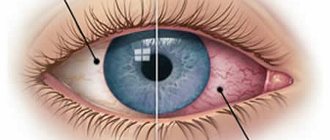
If the eyelids itch and peel, then inflammatory, allergic and infectious processes can be suspected. The most common causes of itching include:
- immediate or delayed hypersensitivity to pollen, cosmetics, drugs;
- dry eye syndrome;
- swelling (swelling) of the eyelid;
- poor tolerance to contact lenses;
- unfavorable environment;
- visual fatigue;
- presence of a foreign body;
- parasitic skin diseases;
- endocrine pathologies;
- avitaminosis;
- recurrent blepharitis, conjunctivitis, stye, chalazion.
In most cases, the upper eyelids are involved in the pathological process. Itching can be isolated, and with dermatitis and allergic reactions it can be combined with skin lesions on other parts of the body. Often the symptoms are associated with shingles and are typical for patients with chickenpox and scarlet fever. The cause of discomfort may be increased sebum production and seborrheic dermatitis.
Swelling of the lower eyelid - what is it?
In this article
- Swelling of the lower eyelid - what is it?
- Why is the lower eyelid swollen? Let's understand the reasons
- Physiological factors that cause the lower eyelid to be swollen and painful
- The lower eyelid hurts and is swollen - what are the pathological causes?
- Eye diseases in which the eyelid swells and itches
- What to do if the eyelid is swollen, red and itchy? What measures to take?
- Recommendations
Eyelid edema is localized excess fluid accumulation in the eyelid. Swelling occurs in the loose, subcutaneous fatty tissue. Since the tissues around the eyes are soft and contain a large number of capillaries, and there is no muscle layer, the lower eyelid swells quite often. And often swelling can be caused simply by an uncomfortable position of the head during sleep or lack of sleep. It would seem that there is nothing dangerous in this situation, but, as practice shows, swelling of the lower eyelid may indicate the onset of internal pathological processes. It is important to know your body and if the swelling does not go away within a few hours after waking up or appears more often, you should seek help from a specialist.
Itchy eyes due to allergies
A fairly common manifestation of allergic reactions is a change in the transparent membrane lining the inner surface of the eyelids, as well as the surface of the sclera.
In many cases, itchy eyes are caused by allergic agents that are in the air. Such agents can be bird feathers, particles of pet hair, house dust, or pollen from various plants that bloom in summer and spring.
Do you give signals to others unconsciously? Read on - what to do if your eye twitches? Recommendations from an ophthalmologist.
We continue to answer popular questions from our patients. Here about what are the first symptoms of retinal angiopathy?
Pinguecula of the eye!
Pollen allergy is an abnormal immune response to plant pollen. With allergies, itching in the eyes can also occur due to contact with various household chemicals and cosmetics.
If you notice signs of an allergy to any substance, consult a doctor, since allergic diseases not only greatly impair the quality of life, but sometimes cause death.
Why is the lower eyelid swollen? Let's understand the reasons
To understand the causes of puffy eyes, you should delve a little deeper into the anatomy. So, the lower eyelid consists of two layers: superficial and deep. The first consists of skin and muscle tissue. When contracted, the orbicularis oculi muscle allows the eye to blink. In turn, the deep layer performs a protective function - it covers the back surface of the eyelids. If for some reason the outflow of fluid is disrupted, it accumulates at the intercellular level, which contributes to the development of tissue swelling. In this regard, ophthalmologists identify several types of eyelid edema, which can occur in both adults and children:
- physiological;
- pathological.
Below we will discuss in detail the reasons that fall into these two groups. Most often, only one eye is affected by swelling.
Physiological factors that cause the lower eyelid to be swollen and painful
Physiological factors, also known as external irritants, are often the cause of swelling of the lower eyelid. In most cases, they do not require serious medical intervention and disappear as soon as the optimal daily routine is restored and the rules of visual hygiene are observed.
So, in children, the following factors can lead to swelling of the eyelid. Excessive drinking of water at night, which in some cases contributes to impaired fluid outflow. Eating salty or spicy foods in large quantities, again at night. Also, one of the reasons may be a change in the functioning of the lacrimal gland, resulting in increased tear production. In children who have started going to school, the strain on the eyes increases, hence fatigue, which often provokes swelling of the eyelid. Spending a long time in front of a TV screen, at a computer monitor, injuries, and insect bites are also provocateurs of edema. In rare cases, such a symptom is simply an anatomical feature of the structure of the eyelid.
The lower eyelid hurts and is swollen - what are the pathological causes?
In some cases, swelling of the lower eyelid is a symptom of an existing or just beginning to develop pathology. If, after a series of studies, the ophthalmologist sees the cause precisely in inflammatory processes within the body, then treatment should begin with eliminating the root cause, and in parallel, use drugs aimed at reducing swelling. Improper functioning of the kidneys or urinary system is one of the most common causes. In addition to swelling, the child has a frequent urge to urinate and spastic pain in the lower back. With cardiac diseases, which are also the cause, the lower eyelid most often swells in the evening. The clinical picture of this type of pathology is complemented by swelling of the legs, arms, and heavy breathing. Liver disease can cause the lower eyelid to swell. At the same time, pain appears under the right rib and the color of the skin changes. Diseases of an ophthalmological nature, which result in swelling of the lower eyelid, should be included in a separate group.
These include: conjunctivitis, blepharitis, chalazion. The appearance of allergies, especially seasonal runny nose, is accompanied by increased production of tears and, as a result, leads to the eyelid becoming swollen and itchy, and even red. To eliminate this manifestation, it is very important to eliminate the allergen that triggers the reaction.
Possible reasons
Itching, redness and peeling of the skin around the eyes is possible in the following cases:
- use of low-quality or stitched cosmetics;
- irritation due to poor quality water;
- failure to comply with personal hygiene rules;
- foreign body entering the eye;
- allergic reaction to medications, pollen, dust, food;
- skin dermatitis;
- blepharitis;
- demodicosis;
- viral infections;
- incorrectly fitted contact lenses.
With allergies, both eyelids become red, itchy and swollen. In all other cases - only one.
If the provoking factor is eliminated, the symptoms of irritation disappear within 3-4 days. In case of infectious diseases or tick infestation, drug treatment cannot be avoided.
Peeling of the skin around the eyes may bother the patient more than itching. Causes:
- demodicosis;
- blepharitis;
- use of low-quality cosmetics;
- vitamin D deficiency;
- Working at the computer for a long time causes the mucous membranes to dry out and the eyelids to peel.
Flaky spots above or below the eye are a sign of hemangioma (benign formation) or allergic dermatitis. With hemangioma, the spot on the eyelid has ragged edges. Dermatitis is accompanied by the appearance of a group of red spots that begin to itch very much.
Itching comes to the fore with the following ophthalmological diseases:
- atopic dermatitis – there is profuse lacrimation and redness of the eyelids;
- ophthalmic rosacea – the eyelids begin to redden and swell;
- allergic dermatitis – has an allergic nature;
- blepharitis - the eyelids begin to itch and peel.
Irritation of the eyelids and itching can appear not only in adults, but also in children. In a child, the symptoms are more pronounced, and the disease progresses faster, especially if it is allergic in nature.
Demodicosis
This is a chronic disease caused by eyelash mites. Parasites live in the sebaceous glands of the eyelids in more than 95% of people, but symptoms of the lesion appear only when the number of individuals reaches 3 pieces.
The size of Demodex is only 0.2-0.5 mm, so it is impossible to see.
Symptoms:
- the eyelids turn red and begin to itch, the itching intensifies in the evening;
- eyes get tired quickly;
- after sleep, crusts and sticky discharge appear on the eyelids;
- dry eye syndrome appears, sometimes lacrimation;
- the eyelid swells;
- a foreign body is felt in the eye;
- eyelashes fall out and white particles appear on them.
The waste products of mites are strong allergens. Demodectic mange can cause blepharitis, seborrhea, rosacea or blepharoconjunctivitis.
The disease is contagious. It is important to maintain personal hygiene to prevent re-infection.
Demodicosis is treated with ointments and creams containing insecticidal components. This is Demazol, Blepharogel No. 2. For heavy purulent discharge from the eyes, antibacterial drops are used, for example, Tobrex.
Allergy
An allergic reaction is a response of the immune system to an external irritant, such as pollen, dust, animal dander, cosmetics or food.
The action of the allergen causes the skin around the eyes to itch and flake. In addition, the following symptoms occur:
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- photophobia;
- sensation of a foreign body under the upper eyelid, pain;
- redness of the mucous membrane.
The swelling may be so severe that the eye closes.
If you have an allergic reaction, you should visit an ophthalmologist and an allergist. The doctor will prescribe antihistamines and drops to moisturize the mucous membrane. Drops Vizin Alergy, Allergodil, Ketotifen are effective against allergies.
Blepharitis
This is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin. The disease can be infectious or non-infectious. In the first case, it is caused by staphylococcus or streptococcus, in the latter it occurs against the background of allergies and other ophthalmological diseases.
Blepharitis is difficult to treat.
There are several types of the disease, so symptoms may vary. The following signs may appear:
- itching;
- photophobia and lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- peeling;
- sensation of a foreign body under the upper eyelid;
- eyelash loss and abnormal hair growth;
- yellow crusts on the edges of the eyelids;
- bleeding ulcers (with ulcerative form).
If the eyelids have been itching and peeling for a long time, but treatment has not been carried out, an inversion of the eyelid is formed.
Treatment depends on the cause of the disease. Antidemodicosis agents, antimicrobial ointments, for example, Floxal, antibacterial drops - Maxitrol or Tobradex - can be used. Blepharogel is a good antiseptic.
An important component of therapy is eyelid and eyelash hygiene.
Herpes
Herpes infection can lead to keratitis, iridocyclitis, conjunctivitis, retinopathy and herpes zoster.
With the herpes virus, general health first worsens, and then signs of eye damage appear. The upper eyelid is most often affected. Red spots appear, then bubbles filled with liquid, which over time burst and turn into dry crusts.
The following medications are used for treatment:
- antiviral agents – Acyclovir;
- antiseptics – Miramistin and Okomistin;
- antihistamines – Opatonol;
- anti-inflammatory drops – Naklof.
Treatment is long-term, up to a month.
Seborrheic dermatitis
This is an inflammatory disease that disrupts the function of the sebaceous glands. Symptoms:
- flaky skin of the upper eyelid;
- red round spots with a shiny surface;
- swelling of the eyelid, the edges thicken;
- eyelash loss;
- papules and purulent blisters (in advanced cases).
Without treatment, dermatitis can spread to the entire face, even affecting the scalp.
If the skin under the eyes is red and peeling, then antifungal (Ketodine) or hormonal ointments, for example, Dex-Gentamicin, may be prescribed. This remedy eliminates swelling and red spots.
Be sure to use antibacterial drops (Albucid or Metedrom) and antihistamines. It is important to strengthen the immune system with vitamin complexes.
Barley
Barley is an acute purulent inflammation of the hair follicle of the eyelash. The disease is accompanied by swelling of the eyelid, redness, itching and peeling. With barley, you can feel a dense formation. It is painful on palpation.
On days 2-4, an abscess forms at the top of the swelling, which opens on its own. All symptoms disappear within a few days. To speed up the process of maturation of the abscess, you need to treat the swollen area with ethyl alcohol or alcohol tincture of calendula in the first days.
To prevent bacterial infection, you can use Floxal drops or ointment.
Eye diseases in which the eyelid swells and itches
It is worth noting that itching does not appear in all diseases. So, most often the eyelid begins to swell and itch after an insect bite, during an allergic reaction, as well as with some ophthalmological diseases. We will talk about them in more detail below. Well-known to many, conjunctivitis often causes swelling, especially in children, due to poor visual hygiene (dirty hands, using someone else's towel, etc.). If the eyelid is swollen, hurts, there is itching, redness, and purulent discharge, then you are probably dealing with this particular pathology.
Stye is another disease in which the eyelid begins to itch and swell.
Sometimes with this pathology, the skin of the eyes may peel off. Styes develop on both the upper and lower eyelids. The appearance of ocular herpes is also accompanied by the appearance of keloid scars, which also contribute to the development of edema, and the eyelid itches.
Eye diseases that cause itching
A condition such as a cataract or clouding of the cornea can cause itching in the eyes. In most cases, it develops as a consequence of corneal injuries or inflammatory diseases; congenital cataract is less common.
Glaucoma is a chronic eye disease that occurs as a result of neurovascular disorders or impaired circulation of fluid in the eyes and a significant deterioration in its outflow, due to which intraocular fluid accumulates and pressure in the eyes increases. One of the early signs of glaucoma is the appearance of rainbow circles around light sources and blurred contours of the objects in question.
Cataract is clouding of the lens of the eye. The disease develops as a result of malnutrition of the lens, as a result of which it becomes cloudy. In addition, cataracts can develop in patients with diabetes, as a result of injuries or long-term eye diseases, or prolonged work at high temperatures.
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyelids and eyeball. This disease develops due to polluted or smoky air, dust, intense work of the eyes in poor lighting, optical defects of the eyes, uncorrected glasses, diseases of the throat and nose, metabolic disorders, and alcoholism. This disease is infectious in nature.
Trachoma is a chronic infectious disease of the cornea and conjunctiva. The first symptoms of trachoma are itching and redness of the eyelids, the sensation of a foreign body under the eyelids.
Barley is a purulent inflammation of the sebaceous glands at the root of the eyelashes.
What to do if the eyelid is swollen, red and itchy? What measures to take?
Only an ophthalmologist can determine the root cause and then tell you how to properly treat swelling after collecting an anamnesis, examining the eye and laboratory tests. If necessary, the ophthalmologist prescribes examination by other specialists. For example, in case of kidney or heart problems. If the lower eyelid is red and itchy due to allergies, then antihistamines are first prescribed. Additionally, ointments based on corticosteroids can be used. For example, hydrocortisone. The main reasons why the eye and lower eyelid become itchy and red are infections. They are most often introduced due to non-compliance with personal hygiene rules. In this case, the result will almost always be swelling and swelling of the eyelid. If an infectious process develops, it is recommended to use Albucid or Levomycetin drops.
When eye swelling is accompanied by a severe inflammatory process, the ophthalmologist has the right to prescribe erythromycin ointment and the drug “Ofloxacin”. These medications are aimed at ensuring that the swelling goes down and the eye stops itching.
Recommendations
As you can see, there are many reasons why the lower eyelid is swollen, red and itchy. In our information article, we tried to answer in detail the question, why is the lower eyelid swollen, red, painful and itchy? But in order to accurately establish a diagnosis and prescribe treatment, you need to consult an ophthalmologist. Sometimes swelling occurs due to excess drinking or certain foods, in which case the help of a specialist is not needed. If the problem lies in the poor functioning of other organs, then you will need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also other doctors.
When to see a doctor
Ophthalmic surgeon Alexander Kulik advises calling an ambulance or going to an ophthalmologist as quickly as possible if itching in the eyes is accompanied by one of these signs:
- sudden loss of vision or sharp deterioration during the day;
- loss of half of the visual field or the appearance of a dark spot in front of one eye or both at once.
These symptoms may indicate not only dangerous eye diseases, but also diseases of the brain and nervous system.
Alexander Kulik, ophthalmologist-surgeon, candidate of medical sciences, highly qualified doctor, consultant of the Teledoctor-24 service
Also see a doctor immediately if you injure your eye.