the inner one. Levomycetin is perfect for a child.
Folk remedies
Chamomile is the best herbal remedy for rinsing the eyes for conjunctivitis. You can even put a weak decoction of chamomile in your eyes. In addition to chamomile, you can use bay leaf. 3-4 crushed leaves are poured into 200 ml. boiling water, infuse, then filter. The resulting infusion is used to wipe the baby's eyes 5-6 times a day.
Also, for conjunctivitis, traditional medicine recommends using cornflower flowers. 1 tbsp. pour 200 ml of boiling water over a spoonful of crushed flowers, leave for 30 minutes, and filter. Wash the child's eyes with the resulting infusion 5-6 times a day.
Usually the disease is treated at home, but for proper diagnosis and treatment, you should consult a specialist (ophthalmologist). The doctor will examine the patient, collect anamnesis and be sure to take a smear of discharge from the eye to determine the causative agent of the infection.
Based on the results of bacteriological culture, the sensitivity of microorganisms to certain drugs can be accurately determined. Symptoms of uncomplicated conjunctivitis disappear within 7 days.
Treatment includes the following steps:
- washing the eyes with a medicinal solution or herbal decoction;
- instilling drops or placing ointment behind the eyelid;
- strict adherence to hygiene - you should thoroughly wash your hands before and after medical procedures.
Prepared solution of furatsilin
Before using medications and folk remedies for any form of the disease, you must rinse your eyes with any of the following solutions:
- furatsilin solution (dissolve 1 tablet in a glass of boiled water, strain through cheesecloth);
- 0.9% sodium chloride solution;
- chamomile decoction (pour 1 glass of boiling water over 1 filter bag, leave for 40 minutes);
- strong brewed black tea.
You need to moisten a sterile gauze pad with the solution and wipe the eye from the outer edge to the inner. A separate wipe should be used for each eye. After this procedure, it is necessary to instill the medicine or place the ointment behind the eyelid.
Pharmacy drugs
Medicines are prescribed depending on the clinical picture and the causes of the disease. Treatment of bacterial and purulent forms of the disease is based on the use of antibiotics, viral - antiviral drugs, if the pathology is caused by an allergic reaction - antihistamines are prescribed.
Antibacterial drops and ointments:
- sodium sulfacyl 20% (Albucid) – instill 1 drop into each eye 4-6 times a day (can Albucid be dripped into the eyes of children?);
- chloramphenicol solution 0.25% - 1 drop 4 times a day;
- Floxal (Ofloxacin) - the drug is available in the form of ointment and drops, use 1 drop 3-4 times a day or place a small amount of ointment behind the eyelid;
- tetracycline eye ointment 1% - put behind the eyelid twice a day.
Antiviral agents:
- Oftalmoferon – 1 drop up to 6-8 times a day;
- Poludan - effective for herpetic and adenoviral conjunctivitis, the drug must be diluted with distilled water according to the instructions and used 1 drop 6-8 times a day;
- Zovirax - place a small amount of ointment behind the eyelid up to 5 times a day (the interval between applications should be at least 4 hours).
Antihistamine drops:
- Opatanol 0.1% - 1 drop 4 times a day;
- Azelastine – 1 drop three times a day.
Conjunctivitis can be cured using folk remedies - medicinal plants and certain foods. This will help relieve discomfort, reduce inflammation and swelling of the eyes.
If you regularly wash your eyes with chamomile decoction, the initial stage of the disease can be cured without pharmaceutical drugs
Homemade folk remedies that can be used to treat this disease in children can be found in any kitchen.
Treatment is carried out with medication, and the approach to it is chosen depending on what form of the disease the baby has.
The dangers of viral and bacterial conjunctivitis
These types of eye pathologies pose the greatest danger to the child’s health. They tend to take an epidemic course, quickly spreading in children's groups through the air and household contacts: shared toys, hygiene items, dishes, etc. In the event of an epidemic of conjunctivitis, quarantine is declared for a period of 10-14 days. At the same time, if possible, it is better to limit visits to kindergarten so as not to expose the child to infection. Inside the premises of the child care facility, a complete sanitary and hygienic treatment is carried out to ensure that all surfaces are as safe as possible. Some types of viruses can survive on them for up to 7-10 days.
How many days does conjunctivitis last in adults?
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory process of the eye mucosa, which is bacterial, viral, allergic and autoimmune in nature.
The disease can be very contagious, especially if it is caused by viruses.
When the first signs of inflammation appear, many patients are interested in how long conjunctivitis is treated and how long it lasts, and how long they will have to be careful not to infect loved ones.
The duration of the disease depends on many factors: the presence or absence of an infectious pathogen, concomitant disorders, the effectiveness and timeliness of treatment. Only viral and bacterial conjunctivitis are contagious. The disease lasts on average 5-7 days, but the patient needs to be treated longer - 10-14 days (to prevent acute purulent process and the development of complications).
Types of conjunctivitis with a description of symptoms and duration of treatment
Common types of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial;
- viral;
- allergic and autoimmune;
- fungal;
- traumatic.
The first manifestations of the disease do not appear immediately - after the end of the incubation period, which lasts 3-5 days. The state of health usually remains normal. An increase in body temperature is possible only with purulent complications or if the child develops the disease.
Conjunctivitis is most severe in children. The child complains of feeling unwell and constantly rubs his eyes with his hands, which automatically increases the risk of a secondary infection.
In children, viral eye inflammation almost always becomes bacterial. Therefore, at the initial stage, doctors prescribe antimicrobial agents in the form of drops and ointments.
A pediatric ophthalmologist should treat a child’s disease.
Parents often try to overcome the inflammatory process using home methods in the first days, and this only worsens the child’s well-being.
Herbal decoctions and infusions will not destroy infectious pathogens and viruses better than modern medications.
It is important to prevent the inflammatory process from becoming chronic, which can lead to keratitis and loss of vision in the future.
How long does it take to treat the viral form?
Viral conjunctivitis usually begins against the background of respiratory viral diseases or adenovirus infection. The risk of getting sick is higher in people with weakened immune systems, poor eye care and non-compliance with infection safety rules.
The pathology is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- moderate lacrimation and redness of the eyes;
- photophobia;
- mucous discharge from the eyes;
- swelling of the eyelids.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis is the most difficult to treat and develop. The disease can last more than 14 days and cause complications. Throughout the entire period while the viral process lasts, there are signs of intoxication: muscle and headaches, weakness, enlarged regional lymph nodes.
It is quite difficult to say exactly how many days viral conjunctivitis lasts in adults or children. The general state of the immune system plays a huge role in the duration of the disease. In weakened people, the inflammatory process can last for several months, subside, and then worsen again.
Duration of bacterial conjunctivitis
The main symptom of bacterial eye inflammation is a viscous mucopurulent discharge. In this case, the conjunctiva turns red and swells, patients complain of dryness and moderate photophobia.
If the bacterial nature of the inflammation is detected, drops and eye ointments with erythromycin and gentamicin sulfate are prescribed. The infection process is stopped by antibiotics.
They must be prescribed a course of 5-7 days. Bacterial conjunctivitis takes longer to cure than viral conjunctivitis.
It is important to establish the cause of the disease—the specific type of pathogen—in order to prescribe the most effective antimicrobial drugs.
The disease lasts differently for everyone: bacterial inflammation of the conjunctiva does not subside within 7-10 days. It is important to prescribe antimicrobial agents in a timely manner to prevent the acute process from becoming chronic.
Treating bacterial conjunctivitis at home. It is difficult to say how many days after the signs of acute inflammation go away, but antibiotics in drops and ointments are prescribed for at least 5-7 days. And the treatment period cannot be shortened.
Otherwise, antibiotics will only dull the symptoms of the disease.
Traumatic conjunctivitis
In the traumatic form of the disease, the mucous membrane turns red immediately after injury. The patient feels a burning sensation, pain, and cannot open his eyes freely. It is important to contact an ophthalmologist as soon as possible to remove the foreign body and begin antibacterial therapy.
Antimicrobial drugs should be used to prevent secondary infection. It is recommended to apply tetracycline ointment to the eyes at night. During the day, use Albucid or other anti-inflammatory drops.
For prophylactic purposes, pimafucin can be prescribed for damage to the eye mucosa and the development of traumatic conjunctivitis.
The duration of the disease depends on the degree of injury and can be completely different, depending on the specific case.
How long does it take to treat allergic conjunctivitis?
Allergic inflammation of the conjunctiva is accompanied by redness of the mucous membrane, the appearance of moderate itching and severe swelling of the eyelids. Additionally, patients complain of itching of the eyes, mucous discharge from the conjunctiva and nasal cavity.
If the exact allergen is identified, it is necessary to stop any contact with it as soon as possible. Additionally, it is recommended to do allergy tests.
This will identify possible triggering allergens and reduce the likelihood of relapse of the disease in the future.
How long does it take to treat conjunctivitis caused by an exacerbation of allergies? If antihistamines are prescribed on the first day of acute symptoms, the illness lasts no more than 10-12 days. A prolonged course is dangerous due to the addition of a bacterial infection.
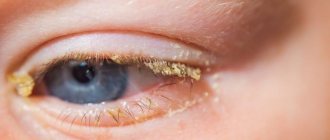
The main sign of complications of the disease is the formation of yellow-green crusts in the eyes and the appearance of purulent discharge.
In this case, in addition to standard rinses with antiseptics and the use of local anti-inflammatory agents, the doctor may prescribe antibiotics (drugs with tetracycline, gentamicin).
Allergic conjunctivitis in a child
This form of conjunctivitis is individual and is not transmitted through contact or air. Various allergens can cause eye irritation:
- pollen of flowering plants;
- animal wool and fluff;
- products, medicines;
- household chemicals, etc.
As soon as a specific allergen hits the child’s mucous membranes, the body immediately begins to react to it. The eyes become inflamed and red, itching, lacrimation, swelling of the nose and eyelids, photophobia, and cough appear. Here are the factors that can cause this pathology.
- Hay fever, or seasonal allergic rhinoconjunctivitis. Occurs in spring and summer when some plants bloom. With hay fever, allergic dermatitis can develop, and it is also characterized by increased fatigue and weakness. Antihistamines are prescribed for treatment, supplemented with corticosteroids in severe cases.
- Drug-induced conjunctivitis. Occurs while taking any medications. Standard signs of allergies may also include skin rashes and severe swelling of the nasal mucosa. If this form of conjunctivitis appears in a child, you should immediately stop taking medications and contact an ophthalmologist to clarify the circumstances.
- Chronic allergies. This disease can accompany a person throughout his life, as it manifests itself on any of the most common components: house dust, animal hair, cosmetics, etc. An irritant reaction can occur at any time upon contact with an allergen. After eliminating the irritant, the symptoms disappear.
For the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis, small children are prescribed drops that relieve swelling and irritation, for example, Vizin, as well as antihistamines Allergodil, Alezastin, Olopatadine. They help reduce the manifestations of the disease.
Please note that all medications must be used strictly as prescribed by an ophthalmologist.
If they are suitable, the symptoms will begin to subside on the second or third day. If this does not happen, consult a doctor - he will prescribe another remedy.
How to treat this disease?
The selection of a course of therapy directly depends on the type of conjunctivitis, the patient’s age and other factors. Therefore, when the first symptoms of an inflammatory disease appear, you should seek medical help as soon as possible. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor will prescribe a series of tests, which will allow you to reliably determine the form of conjunctivitis and select the right medications. Self-medication at home may be ineffective and lead to serious consequences, including the formation of scars on the cornea and deterioration of vision. If during the diagnostic process it is determined that conjunctivitis is caused by a virus, the patient will be prescribed a standard course of therapy (as with influenza or ARVI). You will also need to regularly wash your eyes with saline solution. This will prevent souring. The bacterial form of conjunctivitis is more complex and therefore requires a special course of therapy. In this case, children are often prescribed antibacterial drugs (drops and ointments), such as Levomycetin. It is also mandatory to wash the eyes with a diluted saline solution, for example, Furacilin. Experts recommend applying an ointment with a calming effect at night. It relieves itching and pain, and also helps soften the purulent crust and prevents the eyelids from sticking together.
To treat allergic conjunctivitis, several courses of antiallergic and antihistamine drops are prescribed over 2-4 weeks. A prerequisite for recovery is the elimination of the allergen. Many infants are diagnosed with dacryocystitis. In this case, standard treatment only relieves symptoms, but does not eliminate the root cause of the pathology (clogging of the tear ducts). Therefore, after discontinuation of therapy, the disease makes itself felt again. In this case, the doctor prescribes a massage of the lacrimal sac. Mom can do it herself after each day feeding the baby. In parallel, the use of antibacterial ointments and drops is required, as well as rinsing the organs of vision with saline to remove particles of pus. If massage and a course of therapy do not give a positive result, the baby may be indicated for a simple and painless operation to wash out the lacrimal ducts.
Treatment for conjunctivitis includes:
- use of antibacterial ointments and drops (exclusively as prescribed by a doctor);
- washing the eyes with saline solution;
- therapy aimed at treating a concomitant disease (with a viral form of conjunctivitis);
- massage of the lacrimal sac and, if necessary, surgery to wash the lacrimal ducts (if dacryocystitis is diagnosed).
In general, this disease is quite common among children and does not pose a threat to the health of the baby’s eyes with the correct and timely course of therapy. Experts say that taking an antibiotic for bacterial conjunctivitis is a necessary measure to suppress the disease. In this case, the drug affects only the area of inflammation (locally). However, it should be remembered that any ointments, drops and disinfectant solutions for the treatment of conjunctivitis in children can only be used as prescribed by a doctor. When the first symptoms appear, you should visit a pediatrician and ophthalmologist. In some cases (if dacryocystitis is suspected), additional consultation with an otolaryngologist may be required.
Rules of child hygiene in the treatment of conjunctivitis
It is very important to monitor the child’s personal hygiene during treatment - this will greatly help speed up recovery. Get him separate hygiene items: soap, a towel - it’s better if they are disposable. You should also change bed linen every day and wet-clean surfaces in the room with a disinfectant. During the treatment period, it is better to refrain from visiting public places, going to the pool, or sauna. In general, it is advisable to leave the child at home until complete recovery. It is worth removing sweet, spicy, salty foods from your diet and introducing into your daily menu more foods rich in vitamins A, B, C, selenium, zinc, which are good for eye health. Very often, the occurrence of infection is a consequence of a weakened immune system, so an enhanced vitamin course will help cope with the disease.
Make sure that your child does not spend a lot of time at the computer or with a gadget to prevent dryness and irritation of the eyes. A large percentage of success in treatment depends on compliance with these simple rules.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
Teach your child to wash vegetables and fruits thoroughly. Explain to him the importance of personal hygiene from an early age: why you need to wash your hands after returning from the street and before eating, use your own towel, and also do not bite your nails and fingers, and do not rub your eyes with dirty hands. If signs of illness appear, you should not look for advice on the Internet, but take your child to an ophthalmologist or call him at home. The external manifestations of various types of conjunctivitis are very similar, and only a specialist will establish the true etiology and prescribe an effective medicine. Self-selected medication may worsen the situation. 90% of success in the treatment of this eye pathology depends on timely contact with a specialist and strict adherence to all his recommendations.
The disease in an advanced stage can take a chronic course, and it will be much more difficult to cure it. In addition, some types of conjunctivitis in children can seriously affect the condition of their visual organs. Remember, our health largely depends on our attitude towards it.
Folk remedies
How to treat conjunctivitis in children using traditional home methods? Decoctions and infusions of herbs are used to treat sore eyes, but they do not replace medications. Typically used to wash the eyelids:
- dill water;
- chamomile infusion;
- cornflower flowers;
- cumin seeds;
- parsley casting;
- cucumber pulp;
- calendula flowers;
- infusion of birch leaves;
- a cup of tea;
- aloe juice
Chamomile and dill
Chamomile decoction is good at cleansing eye tissue from contamination, soothing irritated mucous membranes and destroying pathological microorganisms. A pinch of dry inflorescences is poured with boiling water in a ceramic cup, covered and allowed to stand for 25-27 minutes. Then the solution is carefully filtered through several layers of sterile gauze (or cotton wool) to prevent grass particles from entering. Wash the eyelids with this solution using cotton pads or sterile gauze.
Dill water is prepared from dry seeds (bought in gardening stores or pharmacies). Powdered seeds (1 tsp) are poured with boiling water (a cup) and left until cool. Eyes are washed with filtered water or lotions are made.
Aloe and cornflowers
Aloe juice disinfects eye tissue well and also helps eliminate purulent discharge. To prepare a solution with aloe for washing, you need to cut off a thick leaf of the plant and rinse well with boiled water. Next, the juice is squeezed out of the leaf, filtered and diluted with warm boiled water (take 10 parts of water for one part of the juice). This solution is instilled into the eyes twice a day. It is advisable not to squeeze the juice out of the entire leaf so that it does not spoil during storage. Divide the sheet into several parts and keep them in the refrigerator in the side compartment, wrapped in cling film.
An infusion of cornflower flowers is used in ophthalmology as an anti-inflammatory agent. Dried flowers (spoon) are poured with boiling water (cup) in an enamel or glass container and placed in a water bath. The infusion is simmered with the burner on low for about 15 minutes. Then leave it in the kitchen until it cools and filter well. You can simply steam the flowers with boiling water and let them sit for three hours under the lid. The eyes are washed with the decoction and applications are made. A decoction of cornflowers promotes rapid regeneration of affected tissues.
Note! Cornflower is a toxic plant, so its use should be agreed with a pediatrician.
Cumin, parsley and cucumber
Cumin seeds have anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. A spoonful of cumin is poured into a cup of boiled water and placed on the stove in an enamel or glass (fireproof) container, boiled for 10-11 minutes and cooled. The inflamed eyelids are washed with a filtered decoction and applications are made to the eyes.
Parsley leaves eliminate pain, destroy pathogens and stop the inflammatory process. You can use fresh and dried leaves. Boil the herb (a tablespoon) for 10-11 minutes (a glass of water), cool and rinse. You can also make applications on your eyelids.
Cucumber pulp helps eliminate discomfort in the eyelids, eliminates swelling and fights pathogenic microorganisms. Cucumber slices are applied to closed eyelids for several minutes (about ten). You can cover your eyes with a cloth to prevent the slices from rolling off.
Juice from cucumber pulp is used in the form of applications. To do this, the peeled fruit is crushed in a blender, the juice is squeezed out and cotton pads are soaked in it. The application lasts 10-18 minutes (depending on the child’s perseverance).
Note! During inflammatory processes, it is strictly forbidden to warm up.
Calendula and birch
Calendula flowers have a pronounced antiseptic property, relieve pain and itching, and destroy pathogenic microorganisms. Take a pinch of inflorescences per cup of boiling water and leave for 20-22 minutes under the lid. Cotton pads are moistened in the filtered infusion, lightly squeezed and applied to the eyelids. 10 minutes are enough to complete the procedure.
Marigolds also work well against viral conjunctivitis; they can be used to wash the eyelids. Just before doing this, you should filter the infusion through sterile cotton wool so that particles of the herb do not get into your eyes.
A healing infusion is made from birch leaves to combat inflammation of the eye membrane. To do this, fresh leaves are thoroughly washed from dust, poured with a cup of boiling water and covered. After an hour, the strained infusion is heated to 30 degrees, cotton pads are moistened in it and applications are made.
Remember that independent use of herbal treatment without consultation with an ophthalmologist may result in an exacerbation of the disease. First, consult your doctor, and then use traditional medicine recipes. The danger of improper treatment is the spread of the infectious process to tissues adjacent to the conjunctiva and the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms into the blood.