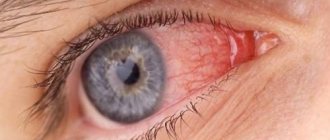
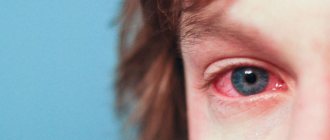
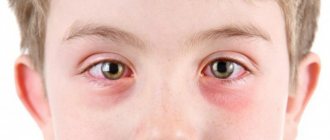
Probably every person has encountered conjunctivitis at least once in their life. When the conjunctiva becomes inflamed, the eyes become red and itchy, and pus or clear discharge appears. Washing the eyes with special solutions helps reduce the manifestations of the disease. We'll talk about which ones in this article.
Conjunctivitis can be viral and bacterial, allergic and fungal. Depending on the causative agent of the pathology, the doctor prescribes drops and ointments with the appropriate effect. But for any type of conjunctivitis, before instilling eye drops, you must first rinse them, removing accumulated dirt, mucus and pus. Ordinary tap water is not suitable for rinsing, as it is not sterile and can increase the inflammation process. Therefore, in case of conjunctivitis, the eyes are washed with special solutions.
Children's conjunctivitis in children is bacterial, viral, purulent: causes
Types of conjunctivitis
Medicine divides three types of conjunctivitis depending on the source of the disease:
- viral conjunctivitis
- bacterial conjunctivitis
- allergic conjunctivitis
Types of conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis
Viral conjunctivitis occurs when the mucous membrane of the eye is damaged by viruses. The disease can appear suddenly with obvious symptoms: swelling and redness of the eyes, itching and burning of the eyelids. There is discharge of pus.
IMPORTANT: Viral conjunctivitis goes away on its own when immunity to this pathogen is developed. The formation of a protective reaction, as a rule, occurs on days 5-7 of the disease.
Typically, viral conjunctivitis does not have a specific treatment, but only requires symptomatic care.
- Regular hygiene will help alleviate the child’s condition: reduce itching and inflammation. Eyes should be washed with saline sodium chloride solution, chamomile decoction, and freshly brewed tea infusion. Use a different cotton swab or gauze pad for each eye.
- If the baby’s condition does not improve with proper eye care, and a bacterial infection is connected to the viral infection, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial eye drops
- If you complain of dryness and burning in the eyes, your doctor may prescribe moisturizing drops
Chamomile infusion for washing the eyes
Let's consider the types of viral conjunctivitis that require mandatory medical intervention and special treatment.
Adenoviral conjunctivitis
- The disease is caused by an adenovirus, which is transmitted by airborne droplets. The baby's temperature rises sharply to 39 degrees, chills, headache and sore throat appear. Noticeably enlarged submandibular lymph nodes
- Usually one eye is affected first, and after three days the disease spreads to the second eye. The eyelids swell, the mucous membrane of the eyelid turns red. Slight grayish discharge appears. Sometimes small hemorrhages occur inside the conjunctiva. The child is afraid of the light, his eyes
- A characteristic sign of adenoviral conjunctivitis is the presence of small films that separate and small bubbles on the inner mucosa of the eyelid
Itchy eyes are a characteristic symptom of conjunctivitis
Herpetic conjunctivitis
- The causative agent, the herpes simplex virus, enters the child’s body through airborne droplets or contact from a sick person. With weakened immunity, the virus can become active and cause damage to the mucous membranes of the baby’s organs, including the conjunctiva of the eye.
- The child begins to behave restlessly: itching, fear of light, lacrimation, swelling and redness of the eyelid appear. Watery blisters of herpes appear on the mucous membrane. In some cases, the temperature rises, the child becomes weaker and capricious.
IMPORTANT: Herpetic conjunctivitis requires mandatory treatment with antiviral drugs prescribed by a doctor.
Classification
Infants are susceptible to three main types of conjunctivitis: bacterial, viral and allergic. The forms of the disease are similar in that they affect the conjunctiva, a special protective film that covers the entire surface of the eye and protects it from foreign bodies, injuries and adverse environmental factors. But the species also have fundamental differences.
Photo 1. Bacterial conjunctivitis in an infant: due to purulent discharge, the areas around the eye are covered with small crusts.
Bacterial conjunctivitis is the most common among infants. About 85% of conjunctivitis in young children is caused by pathogenic microorganisms. Most often, the disease develops due to excessive proliferation of staphylococci, streptococci, E. coli, pneumococci and gonococci. Less common pathogens are chlamydia, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Koch bacteria.
Important! Bacterial inflammation is characterized by the spread of infection to both eyes, as well as a large amount of mucous and then purulent discharge. Often there is so much discharge that the baby’s eyes stick together and become covered with dry crusts.
Bacterial conjunctivitis responds well to treatment; if timely therapy is started, significant improvements occur within 2-3 days.
Photo 2. Bacterial conjunctivitis in an infant in both eyes: copious mucous discharge from the organs of vision is observed.
Viral conjunctivitis is provoked by the herpes virus, adenovirus, and enterovirus. Due to the characteristics of immunity and a number of other reasons, viral eye infections are relatively rare in infants - only in 10% of cases. The pathology is characterized by an almost complete absence of discharge, pronounced redness of the sclera, acute pain when moving the eyeballs, and severe photophobia.
Upon examination, pinpoint hemorrhages are detected on the mucous membrane. Usually only one eye is involved in the inflammatory process. Recovery from viral infection of the conjunctiva is slow. Usually, all symptoms of the disease disappear only after 2-3 weeks; with herpetic conjunctivitis, the disease can drag on for 3-4 weeks.
Photo 3. Allergic and infectious conjunctivitis: the eyes of a small child are very swollen and red, and pus is oozing from them.
Allergic conjunctivitis affects about 5% of infants. This form of the disease is characterized by severe itching and redness. To treat the disease, the allergen is identified and eliminated, and then local and systemic antihistamines are prescribed.
Reference. The earlier the allergen is identified, the faster the recovery.
Conjunctivitis, of course, should be treated by a doctor. But if, due to circumstances, it is impossible to quickly seek medical help, you need to help the child before the medical examination. To do this, it is important to know the types of conjunctivitis, because, depending on the pathogen, treatment will differ.
Bacterial conjunctivitis - there is pus, the eyelids stick together, the conjunctiva and the skin around the eye are dry. At first, as a rule, only one eye becomes inflamed, and later the infection spreads to the second.
Viral is detected. bacterial and allergic types of this disease. Purulent conjunctivitis in children is of a bacterial nature; accordingly, the treatment of purulent conjunctivitis in children is carried out according to the treatment regimen for a disease of bacterial origin.
Types of disease
If the eyes are red and irritated, but there is no pus, we are talking about viral or allergic conjunctivitis (see photo above). If symptoms of pharyngitis and conjunctivitis appear, the development of adenoviral conjunctivitis can be suspected.
Today there are a huge number of different options for the course of the disease. To divide the types and forms of the disease into special categories, doctors use a variety of classifications. This allows you to accurately establish a diagnosis indicating the cause of the disease, the course of the disease, and determine a more likely prognosis for this disease.
If the disease appears in a baby for the first time in his life, then this option is called acute. This type of conjunctivitis is recorded in the baby’s special medical record.
After treatment, the disease should not return in acute forms. If the process repeats after 2 months or more, then this option is called recurrent. This form of the disease usually becomes chronic.
Video: Children's viral conjunctivitis
Bacterial conjunctivitis
Various microorganisms can cause bacterial conjunctivitis in children. Let's consider some types of clinical manifestations of this type of disease by different pathogens.
Acute bacterial conjunctivitis
- The disease is caused by damage to the conjunctival eye sac by a group of pathogens: streptococci and staphylococci
- Children with weak immune systems and chronic diseases are the first to get sick.
- Children from child care institutions: schools, kindergartens are susceptible to infection. The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets or through contact with sick children.
- The disease occurs suddenly and begins with inflammation of one eye. Then the second eye is also affected
- At first, the child experiences discomfort and itching of the eyelids, then the conjunctiva swells and turns red. The surface of the mucosa becomes uneven, and even isolated hemorrhages of the sclera are possible. Pus is released, which dries by morning and sticks the eyelashes together.
Bacterial infection of the eye
Blenorrheal conjunctivitis
The disease is caused by microorganisms - gonococci. A newborn baby can catch an infection at birth from a sick mother. There are known cases of intrauterine infection of a child from an infected mother. There is also contact transmission of the disease through the contaminated hands of a patient while caring for a child.
The baby's eyes become infected 2-3 days after birth. The eyelids quickly swell and turn purple-red. First there is profuse bleeding. Approximately on the third day of illness, yellow-green pus is discharged. This discharge is very dangerous for the baby. The infection can spread to the cornea of the eye and subsequently affect the child’s vision.
IMPORTANT: In maternity hospitals, all newborns are instilled with sodium sulfacyl solution to prevent gonoblennorrhea.
Hygienic procedures and instillation of sodium sulfacyl are mandatory prevention of gonoblennorrhea in newborns
Pneumococcal conjunctivitis
- Infants are the category of children most susceptible to this type of conjunctivitis. Infection occurs through airborne droplets and through contact through infected hands, toys, and various objects. Pneumococci are germs that cause disease
- Signs of the disease are similar to other types of bacterial conjunctivitis. These are: tearing, swelling and redness of the eyes, discharge of pus and mucus
IMPORTANT: A characteristic feature of pneumococcal conjunctivitis is the appearance of numerous films. They peel off easily from the conjunctiva of the eye.
Microorganisms
Diphtheria conjunctivitis
- The disease is transmitted by airborne droplets in a short period of time. Children under one year old are most often affected
- During illness, the temperature may increase to 38-39 degrees. The child becomes lethargic and capricious. The baby's submandibular lymph nodes become enlarged and the eyes become swollen and red. Later, cloudy bloody discharge occurs. The mucous membrane is closed with tight films that are difficult to remove
- Diphtheria conjunctivitis is a dangerous disease. If a disease is suspected, the baby is isolated in a special box in the infectious diseases department of the hospital. Diphtheria conjunctivitis is contagious and requires mandatory treatment
- In advanced cases, the disease can affect the cornea of the eye and cause complications associated with clouding of the lens and loss of vision
Chlamydial conjunctivitis
- The disease is spread by the parasitic bacteria chlamydia. If the expectant mother is diagnosed with chlamydia, then after birth the child is provided with mandatory preventive care in the form of eye ointments with antibiotics
- Children can catch chlamydial conjunctivitis through water, swimming in infected ponds and pools
- The disease most often affects both eyes
- The disease is characterized by redness and swelling of the eyelid, purulent discharge. On the part of the infected eye, enlargement of the auricular lymph node is possible
- When diagnosing chlamydial conjunctivitis, a child requires consultation with other pediatric doctors, since infection of other organs of the baby is possible
Allergic eye inflammation
Allergic conjunctivitis
The presence of a certain group of allergens can cause allergic conjunctivitis. The disease is characterized by swelling and redness of the eyelids, severe itching and excessive burning in the eyes, and profuse lacrimation.
IMPORTANT: Identifying the allergen and eliminating it is the primary task in the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis.
Treatment of allergic conjunctivitis comes down to the use of hormonal and antihistamines prescribed by the attending physician.
Main reasons
If the eye shell ceases to cope with its protective functions, a disease occurs (conjunctivitis).
- infections (bacterial, viral, fungal);
- allergic;
- endogenous.
The immune system of newborn children is still immature. The child's conjunctiva cannot protect the eye from external irritants. Therefore, in a young child, conjunctivitis is almost always of infectious origin.
The main causes of illness in newborns are maternal genital infections. Infection of newborns occurs during childbirth. The incubation period lasts from 2 to 15 days.
Often during childbirth and as the fetus moves through the genital tract, the baby’s eyes are exposed to harmful infections. As a result, inflammation and pus develop around the child's eyeball.
To exclude the possibility of bacteria, upon completion of labor, babies are given sodium sulfacyl or albucid. This does not always protect the child from rotting eyes. Having returned from the maternity hospital, some mothers are perplexed as to what to do if their baby’s eyes are festering.
Causes of rotting
Symptoms of conjunctivitis in children
All types of inflammation of the conjunctiva have similar symptoms. Parents should suspect the onset of the disease if the following symptoms occur:
- sour eyes
- swelling of the eyelid
- red eyes
- swelling
- increased lacrimation
- itchy eyes
- discharge of pus
- eyelashes sticking together after waking up
At the beginning of the disease, the baby vigorously rubs his eyelids. He is irritated by bright lighting: the baby develops a fear of light and the eyelids begin to involuntarily shrink (blepharospasm).
IMPORTANT: In case of severe manifestations of conjunctivitis, the child should be shown to a pediatrician. Proper treatment of the disease will reduce the risk of inflammation of other parts of the eye and deterioration of vision.
Child's illness
Allergic
The cause of the development of this type of conjunctivitis is irritation of the eye mucosa. This happens due to exposure to various allergens (plant pollen, pet hair, etc.). This pathology has a seasonal course. Its symptoms develop quite quickly. It is enough for the irritant to get into the eye, and within 15-60 minutes the little patient will experience swelling of the eyelids, itching of the eyes, pain and hyperemia. Discharge in such pathologies is transparent and insignificant.
What to do if there is a fever with conjunctivitis in children?
- Quite often, the appearance of conjunctivitis is a warning about the development of an infectious disease. You should pay close attention to your child's complaints.
- It is recommended to measure body temperature, examine the throat and lymph nodes. The dynamics of the disease should be closely monitored.
- An increase in temperature can accompany infectious processes in the eyes. It should be remembered that antipyretics are given to children only at temperatures above 38 degrees. An increase in temperature promotes the production of interferon and strengthens the child’s immune mechanism.
- It is recommended to increase the drinking regime and pay attention to the toilet of the eyes: thoroughly rinse and remove crusts of pus.
IMPORTANT: Fever and initial symptoms of conjunctivitis are grounds for mandatory medical examination of babies under one year of age.
Removing crusts from conjunctivitis
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children at home
First aid for inflammation of the conjunctiva in children
The baby should be given help at the first symptoms of eye inflammation before visiting the doctor.
- Thorough cleaning of the eyes by rinsing will help alleviate the child’s condition and prevent the infection from spreading to other parts of the eye.
- If conjunctivitis is accompanied by fever, chills, sore throat, cough, difficulty breathing, the baby should be shown to a doctor.
- It is recommended to protect a child with conjunctivitis from visiting childcare centers and walking in cold air and windy weather.
- Before visiting a doctor, the child should cleanse the eyes of purulent accumulations and crusts.
IMPORTANT: It is not recommended to instill any drops in your baby on your own without a doctor’s prescription. This may distort the picture of the true cause of conjunctivitis and make it difficult to identify the causative agent of the infection.
Young children need medical supervision
Situations when you need a doctor's help
- Young children (up to one year old) require mandatory consultation if eye problems arise.
- If signs of conjunctivitis continue for more than two days
- Photophobia is a symptom that requires immediate medical attention.
- Pain in the eyes
- Deterioration of vision
- The appearance of blisters on the eyelid. This may indicate damage to the eye mucosa by the herpes virus.
IMPORTANT: Only the attending physician can determine the type of conjunctivitis. Each type of disease corresponds to a specific treatment regimen and choice of medications.
Drops for conjunctivitis for children
Medicines to treat conjunctivitis
IMPORTANT: The prescription of drops for the treatment of the disease is determined by the doctor, based on the type of infectious agent, the severity of the disease and the age of the child.
Sulfacyl sodium eye drops
Antibacterial sulfonamide drug. Also known as Albucid. Used to treat bacterial and viral eye infections with streptococci, gonococci, pneumococci, chlamydia.
Solutions of different concentrations are used: 10%, 20% and 30%. The medicine is instilled 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac 4-6 times a day.
Sulfacyl sodium is used for mandatory prevention of blenorrhea in newborns in maternity hospitals immediately after the birth of the child.
Levomycetin solution 0.25%
Eye drops Levomycetin solution 0.25%
An antibiotic that has a bactericidal effect on many types of microorganisms. Used as eye drops for bacterial conjunctivitis.
The drug is instilled 1 drop into both eyes 3 times a day. The usual course of treatment is about 14 days.
Eye drops Floxal 0.3%
Bactericidal eye drops containing the antibiotic ofloxacin. The drug is prescribed by a doctor for various bacterial conjunctivitis of the eyes. Usually prescribed 1 drop 2-4 times a day for two weeks
Tobrex eye drops
Eye drops with the active antibiotic substance - tobramycin. The medicine is instilled 1-2 drops every four hours. Tobrex is used for various bacterial eye infections.
Medicines for the eyes
Eye drops Oftalmoferon
A drug containing the active substance interferon. Drops are prescribed by a doctor in case of viral etiology of conjunctivitis. Oftalmoferon causes the death of viruses, relieves swelling, itching, and has an antiallergic effect.
The drug can be prescribed to babies from the first days of life. Usually the doctor prescribes the medicine in the dosage: 1-2 drops into the conjunctival sac 6-8 times a day.
Eye drops Poludan
- The drug contains an antiviral complex of polyribonucleotides. The medicine is effective in suppressing herpes and adenoviruses. Possible simultaneous treatment with antimicrobial drugs
- Poludan is diluted with water for injection according to the instructions. The diluted medicine should be stored in a cool place for up to 24 hours.
- Eye drops are prescribed 1-2 drops 6-8 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor
The baby is getting eye drops
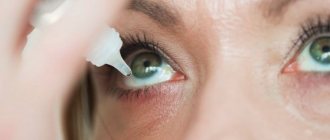
How to properly instill eye drops?
- Before starting the procedure, you should wash your hands thoroughly with running water and soap.
- For instillation, it is advisable to use disposable eye pipettes or droppers on bottles
- During the procedure, avoid contact of the pipette with the surface of the eyelid
- Eye drops should be at room temperature before instillation. Do not instill the drug directly from the refrigerator.
- Both eyes should be instilled, even if one is healthy. This preventive measure will prevent infection from entering the healthy eye.
- Before instillation, pull back the lower eyelid and squeeze out the required number of drops from a dropper or pipette into the lower conjunctival sac of the eye.
- After the procedure, allow the child to blink to ensure even distribution of the medication.
General principles
An ophthalmologist treats conjunctivitis in children. The method of therapy is selected taking into account the type of disease. Acute eye inflammations usually respond well to treatment even at home. However, there is always a risk of complications when carrying out incorrectly selected therapy. That is why independent attempts to get rid of the disease are unacceptable.
The first rule for treating childhood conjunctivitis is to constantly wash the eye. Crusts form on the surface of the organs of vision, which can be softened with chamomile decoction or furatsilin solution. Chamomile flowers are known for their bactericidal properties. The use of a medicinal plant will prevent further infection of the visual system.
IMPORTANT! Even if only one eye is affected by conjunctivitis, treatment procedures should be carried out on both organs of vision, since the infection is quickly transmitted.
To avoid infection, use cotton swabs and swabs for each eye separately. The drops should be used strictly according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor. There is no need to exceed the dosage in order to speed up recovery. This way you can only harm yourself by causing overdose symptoms. It is worth understanding that the conjunctival sac in any case cannot accommodate more than two drops. Never cover your eyes with a blindfold. This will prevent the drainage of pus and tears.
Use of antibacterial drugs as prescribed by a doctor. They can be in the form of drops, tablets or injections. Albucid, tetracycline and chloramphenicol ointments are most often used to treat bacterial eye infections. These drugs have proven themselves in pediatric practice and practically do not cause adverse side effects in children. The ointments are placed with a sterile glass rod behind the damaged eyelid 3-4 times a day. Typically, the duration of such treatment is no more than 10 days. Only a doctor can prescribe antibiotic tablets and injections. In his recommendations, he indicates the frequency, dose and duration of such an antibacterial course.
- Treating conjunctivitis at home
Ensuring proper rest. During sleep, the child's body recovers and gains strength to fight the disease. Every child under five years old must sleep during the day. Children who are sick with an eye infection should definitely rest during the daytime with their eyes closed. At this time, the mucous membrane is restored and healed.
Medical nutrition. During the acute period of the disease, children must receive food with sufficient amounts of protein. Such products will help strengthen the immune system and speed up recovery. For children of any age, poultry and veal, as well as white fish, are excellent protein options. You can supplement your diet with porridge, as well as vegetable and fruit purees.
Optimal water regime. To eliminate all bacterial toxins from the body, the child must drink a lot. It is better that the baby consumes at least 1.5 liters per day during illness. You can drink regular boiled warm water. During the acute period of illness, children are prepared with fruit and berry compotes or fruit drinks. You can make a decoction of rose hips. Such drinks are rich in vitamin C and beneficial microelements.
Maintaining a daily routine. During an acute period of illness, you should not walk outside with your baby. It is better to postpone such walks until you recover. This can be especially dangerous in the summer. Bright sunlight, falling on the irritated mucous membrane, causes additional damage and significantly increases inflammation.
It is also better to postpone swimming in the first days of the disease. Especially if the child has a high body temperature or fever. After bathing procedures, the baby can easily become hypothermic. Hypothermia weakens the immune system, which significantly reduces the baby’s strength in fighting infection.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in children at home begins with proper hygiene
Ointments for conjunctivitis for children
When treating conjunctivitis, eye ointments are prescribed. Doctors often combine treatment with drops and ointments.
IMPORTANT: As a rule, children do not like and do not tolerate eye ointments well. It is best to perform this procedure before your baby goes to bed.
Tetracycline eye ointment 1%
Tetracycline eye ointment 1%
The ointment contains the antibiotic tetracycline. The drug is used by placing it behind the eyelid 2-3 times a day as prescribed by a doctor. The ointment is used for bacterial eye infections.
Erythromycin ophthalmic ointment
Bactericidal eye ointment with the active ingredient erythromycin. Widely used in ophthalmic practice in the treatment of eye infections. The ointment is placed behind the lower eyelid three times a day.
Zovirax eye ointment 3%
Antiviral eye ointment containing acyclovir. Used in the treatment of viral eye infections, in particular herpetic conjunctivitis. The ointment is applied to the lower eyelid 5 times a day every four hours.
Tebrofen eye ointment 0.5%
Antiviral ointment with the active substance tebrofen. The drug is used for viral eye diseases. The ointment is applied behind the eyelid 3-4 times a day. Treatment usually lasts up to 2-4 weeks.
Eye wash solution
Treatment
Treatment of the patient's condition is carried out at home. To do this, he is prescribed a set of medications:
- systemic antiviral drugs, for example, Arbidol;
- local antiviral drops in the eyes (Interferon, deoxyribonuclease), they can be used in long courses, especially if the disease has caused complications, the maximum time of use is 2 months;
- placing antiviral ointments under the lower eyelid (Floreal, Tebrofen, Bonafton);
- antibacterial drops (Vigamox, Tobrex, Levomycetin) and ointments (Erythromycin, Tetracycline), if there is a complication with a bacterial infection, they can be used for no more than 7 days, after this time the bacteria develop resistance to the active substance, so it will be necessary to replace the drug with an analogue based on another active component;
- antihistamines to quickly eliminate swelling, inflammation, redness in the eye area (Allergodil);
- moisturizing eye drops to prevent irritation and damage to the cornea from resulting dryness (Slezin, Defislez).
During therapy, parents must maintain complete hygiene. When using all medications, you must wash your hands thoroughly and do not allow the bottle to touch the child’s eyes, so as not to introduce an infection inside. All medications are used in strict dosages, in a course prescribed by a doctor.
How to wash conjunctivitis in children?
Washing the eyes and removing purulent crusts and mucus is an important procedure in the treatment of conjunctivitis.
IMPORTANT: Before instilling eye drops or placing ointment behind the eyelid, you should thoroughly clean and rinse your eyes.
If there is mucopurulent discharge and crusts, the eyes should be washed with solutions and infusions that you can prepare at home yourself.
- Boiled warm water is good for removing purulent discharge from the eyes
- Saline solution : dissolve a teaspoon of table salt in a liter of warm boiled water
- Furacilin solution 0.02% : one tablet of furatsilin 0.02 g is dissolved in 100 ml of boiling water
- Chamomile infusion : two tablespoons of chamomile flowers are steamed with a glass of boiling water, left for 40 minutes.
- Sage infusion : a tablespoon of sage leaves is steamed with a glass of boiling water
- Tea infusion : pour a tea bag with a glass of boiling water and leave for 10 minutes
Eye wash tea
How to properly wash your eyes?
- Inflamed eyes are washed with a warm solution using a cotton swab or pad. A new swab is taken for each eye
- The moistened swab is led from the outer edge of the eye to the inner corner
- The eye wash procedure is carried out several times a day as needed (6-8 times per day)
Safety measures and procedures
During allergic conjunctivitis, rinsing is not used. This, on the contrary, can only worsen the situation. Frequent rinsing is necessary for viral and bacterial inflammation. How should these procedures be carried out, as well as how to safely and painlessly apply ointment, remove dried crusts, and instill drops?
- All drops, ointments and solutions must be at room temperature.
- For rinsing, use a solution of furatsilin (one tablet of furatsilin in half a glass of water) or traditional methods - a weak decoction of chamomile, strongly brewed tea. Rinsing should be performed every two hours in case of acute conjunctivitis and at the initial stage.
- Anti-inflammatory, disinfectant drops are also used. At the initial stage of the disease - every 3-4 hours, after that less often.
- For older children, Picloxidin, Vitabakt, Futsitalmic, Eubetal, Colbiotsin and other anti-inflammatory drops are used. During the treatment of conjunctivitis in an infant, a 10% Albucid solution is used.
- Rinsing should only be done towards the inner corner of the eyes.
- During inflammation of one eye, all procedures are performed on both.
- In order to instill correctly, you need to carefully pull back the lower eyelid and drop the drug onto the mucous membrane.
- The same method is used to treat with ointment.
- If crusts have formed on the eyelids, they cannot be peeled off dry. The crusts soften after washing, then they are carefully removed using a sterile bandage or napkin.
- After the procedure, there is no need to rub anything; the drug is distributed evenly during blinking.
- Excess medication that has accumulated in the corners of the eyes can be carefully removed with napkins.
- When instilling eye drops into infants, it is necessary to use special pipettes that have rounded ends.
- Older children can be taught to perform the procedures themselves.
- When the baby closes his eyes and is afraid, you can drop the drug between the eyelids. When the eyelids open, the product gets onto the mucous membrane.
- The dose must be monitored closely.
- You also need to monitor the expiration date of the drugs. Many drugs must be stored in the refrigerator after opening; they can be used for a short period of time.
- Doctors advise throwing away all medications after treatment, as the bottle may contain pathogens. Infection can happen again. This is also why the drops must be individual.
Any types of conjunctivitis in children go away quite quickly with timely and correct treatment prescribed by an ophthalmologist. There is no need to make a diagnosis yourself, as this can only make the problem worse. We must not forget that only a doctor, after an examination, will be able to accurately determine the type of conjunctivitis and prescribe the optimal course of treatment, taking into account the age category of the child.
Is it possible to walk with conjunctivitis in children?
Walking or staying at home with conjunctivitis - there is no definite answer. The baby’s well-being, the duration of the illness, and weather factors should be taken into account.
When can you go for a walk with your baby?
- If there is no fever and the child is feeling well
- No acute period of illness
- Under favorable weather conditions: the street is not dusty, there is no strong wind, the weather is not hot. In winter - in the absence of severe frosts
For walks, you should choose green areas: parks, closed courtyards and areas without crowds of people. Since conjunctivitis is a contagious disease, it is recommended to isolate a sick child from contact with healthy children.
Prevention of conjunctivitis
Prevention of conjunctivitis in children
Conjunctivitis is a disease associated with eye infection. Due to childhood, the child’s rather weak immune system, and lack of proper hygiene, the disease is common in children. Therefore, preventive measures should be taken to prevent the occurrence of childhood conjunctivitis.
How to protect your child from conjunctivitis?
- Maintain child hygiene: wash hands after walking, before eating
- For allergic conjunctivitis, eliminate the allergen that causes the disease: house dust, animal hair, pollen from flowering plants
- Keep the apartment clean: wet clean the rooms, remove dust, ventilate the room
- Carry out hardening and health activities with your baby to strengthen the immune system
Healthy baby
Nutrition for inflammation of the conjunctiva
Proper nutrition in the presence of an inflammatory process in the conjunctival area helps to increase immunity and improve eye condition. The diet should contain foods rich in vitamins D and A:
- Fish;
- Sea kale;
- Cod liver;
- Flaxseeds;
- Pumpkin;
- Sunflower seeds;
- Dairy products;
- Berries;
- Chicken eggs.
The benefits of individual products are listed in the corresponding table below.
| Product | Beneficial features |
| Carrot | The vegetable contains a large amount of carotene, which has a beneficial effect on the visual organs. |
| Blueberry | The product is enriched with vitamin A and other nutrients. Blueberries help strengthen the retina and help relieve tired eyes |
| Apricot | The fruit contains quite a lot of potassium and vitamin A. |
| Spinach | Spinach contains lutein. Eating vegetables reduces the risk of various eye diseases. |
| Broccoli | The vegetable is known for its antioxidant properties |
| Wheat grains | Wheat is rich in antioxidants. The product helps reduce inflammation and improves immunity |
| Rose hip | The product has a general strengthening effect on the body. Rosehip, a source of vitamin C, helps strengthen the immune system |
| Onion | Onions have a positive effect on visual acuity |
If a child has conjunctivitis, it is recommended to exclude from the daily menu:
- Salty food;
- Products that contain large amounts of protein;
- Flour products;
- Products that contain harmful preservatives.
How to treat childhood conjunctivitis: tips
The inflammatory process of the mucous surface of the eye worries parents very much. Almost every child at least once, or even several, has encountered this problem. Numerous reviews on the Internet regarding conjunctivitis can be summarized and some useful tips can be given.
- Preventive measures against conjunctivitis are the most effective and help reduce the risk of the disease
- The child should be protected from the possibility of injury to the conjunctiva: contact with the eyes of cosmetics, dust, chemical reagents
- Monitor the time your child spends near the TV and computer. With prolonged “communication” with these information and gaming devices, the process of self-cleaning of the eye may decrease, which is a prerequisite for inflammation of the mucous membrane
- Proper and healthy nutrition, adequate sleep and walks in the fresh air, personal hygiene and physical development are the main components of a child’s health.
How to speed up the healing process?
In the first days after infection with conjunctivitis, an acute reaction to sunlight is often observed. When the sun's rays penetrate the affected mucous membrane, the symptoms of the disease intensify. This can lead to increased pain and increased lacrimation.
In order to intensify the recovery process, it is necessary to limit the time of daytime walks with the child in the first days after infection. The child’s room should be curtained with thick curtains.
If you follow these recommendations, the inflamed mucous membrane will recover much faster.