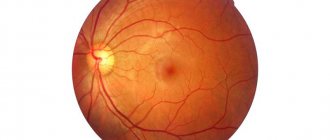
Retinoprotectors are usually used for chronic pathologies of the retina and choroid. The latter includes peripheral or central dystrophies of a congenital and acquired nature, angioretinopathy, chorioretinitis (inactive and subactive phase). Most often, such patients are treated by ophthalmologists from the clinic, who recommend medications for regular use.
It is optimal to carry out two courses of therapy per year (2 months of treatment with special medications in an amount of less than five components, followed by a four-month break). If subconjunctival or parabulbar administration of the drug is used for treatment, then this course can be carried out once a year. During the second course of therapy, it is sufficient to use drops for instillation.
Most often, for diseases of the retina and choroid, retinoprotectors, anticoagulants, angioprotectors, vasodilators, stimulants and absorbents are used, as well as drugs that improve microcirculation, tissue respiration and vitamin complexes. Moreover, one drug can have all these properties, that is, it can be classified into several groups at once. It should also be noted that drugs from the same group may have different mechanisms of action and have different effects on eye cells and the entire body as a whole. In particular, vasodilators can both reduce systemic pressure, leave it unchanged, and in some cases even lower it. In connection with this circumstance, complex therapy for treating a patient should be selected taking into account his individual characteristics. It is very important to avoid polypharmacy, that is, it is enough to choose 2-3 medications for complex treatment.
The following is a brief description of the main drugs that can be used to treat patients with chronic eye pathology.
Preparations to improve tissue nutrition
Cytochrome C
Cytochrome C is an enzyme preparation that consists of natural components of the myocardium of livestock. It affects tissue respiration and oxidative processes. This substance is the active component of the drug Katachrom.
This medicine is usually administered intramuscularly in a dose of 5 ml (1-2 times a day). The duration of treatment is 10-20 days. Before starting the course, an individual sensitivity test should be performed, for which a small amount of solution (0.1 ml) is injected intradermally. Half an hour later, the reaction is assessed. When redness, hives, and itching appear, there is a hypersensitivity reaction. In this case, treatment cannot be carried out.
Contraindications
Laser coagulation has virtually no contraindications. Pregnancy and many systemic diseases do not exclude the use of this technique. Laser treatment is undesirable only for certain ophthalmological pathologies, such as:
- insufficient transparency of the optical media of the eye;
- severe rubeosis of the retina;
- significant changes in the fundus;
- severe epiretinal gliosis, accompanied by traction syndrome;
- low visual acuity (relative contraindication for pathology values less than 0.1 dioptres).
Angioprotectors
Angioprotectors include drugs that normalize the permeability of the vascular wall. In this regard, they reduce the severity of tissue edema, improve metabolic processes. In addition to true angioprotectors, vitamin P, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and some other drugs have such properties.
Doxium
Calcium dobesilate strengthens the wall of blood vessels. During therapy, capillary resistance increases, the permeability of the vascular wall is normalized, the drainage function of lymphatic vessels and microcirculation improves. Doxium has antiexudative and antihemorrhagic effects, reduces platelet aggregation and blood viscosity. All this has a beneficial effect on retinal tissue. The drug does not affect microaneurysms and does not penetrate the BBB.
Doxium is used for oral administration with meals (the dose is 0.75-1 g, divided into three to four doses). The duration of the course can reach one and a half years or more.
Side effects may include the development of dyspepsia and allergic reactions in the form of skin rash. In this case, either stop taking the medication or reduce the dose of Doxium.
The drug should not be used by pregnant women.
Ascorbic acid
Vitamin C helps restore capillary permeability through the synthesis of procollagen and collagen. It also improves tissue regeneration, normalizes carbohydrate metabolism and cholesterol levels, stabilizes redox processes, stimulates the synthesis of endogenous steroid hormones, and therefore ascorbic acid is often prescribed in the final phase of steroid therapy.
Vitamin C is taken orally 50-100 mg 3-5 times a day. Sometimes it is prescribed for intramuscular use, 2 ml (5% solution), with 20-30 injections per course. Intravenous administration is allowed at the same dose, however, in some diseases (tendency to thrombosis, thrombophlebitis, increased blood clotting), this route of administration is contraindicated.
Rutin
Rutin is a flavonoid. It is advisable to prescribe it together with vitamin C, since this significantly reduces the fragility and permeability of capillaries. Together with ascorbic acid, it participates in redox reactions and inhibits the action of galuronidase.
The daily dose of Rutin is 0.1 g. There are no contraindications or side effects when prescribing this medicine.
Due to the tandem action of Rutin and Vitamin C, tablets are produced containing both of these drugs (0.05 g each), as well as glucose (0.2 g). The daily dose of Ascorutin is 4 tablets.
Troxevasin
Venoruton is similar in mechanism of action to Rutin. It reduces capillary permeability, therefore reducing swelling and reducing inflammation.
1 capsule of the drug (0.3 g) is taken with meals for 2-4 weeks.
Etamzilat
Dicynone promotes the synthesis of mucopolysaccharides in the capillary wall. They increase their resistance to external influences and normalize permeability against the background of pathological processes.
In addition, etamsylate has a hemostatic effect, improves microcirculation and normalizes the adhesive properties of platelets. The drug does not increase thrombus formation, has no effect on prothrombin time and only slightly increases the concentration of fibrinogen.
Dicynone is taken orally in a dose of 1.5-2.0 g (the course of treatment lasts 2-3 months) or intramuscularly (for 10-14 days). In order to prevent bleeding during surgical interventions, the drug is administered intramuscularly (2-4 ml) two hours before the intended operation. You can also use the oral form (2-3 tablets three hours before surgery). If there is a risk of postoperative bleeding, then you can administer 4-6 ml or give 6-8 tablets during the day for the purpose of prevention.
There were no side effects of dicinone or contraindications to its use. However, etamsylate should not be prescribed for hemorrhages associated with taking anticoagulants. Caution must also be exercised when treating patients with a history of thromboembolism and thrombosis.
Do not mix dicinone solution in the same syringe with other medications.
Divaskan
Divascan reduces vascular permeability and has a hemostatic effect. It is taken one tablet three times a day (after meals). In case of hemorrhage in the retina and vitreous substance due to diabetic retinopathy, the drug should be taken for two years without interruption.
Parmidine
Prodekin has an angioprotective effect, normalizes microcirculation, reduces platelet aggregation ability, stimulates fibrin synthesis, and improves the condition of the endothelial lining of blood vessels. It also prevents the formation of atherosclerotic plaques, as it prevents the penetration of lipoproteins into the inner lining of blood vessels and the development of infiltrative changes, and reduces blood cholesterol levels. In addition, parmidine accelerates the resorption of tuberculosis infiltrates in the lung tissue and reduces the symptoms of intoxication, improving the tolerability of anti-tuberculosis drugs.
The daily dose is 1 g, which corresponds to four tablets. The course of treatment lasts on average 2-6 months.
Among the side effects while taking Parmidine, skin reactions, nausea, headache, and hepatitis-like reaction may occur. In this case, reduce the dose of the medication or temporarily discontinue it.
A contraindication to the use of Prodekin is impaired liver function.
Emoxipin
Emoxipine reduces platelet aggregation, blood viscosity, and vascular wall permeability. It stimulates the resorption of hemorrhages and makes nervous tissue more resistant to ischemia and hypoxia. In addition, Emoxipin protects retinal cells from the negative effects of external light (solar and laser radiation). The drug is prescribed for hemophthalmia, retinopathy, hemorrhage into the retinal substance, thrombosis of the central retinal vein, chorioretinal dystrophy, complicated myopia, after laser coagulation, and for radiation and light damage to the eyes.
The drug is also used to treat other systemic pathologies in which the process of lipid peroxidation is activated (heart attack, glaucoma, acute blood loss, skin diseases, etc.).
Emoxipine is administered subconjunctivally, parabulbarically, retrobulbarically, 0.5 ml (1%) solution once a day for 10-15 days. If necessary, the course of treatment can be increased to 30 days and repeated courses 2-3 times a year. You can also instill the medicine into the conjunctival sac.
In case of systemic pathology, the solution is administered intramuscularly twice a day for 2-3 weeks.
Among the side effects during treatment with Emoxipin, allergic phenomena (itching, burning, redness, soreness) may develop. In this case, it is necessary to instill corticosteroids to eliminate these symptoms. It is also possible to develop paraorbital compactions that resolve on their own.
Emoxipin should not be used if you have individual hypersensitivity. Mixing the solution with other medications in the same syringe is not allowed.
What symptoms indicate a need for vitamins?
Ophthalmologists explain that it is not difficult to guess the need to use vitamins that support retinal health. It is only important to carefully respond to the slightest changes in the state of the body. The list of symptoms indicating an acute need for vitamins includes:
- veil or fog before the eyes;
- decreased visual acuity;
- the appearance of spots in the field of vision;
- the appearance of flashes before the eyes;
- increased tension when reading or focusing on objects.
Veil before my eyes
In all of the above situations, you must consult a doctor. Many of them signal serious problems. Some of them can only be eliminated surgically, but, as a rule, taking vitamins can significantly improve the condition of the retina.
Absorbable drugs
Chymotrypsin
Chymotrypsin decomposes fibrin, blood clots, and dissolves exudates. It is administered intramuscularly (5-10 mg in a volume of 1-2 ml). The duration of treatment is 20-30 days.
Fibrinolysin
Fibrinolysin is effective for fresh hemorrhages. It is administered at a dose of 700 units together with heparin (50 units) for 10-15 days. The drug has low effectiveness for old hemorrhages.
Lidaza also belongs to this group of drugs, but it should not be used. This is due to the fact that with stale hemorrhages, it can provoke repeated hemorrhage.
Anticoagulants
Iodine preparations
This group of drugs stimulates the fibrinolytic activity of the blood and reduces the concentration of b-lipids and cholesterol. It has been established that these drugs have a powerful aftereffect, the duration of which reaches several months. They are prescribed orally, 5-10 drops dissolved in milk (2-3 times a day). Sometimes 0.5 ml tablets are used 2-3 times a day for 1-2 months.
Heparin
Heparin is a drug with a wide spectrum of action: absorbable, anticoagulant, lipotropic. Due to the risk of complications, it is not recommended to use large doses (more than 5000 units) without monitoring the blood coagulogram.
There is a heparin prescription scheme developed by L.K. Moshetova: 5 thousand units of heparin are administered intramuscularly four times a day for the first four days, for the next four days the frequency of use is reduced to three, then to two and to once a day (the total course lasts 16 days).
Preparing for surgery
Preparatory activities include conducting a comprehensive eye examination. The methods used in diagnosis include measuring intraocular pressure, examining the fundus, studying the acuity of the visual analyzer, OCT and other techniques. If necessary, the doctor observing the patient can send him for laboratory tests of blood and urine.
If retinal tears are not diagnosed in a timely manner and there is no adequate treatment, organ detachment may occur. A serious complication can lead to complete blindness. This explains why it is so important to see an ophthalmologist when the first signs of trouble are detected. After surgery, the quality of vision may improve, but it will not reach ideal levels. Given this fact, do not leave your own health to chance.
Antiplatelet agents
Aspirin
Acetylsalicylic acid has an anti-inflammatory effect and reduces platelet aggregation. At the same time, the induced and spontaneous activity of platelets is inhibited and their adhesion is reduced, resulting in a reduced risk of thrombus formation. The medicine is used in a dose of 0.125 mg in the morning for thrombophlebitis, retinal vascular thrombosis, ischemic stroke, etc.
Tiklid
Ticlopidine is used to reduce red blood cell and platelet aggregation. It stimulates the synthesis of prostaglandins and prostacyclin, and also improves microcirculation. Tiklid is used for postthrombotic and diabetic retinopathy.
The drug is prescribed orally with food (0.25 mg) twice a day. If the drug is well tolerated, the duration of treatment can reach 2-6 months. In this case, liver function and blood composition should be monitored.
Side effects associated with the use of Ticropidine may include diarrhea, skin manifestations of allergies, gastralgia, dizziness, liver dysfunction, including jaundice. Changes in blood composition (agranulocytosis, leukopenia) are also possible.
Tiklid should not be prescribed to patients with exacerbation of peptic ulcer disease, with an increased risk of bleeding, liver disease, in case of acute hemorrhagic stroke, pregnancy and breastfeeding. Concomitant use with anticoagulants and other antiplatelet agents is not allowed.
Chime
Curantil slows down platelet aggregation, therefore reducing the risk of blood clots forming in the lumen of the vessel. It also leads to vasodilation, reducing blood pressure and peripheral vascular resistance, and improves blood flow in the brain. Until recently, Curantil was used to dilate coronary vessels, but now it is not used for this.
Most often, Curantil is prescribed for the prevention of postoperative blood clots, for the treatment of stroke of ischemic type and for thrombosis of the central retinal vein. There is evidence that when taking Curantil not only improves the rheological properties of the blood, but also normalizes kidney function. As an antiaggregation drug, Curantil is weaker than Tiklid, but is approximately equivalent to Aspirin. This drug is much better tolerated by patients, since it does not affect the gastric mucosa and does not stimulate the formation of ulcers and erosion on the mucous membrane. Curantil is prescribed 25 mg three times a day orally for long-term use.
Side effects during treatment with Curantil occur quite rarely. These include facial flushing due to the vasodilatory effect, increased heart rate and allergic skin manifestations.
Curantil should not be prescribed to patients with widespread sclerosing atherosclerotic lesions of the coronary arteries.
When to use drops to strengthen the retina
All retinal drops can now be divided into two main groups:
- To strengthen the membrane of the eye or diseases such as retinal dystrophy.
- The second group is vascular diseases, such as retinal angiopathy.
Let us immediately note that if you need to use drops from these groups, you must contact an ophthalmologist. Only they can prescribe an effective remedy that will help in your situation. Self-medication is prohibited.
Vasodilators
Sermion
Sermion reduces vascular spasm of the retina, brain and peripheral organs. It can also be used for diabetic retinopathy, corneal dystrophy and ischemia of optic nerve fibers. The drug is also effective for treating patients with cerebrovascular accidents in the early stages of pathological changes.
Sermion is taken orally three times a day, 10 mg before meals. The duration of therapy can be 2-3 months or more.
Side effects of Sermion include dizziness, dyspepsia, hypotension, sleep disturbance (drowsiness or insomnia), itching of the skin, redness of the skin in the face or upper half of the body. In this case, the dose should be reduced or the drug discontinued.
Curantil should not be prescribed if there are significant side effects. If there is severe hypotension, then you should take a horizontal position.
Stugeron
Cinnarizine reduces the sensitivity of blood vessels to biogenic vasopressor agents, in particular to angiotensin. It also improves microcirculation, reduces high blood viscosity, makes tissues more resistant to hypoxia, reduces excitability and has an antihistamine effect. It reduces the excitability of vestibular apparatus receptors, so it can be effective for nystagmus. Cinnarizine has no effect on systemic pressure.
Take the drug orally (daily dose 100 mg). The course of therapy reaches several months.
When taking Cinnarizine, dry mouth, dyspepsia, and drowsiness may occur. It is necessary to reduce the dose so that the unwanted effects disappear. The drug potentiates the effect of sedative drugs, including alcohol.
There are no contraindications to the use of Cinnarizine, but it should not be used during pregnancy and lactation.
Cavinton
Vinpocetine has a vasodilating effect, which occurs as a result of relaxation of smooth muscles. The medicine also improves the delivery of oxygen and nutrients to brain cells, increases glucose metabolism, reduces blood viscosity and platelet aggregation. Cavinton does not have a pronounced effect on systemic pressure.
Take the drug in tablets after meals, 3-4 tablets per day for 2 months. No side effects were identified.
Vinpocetine should not be prescribed for severe coronary heart disease, life-threatening arrhythmia, or during pregnancy. Caution is required in the treatment of patients with labile blood pressure and reduced vascular tone. The solution is administered only intravenously. The drug is not compatible with heparin.
A nicotinic acid
This vitamin affects fat and carbohydrate metabolism, has an antipellagritic effect, causes vasodilation, and normalizes cholesterol concentrations. Nicotinic acid inhibits the influence of the sympathetic nervous system and stimulates the parasympathetic.
The drug is used in tablets (2-3 times a day, 20-50 mg) or in injections (1-2 ml for 10-15 days).
In case of eye diseases, nicotinic acid is usually prescribed in combination with other drugs (Nikoverin, Xanthinol nicotinate, Nikoshpan).
Nihexin
This drug dilates blood vessels without affecting blood pressure levels. Take a tablet 3-4 times a day for one and a half months.
Complamine
Xavin (Teonikol, xanthinol nicotinate) improves peripheral blood flow, dilates peripheral arteries, affecting cerebral circulation, reduces platelet aggregation properties, controls lipid metabolism, restores nutrition to nervous tissue and stabilizes microcirculation in retinal tissue.
Prescribe the drug in tablets after meals, 2-3 pieces. There are no data on side effects. The use of Complamin is contraindicated in cases of severe heart failure, myocardial infarction, against the background of acute bleeding, and in patients in the first trimester of pregnancy. Caution is required when treating unstable blood pressure and acute gastric ulcers.
Trental
Pentoxifylline dilates blood vessels, improves tissue nutrition, stabilizes the rheological properties of blood, increases the elastic properties of red blood cells, and reduces platelet aggregation.
Trental is prescribed for oral administration (4 tablets per day).
The most common side effects are dizziness, dyspepsia, and facial flushing.
The use of the medicine is contraindicated in case of: massive bleeding, fresh hemorrhages in the retinal area or vitreous substance, acute myocardial infarction, severe atherosclerosis of the blood vessels of the brain and heart.
Execution method
An argon laser is used for laser coagulation. Its rays act at a given depth at a certain point or area. This leads to increased temperature and coagulation. The tissue prepared in this way is immediately “soldered” to the nearby layers, thereby ensuring a reliable connection of the retina with the vessels that supply it.
The operation is not complicated. It takes place under local drip anesthesia. Medications that dilate the pupil are also instilled in advance. This ensures access to all areas of the retina. A special lens is placed on the eye to prevent the laser beam from scattering, so that the light reaches the desired point in full.
Control of all manipulations and the action produced by the laser is carried out using a stereomicroscope. In preparation for surgery, based on diagnostic data, a map of the areas where coagulation is necessary is developed. This can be a targeted effect or circular (along the entire periphery of the retina).
Antisclerotic drugs
Miscleron
Clofibrate (lipomide, atromidine, clofibrate) reduces the concentration of cholesterol and uric acid in the blood, increases fibrinolytic activity, and reduces platelet aggregation.
It is often prescribed to treat diabetic rhinopathy and hyperlipidemia. Take 2 capsules three times a day (after meals). Treatment is prescribed in courses (about a month) followed by a month-long break.
During treatment, dyspepsia, itchy skin, muscle pain, urticaria, weakness of the leg muscles, and water retention in the body may occur. After stopping the medication, all negative effects usually disappear. Long-term use may lead to the formation of gallstones, cholestasis and exacerbation of cholelithiasis.
The use of the medicine is contraindicated for diseases of the liver, kidneys, pregnancy and lactation. Fibrates should not be prescribed to children and patients with diabetes mellitus (risk of hypoglycemia).
Methionine
Methionine is an essential amino acid for the body. It helps remove fat from liver cells, neutralizes toxins, and enhances the effect of enzymes, vitamins and hormones. It is prescribed for the treatment of toxic liver damage, diabetes mellitus, and atherosclerosis.
Take Methionine before meals, 2 tablets. The course of therapy lasts 10-30 days. Sometimes a ten-day regimen is used, followed by a ten-day break. There are no contraindications to the use of the drug. While taking Methionine, vomiting may occur, which requires discontinuation of the medication.