Conjunctivitis that occurs during pregnancy cannot but worry the expectant mother. Any disease when carrying a child requires special treatment, because many traditional methods of treatment are not available during this period, since they can harm the baby, but the infection itself can also have a negative effect. At the same time, eye inflammation in expectant mothers is not so rare, since the body becomes more vulnerable and susceptible to infection. Therefore, it is important for the expectant mother to know how to cope with the disease.
Description of the disease
Inflammation of the conjunctiva is called conjunctivitis. The conjunctiva lines the inner surface of the eyelid and the sclera, acting as a barrier between the visual organs and the environment. Depending on the nature of the damage to the mucous membrane, conjunctivitis can be of an infectious or non-infectious nature.
Classification of conjunctivitis:
- bacterial;
- chlamydial;
- viral;
- fungal;
- allergic;
- traumatic;
- metastatic.
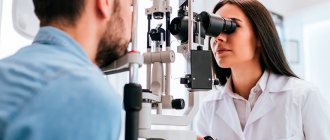
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the type of disease based on laboratory tests. Therefore, you cannot treat the infection yourself.
Bacterial conjunctivitis appears through contact infection. Bacteria actively multiply on the membranes of the eye, provoking an inflammatory process. Microorganisms can be different: coccal in nature, intestinal or Pseudomonas aeruginosa, tubercle bacilli, etc.
The most unsafe are viral infections transmitted during conversation and inhalation of contaminated air. This type of infection can be directly related to herpes and other viruses.
Non-infectious conjunctivitis can be caused by mechanical damage to the organs of vision, chemical burns or irritation from dust. Tobacco smoke, vitamin deficiency or irritation of the sclera by ultraviolet rays can also be a provoking factor.
Conjunctivitis can occur when contact ophthalmic lenses are used incorrectly.
Is conjunctivitis dangerous during pregnancy? The disease itself is not dangerous for the embryo. Medicine that enters the mother's bloodstream can cause harm. With the blood, chemicals penetrate the placenta, which can greatly harm the small organism. The use of medications in the first trimester of pregnancy is especially dangerous.
Causes and types of inflammation
During pregnancy, the immunity of the female body is greatly reduced, and against this background, the pathological process is activated under the influence of the following factors:
- colds of viral etiology;
- insufficient intake of vitamins necessary to nourish the visual organs;
- impact on the body of physical and chemical factors;
- pathologies of the throat, nose and ear, occurring in acute and chronic forms;
- violation of the rules for wearing contact lenses;
- improper and unbalanced diet;
- severe myopia;
- severe hypothermia of the body.
During pregnancy, conjunctivitis develops for the same reasons as in normal situations. The disease can be provoked by:
- bacterial infections;
- viral infections;
- various types of allergens;
- foreign bodies penetrating the organs of vision;
- sexually transmitted microorganisms.
Only an ophthalmologist can diagnose the cause of conjunctivitis and determine its type, so when the first signs of the disease appear, a woman should visit him as soon as possible.
Symptoms of the disease
Conjunctivitis is easily transmitted by contact with an infected person or by using his things. Conjunctivitis is especially dangerous for pregnant women, whose immune system is in low tone. If a person in good health may not worry about contracting an infection, then for a pregnant woman any contact with a sick person can turn into a big problem.
When the conjunctiva is infected, the patient experiences:
- burning sensation in the visual organs;
- uncontrolled flow of tears;
- constant itching.
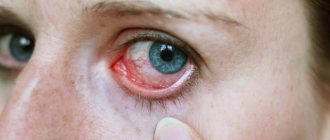
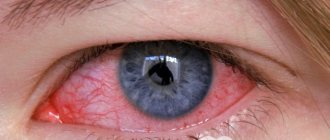
The disease is accompanied by swelling of the covering membranes of the eye, redness of the sclera, and discharge of pus and mucus from the orbit. When waking up, the patient is unable to open her eyes due to the sticking of the eyelashes by the purulent exudate. Usually the disease attacks both eye sockets, but alternate inflammation of the mucous membrane of the visual organs also occurs.
In the acute form, the patient’s general well-being worsens, hyperthermia appears, and intense pain is felt in the head. This form of conjunctivitis can last two to three weeks. In the subacute form, typical symptoms are less pronounced. The chronic form is characterized by discomfort in the eye organs, a sensation of a foreign object or small grains in the eye sockets. The conjunctiva becomes loose and moderately edematous. However, the chronic form may be accompanied by keratitis, which aggravates the course of the disease.
The bacterial form can be determined by the expiration of purulent exudate from the eyes. The viral form is characterized by clear discharge from the mucous membrane, photophobia and (sometimes) enlarged lymph nodes.
The allergic form is accompanied by a strong burning sensation, swelling of the sclera, profuse lacrimation, coughing and other manifestations of allergies. When the eye organs are damaged by chemicals, an acute pain syndrome appears when turning the eyeball, lowering the eyelids and blinking.
What is conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is a disease that occurs quite often in humans. With this pathology, the mucous membrane of the organ of vision is affected and its main cause is allergens of various types and infections.
Characteristic manifestations of conjunctivitis are:
- irritation of the mucous membrane of the organ of vision;
- increased lacrimation;
- red staining of the conjunctiva;
- mucous discharge mixed with purulent exudate.
An ophthalmologist, whom the patient should consult during pregnancy, can determine the pathology and select the most effective treatment. Today there are:
- allergic;
- viral;
- bacterial form of conjunctivitis.
The simplest form of eye damage is considered to be bacterial, and after a few days the irritation disappears on its own without special treatment. It is possible to cope with the allergic form of pathology by limiting contact with irritants.
Therapy for the viral form of conjunctivitis is carried out using ointments and drops that contain antibacterial components. Women are not allowed to use antihistamines as they may adversely affect the development of the baby. Such drugs should only be used in extreme cases and only as prescribed by a specialist.
During pregnancy, women experience disruptions in the functioning of the body's immune system and increase vulnerability to various viruses. It is for this reason that the infectious form of the pathology is most often diagnosed, which requires effective treatment.
Diagnostics
The causes of damage to the conjunctiva are different - external and internal. The conjunctiva performs a barrier function and is in an accessible location for adverse environmental influences. Inflammation of mucous tissues can be aggravated by other ophthalmological diseases: keratitis, blepharitis, dry eye syndrome, etc.
Depending on the course of the disease, conjunctivitis is:
- spicy;
- subacute;
- chronic.
There are also clinical forms of conjunctivitis, characterized by the unique course of the infection.
The ophthalmologist finds out what triggered the development of the infection: external factors (infection from an infected person) or internal causes (complications of other somatic diseases).
Diet during treatment
When treating blepharitis, a diet is recommended, since the patient must receive enough vitamins (especially A, D, B), proteins and unsaturated fatty acids from the diet. It is recommended to include in the menu:
- fish and seafood;
- meat and liver;
- dairy products and eggs;
- cereals, legumes;
- nuts, dried fruits, mushrooms;
- vegetables - potatoes, carrots, cabbage, beets, bell peppers;
- fruits - melon/watermelon, pomegranate, apricot/peach, citrus;
- onions, garlic and herbs - lettuce, dill, spinach, horseradish;
- any compotes and natural juices.
Fried foods, pickles and marinades, and sweets are excluded.
Treatment of conjunctivitis during pregnancy
Treatment is prescribed after identifying the causative agent of the infection. Chlamydial and viral conjunctivitis are more difficult to treat. Since the usual therapeutic regimen is not suitable for pregnant women, this greatly complicates the matter. Immunity weakened by pregnancy also contributes.
Allergy
The allergic form is treated by eliminating the allergen from the pregnant woman's diet. Dust, plant pollen, poplar fluff and cosmetics can also be a source of allergies. It is important to correctly determine what exactly provokes the inflammatory process. This is quite easy to identify, since an allergy attack appears immediately after exposure to the pathogen. Perhaps this is a household chemical product.
With allergies, both eyes become inflamed at the same time.
Allergies do not appear due to pregnancy; this disease accompanies a woman from adolescence or childhood. Therefore, it is easy to determine the source of eye inflammation. Antihistamines cannot be used during pregnancy, with the exception of sodium cromoglycate.
Drops can be used for therapy:
- Allergodil;
- Opatanol.
Therapy takes place with constant examination by a gynecologist. Usually the allergy subsides after eliminating the allergen, but there are cases of complications.
Bacteria
This form of conjunctivitis can go away on its own in 2-3 days, but you can’t take risks during pregnancy. Chlamydial infection, which is a type of bacterial infection, is especially dangerous. Antibiotics for conjunctivitis in pregnant women are extremely undesirable. The therapy is carried out under the constant supervision of a doctor; the pregnant woman’s husband should also be treated for the infection. Intimate contacts during treatment are completely prohibited.
The ophthalmologist prescribes the patient to wash the eyes with chamomile solution, which eliminates purulent exudate and relieves irritation. You can also use a solution of furatsilin to wash the organs of vision; it is safe for the fetus. A weak solution of potassium permanganate will also not cause harm, but will disinfect the mucous membrane well. Medicines that may be prescribed include Albucid and Tobrex drops. Relatively safe products include drops:
- Vigamox;
- Ciloxane.
Antibiotics are prescribed only if the mother's health is threatened or vision loss occurs. This issue is decided by a gynecologist.
Viruses
To heal this form of inflammation, strong drugs are required, which are prohibited for pregnant women. In this case, the ophthalmologist can prescribe Ofalmoferon drops to the woman. To eliminate irritation, you can use an artificial tear preparation (it is completely safe). Since viral conjunctivitis is often accompanied by a bacterial infection, medications are prescribed to eliminate both forms of the disease. Medicines against viral infections use interferon, which can suppress the activity of microorganisms.
Medicines against viruses:
- Aktipol;
- Poludan;
- Tebrofen.
The last drops are the safest for healing from viral conjunctivitis, as they are used to treat newborns.
What risks are associated with conjunctivitis?
Expectant mothers are often alarmed by how dangerous conjunctivitis can be in pregnant women. Experienced doctors note that eye disease cannot affect the course of pregnancy. Initially, there is no cause for concern. The main task is the correct approach to carrying out therapeutic measures, which become available only with the help of an experienced doctor.
The most important thing is timely treatment of conjunctivitis. Most drugs that are prescribed in the 21st century to eliminate pathogenic bacteria in the eyes and fight the disease can enter the bloodstream
If a pregnant woman takes such medications, it is possible to assume the following development of the situation: the active components of the medicine enter the bloodstream and the baby, having a negative effect on the intrauterine development of the baby. As a result, it is not conjunctivitis that poses a potential danger, but the medications used.
An additional risk of eye disease comes from potential mother-to-child transmission during childbirth. If such a situation arises, treatment of an infectious eye disease in a child will be difficult and cause serious trouble. To reduce this risk, it is recommended to consult an ophthalmologist in a timely manner and take all necessary actions, after which you should take care of thorough and ongoing prevention.
The most dangerous form of conjunctivitis is chlamydial, for this reason it is recommended to consult a specialist as soon as possible to determine the correct diagnosis and begin timely treatment measures. Otherwise, the situation will only get more complicated.
Traditional methods
Herbal remedies and infusions may appear to be safe for treating conjunctivitis, but this is deceptive. Not all herbs are suitable for healing; some of them are quite dangerous for the fetus. Therefore, the approval of a gynecologist is necessary before treatment.
Aloe
Aloe juice eliminates any inflammatory processes well and has antibacterial properties. It is a natural healer that has been used in healing for centuries. It is necessary to prepare juice from the lower leaves of a plant that is at least two years old. The juice is diluted with boiled water, cooled at room temperature. Dilution ratio: part juice to ten parts water. Wash your eyes several times throughout the day. The next day, prepare a new portion of juice, since it cannot be stored.
Kalanchoe
The juice of this plant is widely used to remove mucus from the nasal passages during a runny nose, as well as to treat conjunctivitis. There is no need to dilute this juice with water. Squeeze the juice out of the leaves using a spoon, moisten cotton balls and apply to your eyes for 10-12 minutes. The compress quickly eliminates irritation and alleviates the condition.
Althea
Dry marshmallow root is sold in pharmacies. Take 4 tbsp of roots per cup of boiled, cooled water and leave for a day in a dark place (in a closet). The filtered infusion is used to wash the eyelids throughout the day. The more often you wash, the faster you can get rid of the disease.
cornflower
Dried flowers and cornflower herb are steamed with boiling water. Take a pinch of plant material per cup of boiling water and leave for half an hour. The eyelids are treated every hour. The next day you need to make a new infusion.
Potatoes and protein
The mixture for applications is made from grated raw potatoes mixed with egg white. The raw materials are placed on a piece of bandage and an application is made for 12-15 minutes. Afterwards, carefully wash the eyes with a cotton pad soaked in boiled water.
Dill
To heal eye inflammation, use fresh herbs and dry dill seeds. Make juice from a bunch of fresh dill in a juicer or blender, soak cotton pads in it and apply the application for 12-15 minutes.
An infusion is made from the seeds. A teaspoon of seeds is steamed in a cup of boiling water for an hour. The infusion is filtered and used for applications to the eyes. Hold until the discs cool down. Apply applications every hour or two.
Propolis
If you are not allergic to bee products, you can use propolis drops. Propolis copes well with viruses, fungi and microorganisms. Propolis tincture also strengthens the immune system.
The raw materials are placed in the freezer for a while to make it easier to grate. Grated propolis is ground into powder using a mortar. Then the powder is poured with cool boiled water and placed in a closet for an hour to free the substance from impurities. The settled mixture is shaken, then the floating particles of impurities are removed. The water must be completely drained and the powder dried.
To make an aqueous solution of propolis, you need twice-frozen water or spring water. This water has healing properties, is purified and suitable for treatment. For a 20% propolis tincture, take 20 g of raw material per 100 ml of purified water. Since propolis dissolves only in hot water, it is prepared in a thermos (2 days) and in a water bath for an hour. If you prepare the infusion in a bathhouse, stir the contents of the saucepan periodically.
Shake the propolis infusion before use.
To achieve better fermentation of the solution, propolis is first prepared in a water bath, and then poured into a thermos and kept for two days. To enhance the healing effect of propolis, it is prepared with chamomile water. This solution can be stored in a dark place for 20 days.
For instillation, the liquid must be carefully filtered. This is done using a gauze or bandage folded in three layers. To get rid of conjunctivitis, instill 2 drops into each eye twice a day. After a month the disease goes away. If symptoms persist, the course is repeated after a couple of weeks.
Tea
To wash the eyes, use fresh tea leaves, which are infused for 40 minutes. Enzymes from tea leaves eliminate inflammation and cleanse eye tissue. You can take any tea: green or black. Large-leaf tea is poured with boiling water (a tablespoon of leaves is used for a cup of boiling water). In the finished infusion, moisten cotton pads and apply to the eyes or simply rinse.
Bay leaf
Laurel infusion quickly relieves irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane. Wash a couple of large laurel leaves and steam with boiling water (a cup). The infusion should stand for half an hour. Then it is used for applications or washing in a warm form. Three times a day is enough.
Treatment of conjunctivitis in expectant mothers
In principle, the disease is treated quickly and goes away without complications for the pregnant woman and the fetus. True, this does not apply to herpetic, chlamydial types of disease, as well as inflammation of the conjunctiva caused by adenoviruses.
Taking over-the-counter medications on your own without consulting a doctor is a sure way to harm yourself and your unborn child. Most drugs are generally contraindicated during pregnancy.
Basic principles of therapy
The patient’s first visit is to the ophthalmologist: the doctor prescribes medications that, in his opinion, are better suited for treating this type of conjunctivitis. Next, the woman goes to the gynecologist’s office, where she finds out which of the prescribed medications she can take and which cannot.
Standard therapy for pregnant women for inflammation of the conjunctiva looks like this:
- Viral conjunctivitis is treated with topical drugs containing oxoline and tebofen. Interferon and other immunostimulants are also used (preferably in later stages, in the form of ointments and suppositories). For herpetic conjunctivitis, Acyclovir eye ointment is prescribed.
- Bacterial conjunctivitis is eliminated by washing the infected eye with Furacilin or boric acid (2%). Tobrex drops and topical antibiotics enhance the therapeutic effect.
- Allergic conjunctivitis, as a rule, recedes if the source of the allergy is removed from the patient. When such a measure is not enough, they are treated with antihistamines Zyrtec, Suprastin, as well as Hydrocortisone ointment (for all drugs - a short course of administration).
The doctor prescribes oral medications (for oral administration) if local therapy has not given positive results within 7 days or in cases of severe damage to the conjunctiva.
Drug treatment
In the 1st trimester, it is better for the expectant mother to limit herself to local therapy; Take medications orally only when absolutely necessary. The fact is that the substances of synthetic drugs penetrate through the mother’s bloodstream into the fetus, which is not yet protected by the placenta.
For the 2nd and 3rd trimesters, some antibacterial solutions, drops, and eye ointments are considered safe.
Prohibited during pregnancy:
- hormonal drugs;
- toxic antibiotics;
- ophthalmic solutions containing heavy metal salts.
Tobrex
Tobrex drops and ointment are widely used to get rid of bacterial conjunctivitis. The active substance is the antibiotic tobramycin, which destroys almost all types of bacteria that cause the disease.
Tobrex drops prevent the proliferation of staphylococci and streptococci that have colonized the conjunctiva
When applied topically, the medicine almost does not enter the circulatory system, therefore it is considered safe. However, the instructions recommend avoiding Tobrex during pregnancy: too little data has been collected on its effect on the fetus. Since there is no direct ban, doctors prescribe the drug to expectant mothers.
Drops come in two types:
- Tobrex. According to the instructions, instill 1 drop 4-5 times a day.
- Tobrex 2x (with a thicker consistency). Instill 1 drop 2-3 times a day.
The ointment is squeezed out into 1 cm columns; use 2 times a day. The course of treatment with Tobrex is 7–10 days.
There is only one contraindication - hypersensitivity to the components of the drug.
Adverse reactions are rare. Among them:
- itching, tearing;
- swelling, redness of the conjunctiva;
- inflammation of the eyelid;
- inflammation of the cornea.
An overdose threatens the appearance of a fungal infection: fungi are insensitive to tobramycin and easily colonize the conjunctiva.
The price of Tobrex drops and ointment is 190–217 rubles per package.
Albucid
The active substance of Albucid drops is the antibiotic sulfacetamide; effectively fights conjunctivitis pathogens.
Once in the eye, the medicine quickly spreads through the tissues, blocking the proliferation of pathogenic microbes. Penetrates into the bloodstream in small quantities.
The drug is not prohibited during pregnancy, but be sure to consult your doctor about taking it: Albucid can cause allergies.
The effectiveness of Albucid has been confirmed by positive reviews from doctors and patients, but pregnant women should use the drops with caution
Contraindications:
- allergy to medication components;
- renal failure;
- liver dysfunction;
- joint use with substances containing silver ions.
Dose: 3 drops 6 times a day. The course of admission is 1 week.
The price for a bottle of Albucid starts from 25 rubles.
Furacilin
Tablets and ointment are used to treat conjunctivitis. Furacilin has an antibacterial effect, but the effect does not occur immediately. Useless against fungi and viruses.
Mainly used to remove mucus and pus from the eyes. A solution is prepared from the tablets: 1 piece is dissolved in 100 ml of warm water. The resulting mixture is used to wash the eyes several times a day. Furacilin ointment is applied to the eyelids.
Contraindications: intolerance to the drug, bleeding, dermatosis. Can be used by expectant mothers. In rare cases, the medicine causes allergies.
In pharmacies, Furacilin costs approximately 25–75 rubles.
Furacilin appears in the home medicine cabinet at the first suspicion of conjunctivitis
To wash the eyes, along with Furacilin, they often take a composition called Artificial tear: it contains no chemicals and is safe during pregnancy.
Oftalmoferon
Oftalmoferon drops are used in cases of viral infection of the conjunctiva. The active ingredient, interferon, fights microbes and at the same time strengthens the immune system. The drug is also effective for allergic conjunctivitis.
Oftalmoferon contains diphenhydramine, which relieves eye pain. And the cornea is protected from the irritating effects of diphenhydramine by other excipients.
Oftalmoferon combines antiviral and antihistamine properties
The only contraindication is an allergy to the components. No side effects were found. The drug is not prohibited for expectant mothers.
Dosage: 1-2 drops 6 to 8 times a day. It is better to check the duration of treatment with your doctor.
You can buy a package of Oftalmoferon for 270 rubles.
Opatanol
An antihistamine created specifically for the treatment of allergic conjunctivitis; Available in the form of eye drops. A small amount of the drug is absorbed into the blood.
The instructions say that the effect of Opatanol on pregnant women and the fetus has not been studied, so it can only be used in difficult cases when the threat to the health of the mother is high.
Do not drop Opatanol into the eye if you are individually intolerant to the drug. Among the adverse reactions:
- burning in the eyes;
- blurred vision;
- redness of the sclera;
- swelling of the eyelid;
- headache;
- nausea;
- runny nose.
Dose: 1 drop 2 times a day. The duration of therapy is determined by the doctor.
Opatanol is not a cheap remedy: it is sold in pharmacies for 370 rubles.
Opatanol relieves allergic conjunctivitis, but expectant mothers should use the drug only as prescribed by a doctor
Traditional medicine
To get rid of conjunctivitis, “grandmother’s” recipes are often enough. The action of medications is aggressive, so the doctor, having determined the causative agent of the disease and the degree of damage to the conjunctiva, can recommend herbal medicine.
The role of anti-inflammatory decoctions and infusions, which also have bactericidal properties, increases in the 1st trimester of pregnancy, when it is better to do without taking drugs orally.
Popular recipes for remedies for conjunctivitis:
- Compress with chamomile. 1 tsp. Dissolve chamomile flowers in 1 cup of boiling water. The infusion should cool to room temperature. Dip cotton pads into the liquid and apply lotions to the affected eye (4-5 times a day).
- Fresh dill. Grind the herb and squeeze out the juice. Soak a cotton swab with dill juice and wipe your eyes. Repeat the procedure several times a day.
- Potatoes with eggs. Grate the raw potatoes on a fine grater. Separate the white from the egg, pour into the potatoes, stir. Wrap the mixture in gauze and keep it on the sore eye for 15 minutes as a compress.
- Aloe juice. Squeeze the liquid from the leaves of the plant (from 2 years old). Dilute with water in a ratio of 1:10. Rinse your eyes with the resulting solution.
Photo gallery: folk remedies against conjunctivitis
Chamomile will ease the symptoms of conjunctivitis and have a bactericidal effect
Potato compress helps with mild forms of the disease
Aloe has long been used to treat infectious inflammations.
It’s not easy to squeeze juice out of dill, but this remedy will help overcome conjunctivitis.
Prevention and treatment rules
To avoid getting conjunctivitis, you should carefully observe hand and eye hygiene. You should not touch your eyelids with dirty hands, rub your eyes, or try to remove specks with your fingers. During pregnancy, it is not advisable to use decorative cosmetics so as not to provoke allergies and irritation.
A pregnant woman should use a personal towel for her face and hands that only she uses. The towel should be washed regularly, dried in the open air (preferably) and ironed with a hot iron. You can't sleep on someone else's pillow with a dirty pillowcase, but only on your own. The pillowcase also needs to be ironed with a hot iron after washing.
If you feel itching in your eyelids, you need to wash them with infusions of medicinal herbs (chamomile, sage). If you suffer from allergic conjunctivitis, herbal applications should be cold. For viral/bacterial infections, compresses should be warm.
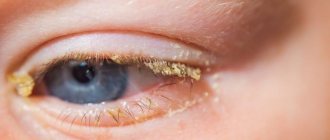
When crusts appear on the eyelids, they must be removed. Rinse your eyelids with boiled cool water and use tea leaves. The crusts must first be soaked and then carefully removed with a cotton pad. For disinfection, use a solution of furatsilin or a slightly pink solution of potassium permanganate.
If your eyes are very itchy, use safe drops such as artificial tears: they temporarily relieve discomfort in the eyes. These drops do not have a negative effect on the fetus, since they do not penetrate the mother’s bloodstream.
To defeat the disease, it is necessary to strengthen the immune system. Eat more fresh vegetables, herbs and fruits. In winter, you need to use vitamin complexes after approval by the gynecologist.
Recommendations for eyelid hygiene
Eyelid hygiene for blepharitis is the basis of treatment. This is confirmed by a number of scientists from the Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, Research Institute of Eye Diseases, Russian Academy of Medical Sciences, who observed several dozen patients suffering from blepharoconjunctivitis and developed a number of measures for eyelid hygiene, including preventive and therapeutic measures.
For this purpose, a whole range of effective hygiene products has been developed: Blefarogel 1, Blepharogel 2, Blepharogel, which are based on natural plant extracts and hyaluronic acid.
With daily use of compresses and self-massage with the help of these drugs, they cleanse, moisturize the skin, increase elasticity, and have antiseptic properties. In addition to professional products, you can cleanse with a decoction of calendula, chamomile, and furatsilin solution.
To do this, use a sterile cotton swab moistened with a solution to wipe the eyes from the outer edge to the inner. The procedure must be carried out 3-4 times a day. To remove sebaceous secretions, use alcohol tincture of calendula and wash with baby or tar soap.
Easily becoming chronic, blepharitis can cause serious complications. Therefore, during treatment, it is important to observe hygiene procedures and use medications as directed by the doctor. In addition to drops, ointments, folk remedies, and physiotherapy are used to treat blepharitis. Complex cases require antibiotics and injections.
Bottom line
Before treating conjunctivitis during pregnancy, you need to consider the safety of the fetus. Even local use of medications is unsafe for the fetus, because the chemical components partially penetrate into the mother’s blood. This is also unsafe for the child. Therefore, medications are prescribed to pregnant women in exceptional cases if there is a risk to the mother’s health. The therapy is carried out under the constant supervision of a gynecologist who monitors the baby’s condition.
If a woman falls ill with a non-dangerous form of conjunctivitis, you can get by with traditional medicine - herbal remedies, propolis water or tea leaves. Symptoms of conjunctivitis quickly disappear with frequent use of rinsing and application to the eyelids. In the acute form, applications are done every hour; in the subacute form, you can wash the eyelids (4-5 procedures per day). Everything is determined by the form of conjunctivitis and the source of the disease. In case of allergic inflammation of the visual organs, you can get by by eliminating the source of irritation.
Sources used:
- Atlas of Clinical Ophthalmology / D.J. Spalton. - M.: MEDpress-inform, 2007.
- Objective study of pupillary reactions and movements of the eyeballs / A.R. Shakhnovich, V.R. Shakhnovich. - M.: Medicine, 2005.
- Damage to the organ of vision in infectious diseases / Yu.Ya. Vengerov. - M.: Medicine, 2006.
- IU School of Medicine Department of Ophthalmology