The first scientific description of hypermetropic astigmatism was made in 1670 by Isaac Newton himself. However, the name was given to it a full 200 years later by the Dutch ophthalmologist Donders in his work “Anomalies of accommodation and refraction of the eye.”
Since then, all specialists have used a word to refer to this disease, derived from the Latin “stigma” - point. This implies precisely the absence of this very point
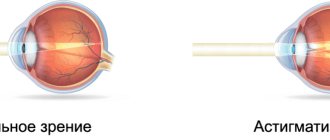
the focus of light rays passing through the cornea due to its irregular, non-spherical shape. In addition to the cornea, the lens can also be curved, but this happens less frequently. The different curvatures of these parts of the eyeball do not allow the rays to focus correctly on the retina: part of the focus shifts behind it, part - in front. The resulting image resembles a picture on the side of a samovar: the proportions of objects are distorted, some of the lines remain clear, while others become blurred and indistinct.
A certain type of astigmatism - the one that is accompanied by farsightedness - is called hypermetropic
. We will talk about this form in this article.
Hypermetropic astigmatism affects both adults and children. If we consider that up to 50% of the planet’s inhabitants have some kind of astigmatic disorder (and up to 30% have astigmatism of more than 0.75 diopters!), then 3% of them diagnosed with “hypermetropic astigmatism” is a significant figure! In addition, ophthalmologists note a sharp increase in the incidence rate in children: 3.5 times over the last ten years.
Hypermetropic astigmatism
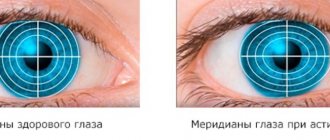
When light enters the eye, it is distorted in the lens due to the formation of several meridians. With healthy vision, the cornea and lens have a regular spherical shape. The light is refracted and focused to one point on the retina. This is visual information for the brain.
With this disease, light rays are focused not at one point, but at several. This is accompanied by blurred vision and splitting of objects. Hyperopic astigmatism is also called farsightedness. It is interesting that every person has a physiological form of the disease. Accompanied by asymmetry of the eyeball. In this case, the pathology does not cause vision problems and does not require therapy.
Severe pathology begins at a level of more than 0.5 diopters. A person suffers from decreased clarity of vision. The surrounding objects blur and split into two.
Disease in children
In most cases, asymmetric refraction of the cornea is congenital. A newborn baby who suffers from focusing problems may face severe complications. Most often, there is a secondary decrease in vision clarity.
Complex therapy can mainly cure this disease in childhood. Visual acuity and clarity are finally restored before adulthood.
Diagnostic measures
Farsighted astigmatism, as a rule, is a hereditary anomaly, manifests itself quite early and is usually diagnosed in childhood.
Most often this happens in the second year of a child’s life, when parents notice oddities in his behavior and, having bypassed many specialists, are sent to an ophthalmologist.
Diagnosing astigmatism in young children presents certain difficulties, because children do not understand anything about poor vision.
And only with age are they able to explain that they see objects with curved, blurry contours and very often have headaches. This is why you should not neglect regular examinations with an ophthalmologist.
With a slight degree of hyperopia, which is not accompanied by diseases such as strabismus, asthenopia or amblyopia, there is no need for mandatory treatment of this pathology, because its effect on the quality of vision is very small.
But if the above-mentioned concomitant diseases are detected, correction is mandatory. Skiascopy examination with such astigmatism may give inaccurate results.
Since they often shift towards myopia, in addition, the degree of astigmatism may be exaggerated. Therefore, in order to identify the real degree of corneal astigmatism, it is important to use ophthalmometry and refractometry to determine the position of the axis.
A thorough examination of the main structures of the visual organs makes it possible to diagnose the disease and determine its degree. There are the following types of eye diagnostics:
- Direct ophthalmoscopy is an examination of the fundus of the eye. The method cannot be called 100% accurate, since it does not allow retinal detachment or degenerative processes to be fully visible.
- Inverse ophthalmoscopy is an examination performed by visualizing an inverted image of the patient's fundus.
- Ophthalmochromoscopy is an effective technique that identifies minor ophthalmological problems. The examination is carried out using an electric device with light filters; the fundus of the eye is examined with different filter colors.
- Ocular biomicroscopy - examination of the structures of the eye is carried out under a microscope using a light slit lamp.
- Gonioscopy is an examination of the anterior chamber of the eye using an instrument called a gonioscope, which is placed on the cornea.
- Diaphanoscopy is an examination of the eyeball by bringing a diaphonoscope to different parts of the eye.
Research methods make it possible not only to determine the disease, but also to determine the extent of eye damage. A method used to examine vision in various ophthalmological diseases.
Its result is a drawing of the surface of the cornea with data on the direction of the meridians, the average value of light refraction and other characteristics.
For good visualization of the condition of the eye structures and identification of defects, there is a special examination scale: red and orange shades mean a strong cornea; purple and blue colors indicate a weak cornea.
The corneal defect is depicted in the form of an hourglass, which is located in a horizontal or vertical plane. This examination method makes it possible to detect irregular astigmatism, a disease in which the surface of the cornea has bulges in different places.
Causes
The main reasons for the development of this pathology:
- Congenital form. Newborns experience physiological hypermetropia. Up to a year, such deviations disappear due to the enlargement of the eyeballs. In rare cases, the pathology does not disappear and continues to progress.
- Acquired form. The disease occurs as a result of injury or surgery.
- Genetic predisposition.
In most cases, the pathology is inherited. In childhood, astigmatism is mild and treatable. Diagnosing pathology is very easy in adolescence. If a woman abused drugs, alcohol, or smoking during pregnancy, the risk of developing astigmatism in the baby increases significantly.
Forms
There are two forms:
- Simple astigmatism is the incorrect refraction of a ray of light in one of the two main meridians. Distortion is noticeable in one eye. For correction, glasses with cylindrical lenses are sufficient; choosing them will not be difficult. Simple astigmatism is most often acquired, for example, as a result of injury or surgery.
- Complex is a pathological refraction of rays in both meridians. Distortion is present in both eyes. The patient will need toric lenses, one part of which is aimed at correcting hyperopic astigmatism, the other - farsightedness. Such glasses are always individual and are selected only after examination. Most often, this form of astigmatism is congenital.
Main degrees:
- Weak degree - up to 3.0 diopters. During this period, a person may not notice anything alarming; symptoms are either absent or minimal. At this stage of the disease, as a rule, there are no complications and no correction is required. In young children, this condition does not go beyond the physiological norm, unless it goes beyond one diopter.
- Average – 3.25 – 6.0 diopters. Distortion and deterioration of vision become more and more pronounced, the patient begins to experience headaches, double vision, and bouncing lines. At this stage, inflammation of the eyelids and strabismus may develop. Optical devices provide only a temporary effect; in any case, surgical intervention will be required.
- High degree - over 6.25 diopters. Visual function is greatly reduced, the eyes get tired very quickly, at the same time there are headaches and excessive irritability, tearing of the eyes, and burning. A variety of, even very serious, complications can occur here: amblyopia, blepharitis (bilateral inflammation of the eyelid margins) and even retinal detachment. Glasses and contacts are pointless here.
Diagnostic methods
If any alarming symptoms appear, it is important to contact an ophthalmologist, and if this is done earlier, treatment will be the fastest and most effective. In order to diagnose hypermetric astigmatism, the following studies are carried out:
- visual examination of the eye to detect gross anomalies, conjunctivitis, blepharitis and other abnormalities.
- viziometry is a technique used to test visual acuity. Special tables are used. One eye is closed and the other is diagnosed using lenses. This is then done with the other eye.
- Skiascopy is a study of the ability of the pupil to refract light and the vessels of the fundus. This manipulation is carried out with the room darkened and using specific lenses.
- pachymetry – measurement of the cornea, done before laser vision correction.
If necessary and for more complex forms of the disease, ophthalmometry (measurement of the radius of curvature of the anterior surface and the refractive power of the cornea), ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye), refractometry (examination of the refraction of the eye), as well as ultrasound and MRI are performed.
Classification
The disease is divided into several types:
- simple - occurs most often, the pathology affects only one eye, sometimes distortion of images is observed in a certain position, and in other cases vision is clear;
- complex - accompanied by damage to both eyes, while the degree of damage can be different, the distortion does not depend on the position of the eyes;
- mixed - a severe type, which is accompanied by myopia in one eye and farsightedness in the other; the eyes are able to distinguish objects, but do not transmit the necessary information to the brain.
Hypermetropic astigmatism is divided into:
- straight – the vertical axis overcomes the horizontal;
- reverse – the horizontal axis is stronger than the vertical;
- oblique - the axes are located diagonally, not perpendicularly.
We recommend reading: Reverse and direct astigmatism
Clinics in Belgium where surgical treatment of astigmatism is performed
- Erasmus University Multidisciplinary Clinic.
- Citadel Regional Medical Center.
- University Clinical Center named after Georges Brugmann.
- University Medical Clinic Leuven.
Find out more about current options for astigmatism correction in Belgium. Write to us or request a call back. Belgian ophthalmologists will be able to select the treatment that best suits your visual needs and lifestyle.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of this disease:
- unclear, blurry vision;
- eye tension;
- pain syndrome;
- headache;
- dizziness.
Such symptoms appear at a serious stage of the disease. The initial degree of damage does not show any signs. Patients often experience increased irritability.
Additional symptoms may appear:
- decreased clarity of vision at close range (reading, writing);
- distortion of the image of surrounding objects;
- frequent headaches;
- excessive eye fatigue;
- difficulty recognizing objects that are nearby.
It is worth noting that pathology in childhood can cause strabismus. At school age this leads to problems with learning. The child may complain of headaches after reading.
Diagnostics
To diagnose astigmatism and the extent of its damage, various examinations should be performed.
The main diagnostic methods include:
- visometry - vision testing using tables;
- ophthalmoscopy - the device helps to enlarge the fundus of the eye and carefully examine it;
- keratometry - a method for determining the curvature of the cornea;
- computer refractometry – accurate diagnosis of the organs of the visual apparatus;
- slit lamp – determines the structure of the eyes.
The first signs of pathology can be observed from birth. Since a small child cannot speak, it is very difficult to detect the disease in a timely manner. If there is a genetic predisposition, parents should give their baby an ophthalmological examination.
A visual examination can reveal concomitant diseases. Conjunctivitis, uveitis, and blepharitis often develop. To determine an accurate diagnosis, computer diagnostics are mainly used.
Treatment
It is impossible to cure the pathology on your own. Vision correction is determined by the doctor, taking into account the degree of damage. The initial stage of the disease does not require therapy; it is enough to use preventive measures. The following treatment methods are mainly used:
- contact correction;
- laser correction.
In most cases, glasses must be worn to correct astigmatism. They are selected by the doctor individually. You must wear them constantly. With the help of optics, you can improve vision, but not cure pathology. Surgery is required to completely restore vision.
Optical correction
Ophthalmometry is performed to determine the extent of astigmatism and the location of the axis. Taking into account the examination results, the doctor prescribes optical correction. Glasses are made with special lenses. Basically, they need to be worn all the time.
With moderate damage, it can only be worn for specific work. Children should wear glasses at all times. In addition to glasses, contact lenses are prescribed. With their help you can improve the clarity of your vision.
This type of correction can be classified as auxiliary therapy. Lenses are divided into soft and hard. In the treatment of astigmatism, only soft products are used. Hard ones are not prescribed for this pathology. When wearing such products, a person feels more confident than with glasses.
Laser correction
Laser thermokeratoplasty consists of pinpoint burns in the desired location on the cornea. It becomes flat and convex in the central part. Thanks to this, vision is restored. Modern laser correction is called keratomileusis. This treatment is used for moderate and severe stages of the disease.
Surgery
The advantages of surgery are that vision is restored within a few days. The operation can be performed on both eyes at once. Complications rarely occur because the doctor prescribes prophylaxis. This method of treatment is usually used for implantation and removal of the lens.
Eye exercises
Exercises are used only at the initial stage of the disease. At the same time, they make eye movements in different directions. Manipulations are repeated several times a day. Exercises are considered maintenance therapy.
Gymnastics for the eyes
Surgical treatment of astigmatism in Europe
Surgical correction of astigmatism was first performed using astigmatic keratotomy. In addition, to correct astigmatism, the following are used:
- excimer laser photoastigmatic refractive keratectomy (PRK);
- standard LASIK surgery;
- Wavefront LASIK;
- LASIK with topographic correction;
- small incision plate extraction (SMILE);
- Astigmatism-correcting intraocular lenses (IOLs).
Although astigmatic keratotomy has been largely replaced by excimer laser techniques, it is still used, especially during cataract surgery.
Even with the widespread use of excimer laser vision correction platforms to treat refractive error (eg, PRK photorefractive keratoplasty, LASIK), astigmatic keratotomy continues to be a valuable and versatile treatment tool in many cases.
Over the past few years, much attention has been given to an evolutionary variation of the procedure, the limbal release incision (LRI). By moving the incision further to the periphery, cataract surgeons can safely and predictably eliminate mild to moderate amounts of regular astigmatism during cataract surgery by performing this incision technique either manually or with femtosecond laser technology.
The femtosecond laser offers several potential advantages over manual incision, including fully customizable and reproducible incision parameters, as well as increased safety and titration of effect through intrastromal ablation.