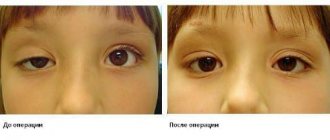
Strabismus may be congenital. It is diagnosed, as a rule, in the first days after birth. With something purchased, everything is much more complicated; small deviations are not always immediately noticeable. Only a specialist, an ophthalmologist, knows how to determine strabismus by type and type, and assess its severity.
The disease can also appear with age. Therefore, at the first suspicion of a disease, you need to consult a doctor. You can determine strabismus yourself by passing a simple test.
Definition of phoria for distance
You need to look out the window and focus on a small, contrasting, stationary object. A bird sitting on an antenna is suitable for this. It will stand out well against the background of a light sky. Having fixed your gaze, you need to alternately cover your left and right eyes with your palm. The palm should be at some distance; you should not press it to your face. The duration of the test is 1-3 minutes, and the frequency of eye changes is 1-2 seconds. You cannot look at an object with both eyes at the same time. In patients with normal vision, the image looks like a picture through a transparent palm, which is located next to an opaque one. If the object (in this case a bird) does not move from side to side and does not jump up and down, then there is no hidden strabismus.
If there is movement of the object to the side, then hidden horizontal strabismus is diagnosed.
If, when changing palms, the object shifts towards the eye that is being opened and at the same time it is necessary to turn the head in the same direction, then we are talking about hidden convergent strabismus (inphoria, esophoria). If, on the contrary, the object shifts in the opposite direction when the eye opens, then a diagnosis of hidden divergent strabismus (exophoria) is made.
When an object moves up or down, vertical hidden strabismus is diagnosed. This condition is quite rare and is divided into four types:
- If there is a symmetrical downward displacement of the object when opening and closing both eyes, then the pathology is called hypersupraphoria (hidden upward deviation of both eyes).
- If, when opening different eyes, the object moves first up and then down, then the pathology is called hyperinfraphoria.
- With a simultaneous downward displacement of the object, which is symmetrical on both sides, the disease is called hypoinfraphoria.
- If there is a hidden deviation of the right eye downward and the left eye upward, then the pathology is called hyposupraphoria.
Symptoms and signs of strabismus
The deviation, if it is not congenital, often appears and develops at an early age. It does not always manifest as a visually noticeable disorder. According to its origin, heterotropia can be of two types, paralytic and concomitant, it depends on the etiology.
Friendly strabismus
With this type of strabismus, the following symptoms appear:
- three-dimensional vision impairment;
- both eyes can squint in turn;
- if the gaze stops at a static object, one of the eyes deviates;
- ametropia or anisometropia are present;
- the mobility of the eyeballs is free and without disturbances;
- the deflection angles are equal to each other (primary and secondary);
- when looking at objects, double vision does not occur;
- a squinting eye may see worse.
There are several forms of such strabismus. According to the classification, they are divided into non-accommodative, accommodative or partially accommodative.
Paralytic strabismus
This type of heterotopia occurs due to damage to the eye muscles. As a rule, only one eye squints. The signs of paralytic strabismus are:
- three-dimensional vision is impaired;
- periodically feel dizzy;
- diplopia (split objects) is observed;
- the head tilts towards the squinting eye;
- The secondary deflection angle is greater than the primary one.
The main feature of paralytic strabismus is that the movement of the diseased eyeball in the direction of contraction of the affected muscle is limited.
Determination of strabismus in near vision
For objects located nearby, a similar study is carried out, which makes it possible to identify phoria. To do this, fix your gaze on a close object, for example, a finger or pencil. Most often, the object is placed at a distance of 35-45 cm. Decoding deviations for strabismus does not differ from the test for distant objects. It is very important to maintain fixation on a nearby object during this test. In some cases, the patient can imperceptibly shift his gaze to an object located in the distance.
Treatment methods for strabismus
Medication alone cannot cure strabismus, however, they can speed up the healing process. These include drops to improve vision, drugs that relax the muscles of the eye and prevent pupillary constriction. And the main methods of treating strabismus include non-hardware procedures (sets of exercises, glasses and lenses), hardware treatment and surgery.
Acquired strabismus in adults is more difficult to correct, since their vision has already been fully developed. In such cases, often with the help of optical methods, a new model of stereoscopic vision is formed (that is, with the help of lenses a person sees better, but the problem is not solved).
Surgical intervention is necessary in cases where a person is not content with a partial improvement in appearance: after all, the surgeon will not restore binocular vision, but he can “put the eyes back in place” by removing or weakening the eye muscles.
And only modern hardware procedures can “teach” the eyes to see correctly. Here are some popular hardware techniques that your doctor may suggest to eliminate strabismus.
You may be interested in: Strabismus is being treated in a new way in Ukraine
Determination of phoria value
It is not always possible to determine the size of the phoria alone, so it is better to seek the help of a friend. It is necessary to install the chair at a distance from the window that is a multiple of one meter. This can be any distance. But the farther the chair is from the window, the more accurate the study. After this, you must complete all the points necessary to determine phoria. During the study, it is necessary to mark on the glass the points at which the object appears when the right and left eyes are opened. Usually an assistant is required for this manipulation. You can point him to a specific point using a laser pointer.
After the test, you should measure the distance between these points, and then, using the resulting indicator, calculate the phoria value using the formula:
- R=I/L, where r is the phoria value, I is the distance between points on the glass in centimeters, L is the distance from the chair to the glass in meters.
For clarity, let’s consider an example: the study was carried out from a chair located at a distance of three meters from the window. The distance between the points on the glass was 30 cm. Therefore, the phoria value in this example will be 10 prism diopters. If you convert it into degrees (the prism diopter is 0.5 degrees), you get that hidden strabismus is 5 degrees.
Hardware methods for treating strabismus
The monobinoscope device is used in the treatment of amblyopia and double vision. In such cases, the retina of the eye is exposed to light rays. The choice of this method depends on the age of the patient and the stage of development of strabismus.
A set of computer programs for restoring binocular vision (both eyes see the same picture) allows you to correct strabismus defects in 70% of cases.
Infrared laser therapy. This method of laser vision correction can help the eyes focus correctly; infrared radiation restores the muscles of the eye, improves tissue nutrition and eliminates spasms.
Magnetotherapy (ATOS). This device affects the eyes using a magnetic field. It is usually used for inflammation of the eyes, but in combination with a special attachment, magnetic therapy is effective for treating the problem of the “lazy eye” - amblyopia.
The Forbis device is used for diagnosis and treatment using the diploptic method (a procedure for consolidating restored binocular vision).
Synoptophore “Sinf-1” is suitable for complex treatment of strabismus and helps restore a single image, training general eye mobility.
You may be interested in: How to treat strabismus in children?
conclusions
- Identifying strabismus is a complex process. To make a full diagnosis, you need to undergo a series of medical tests and collect a complete medical history of the patient.
- When identifying pathology, congenital and acquired factors are taken into account, because In most cases, strabismus is a hereditary disease.
- To correctly prescribe treatment, you need to determine the type and angle of strabismus. For this, the following methods can be used: identification of the strabismus angle according to Hirshberg, study with Synoptophore, Belostotsky-Friedman color test, Worth test, raster haploscopy.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease is not difficult. It is enough for the doctor to disrupt the patient’s binocular perception by closing one eye. If the organ of vision affected by hidden strabismus remains open, this will become noticeable by the pupil slowly “floating” to the side.
To confirm the diagnosis, additional measures will be required:
- collecting anamnesis and complaints to identify additional signs and symptoms of the disease, as well as to establish heredity or other causes of the deviation;
- ophthalmoscopy to identify fundus pathologies that can lead to changes in the functionality of the extraocular muscles;
- checking visual acuity (visometry) to identify visual impairments (farsightedness, myopia, etc.), which may be the main cause of the disease;
- tests according to the Maddox and Graefe method, establishing the degree of change in the functions of the eye muscles;
- checking the patient’s visual field (perimetry), which allows to identify eye diseases that cause hidden forms of strabismus;
- biomicroscopy, revealing hidden infections of the conjunctiva that can provoke the disease.
These diagnostic techniques will help to establish the causes of the pathology and select optimal treatment regimens.
Types of research - how to test yourself for strabismus, what norms and deviations exist
To establish an accurate diagnosis and measure the angle of strabismus, specialists can resort to various diagnostic methods. This material will tell you about heterophoria in adults and children.
These include the following:
- determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirschberg;
- study with synoptophore;
- Belostotsky-Friedman color test;
- Wars test;
- raster haploscopy.
Let's look at each of the methods in more detail.
Determination of the strabismus angle according to Hirschberg
As part of the diagnosis, an ophthalmoscope is used. The scheme includes the following stages.
- Turning on the device.
- Direction of the patient's gaze to the hole located in the central part of the device.
- Fixing the location of light glare by an ophthalmologist.
- The glare on the healthy eye is located strictly in the central part of the pupil.
- The diseased eye demonstrates fixation of glare at some distance from the pupil.
- Measuring the deflection angle.
- Switching off the device.
This article will tell you about concomitant strabismus and how it manifests itself.
The angles of strabismus can be different, depending on the location of the flare. The standards are as follows:
- if the glare does not leave the pupil, the angle is at 10 degrees;
- when the light point is located at the edge of the pupil, the deviation angle will be 15 degrees;
- when the highlight is in the middle of the iris, the angle varies from 25 to 30 degrees.
After the diagnosis is completed, the specialist compares the primary and secondary strabismus angle. Primary is the angle affected by strabismus, secondary is an indicator of a fully functioning eye. Conclusions are drawn about the need for surgical intervention. Find out what orthoptics and diploptics are here.
If the reading exceeds 15 degrees, surgery is performed. In other cases, vision is corrected using hardware.
How to determine the angle of strabismus with Synoptophore
Synoptophore is one of the most popular devices for haploscopic diagnostics. The device mechanically separates the fields of view. For this purpose, two optical movable tubes are provided. With their help, testing is carried out using paired test objects.
The use of the device is also practiced for the purpose of conducting a set of orthopedic exercises.
Inside the device, test objects can move in the vertical, horizontal direction, counterclockwise and clockwise. They differ in the type of control elements for each eye. By combining paired drawings, you can understand whether binocular fusion is present or absent. If it is absent, this indicates the presence of a functional scotoma. Having discovered that there is still a fusion, fusion reserves are determined. To do this, the test objects are brought together or separated until doubling of the test objects appears. The presence of positive or negative fusion reserves is determined. Is it possible to get a license with protanopia? Find out here.
The use of Synptophor makes it possible to establish the angle of strabismus (objective or subjective), determine the ability to merge images of objects, establish fusion reserve, and detect functional scotoma.
Bialystotsky-Friedman four-point color test for binocular vision analysis
As part of the Belostotsky-Friedman four-point color test, two blue or green circles are used, the rest are red and white. The patient looks at them through red-green glasses. A red filter appears near the right eye, and a green filter appears near the left eye. The white circle located in the center, when viewed through green and red filters, will be perceived as red or green, based on how dominant the vision of the left or right eye is. If there is monocular vision in the right eye, the subject will see two red circles (when viewed through a red glass). In the case of the left eye, only three are green. Simultaneous vision involves viewing five circles - 3 green and 2 red. Simultaneous vision is characterized by viewing four circles - a pair of green and red.
Using polaroid or raster Bagolini filters, as in the case of using a color device, there is a common object to merge, as well as several objects that can be seen with only one eye.
Note that color tests are used not only to determine strabismus, but also to identify color blindness. For this purpose, a table of color perception for drivers with answers can be used.
The methodology for analyzing binocular vision differs depending on the degree of “dissociating” action. In color equipment it is characterized by greater severity, while in raster and polaroid tests it is less pronounced. The reason is that with glasses the conditions become as natural as possible.
Worth's test - a method for testing vision in adults and children
The Wars test is carried out using a sign projector. It allows you to evaluate the nature of vision when both eyes are open. The test allows you to determine what kind of vision children and adults have - monocular, simultaneous or binocular type. The technique also helps to identify vertical phoria.
The test involves two green figures perceived by a person through green glass. There is also one red figure, which the patient looks at through red glass. A white figure is visible with both eyes at once.
With binocular vision, a person sees four figures at once, and five at the same time. Monocular vision involves recognizing either three green or two red shapes.
The four-point test is one of the most popular. Before the test, the patient must move 1-5 meters away. The doctor puts on glasses with light filters. Their right side is equipped with a red lens, the left - green.
Raster haploscopy (Bagolini test)
The Bagolini test involves the use of striped glass in several copies. They are located in a trial frame in a mutually perpendicular direction. The patient wearing these glasses must look at the light source located at a point. Vision is assessed as binocular if, during testing, a person clearly recognizes one light source, and two rays intersect on it, resembling the shape of a cross. In the presence of simultaneous vision, the patient also clearly sees a cross-shaped figure, but the number of sources is increased to two. Monocular vision, accordingly, involves viewing only one beam or two alternating ones in the presence of alternating monocular vision. Read about paralytic strabismus in adults at this link.