Surgery to correct strabismus is possible at any age. It is designed to correct an imbalance in the motor activity of the six eye muscles that control the position of the central axis of the eye. During treatment, the surgeon weakens or strengthens certain muscles, which leads to correction of the position of the pupil in a stationary position and when it moves, when the gaze is transferred from one object to another. The advisability of performing surgery for strabismus in childhood or later is determined by the results of an ophthalmological examination.
General characteristics of childhood strabismus
In this article
- General characteristics of childhood strabismus
- Types of strabismus
- Imaginary strabismus in children
- Causes of strabismus in children
- Diagnosis of strabismus in children
- Treatment of strabismus in children
- Correction of children's strabismus using optics
- Hardware treatment of strabismus in children
- Surgical intervention
- Prevention of strabismus in children
The scientific name for strabismus is strabismus. The pathology is characterized by deviation of the visual axis of one or both eyes while focusing on an object. Simply put, strabismus is a non-synchronous movement of the eyeballs. Normally, the eye muscles move simultaneously when focusing, providing binocular vision, that is, the ability to see surrounding objects with both eyes. Thanks to binocular vision, we see three-dimensional space, the volume of objects, their size, height, distance to them. Newborns lack binocular vision. After 6-8 months, the baby can already focus his gaze on an object, but full binocular vision is formed only by the age of 12.
If any deviations occur during the formation of vision, binocularity will not be formed or will not be formed correctly. Strabismus leads to disruption of the coordinated functioning of the eyeballs. It is not difficult to visually notice the pathology. With strabismus, one or both eyes deviate from their central position. To understand how vision is formed in strabismus, one must understand the difference between the visual and optical axes. The visual line connects the central fovea of the retina with the object being viewed. The optical axis is a straight line that passes through the centers of the refractive surfaces of the lens and cornea. These lines don't match. An angle γ (gamma) is formed between them. When its size is larger than normal, strabismus develops.
In normal binocular vision, images from the right and left eyes are combined into one image. When vision is divided, a single picture is not formed, but double vision occurs. Gradually, the eye with the pathology is switched off from work. The brain begins to perceive visual information with only one eye. Over time, this leads to atrophy, as a result of which monocular vision develops, that is, not three-dimensional, but two-dimensional. The child feels strabismus as a split image.
Results of the operation
Strabismus surgery helps eliminate the patient’s existing cosmetic defect. It turns out that surgery itself does not always lead to the restoration of normal vision. This is due to the fact that while the patient has strabismus, his brain tries to adapt and compensate for the existing lack of vision in accessible ways: very often strabismus is accompanied by the development of amblyopia, in which the affected eye practically does not participate in the visual process. After surgery and restoration of the normal position of the eyes, the patient must actually relearn how to see with both eyes at the same time (binocular vision), and this can take a lot of time and effort. For the speedy restoration of binocular vision, our specialists, according to indications, recommend that all operated patients undergo a course of hardware treatment.
All photographs of patients before and after surgery
Types of strabismus
There are different types of strabismus. Thus, strabismus can be congenital or acquired. In the first case, the deviation is noticeable immediately after the birth of the baby. Its causes are hereditary factors or abnormal development of the fetus during pregnancy. In the course of life, ophthalmological diseases, heavy load on the organs of vision, head injuries and other reasons lead to strabismus.
The disease can manifest itself externally in different ways. Based on the trajectory of the displacement of the visual axis, strabismus is divided into:
- horizontal;
- vertical.
Horizontal strabismus is divided into:
- convergent strabismus (esotropia), in which the eyeballs converge towards the bridge of the nose. It is considered the most common among other forms of strabismus in children.
- divergent (exotropia), when the eyes squint towards the temple.
Vertical strabismus has the following subtypes:
- hypertropia - one or both eyes are shifted upward;
- hypotropia - one or both eyes are directed downwards.
- mixed, a form of strabismus in which the eye can move up to the temple, or down to the bridge of the nose and vice versa.
The deviation can occur in one or both eyes alternately, either on the right or on the left eye. When only one eye squints, such strabismus is called monolateral. With alternating strabismus, the right and left eyes alternately squint.
According to the manifestation of symptoms, strabismus is:
- hidden (heterophoria). Occurs as a result of disruption of the eye muscles. When one eye closes, the other begins to squint. The rest of the time there is no deviation. It occurs rarely and in most cases does not affect vision.
- compensated. This type of pathology can only be detected by a doctor during a special examination.
- subcompensated. Associated with weakening of the muscles of the organs of vision. The cause may be nervous disorders or illnesses.
- decompensated. Appears for no reason. Typically, a concomitant symptom is severe visual fatigue.
Strabismus is also divided into friendly and paralytic. In the first option, the mobility of the eyeball is preserved. It functions as follows: the healthy eye has the same angle of deviation as the sick eye, but in the opposite direction. In this case, binocular vision is not impaired, and the picture does not double.
Paralytic strabismus is characterized by paralysis of one or more extraocular muscles. The eye deviates in the direction of the damaged muscle.
Sometimes strabismus can develop as a result of inflammation or damage to the nerves that innervate (supply) the extraocular muscles. This type of strabismus is called neurological. Quite often, different types of strabismus are combined in a child. So, for example, it occurs:
- intermittent divergent strabismus;
- if the pathology is complicated by myopia, then divergent concomitant strabismus may occur;
- with farsightedness, concomitant strabismus can be convergent.
Imaginary strabismus in children
Let us separately note another type of strabismus in children. In the first weeks after the birth of a child, parents may notice that the baby's eyes are looking in different directions. “Wandering” eyes are not always a symptom of a deviation. This impression is often created due to the structural features of the facial skeleton of a newborn. Many babies have skin folds above the eyelids that cover part of the eye. Therefore, it may appear that the child has strabismus. As the baby grows up, the folds smooth out and the symptoms of strabismus disappear.
These are the causes of imaginary strabismus in children. This type of deviation is not a visual impairment. With false strabismus, the eyeballs move fully, the image does not double. The external manifestation of strabismus should subside a few months after birth. It doesn't need treatment. However, if parents notice a strabismus in the child after birth, it should be shown to a doctor. Only a doctor can distinguish imaginary strabismus from true ones as a result of a special study.
Causes of strabismus in children
Multiple factors can lead to strabismus in children. Congenital and acquired strabismus have different causes. If the disease is diagnosed immediately after birth or in the first three years of the baby’s life, its prerequisites could be:
- disorders during intrauterine development;
- premature birth;
- prematurity;
- hereditary or genetic factor;
- Down's disease, brain tumors, cerebral palsy;
- high intracranial pressure;
- the presence of bad habits in the mother during pregnancy;
- radiation, medication, intoxication, trauma during pregnancy.
Acquired strabismus has other causes and, as a rule, they are associated with ophthalmological diseases. So, the causes of the disease that appeared during life are:
- high degree of farsightedness;
- astigmatism;
- high degree of myopia;
- cataract;
- glaucoma;
- bruises and injuries to the head and visual organs;
- heavy strain on the eyes;
- tumors and neoplasms;
- severe psychological shock, stress.
The manifestation of the disease, as well as subsequent treatment, largely depends on the cause of strabismus.
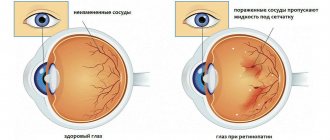
Diagnosis of strabismus in children
Unlike many other eye diseases, strabismus can be detected immediately after it appears. In medical institutions, specialists conduct not only a visual examination, but also a thorough examination of the visual organs with pathology. Modern equipment allows you to correctly recognize the type of disease and determine the cause of the disease.
After identifying external signs of deviation, specialists conduct visual acuity testing and other examinations. These include:
- skiascopy is a method of studying the ability of the eyes to refract rays by illuminating the eye with a beam of light reflected from a mirror;
- determining the angle of strabismus using an ophthalmoscope;
- ophthalmoscopy - examination using special instruments of the fundus to evaluate the retina, optic nerve and blood vessels;
- perimetry - a method of determining visual fields using computer equipment;
- Ultrasound examination (ultrasound) of the eyeball.
Having received a complete picture of the disease, the specialist prescribes treatment, which should be started immediately.
Treatment of strabismus in children
The key to successful and quick treatment of strabismus is early diagnosis. Visiting a specialist immediately after the onset of symptoms of the disease is the first step towards getting rid of the disease. When the disease is detected at the initial stage and the changes have not yet significantly affected the organs of vision, conservative treatment is used, that is, non-surgical.
Correction of strabismus in children is carried out using four main methods:
- correction of strabismus using optical means (glasses or special lenses);
- pleoptic treatment is a method of treating functional underdevelopment of the visual organs;
- orthoptic treatment - hardware therapy that allows a child to develop binocular vision;
- surgical intervention - is carried out with a high degree of change, when the angle of strabismus is large;
- orthoptic postoperative therapy - training with the help of special cartoons and pictures to see with both eyes.
Let's take a closer look at each treatment method separately.
Advantages of surgical treatment of strabismus in the Moscow City Hospital
Our clinic provides its patients with the best conditions for surgical treatment of strabismus. The Moscow Eye Clinic is equipped with the most modern equipment from leading global manufacturers, which does not allow for the possibility of diagnostic errors and negates the likelihood of technical errors during the operation.
The clinic’s specialists are world-class professionals who have all the necessary knowledge and practical skills for the effective treatment of eye diseases of varying degrees of complexity. Our doctors have tens of thousands of successfully performed interventions and satisfied patients with the results of treatment.
The treatment of strabismus in the Clinic is carried out by Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor, Ophthalmic Surgeon Alexander Vyacheslavovich Apaev, who is a senior consultant on the problems of diagnosis and treatment of all types of strabismus, diplopia, complex vision correction, and headed the department of binocular and oculomotor pathology of the Moscow Research Institute of Eye Diseases. Helmholtz.
The operation to correct strabismus is carried out, if possible, in a “one-day” mode, which allows the patient to return home after the operation on the same day, to their usual conditions. Before performing the operation, the doctor will answer all your questions in detail, and after the operation he will tell you in detail what needs to be done to avoid complications and quickly return to the patient’s usual rhythm of life.
We care about our patients, so our doctors provide regular examinations and quality care for all patients until full recovery. We are open seven days a week from 9am to 9pm.
Correction of children's strabismus using optics
Special contact lenses or glasses eliminate the difference in visual acuity between the eyes. With the help of these remedies at an early stage you can completely get rid of strabismus. Special lenses help to form binocular vision, that is, to receive the same images from both eyes and combine them into one clear image. Over time, three-dimensional vision is formed, which will synchronize the work of the eyeballs without the help of optics. In the future, you can refuse glasses.
Conservative treatment of strabismus (without surgery)
The most general, universal approach to non-surgical treatment of strabismus includes the following measures:
- therapy for “lazy blindness” (meaning amblyopia - loss of visual functions and qualities by the squinting eye due to the fact that the central nervous system turns it off from the process of forming a visual image);
- correction of refractive error (farsightedness, astigmatism, myopia);
- calculation and prescription of corrective glasses or contact lenses with periodic changes in their optical power according to an individual scheme;
- restoration of binocular vision function (the ability of the brain to synthesize a holistic image using and combining images from both eyes);
- stimulation of insufficiently active elements of the visual system.
Any course of treatment for strabismus involves constant monitoring of the condition of the retina, fundus, and optic nerve - in order to exclude any complications or side effects.
Pleoptics
Like optics, the pleoptics method is one of the options for correcting childhood strabismus without surgery. The essence of the therapy is to completely cover the healthy eye with an overlay. This method is called occlusion. Having lost the ability to receive an image from a healthy organ of vision, the brain connects the eye with pathology to work.
Another option for the same therapy is the use of the drug atropine. The product is instilled into the healthy eye and temporarily relaxes its accommodation. This is the ability of the eye to see equally well at both close and far distances. Thus, the drug forces the eye to work abnormally. The bandage is not used in this case.
Possible complications after surgery to correct strabismus
Modern ophthalmic surgery gives very high results in the surgical treatment of strabismus. Only in 10-15% of cases there is a residual slight strabismus. In this case, it is not entirely correct to say that there is a “complication”, since this mild violation does not affect the quality of life and professional activity. If, as a result of the operation, the strabismus remains significant, a repeat operation is possible. Treatment of strabismus affects only the extraocular muscles, so surgical procedures do not pose a risk to vision. Re-intervention is recommended if there is significant residual eyeball obliquity.
One of the possible complications after surgical treatment of strabismus may be infection of the surgical field. However, this problem is easily solved with drops containing antibiotics. These drugs can also be prescribed for prophylactic purposes in the first postoperative days.
In the first hours or days after surgery for strabismus, double vision (diplopia) may be observed. If vision does not return to normal within a few days, additional corrective measures may be required. Fortunately, this complication is extremely rare.
Hardware treatment of strabismus in children
After the defect is eliminated, it is necessary to develop three-dimensional vision in the child and teach the brain to perceive visual information with two eyes. For this purpose, hardware treatment is used. The method is based on the use of specially developed computer programs. The field of vision of both eyes of the patient is divided and certain pictures are shown. Combining them into one image helps form binocular vision. Children are shown cartoons using a special device called Amblyocor, which changes the sharpness of the image. At this moment, the brain tries to find a way to get a clear image, which turns out to be binocular vision.
Postoperative period and rehabilitation
Surgical treatment of strabismus gives an immediate visible result - the position of the eyeballs during the visual process becomes correct (symmetrical). However, eliminating a cosmetic problem does not mean complete normalization of visual functions. Since strabismus leads to significant disturbances in the brain processes of visual perception and image analysis, the patient, as a rule, after surgery will undergo a course of exercises and procedures that help restore binocular vision and three-dimensional perception of the surrounding picture of the world. The main task of postoperative rehabilitation after surgical treatment of strabismus is to “teach” the visual system to function correctly again. Most often in modern ophthalmology, hardware treatment is used for these purposes. An individual course of rehabilitation exercises allows you to expand the fusion reserve and re-include the eye in which the movements of the eyeball were impaired in the work of the visual system. The goal of such a course is to achieve an equivalent perception of the pictures formed on the retina of both eyes, and to merge them in the corresponding structures of the brain into a single image.
The Moscow Ophthalmology Center offers patients with strabismus a comprehensive examination and multi-stage treatment, including surgery and rehabilitation, individual programs of conservative care, hardware and physiotherapeutic procedures.
Surgical intervention
Surgery to correct strabismus in children is performed only when conservative treatment has failed. In modern ophthalmology, this type of surgical intervention is considered uncomplicated. The operation is performed under local anesthesia and lasts about 30-45 minutes.
The prerequisites for the operation are:
- large angle of strabismus;
- paralysis of the eye muscles;
- damage to the extraocular muscles;
- disruption of innervation.
During the operation, overstressed muscles are loosened and weak ones are strengthened through surgery. This method helps to achieve balance for the correct location of the eyeball in relation to the central axis. In some cases, not one, but several operations are required.
It should be noted that this operation is not associated with the return of visual acuity. Its goal is to restore the synchrony of eyeball movements. Next, you will have to correct your vision with glasses, visual gymnastics and hardware treatment. Gymnastics for the eyes
To remove overstrain and relieve eye fatigue, experts have developed simple exercises. Two adults need to do eye exercises with children. One of them should hold the child's head so that he performs the exercises only with his eyes.
For the youngest patients, visual gymnastics will resemble a game. You should take the toy and move it sideways at a certain distance: up and down and left and right. Movements must also be made in a circle, diagonally and in a spiral. Schoolchildren can do eye exercises on their own. Exercises involve focusing on an object located at a far and close distance. You need to take turns looking at the thing that lies nearby and the one that is further away. There are many types of concentration exercises. The attending physician will certainly recommend several suitable ones. They should be performed daily at a slow pace before bed. Each must be done 3-5 times.
Types of operations
All interventions performed for strabismus can be divided into weakening and strengthening. In the first case, the doctor changes the place of attachment of the muscle, that is, it is transplanted further from the cornea. As a result, the influence of the muscle on the eyeball decreases. This operation is performed on the muscle located on the side of the eye deviation.
During augmentation surgery, the muscle is shortened by removing part of it. The attachment of the muscle to the eye is not moved. This operation is suitable for the muscle that is located on the opposite side. As a result of surgery, the doctor restores the correct muscle balance.
The type of surgical intervention can only be determined during the manipulation, because a number of important features are taken into account (anatomical features of the location of the muscles, the angle of strabismus, the general condition of the oculomotor system, the age of the patient). Usually the operation affects several muscles. If there is alternating strabismus, then it is advisable to perform a simultaneous operation on the same muscles of the eyeball on both sides.
If there are indications, combined operations are performed, during which a weakening intervention is performed on one muscle, and a strengthening one on the other.
Prevention of strabismus in children
Fragmentation of the eyes is not only an external defect, it is also a serious vision problem. For people with strabismus, a fairly large list of professions may be prohibited. Meanwhile, simple prevention methods will help you avoid the disease. The room where the child is located should be well lit. It is advisable to place the crib next to a window to allow more daylight. Today, almost every baby’s crib has a mobile with toys hanging over it. However, most parents do not attach importance to its location. Adults do not realize that an object can have a significant impact on a baby’s vision. The baby's attention is attracted by bright toys, he watches their movement. They should be at a distance of about 50 centimeters from the baby’s head and placed in such a way that the child does not squint his eyes when looking at them.
Growing up, the baby begins to draw, color pictures, and sculpt. During this period, it is important to monitor visual load. Overstrain of the visual organs can lead to strabismus. You should not give your child gadgets too early. It is better to postpone acquaintance with technology until the age of 7. But even after reaching this age, passion for phones and tablets should be limited.