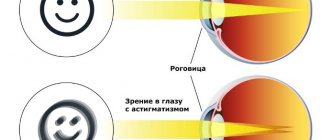
Main symptoms:
- Pain in the eyes
- Pain when moving the eyeball
- Hypersensitivity to light
- Headache
- Inability to fully open the eye
- Corneal edema
- Feeling of sand in the eyes
- Fever
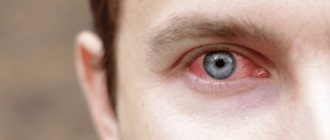
- Redness of the eyes
- Corneal opacity
- Tearing
Electroophthalmia is an inflammation of the outer membranes of the eyes that occurs as a result of strong exposure to ultraviolet rays, which are actively absorbed by the retina and cause chemical changes in it. This pathological process has other names - photoophthalmia or snow blindness.
- Etiology
- Classification
- Symptoms
- Diagnostics
- Treatment
- Possible complications
- Prevention
Electroophthalmia occurs quite often, is mostly an occupational disease, observed in welders, climbers, polar explorers, and skiers. It is diagnosed at the first examination by an ophthalmologist. If the degree of eye damage is not higher than average, then the prognosis from therapeutic measures is positive; the main thing is to immediately consult a doctor and begin timely treatment.
Effects of ultraviolet radiation on vision
Ultraviolet radiation has several sources. The main source of radiation is natural. The ozone layer of the earth is a filter for a large number of light spectra - up to 29 nanometers. This is the most harmful spectrum of radiation. However, waves above this value can be harmful to the eye, causing damage to the organs of vision.
Such effects occur when a person is high in the mountains among mountain peaks covered with snow, illuminated by the sun. The shine of snow crystals is reflected on the eye membranes; ultraviolet rays can contribute to the appearance of photoophthalmia.
The concept of “snow blindness” characterizes a type of disease when a person looks at the bright rays of the sun for a long time without glasses with tinted lenses. Another name is “glacier catarrh”. It is found among climbers, skiers, and in polar conditions among employees of Arctic and Antarctic stations.
A similar natural effect is possible when a person looks at lightning or flares in the sun. Observers of solar eclipses often suffer eye burns.
Artificial sources of ultraviolet radiation - electric arc welding, various medical lamps, including quartz, and other lighting devices. They determine the risk of exposure to radiation on the organs of vision for people in relevant professions:
- welders involved in welding work, widely used in construction, in metallurgy in the production of pipes and rolled metal;
- medical workers who quartz rooms or use lamps to treat respiratory, skin and other diseases;
- employees of beauty salons where solariums of various modifications are installed.
Electroophthalmia is diagnosed simply, the symptoms are clearly manifested. If you consult a doctor in time, the treatment will take place without consequences. But lack of medical care can lead to partial or even complete blindness.
Symptoms of electroophthalmia
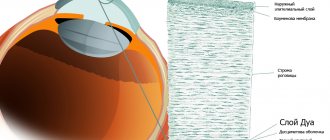
Electroophthalmia (ultraviolet keratitis) is a pathology accompanied by inflammation. It leads to thinning of the tissues of the eye. A burn occurs in the cornea, the transparent membrane of the eyeball that refracts the light flux.
The impact of UV radiation occurs not only on the superficial layers of the cornea, but also on the deeper ones. Gradually, the phototoxic process penetrates the structures of the organ of vision and, without medical assistance, leads to unpleasant consequences, including blindness.
The inflammatory response is the body’s defense process to exposure to light that is excessive and traumatic. Symptoms appear 4-6 hours after exposure to radiation. At the first moment of the pathophysiological course of the disease, the sensitivity of the cornea is lost, the gradual restoration of sensitivity manifests symptoms.
The first to react are the nerve endings and blood vessels of the eyeball.
Signs of electroophthalmia can be subjective and objective, that is, visible from the outside.
Observed
- Swelling of the corneal epithelium, the transparent membrane of the eyeball.
- Redness of the conjunctiva, the connective membrane of the eye.
- The epithelial layer of the cornea becomes cloudy.
- Tearing.
- Blepharospasm, involuntary blinking, twitching of the eyelid, closing it.
- Decreased visual acuity.
- Increased body temperature.
- Headache.
- Photophobia, which manifests itself in particularly strong sensitivity to light. There is an involuntary closing of the eyelids, an involuntary desire to close the eyes in order to protect them.
- Sensation of a foreign body, dust and sand in the eyeball.
Degrees of eye damage due to ultraviolet keratitis
In ophthalmological practice, 4 degrees of damage from ultraviolet radiation are considered:
- Easy. It is characterized by mild clouding of the cornea, a reddish color around the eyes, a burning sensation and itchy pain.
- Average. Associated with corneal erosion, severe itching, painful symptoms, photophobia, and a desire to protect the eyes.
- Heavy. There is a decrease in visual acuity, nagging pain, and unpleasant painful sensations in the eyelid area. There is severe swelling of the eyelids and significant clouding of the cornea.
- Very severe electroophthalmia. May lead to complete or partial blindness. It is impossible to open your eyes due to severe pain. This is a manifestation of the process of desquamation of the epithelium, the death of damaged cells of the conjunctival membrane.
Basic Physics
Ultraviolet radiation is a wave whose length ranges from 10 to 400 nm. Visible light has a wavelength above 380 nm, X-rays emit a wavelength less than 10 nm. The effect of radiation on the human body depends on the length of its waves. The longer, the weaker the impact. People practically do not feel UV A rays. With prolonged exposure, UV B rays can cause burns to the mucous membrane or skin. UV rays shorter than 280 nm have a very aggressive effect. They easily penetrate all layers of the eye and destroy the retina.
Welding is used in construction. Products and blocks are connected using a welding arc. An arc is an electrical charge that has great power and lasts for a long time. In a welding arc, waves have a length of 100 to 300 nm. The most common sources of UV rays are electric arcs and autogen. These are the so-called temperature emitters. Also, medical personnel are exposed to UV exposure when working in physiotherapy rooms, who are engaged in photocopying and water sterilization.
With constant exposure to UV radiation, acute and chronic eye diseases occur. Acute pathology is electroophthalmia or photoophthalmia. Conjunctivitis develops. In case of chronic damage - conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
You may be interested in Episcleritis: symptoms, diagnosis, treatment
Occupational eye injuries have a very wide spectrum. Numerous injuries and burns are not all the charms. There are chemical and toxic effects on the organs of vision. Harmful effects occur in industrial enterprises. Cement, coal, sawmills. Especially the chemical industry, where people work with acids and alkalis. Vapors of benzene, phosphorus, lead, iodine compounds at high concentrations cause a burn of the conjunctiva, as a result of which pathological changes begin in the eye.
As a result of toxic effects, the retina and optic nerve are affected. And there are frequent cases of toxic glaucoma and cataracts. And in all cases of changes in the organ of vision, special attention is paid to the effects of various types of radiant energy: infrared, ultraviolet, ultrasound, x-rays, radio waves, microwaves. Contact with these rays causes the disease – electroophthalmia.
— Infrared irradiation causes cataracts in steelworkers, glassblowers, and, in general, in hot shop workers. May lead to hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous body.
— X-ray radiation can also lead to the development of cataracts. It all depends on the radiation dose.
— Hard gamma radiation causes the development of cataracts, similar in nature to x-rays.
— Excess microwave radiation leads to clouding of the lens of the eye.
What can make problems worse
When symptoms of electroophthalmia appear, there is an immediate urge to rub your eyes. This cannot be done. Rubbing your eyes can cause an infection.
Rinsing with clean water requires caution, as it carries the risk of creating an additional irritant.
You should not use folk remedies such as tea leaves, honey, aloe juice immediately after the onset of symptoms. They may cause irritation. It is possible to add eye baths after a day or two, when the symptoms of the acute condition have subsided.
Eye drops not specifically intended for burn conditions should not be used. They cause irritation.
Treatment
Before going to a medical facility, the patient should be given first aid for electroophthalmia, namely:
- it is necessary to apply a cold bandage or compress to the eyes;
- eliminate the influence of ultraviolet radiation.
To relieve pain, special drops or ointments with an analgesic effect are prescribed, and compresses may be prescribed.
Antibacterial drops are used. Vasoconstrictor and anti-inflammatory drops may also be additionally prescribed.
Until vision is completely restored:
- Do not rinse your eyes with tap water, as this can cause infection;
- you should not rub your eyes so as not to aggravate the condition;
- use folk remedies only after consultation with your doctor;
- Take painkillers correctly, as excessive use slows down the healing process.
After rehabilitation, it is necessary to visit an ophthalmologist to prevent the development of complications. Self-treatment is unacceptable.
Treatment of ultraviolet keratitis
When symptoms appear, you should apply a cold lotion to the eye area and wear dark glasses. You can rinse your eyes yourself with saline solution or clean, bottled water.
You can apply tea bags or a compress with chamomile infusion. It is acceptable to use artificial tears and eye moisturizers.
Medical care begins with examination and diagnosis.
Diagnostics
Examination and questioning of the victim allows us to draw up a clinical picture of the disease. It needs to be clarified through a medical examination.
The diagnosis is made based on medical history, the presence of clinical symptoms and the results of hardware examination.
- The medical history includes a description of the ultraviolet exposure factor.
- Clinical symptoms include a set of symptoms and signs of the disease that describe the condition of the damaged eye. The severity of each symptom and their combination is determined.
- Visometry is performed - a procedure for establishing visual acuity using tables.
Hardware studies are carried out using ophthalmoscopy and biomicroscopy methods. They are used to clarify the diagnosis and differential diagnosis, that is, to identify previously occurring diseases of the visual organs.
The ophthalmoscopic method involves examining the fundus and retina using an ophthalmoscope instrument or special lenses.
To perform biomicroscopy, a microscope with a special light system is used. The method allows you to detect the slightest changes and disturbances inside the human eye.
Making a diagnosis allows you to apply the necessary treatment methods. Therapy must be comprehensive so that complications and vision problems do not arise later.
It is necessary to use medicinal methods to influence various groups of symptoms.
Directions of treatment
- Relieving pain syndrome.
- Reduced corneal edema.
- Anti-inflammatory therapy.
- Prevention of bacterial infection
- Stimulating the epithelization of corneal defects, that is, the tightening of the damaged surface with a new epithelial layer. This takes two to three days.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of pathology involves an initial examination. In addition, the specialist must find out the cause of the inflammatory process in the cornea and differentiate the disease from other similar diseases. Special studies are prescribed to examine the condition of the fundus, retina and corneal layer. In addition, the degree of inflammation must be assessed.
Electroophthalmia can be diagnosed using:
- visometry;
- ophthalmoscopy;
- biomicroscopy;
- fluorescein test.
After all the research has been carried out and an accurate diagnosis has been made, a set of treatment measures is selected.
Drugs
Painkillers
Painful sensations are relieved with the help of anesthetic solutions - local pharmacological painkillers: Lidocaine, Trimecaine, Novocaine, Dicaine, Tetracaine. They act on nerve endings, isolating impulses leading to the central nervous system - the central nervous system, relieving pain.
When the pain syndrome manifests itself in a severe form, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) are acceptable: Diclofenac, Indocollir, Indomethacin. They have a complex effect: in addition to the analgesic effect, they reduce inflammation and reduce temperature.
Relieving swelling and inflammation
Swelling, inflammatory manifestations, itching, redness are relieved by pharmacological agents of the vasoconstrictor type. These include drops: Visin, Proculin, Visoptin. These medications are designed specifically to treat the eyes, acting on the alpha-adrenergic receptors in the blood vessels of the eye. Vasoconstriction can lead to increased intraocular pressure; this indicator must be monitored.
Infection is prevented by using medications containing various antibiotics. Manufactured in the form of drops or ointments: Tsipromed, Gentamicin, Erythromycin, Signicef, L-Optic, Rompharm. They are classified as topical ophthalmic drugs.
Regeneration
Tissue healing, the regenerative function of the cornea, the possibility of restoring epithelial tissues are supported with the help of pharmaceuticals Solcoseryl, Actovegin, Korneregel, Balarpan. Once on the tissues and mucous membrane of the eye, they compensate for the need for various substances, such as collagens, pantothenic acid, which promote the renewal of cells in the tissues of the eye membranes.
Metabolic drugs promote tissue repair. Taufon drops are highly effective. Contains the amino acid taurine, an anti-cataract agent.
Recently, some of the drugs that relieve pain, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and antibacterial ointments containing antibiotics, are used less and less for treatment, since they have been found to slow down the restoration of the epithelial layer of the cornea.
They are replaced by antibacterial eye drops: Tobrex, Tobradex, Levofloxacin, etc. They belong to the group of aminoglycosides, natural and semi-synthetic antibiotics that fight bacteria, penetrating cells and destroying pathogens. They have a wide spectrum of antibactericidal action, one of the areas is ophthalmological practice with a set of symptoms characteristic of burn damage to the membranes of the eye.
The treatment regimen should be developed by an ophthalmologist after identifying all concomitant diseases, the presence of allergic reactions and individual sensitivity to various groups of dosage forms.
The main complications of photoophthalmia
- Chronic redness, hyperemia of the eyes.
- The appearance of clouding of the transparent cornea of the eye - leukoma, which in everyday speech is called a cataract.
- Injuries to the cornea leading to tissue damage or scarring.
- Loss of vision, partial or complete.
What brands of contact lenses are you familiar with?
- Acuvue lenses 43%, 3543 votes
3543 votes 43%3543 votes - 43% of all votes
- Air Optix lenses 17%, 1386 votes
1386 votes 17%
1386 votes - 17% of all votes
- Optima lenses 17%, 1358 votes
1358 votes 17%
1358 votes - 17% of all votes
- Pure Vision lenses 11%, 925 votes
925 votes 11%
925 votes - 11% of all votes
- Biofinity lenses 6%, 477 votes
477 votes 6%
477 votes - 6% of all votes
- Biotrue lenses 4%, 340 votes
340 votes 4%
340 votes - 4% of all votes
- Clariti lenses 2%, 176 votes
176 votes 2%
176 votes - 2% of all votes
Total votes: 8205
Voted: 4677
17.01.2018
×
You or from your IP have already voted.
Prevention of electroophthalmia
There are situations when it is necessary to take special measures to prevent vision problems associated with burn processes. This applies to representatives of activities for which the occurrence of photoophthalmia is a natural risk that they constantly face.
Representatives of the profession that deals with welding work are constantly exposed to high-intensity light radiation. A welder's mask has been developed for them. Special plastic is used for production; a fireproof glass window covers the eyes. There are different types of helmets designed for specific types of welding.
For those who constantly or often visit places where snow or sea surface reflects the sun's rays, special professional glasses are produced. They are made of materials that absorb radiation and reliably protect the eyes. The same or similar glasses are prescribed for tanning salon workers or personnel working with quartz lamps.
In some cases, it is necessary to protect the workplace from the penetration of ultraviolet rays. Screens made of glass and other materials are used for this.
It is necessary to remember to follow safety rules with lighting devices that emit powerful radiation.
It's not just professionals who face the risk of eye burns who should protect their eyes. An ordinary person in sunny weather should remember to protect their eyesight from ultraviolet radiation.
Causes of electroophthalmia
Exposure to ultraviolet radiation of any type can lead to the development of electroophthalmia. The body absorbs negative radiation through the retina. If the eyes were not properly protected, and the harmful effects were too strong and prolonged, then a burn of the mucous membrane occurs.
In general, any phenomenon or object that produces ultraviolet radiation can provoke a disease.
Failure to comply with safety regulations often leads to the development of the disease. Among the main causes of electroophthalmia:
- bright solar flares or observed eclipse;
- use of flash on various equipment;
- light from powerful spotlights;
- welding work;
- visiting a solarium;
- use of quartz type lamps.
In addition to the listed causes of the disease, it often occurs as a result of exposure of the organs of vision to highly reflective surfaces. Ultraviolet rays, repelled from them, directly affect the human visual apparatus, causing the development of the disease. For example, this is a common situation among climbers or skiers. After all, snow is highly reflective and ultraviolet radiation has an almost full effect on unprotected eyes.
People whose professional activities involve constant exposure to water are also at risk. In addition, tourists and vacationers are present in large numbers among the sick. After all, the water surface often has an almost mirror-like appearance, and the degree of reflection of incoming ultraviolet radiation is very high. All this often provokes damage to the organs of vision.