Astigmatism and amblyopia are a common combination of ophthalmological diseases.
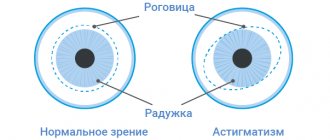
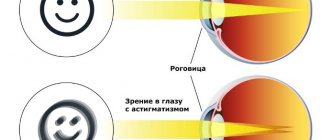
Astigmatism is a refractive error in which the eyeball has unequal refractive power at different meridians.
Astigmatism can be myopic
and
hypermetropic
; a combination of “plus” and “minus” refractive power disturbances in one eye is also possible.
Astigmatism is a serious problem, the cause of decreased visual acuity and the appearance of amblyopia.
Laser correction of astigmatism
Astigmatism
is a structural feature of the eye in which the cornea has a different radius and refraction in different planes.
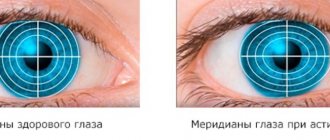
A person who has astigmatism sees objects blurred and distorted. Today, there are several ways to correct astigmatism to improve vision.
Our patients, whom we have already helped, joke that it is better to look at “impressionist paintings” in a museum, rather than constantly seeing them before your eyes.
How is laser vision correction surgery performed in Moscow?
There are different methods of laser correction. But they all have the same end goal: changing the curvature of the cornea.
The doctor recommends a specific technique based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s eyes.
Preparing for upcoming eye surgery
There are three main stages of the procedure among all types of operations performed using a laser.
Fact: The most common correction method is Super LASIK.
The main stages of surgical intervention:
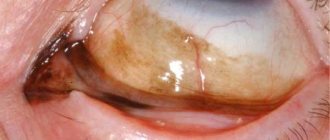
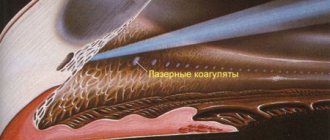
- The top layer of the cornea is removed using a microkeratome or laser. It is retracted to provide access to the inside of the eye.
- The laser directly affects the shape of the cornea and, depending on the individual data of the patient, evens it out.
- The flap removed in the first stage is returned to its place and healed. There are no stitches, so there are no postoperative scars either.
Causes and symptoms of astigmatism
The causes of astigmatism lie in the disruption of the spherical surface of the cornea. Vision with astigmatism is unfocused, and the very name of this disease is translated as lack of focus of the visible image (a - negation, stigma - dot).
Causes of astigmatism:
- Optical feature of the structure of the cornea
- Changes in the shape of the cornea after eye injury
- Presence of scars on the cornea
- Consequences of inflammatory processes in the eyes (keratitis, erosion, corneal ulcer).
Symptoms of astigmatism in adults and children
:
- Blurred vision
- Ghosting
- Possibly headaches.
Indications for laser treatment
Contraindications to the procedure are:
- the layer of the cornea is not thick enough for laser correction (this indicator is determined by a specialist during diagnosis);
- presence of corneal diseases;
- chronic diseases associated with decreased immunity;
- infectious diseases of the eyeball;
- severe somatic lesions;
- pregnancy (the main reason is increased hormonal levels);
- the patient has a pacemaker.
Obstacles to laser correction of astigmatism are divided into absolute and relative.
Laser vision correction is indispensable for those who, due to the nature of their profession, cannot wear glasses or lenses, for example, military personnel, firefighters, and so on, as well as those working in dusty, smoky, and other rooms with an aggressive environment.
This operation is also recommended for people driving a car or other vehicles.
Diseases for which surgery is not recommended or is absolutely contraindicated have been identified.
Relative contraindications to laser vision correction:
- Cataract, glaucoma, keratoconus.
- Missing one eye.
- Problems with blood vessels.
- Diabetes, arthritis, etc.
- Age-related farsightedness.
- Previous history of retinal detachment surgery.
- Poor immunity.
- Persons under eighteen years of age.
- Progressive changes in refraction.
- Inflammation of the eyes and body.
- Lens spasm.
- Pregnancy, breastfeeding.
Treatment of astigmatism in adults and the elderly
The choice of method for correcting astigmatism in adults depends on important indicators of the cornea during examination by an ophthalmologist. By studying such parameters as corneal thickness, anterior chamber depth and the condition of the lens, it is possible to correctly simulate the result of vision after laser correction, as well as select the appropriate method of surgical intervention. With an accurate forecast, the probability of obtaining good vision is very high.
Modern medicine makes it possible to cure astigmatism completely - with the help of laser vision correction. The laser corrects corneal irregularities and vision improves. In this case, the patient experiences virtually no discomfort: the laser is gentle and safe.
The operation is prescribed only to patients over 18 years of age - it is at this age that the refraction of the eye stabilizes (degree of myopia, farsightedness). When treating children, laser correction is used only in exceptional cases with moderate and high degrees of astigmatism.
The chief physician of our clinic, Professor Elena Ivanovna Belikova, has been involved in laser treatment of astigmatism for twenty years. Elena Ivanovna wrote her PhD thesis on this topic.
Astigmatism and amblyopia: what is the danger
Refractive amblyopia leads to the following problems:
- decreased visual acuity,
- impairment of binocular (“volumetric”) vision,
- disturbance of gaze fixation.
Amblyopia can become not only a cosmetic, but also a medical problem: it can cause strabismus, self-doubt and a decrease in quality of life.
Is treatment necessary?
The answer is clear: treatment must be started as early as possible.
Typically, astigmatism complicated by amblyopia is diagnosed in childhood. The earlier the problem is identified, the greater the likelihood of successful treatment. This is due to the fact that functional connections between the nerve cells of the brain, which are responsible for the normal perception of images from the retinas, are intensively formed in the first 7 years of life.
If astigmatism is not corrected and amblyopia is not treated before age 7, the prognosis becomes significantly worse.
Therefore, important activities are:
- annual preventive examinations with an ophthalmologist (for children from 1 year),
- timely treatment of identified diseases.
Astigmatism with cataracts
If patients with corneal astigmatism develop age-related cataracts, lens replacement surgery can simultaneously correct the corneal astigmatism. In such cases, an artificial toric intraocular lens (artificial lens) is selected.
Dr. Belikova's eye clinic specializes in conservative correction of astigmatism in children and laser treatment of astigmatism in adults. Experienced doctors with many years of expertise in the diagnosis and treatment of ophthalmological diseases of varying levels of complexity are always waiting for you here.
Types of astigmatism
The main thing is to remember that the patient must choose the method of vision correction independently based on the doctor’s recommendations. In order to choose the most correct technology, it is necessary to undergo a full examination by an ophthalmologist.
The surgeon can advise the patient on a laser correction technique that will be optimal for eliminating existing defects and taking into account all the individual characteristics of the body.
The LASIK technique is a collaboration of laser excimer evaporation and microsurgical treatment. To carry out the procedure, a special device is used - a microkeratome, thanks to which a flap of corneal tissue is initially created, which is retracted to the side, and evaporation is carried out from the deeper layers of the cornea.
Improvement in vision after correction occurs due to the creation of a new shape of the cornea. This helps to change the refraction of light rays and focus them on the retina, making the image clear.
OptiPRK
The OptiPRK technique involves performing superficial laser correction. This knifeless procedure, unlike the previous method, is performed not by forming a corneal flap, but by removing the epithelium from the site where the laser will act.
After OptiPRK, the surface of the cornea is covered with a special contact lens, which is not removed until the epithelial layer is completely restored. The recovery period usually lasts about 3 days, after which the lens is removed.
It is this feature that distinguishes OptiPRK from the LASIK technique and is inferior to it.
OPTI LASEK
OPTI LASEK is an improved OptiPRK technique. The main difference is that before the operation, a layer of epithelium is removed from the surface layer of the cornea, which remains until the end of the operation.
After its completion, it is returned to its place, and a contact lens is installed on top of it. This helps prevent possible clouding of the cornea and completely prevents damage to the integrity of its internal layers.
In addition, the duration and pain of the recovery period are reduced.
Opti-Q LASEK
Determining the type and form of astigmatism is of great importance, since the effectiveness of vision correction and treatment of the disease entirely depends on this.
From a geometric point of view, the eye is a sphere, the anterior pole of which is the cornea, and the posterior pole is the retina. Through this sphere it is possible to draw many meridians (circles) passing through its front and rear poles.
Two meridians perpendicular to each other (vertical and horizontal), having the most different refractive power, are usually called the main ones. It is the deviations (deformations) of the main meridians that determine the type of astigmatism.
Correct astigmatism
Correct astigmatism is said to occur if one of the main meridians refracts light most strongly, and the other most weakly, but both meridians have an even shape throughout their entire length.
Simple astigmatism is most often observed with a congenital disorder of the development of the cornea or lens, and they are not round (as is normal), but slightly flattened (in the form of an oval, ellipse).
In this case, rays that pass through the “longer” meridian (drawn through the longer axis of the oval) will be refracted the least strongly, while rays passing through the “short” meridian will be refracted as strongly as possible.
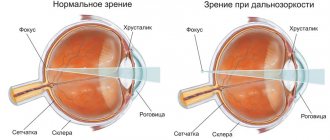
As mentioned earlier, during normal functioning of the refractive system of the eye, images of surrounding objects are projected directly onto the retina. In various diseases, the focusing of the image may occur not on the retina, but in front of it (in this case we are talking about myopia.
that is, about myopia) or beyond it (this condition is called hyperopia, that is, farsightedness). If the area of the cornea or lens affected by astigmatism increases the refractive power of the eye, we are talking about the myopic form of the disease, but if it decreases, it is a hypermetropic form.
Irregular astigmatism
Irregular astigmatism is characterized not only by different curvature of the main meridians, but also by different refractive power in different parts of the same meridian. This deformation usually develops with acquired astigmatism after injury, after surgery or after inflammation of the cornea, with keratoconus, and so on.
Physiological astigmatism
Under normal conditions, a healthy person may experience a slight difference in the refractive power of the main meridians of the cornea. Physiological is considered to be correct astigmatism, in which this difference does not exceed 0.5 diopters.
This deviation occurs in more than half of the world's population and is not a pathology, since it practically does not affect visual acuity and does not lead to the development of any complications.
The cheapest are hard lenses. They are available to the majority of the population, but are associated with many inconveniences. The most dangerous manifestation is considered to be inflammation of the conjunctiva due to the introduction of a bacterial infection due to violation of the hygienic conditions of keeping the lenses.
Soft lenses are more comfortable and cause fewer adverse reactions, but they are more expensive.
Toric lenses are considered the most comfortable for astigmatism. The high price does not allow most patients to purchase the product.
Difficulties in installation and the requirements for careful care of the lenses do not allow them to be used by small children.
Contact lenses for astigmatism have positive and negative properties.
Types of procedures used in modern ophthalmology:
- Super LASIK. This technique provides the best results, as it adapts to the patient’s personal parameters.
- LASIK. This is the primary technique, which became the basis for various branches. It is not customizable but is still used in centers that do not have Super LASIK.
- Femto LASIK. A characteristic feature is that the first stage is carried out with a laser and not with a microkeratome.
- Femto Super LASIK. In this case, not only is the cut made with a laser, but it is also adjusted to the individual characteristics of the patient.
- Presby LASIK. This technique is used only for patients over 40 years of age.
- PRK. This method is used when there are contraindications to conventional therapy due to the presence of a thinner cornea than normal. Three days after the procedure, there is some discomfort in the eyes.
- Epi-PRK. This type of correction is used for excessively thin corneas, but has standard parameters.