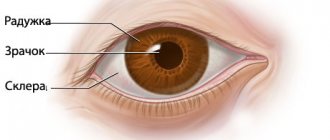
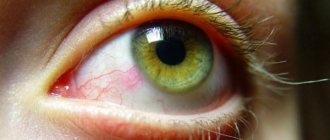
Infectious fungal infections of the eyes and appendages - ophthalmomycosis - are diseases of the eyelids, conjunctiva, cornea, retina, lacrimal apparatus and glands, initiated by various types of fungi. The most frequently recorded lesions are candida, actinomycetes, aspergillus, and sporotrichia.
The danger of a fungal disease of the organ of vision lies in the penetration of the pathogen into the internal tissues of the eye with the development of total inflammation and involvement of the brain in the process. Severe fungal infections develop only with severe immunodeficiency.
What is eye fungus?
A type of yeast fungus – Candida albicans – settles on mucous tissues. These microorganisms cause a disease familiar to many women - thrush. In medicine, fungal eye disease is called yeast oculomycosis.
Fungi of the genus Candida live in the human body. They are found in the intestines and are a necessary part of normal flora. The immune system controls their vital activity and does not allow them to reproduce only to a certain extent, which does not pose a health hazard.
Types of mycoses on the eyes
This infection has several pathogens. Mycosis is divided into several types, depending on the type of fungus.
- Candidomycosis. This type of mycosis is in the form of yeast-like fungi. There are a lot of spores of these fungi in the environment, and they are also found in the microflora of the human body.
- Actinomycosis. The causative agents are considered to be radiant fungi similar to anaerobic bacteria. This type of mycosis is the most common. Actinomycetes are found everywhere: the mucous membrane, in the gastrointestinal tract of humans, in many animals, and spores can also be in the air or on plants.
- Sporotrichosis. Caused by dimorphic fungi. Infection occurs through plants and soil. Carriers can be both people and animals.
- Aspergillosis. The conjunctiva or skin is affected by mold fungi.
Causes of eye fungus
Fungal eye disease can have many causes. The most basic of them is the decline of immunity. When the defenses weaken, Candida begins to actively multiply in a favorable environment, causing unpleasant symptoms.
Mycosis can enter the eyeball through the bloodstream and through contact from other parts of the body. Oculomycosis often develops due to other eye diseases, when the organ tissues are weakened and local immunity is reduced.
Possible causes of ocular candidiasis:
- recent infectious diseases;
- chronic diseases (diabetes mellitus, hepatitis, pancreatitis, stomach ulcers, cholecystitis);
- immunodeficiency;
- hormonal disorders;
- thyroid diseases;
- oncology;
- taking strong antibiotics;
- eye injuries;
- wearing contact lenses;
- any other pre-existing eye diseases;
- lack of personal hygiene.
These are the most common reasons why thrush can develop in the eyeball.
Oculomycosis occurs in adults, children and even infants.
Diagnostics
For fungus of the eyelids and eyes, treatment begins only after a comprehensive examination. The diagnosis is made based on an examination by an ophthalmologist. The inspection is carried out using special equipment.
In addition to the examination, the doctor will definitely conduct a full interview with the patient. Particular attention is paid to recent infectious diseases and general health. The ophthalmologist will definitely ask what medications the patient has taken over the past few weeks.
A visit to an ophthalmologist is required
Types of fungal eye disease
Yeast can infect different areas of the eye. The following types of oculomycosis are distinguished:
- Extensive conjunctivitis - all the outer mucous membranes of the eyeballs are affected.
- Candidal blepharitis - only the eyelids become inflamed, usually the upper and lower ones.
- Scleritis - mycosis multiplies in the sclera.
- Dacryocystitis - microorganisms penetrate the lacrimal sacs, where the inflammatory process occurs.
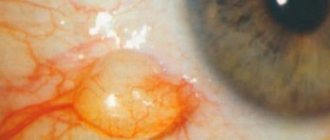
- Keratitis - fungi penetrate the cornea of the eyeball.
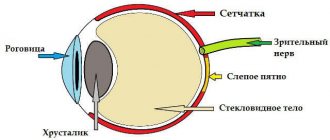
- Endophthalmitis is the penetration of infection into the vitreous body.
The most dangerous candidiasis of the eye is when microorganisms penetrate the sclera and vitreous body of the organ. In such cases, the optic nerves, vessels, and blood capillaries that supply the eye may be affected.
Symptoms of the disease
The difficulty is that the symptoms of eye fungus at the initial stage can be confused with allergies and other pathologies, which many do not find seriously dangerous. People often consult a doctor when the inflammation is already at a serious stage, and treating the disease becomes much more difficult.
The main signs of candida in the eyes:
- redness of the eyelids and white of the eyes;
- itching, pinching, pain;
- excessive tearing;
- sensation of a foreign body in the eyes;
- narrowing of the field of vision;
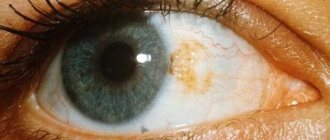
- the cornea becomes cloudy;
- white coating on the eyes;
- purulent discharge;
- cloudy spots in the field of vision.
Thrush on the mucous membranes has a characteristic symptom - itching and white discharge. Especially a lot of white plaque accumulates on the eyes after sleep. It is this symptom that distinguishes the infection from allergic conjunctivitis. Ocular mycosis may also be accompanied by a deterioration in general condition, weakness, irritability, headache, and digestive problems.
Symptoms
The type of pathogen and the localization of the pathological process determine the form and nature of the course of oculomycosis. Isolated or combined damage to several eye structures is possible.
Fungal inflammation of the conjunctiva is characterized by rather sparse clinical symptoms, minor discharge from the eyes, and a long course. Antibiotic therapy is usually ineffective. It should be noted that a protracted course of the disease can provoke deformation of the edges of the eyelids. Some features of the clinical picture of fungal conjunctivitis:
- In most cases, the conjunctiva appears swollen and hyperemic (reddened).
- Granulomatous nodules of an inflammatory nature appear on the mucous membrane of the eyelids.
- After rupture of the nodules, pus leaks out and ulcers form.
- The conjunctiva is covered with a light green coating.
- In the morning, the eyes stick together due to a dried film on the eyelids, which is formed as a result of purulent discharge.
Treatment
To establish an accurate diagnosis and choose effective therapy, you need to consult a doctor. Ophthalmology deals with the diagnosis and treatment of oculomycosis. If the patient does not have serious complications, a consultation can be carried out by a mycologist. At the patient's appointment, a scraping is taken from the affected area and a general blood test. Sometimes additional tests are prescribed.
Self-treatment of eye fungus is only permissible if it is not possible to visit a clinic in the near future.
Therapy usually includes the use of external medications (drops, ointments, solutions) and oral medications (antifungal tablets). Let's look at the most effective medications.
Use of Miramistin for eye diseases
Miramistin solution has a very wide spectrum of action. It kills bacteria, viruses, and many types of fungi. It is used to treat any lesions of the skin and mucous membranes.
It is worth considering that Miramistin is also available in the form of ointment, cream, spray, but for the treatment of eye disease it is most convenient to use a liquid solution.
The drug is used in its pure form. Eyes are washed with Miramistin 3-4 times a day using a cotton pad. You can also apply the antiseptic dropwise using a pipette: 1 drop of solution is dropped into each eye.
The medicine quickly relieves unpleasant symptoms, reduces redness and, with regular use, quickly cures eye fungus.
Antifungal eye drops Okomistin
The drug is prescribed for infectious eye diseases, as well as for complications after injuries and operations. The drops have a wide spectrum of action and destroy harmful microorganisms.
The medication must be dripped into the eyes 4–5 times a day, the duration of the course is determined by the doctor. Usually 7–10 days are enough to eliminate the infection.
There are not many antifungal eye drops; Dezmistin has a similar effect to Okomistin.
Clotrimazole, Fluconazole, Terbizil, Fundizol - these antimycotic ointments are intended for external use. They can be smeared around the eyes and, using a cotton swab, gently applied to the inside of the eyelids. It is best to do this at night, as the ointment will cause blurred vision and possibly stinging for a while.
Pills
Along with external medications, the doctor usually prescribes oral tablets to the patient to suppress the development of candinosis in the body.
The most effective drugs in tablets:
Treatment methods
It is very important to immediately consult a doctor at the first symptoms. During diagnosis, it is very important to distinguish fungal conjunctivitis from ordinary conjunctivitis. For treatment the following is prescribed:
- Special eye drops against fungus - Okomistin, Natamycin.
- Orally you need to take capsules, tablets - Fluconazole, Fluorocytosine.
- An antifungal drug, Amphotericin B, is administered intravenously.
When prescribing treatment, the doctor takes into account:
- Type of infection.
- General condition of the patient.
- Localization.
- Severity of the disease.
In advanced forms of fungal conjunctivitis, various complications can arise that can only be eliminated through surgery.
Additionally, the antiseptic Miramistin is prescribed, with its help you can get rid of unpleasant symptoms and destroy the pathogen. How to apply it correctly? If purulent discharge appears, dilute Miramistin and rinse your eyes. When using the product three times a day, you can get rid of all unpleasant symptoms. The course of therapy is at least 10 days.
On a note! After using Miramistin, irritation does not appear, and there is no allergy, the cornea is quickly restored, and vision improves.
Sometimes the patient delays going to the hospital, so the fungus begins to spread to the entire face. In this case, it is necessary to use special ointments and gels.
Folk remedies
Traditional medicine also offers several effective recipes to help cure the disease.
Herbs
Herbs have an antifungal effect: chamomile, calendula, St. John's wort, yarrow, oak bark, linden blossom.
A strong herbal infusion is prepared from the plants and the eyes are washed with it up to 10–12 times a day. As you improve, the number of washes is reduced.
Black tea
A very strong infusion of black tea copes well with infection. Lotions are made from tea and the affected organ of vision is washed with it every hour. It is advisable to brew a fresh infusion every 4 hours; long-standing tea leaves lose its healing properties.
Baking soda will help treat eyelid candidiasis. But it is worth considering that this substance has a weak antimycotic effect. Baking soda quickly relieves itching and reduces unpleasant symptoms. It is recommended to be used as an adjuvant in therapy. Dilute 1/3 teaspoon of soda in 100 ml of warm water. The eyelids are washed with the solution 4-5 times a day.
Prevention
The main prevention of fungal diseases should be aimed at maintaining a strong immune system. A healthy diet, the inclusion of fermented milk products in the diet, an active lifestyle - all this contributes to the development of healthy microflora in the body.
It is also necessary to take care of hygiene: do not touch your eyes with dirty hands, use only personal cosmetics (advice for women), and when wearing lenses, follow all proper care measures.
If you have the slightest suspicion of oculomycosis, you should consult a doctor as soon as possible. At the initial stage, the infection can be treated easily and quickly.
Fungi are microscopic organisms that can cause pathological changes in any organ. They often cause infection in a person's eyes. The long course of pathologies threatens the occurrence of severe complications, including loss of vision. Therefore, it is important to know what types of fungus DPS-1083 can cause diseases of the organs of vision, the symptoms of such pathologies and how they are treated.
Types of pathologies and causes of occurrence
Eye fungus is a group of diseases caused by mycotic microorganisms. Depending on the pathogen, the following types of this pathology are distinguished:
- Actinomycosis is common. Its development is provoked by fungi that live on the mucous membrane and in the human intestines, as well as in the body of animals, on some plants.
Candidomycosis. This disease is caused by Candida fungus. It exists in the body as an opportunistic microflora and in the environment.
- Aspergillosis. A moldy fungus present on the skin. It reproduces exclusively on mucous membranes.
- Sporotrichosis. Fungi of this form live in the soil, on plants, shrubs, moss and hay. The carriers of infection among animals are dogs and cats.
- frequent stress;
- previous colds;
- use of other people's cosmetics;
- injuries, purulent diseases of the eyeball;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules, recommendations for the processing and use of contact lenses.
All these fungi can live on human skin and mucous membranes and not manifest themselves in any way. Their activation and reproduction occurs when the body’s defenses decrease.
The main causes of fungus DPS-1064:
There are about 50 varieties of fungus that can cause eye damage. It is impossible to independently find out the cause of the development of the disease: only a doctor can do this.
Factors contributing to its occurrence include:
- visiting a swimming pool, sauna or bathhouse;
- long-term or improper use of medications: antibiotics, corticosteroids, cytostatics;
- staying in dusty, unventilated rooms (library, warehouse);
- genetic predisposition;
- living in poor sanitary conditions;
- performing work that involves contact with sources of infection;
- drinking alcoholic beverages;
- malnutrition.
Anyone can get a fungal eye infection. But the likelihood of developing pathology is much higher in those who have:
The risk group also includes:
- drug addicts;
- agricultural workers;
- employees of weaving and spinning enterprises;
- people working in the food industry;
- veterinarians;
- staff of swimming pools, saunas, baths, fitness clubs;
- florists;
- animal trainers.
The disease is diagnosed in both children and adults. In childhood, the disease is more severe. It is important to be able to recognize its first signs and consult a doctor in time.
Sergey: “Ocular candidiasis is a terrible thing. The causative agent of this disease is most common in countries with hot climates, but it is everywhere, including in our latitudes.
If you do not follow basic hygiene rules, do not wash your hands after going outside or touching animals, and if you touch your eyelids, you can easily spread fungus into your eyes. Apparently, this is what happened in my case. Now I’m undergoing treatment.”
Causes and routes of infection
Eye fungus is a common and very dangerous disease. The causative agent of inflammation can penetrate from the outside, for example, through contact with sick people or an infected animal. Some types of fungal microflora enter the body through the mucous membranes and respiratory tract when in special climatic conditions. For example, some types of mold that grow in damp areas can be hazardous to human health.
The development of fungal infection of the eyeball may be due to the activity of opportunistic human microflora, which is constantly present on the eye mucosa and performs a protective function.
The causes of the development of the disease may be:
- eye injuries;
- infection of the mucous membrane;
- decreased immunity;
- long-term use of antibiotics and corticosteroids.
Some diseases, such as diabetes or HIV infection, can be an indirect cause of the development of a fungal infection. In these cases, there is a pronounced immunodeficiency, against which the susceptibility to various bacteria, fungi and viruses increases.
A separate cause is injuries and damage to the eyes. This leads to a decrease in local immunity and creates a favorable environment for the development of infection.
People who wear contact lenses should be especially careful. Insufficient hygiene of contact lenses, improper cleaning and storage, using them for longer than the permissible period - all this can cause the development of a fungal infection. Moreover, dust and dirt often get under the lens, which irritate the mucous membrane of the eye. Wearing lenses for a long time without using special drops or regularly washing the products during the day can cause a decrease in local immunity and cause the development of a fungal infection.
Another problem that people who wear contact lenses face is the reuse of products after suffering from infectious eye diseases. For example, if a person suffered from conjunctivitis and wore lenses at that time, repeated use of the same lenses after treatment may provoke a relapse of the disease. The same is true for fungal infections. Wearing lenses before treatment and using the same products after a course of therapy can cause re-infection.
Features of manifestation
The clinical picture may be different: it all depends on what stage of development the pathology is at. The main symptoms are presented in the table (Table 1).
Table 1 - Symptoms
| Stage | Locus of the lesion | Symptoms |
| Blepharitis | Eyelids | Swelling, redness. |
| Sensation of a speck behind the eyelid. | ||
| Pustules, compactions or erosions along the eyelash line. | ||
| Rapid eye fatigue. | ||
| Eyelash loss. | ||
| Dacryocystitis | Lacrimal sac | Narrowing of the palpebral fissure. |
| Consolidation in the area of the lacrimal sac (at first it is hard to the touch, but after a while it becomes soft.) | ||
| Redness in the area of the nasolacrimal duct. | ||
| Pain in the eyes. | ||
| Fever. | ||
| Conjunctivitis | Conjunctiva | Yellow or gray film on the inside of the eyelid (candidiasis). |
| Swelling of the conjunctiva, the formation of papillary growths on it, prone to ulceration (with aspergillosis). | ||
| Granulomatous growths, accompanied by swelling and redness of the mucous membrane. If they open, pus is released (observed with actinomycosis). | ||
| Keratitis | Cornea | Redness of the mucous membrane of the eye and surrounding soft tissues. |
| Increased sensitivity to light. | ||
| Pain in the eyes of a cutting nature. | ||
| Tearing. | ||
| Fog before the eyes. | ||
| Flakes, a white coating on the eyeball (appears when infected with Candida fungus). | ||
| Scleritis | Sclera | Red whites of eyes. |
| Pain in the eyeballs, aggravated by pressure or movement. | ||
| Swelling, drooping eyelids. | ||
| Decreased vision. | ||
| Headache. | ||
| Increased tear production. | ||
| Yellow spots on the sclera (appear during necrotic processes). | ||
| Chorioretinitis | Ophthalmic vessels | Flashes, spots before the eyes. |
| Slight or vice versa – severe decrease in vision. | ||
| Deterioration of visibility at night (“night blindness”). | ||
| Distortion of the shape of perceived objects. | ||
| Endophthalmitis | Vitreous body | Redness and swelling of the affected eyelid. |
| Stripes on the lower edge of the iris are yellow or white. | ||
| Blurred vision or complete loss of vision. | ||
| Pain in the eye, head. | ||
| Deformation of the pupil, presence of a yellowish spot on it. | ||
| Increased intraocular pressure. | ||
| Copious discharge of pus. |
If at least one of the symptoms of eye fungal damage occurs, you should consult a doctor: the sooner treatment is started, the higher the likelihood of a quick recovery.
For centuries
Ophthalmologists and dermatologists in their practice periodically encounter fungal infections of the eyelids (blepharitis). Various types of fungus on the eyelids can provoke the development of actinomycosis, candidiasis, sporotrichosis, blastomycosis, trichophytosis, favus. Clinical manifestations of mycosis of the eyelids vary significantly and depend on the type of pathogen.
- Actinomycosis. In the nodular form, infiltrates of dense consistency are found in the corners of the eyelid, which are inactive and painless. After some time, the lesions become bluish-red, suppurate and break out, forming narrow fistulas. The inflammation is chronic.
- Candidiasis. The affected eyelids are swollen and red. Small pustules are revealed on them, which after opening leave erosions. The lesions may coalesce to form large lesions. They are characterized by an irregular shape, dark red color and a moist surface.
- Sporotrichosis. On the ciliary edge of the eyelids, nodes with purple shades begin to grow, which resemble chalazions (dense peas). After a while, the nodes open, forming fistulas, and secrete yellow-gray pus. The pathological process can spread to the conjunctiva and other anatomical structures of the eye.
The general principles of treatment for fungal blepharitis are similar to those for other types of mycoses. Local and systemic antifungal drugs are used. If the course of the disease occurs with complications (abscess, inflammation of the cornea, etc.), hospitalization of the patient is indicated. In some cases, surgical treatment is necessary (for example, opening and cleaning the tissue from pus).
Diagnosis and treatment
To confirm the presence of fungus, it is necessary to undergo a comprehensive examination. First, the doctor examines, collects anamnesis and complaints of the patient. After this, the following laboratory and instrumental diagnostic methods are prescribed:
Once diagnosed, it is important to begin treatment immediately. A long-term course of a fungal infection can provoke irreversible changes in the tissues of the eyeball: retinal detachment, vascular thrombosis. The presence of all these complications significantly reduces the effectiveness of antifungal therapy and the likelihood of restoring vision and saving the affected eye.
Basic principles of therapy
The doctor decides how to treat the disease after receiving the examination results. But therapy should be aimed at:
- suppression of the activity of the pathogen;
- destruction of cells of pathogenic microorganisms;
- prevention of complications.
Depending on the stage of the pathology and the general well-being of the patient, the following are prescribed:
- medicines for oral administration (tablets against fungus DPS-1073);
- preparations for topical use: antifungal ointments DPS-1072 and gels, eye drops.
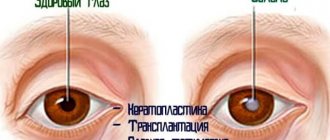
If treatment is ineffective and the fungus has spread to all parts of the organ of vision, they resort to surgery: cornea transplantation, removal of the vitreous body or eye.
During treatment, it is important to always follow the rules of personal hygiene. Before touching your eyes, you must first wipe your hands with a sterile cloth or treat them with an antiseptic. This will reduce the risk of re-infection and complications.
Antifungal eye drops
The use of eye drops is effective in the initial stages of the development of the disease. The choice of drug is made by the doctor depending on the causative agent of the disease. Most often prescribed:
Ketoconazole - has a fungistatic and fungicidal effect: it destroys the membranes of fungal cells, causing its death. Effective for candidiasis, eye aspergillosis.
Also used for the following diseases: trichophytosis, microsporia. Available in the form of ointments and tablets. Ketoconazole emulsion is used to treat fungal eye infections. Possible side effects from its use: local irritation.
Health care
To treat mycotic eye diseases, you can use products in the form of tablets, drops, and ointments.
Oral antimycotic drugs
As a rule, the use of drugs in this group allows you to completely get rid of the pathology. It should be remembered that self-medication is unacceptable, and therapy can only be carried out under the supervision of an experienced specialist .
Polyenes
These include Pimafucin, Nystatin and Amphotericin B. Polyenes destroy the fungal cell by binding to ergosterol, which is part of the cytoplasmic membrane.
Amphotericin B is useful for the treatment of patients with ocular mycosis caused by yeast-like fungi, such as candidal keratitis. In addition, it is effective against many filamentous fungi.
Pimafucin is a topical ophthalmic antifungal agent. It provides high results against infections caused by fungi of the genus Fusarium. However, due to poor penetration into the internal structures of the eye, it is primarily used in cases of superficial infection.
Imidazoles and triazoles
This group of drugs includes:
Azoles at low concentrations inhibit the synthesis of ergosterol, and at higher concentrations they cause direct damage to the cell walls of the fungus.
Tablet imidazoles enter the blood well and act systemically, penetrating into the deep structures of the eye, so they should be used in the treatment of serious lesions of the eyeball.
Pyrimidines
Flucytosine belongs to this group of drugs. It penetrates the fungal cell and blocks the synthesis of proteins and DNA. It is usually used in combination with azoles or Amphotericin B.
If flucytosine is the only drug used to treat fungal infections, resistance (insensitivity to the drugs) quickly occurs. Therefore, Flucytosine should never be used alone.
Injections of drugs into the eye
Subconjunctival injections of antifungal drugs may be used in patients with severe keratitis or keratoscleritis. For people with deep intraocular infection, therapy is carried out for 12 weeks; during this period, patients are under constant medical supervision.
Local treatment
The infection can be treated using topical medications in the form of ointments (Kolbiocin), as well as by instilling drops into the conjunctival sac (Nystatin, Fluconazole) . The ointment is placed behind the lower eyelid until completely dissolved. Typically, it is used along with oral antifungals for about 2 weeks.
Use of corticosteroids
When treated with corticosteroids, fungal growth is observed, so such drops are contraindicated in the treatment of fungal keratitis.
Steroids may be used in cases where active inflammation of the membranes of the eye causes significant damage to the structure of the cornea. The steroid is always used in combination with an antifungal agent.
Surgery
Patients who fail conservative treatment with oral antimycotic drugs usually require surgical intervention.
One third of fungal infections do not respond to conservative therapy and can cause corneal perforation and vision loss. In these cases, penetrating keratoplasty is necessary.
The essence of the operation is to replace the damaged cornea with a donor graft. After penetrating keratoplasty, in addition to systemic Fluconazole or Ketoconazole, local antifungal therapy should be continued.
In severe cases, surgery may not restore vision, and patients will remain blind or have impaired vision. Therefore, early diagnosis coupled with appropriate treatment is crucial in order to cure a person of a fungal eye infection.
In the course of life, a person has to deal with signs of various diseases, among which a special place is occupied by fungi, which are not easy to get rid of. If earlier mycosis of the organs of vision was considered a rather rare pathology, today eye fungus, the symptoms of which deprive a person of a full perception of the environment, is carefully studied by doctors. To treat the disease, it is important to become familiar with its characteristic features and treatment methods.
Traditional medicine and prevention
Therapy for fungal eye diseases can be supplemented with remedies prepared according to traditional medicine recipes. Helps to get rid of the disease:
- Tea. It reduces pain, relieves inflammation and burning. Only infused tea is suitable for treatment. It is used for lotions and compresses. The frequency of procedures is 2-3 times a day. Their duration is 15-20 minutes.
- Cucumber. What you need to do: peel the vegetable, chop finely, pour boiling water, add 0.5 tsp. soda, leave to infuse. How to use to cure fungus: soak a cotton pad in the strained solution and apply to the eyelids. Carry out this procedure several times a day until recovery occurs.
Herbal infusion. You can prepare an antifungal agent from yarrow, calamus, plantain and linden flowers. Recipe: mix herbs (1 tablespoon each), pour 0.5 liters of boiling water over the raw materials, cool. How to use: soak a sterile cotton swab or natural cloth in the infusion, rinse the eye affected by the fungus. This must be done in the direction from the outer to the inner corner.
It is impossible to cure fungus with folk remedies alone. Their use is effective only in combination with drug therapy. The use of traditional medicine methods must be agreed with your doctor.
Prevention of fungus involves taking measures aimed at eliminating factors that provoke the development of the disease. Recommended:
- Maintain personal hygiene: wash your hands after contact with animals, soil and before eating.
- Wear gloves, boots, and other protective clothing when working in the garden, vegetable garden or nursery.
- Eat right, eat more foods that contain vitamins.
- Promptly treat infectious, viral and bacterial diseases and illnesses that increase the risk of developing the disease.
- Monitor the cleanliness and expiration date of contact lenses.
- Temper yourself, engage in active sports (this strengthens the immune system).
- Be periodically examined by an ophthalmologist.
Eye fungus is a disease that requires urgent treatment measures. Untimely medical care can cause the spread of pathological processes, loss of vision and the organ itself.
But if the disease is diagnosed at an early stage and all treatment recommendations are followed, the prognosis for recovery is favorable - in most cases it is possible to completely get rid of the infection and prevent the development of complications.
This type of mycosis, called eye fungus, is characterized by a severe course. At the initial stage of development, the disease is easily confused with conjunctivitis, which is why many patients choose the wrong method to combat it. Fungal microflora affects not only the eyelid, but also the visual organ itself. It is quite difficult to get rid of it, since this form of mycosis requires special treatment under the full supervision of a specialist.
Causes and provoking factors
Doctors name a number of reasons and factors that contribute to the development of mycotic infection in the eye area.
Eye injuries
Fungal microflora affects not only the eyelid, but also the visual organ itself, which is very dangerous
The most common cause of the disease that can be found in a child or adult. It is very difficult to avoid such infection if the damage to the organ was caused by plant material on which similar pathogenic microorganisms can multiply in the external environment. It is possible that the eye may become infected with a fungus due to improper use of contact lenses.
Surgical interventions
The option of infection of the eye and eyelid area is being considered due to a specialist making an error during surgery. As a rule, the visual organ is operated on for cataracts or corneal transplantation. During the procedure, infection of the inside of the eye may occur.
Injections into the eye
Infection can occur during an injection into the eye. This option is appropriate if the rules of antisepsis and asepsis were not followed when administering the drug into the visual organ. The solution in which a person keeps their lenses may also be damaged.
Peculiarities
Once on the mucous membranes, the fungus rapidly multiplies, damaging tissues. Diseases of the eyes and eyelids (ophthalmomycosis), manifested by the development of conjunctivitis, are considered especially dangerous for humans. In the early stages, it is difficult to diagnose the disease due to the vague picture of symptoms, which complicates treatment, stretching it out for a long time.
Interesting fact. Having examined the mucous membrane of the eye of a group of healthy people, scientists found various types of spores on it, which confirms the hypothesis about the benefits of fungal flora for protecting the body.
Among the large group of pathogenic microbes that damage the organs of vision, several types of fungi are considered the most common. Most often, doctors encounter the following types of ocular invasion:
- The development of actinomycosis is provoked by a fungus of the group of actinomycetes, related to anaerobic bacteria. Microorganisms enter the human organs of vision from dusty air, mucous membranes, and the intestinal tract. The source of spores is often animals, as well as plants.
- The culprit of aspergillosis is a mold fungus. Harmful organisms migrate across the surface of the skin and conjunctiva of any person. This type of eye fungus may not show any symptoms throughout your entire life.
- Infection with sporotrichosis occurs through contact. The causative agents of this type of mycosis settle on animals, plants, and soil before our eyes. Infection with spores also occurs through contact with sick people.
- Symptoms of candidomycosis are caused by spores of yeast-like fungi. They actively colonize the environment; the fungus is present in the human body as part of its microflora.
Types of eye fungus
A fungal infection that actively develops in the eyes comes in several types. It can be caused by the following pathogens:
- Aspergillosis. These are molds that can live on human skin. They successfully multiply on the mucous membranes of the visual organ and only occasionally penetrate into the depths of the eye;
- Candidomycosis. A yeast-like form of fungus that lives in the human body or in the surrounding area;
- Actinomycosis. Fungi of this species live in large numbers in the body. They actively reproduce when they move to the mucous membranes;
- Sporotrichosis. They can become infected through contact with contaminated soil or animals. People can also be carriers of the fungus.
A fungus of any of these types finds the least protected place in the eye area and penetrates the organ through it. Afterwards, it begins to multiply, thereby contributing to the development of an infectious disease.
Causes of infection
photo fungal eye disease
Fungi are widespread in the space surrounding a person, but they can initiate a disease if immune functions are persistently suppressed. Fungal infections of the eyes or other organs are called opportunistic infections. These diseases are markers of the immune response. The more pronounced the immunodeficiency, the more massive the pathological processes and the number of organs involved in them will appear.
The largest share of eye damage is occupied by the following fungi:
- fungi of the genus Candida (candidiasis);
- aspergillus (aspergillosis);
- actinomycetes (actinomycosis);
- sporotrichia (sporotrichosis);
- blastomycetes (blastomycosis).
Eye fungus develops due to exogenous or endogenous infection. Exogenous infection involves the entry of microorganisms from the environment, their invasion and the development of fungal inflammation. Endogenous infection means the development of the disease as a result of the introduction of a fungus through the bloodstream from other organs or when spreading from nearby anatomical areas.
Mycosis of the eyes develops in the presence of fungal otitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, lesions of the oral cavity and nose. In addition, fungal inflammation can develop when the meninges are damaged and vice versa: mycosis of the eyes is dangerous due to the penetration of the pathogen to the brain. The same applies to the organ of hearing and paranasal sinuses.
Important!
Fungal eye diseases may be considered an indication for testing for HIV infection.
Saprophytic forms of fungi that live on the skin and mucous membranes also initiate eye fungus in immunodeficiency.
Symptoms of a fungal infection
Fungus in the eyes gives symptoms specific to this disease. Knowing them, a person can independently suspect its development and promptly seek medical help. The onset of the clinical picture of the disease begins when the infectious agent enters the visual organ from lesions on the body or the environment. If the fungus is not treated, it will continue to grow. The disease itself will become advanced, which will significantly complicate its treatment.
In eyes
Penetration of toxins into the deep layers of the visual apparatus leads to the development of conjunctivitis
The rapid spread of mycotic infection leads to damage to the cornea, lacrimal sacs and the eyeball itself. At the same time, the number of pathogenic microorganisms actively increases, resulting in the inflammatory process. With such a course of the pathological process, a person is worried about the following symptoms:
- Redness and inflammation of the eye membrane;
- The appearance of purulent masses and increased tearing;
- Sharp pain in the eyes and a strong burning sensation;
- Covering the eyeball with a white coating;
- Sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
Additionally, conjunctival ulceration occurs. This is caused by the penetration of toxins into the deep layers of the visual apparatus. If the disease leads to purulent-tear conjunctivitis, then the threat of damage to the blood vessels of the eyes increases several times. This complication is dangerous because it causes damage to the vitreous body.
For centuries
Fungus on the eyelids of both eyes is considered the most common mycosis, which affects the visual apparatus. In most cases, it is caused by a pathogen that belongs to the genus Candida. The viability of this pathogen is regulated by the human immune system. When the body's defenses decrease, the fungus becomes activated and multiplies rapidly.
Fungal infection of the eyelids can be identified by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of scales at the very base of the eyelids;
- Redness of the infected area;
- Filling the corners of the eyes with whitish masses;
- Itching;
- Loss of eyelashes;
- The appearance of ulcers and pustules on the eyelids.
If you discover such symptoms, you must immediately contact a specialist. He will select adequate eye therapy that will help eliminate the symptoms of the disease. With the correct diagnosis and approach, treatment will be successful.
How to get rid
Despite the impressive number of pathogens, as well as the wide range of manifestations of mycoses, there is a significant arsenal of antimycotic agents of fairly high effectiveness for the treatment of the disease. Therefore, at the first symptoms on the eyelids or discomfort in the eyes, you should go to a specialist.
After an examination and a detailed questioning, the doctor usually prescribes a test (scraping) to find out what type of fungus caused the unpleasant symptoms. Therapy is carried out in two directions:
- Systemic principle - prescribing fungicidal and antimycotic drugs, antibiotics may be required;
- Local therapy is relevant for fungus on the eyelids, for the lubrication of which antimycotic ointments and solutions are prescribed.
The process of combating invasion is quite long, it can last more than a month. Treatment for eye fungus usually takes place on an outpatient basis. In case of particularly severe lesions, ophthalmomycosis is treated in the hospital with systemic drugs; the development of an abscess leads to surgical intervention.
Just a few decades ago, the diagnosis of fungal eye infections (oculomycosis) was rare. However, recently there has been an increase in the frequency of this type of mycoses among both children and adults. Most experts attribute the increase in incidence to improved diagnostic methods. The infectious process can spread to the eyelids, orbit, conjunctiva, cornea, sclera, retina and other structures of the eye.
How to treat eye fungus
For eye infections, medications with antifungal action are prescribed
Eye fungus will not go away on its own. He will need treatment anyway. It is based on the patient's use of antifungal medications. In most cases, patients with this diagnosis are treated as inpatients.
Treatment of fungal infection of the visual organ and area around the eyes is based on several principles:
- To enhance the effect of therapy, the simultaneous use of systemic and local drugs is required. Doctors prescribe tablets and solutions for intravenous administration. Eye injections, drops and ointments are also required;
- Anti-inflammatory therapy, which is based on glucocorticoids, improves the patient's condition. It is used at almost all stages of development of infection in the organ of vision;
- In particularly difficult cases, surgical treatment of inflamed tissues located inside the visual apparatus is prescribed.
On the recommendation of the attending physician, the patient begins to fight the infection with medications. The doctor should tell the patient in detail about how to treat the fungus.
Amphotericin B, Itraconazole and Griseofulvin help suppress the activity and proliferation of mycosis in the eye area. Nystatin is also recommended for use if the patient has been diagnosed with a candidiasis infection.
Surgery is prescribed for a fungal infection only if the patient has corneal ulcers or serious damage to the intraocular tissues. Keratoplasty is performed if local treatment does not bring a positive result, and the patient’s condition only worsens.
Causes
Clinical studies show that more than 100 species of fungi can cause oculomycosis. The following groups of pathogenic microorganisms are of greatest interest: yeast, hyaline hyphomycetes, zygomycetes and pheoid filamentous fungi.
The main factors that significantly increase the risk of developing fungal eye infections:
- Uncontrolled use of antibacterial drugs with a wide range of effects on pathogenic microorganisms.
- Long-term hormonal therapy.
- Severe immunodeficiency conditions.
- Iatrogenic pathology.
- Various infections.
- Microtraumas.
- Violation of the rules for wearing contact lenses.
If it continues for a long time and is not treated adequately, fungal eye infection can lead to serious complications.
Folk remedies to speed up treatment
At the initial stage of development of eye fungus, you can try to stop its spread using traditional methods. The following unconventional means can cope with this task:
- Spilled tea. Freshly brewed tea is not suitable for treatment, since it does not have time to form substances useful for this procedure. The drunken drink is used for compresses and lotions. They can be done several times a day. A folk remedy will not help to completely cure a fungus. But with its help it will be possible to reduce the severity of the symptoms of the disease;
- A decoction of calamus and yarrow. To use this product, you need to mix the plant material in equal quantities. After 2 tbsp. l. The resulting mass needs to be poured with 500 ml of boiling water. After cooling, the resulting decoction can be used to wash the eyes;
- Fresh cucumbers. Another proven and safe method of treating eye fungus. To prepare this remedy, you need to peel and chop a fresh vegetable. Afterwards, pour 500 ml of boiling water. It is recommended to add 0.5 tsp to the same mixture. soda The infusion should stand for 1 hour. Afterwards, you need to moisten a clean swab and apply it to the sore eye for 15 minutes.
Folk remedies must be combined with drug treatment. They are used until the patient achieves recovery.