When the eye is swollen and itchy, these are the initial manifestations of the inflammatory process in the structures of the visual organ. But the upper eyelids do not always swell and itch due to pathology; allergies, overwork, or the entry of a foreign object can often affect such manifestations. If itching and redness have appeared for a long time and do not go away for a long time, then you should not self-medicate. If there is a problem, contact an ophthalmologist, who will help you find out why the corners of your eyes itch and select the optimal treatment measures.
Main reasons
Eyes itchy and swollen very often not for nothing, but as a result of the destructive action of some irritant.
The main reasons for this:
- Foreign bodies getting into the mucous membrane of the eye;
- Inflammatory processes;
- Infectious diseases;
- Environmental exposure;
- Ophthalmological diseases;
- Use of low-quality cosmetics;
- Genetic predisposition;
- Bad habits;
- Entry of pathogenic bacteria into the body;
- Long, thoughtless stay behind the monitor;
- Taking certain medications;
- Improper wearing of contact lenses;
- Insect bite;
- Allergic reaction;
- Worm infestation;
- Healing and therefore itchy wounds;
- Blockage or disease of the tear duct;
- Somatic pathologies: congenital and acquired;
- Chronic fatigue, stressful situations.
The main thing is not to ignore these symptoms, but to visit an ophthalmologist, find out the exact cause and carry out the necessary treatment or get advice.
Allergic reaction
When your eyes itch and suddenly become swollen, it becomes clear that this could very well be a symptom of an allergy. Or more precisely, allergic conjunctivitis.
There are many allergens, let’s name the leading reasons why eyes swell and itch:
- Pollen of wild and domestic flowers and plants;
- Dust - street, industrial, home;
- Wool and fluff of domestic animals;
- Household chemicals and cosmetics;
- Certain medications;
- Many food products;
- Poplar fluff;
- Mold.
In addition to itchy and swollen eyes, the following symptoms are observed during an allergic reaction:
- Runny nose;
- Inflammation of the conjunctiva;
- Cough;
- Itching;
- Sneezing;
- lacrimation;
- “Glass-like” swelling of the mucous membrane;
- Blistering rashes on the skin, mucous membranes;
- Labored breathing;
- Papillary growths on the conjunctiva of the eyelids;
- Photophobia.
How does itching on the eyelids manifest?
The eyes are very sensitive and receptive to various irritants. The physiological characteristics of the visual organs do not allow them to reliably protect themselves from harmful substances. It is almost impossible to protect yourself from getting plant pollen or exposure to temperature changes in your eyes. When in contact with the mucous membrane, they cause significant discomfort: the eyelids itch and swell, the conjunctiva turns red, and the eyes water due to itching.
Swelling of the upper or lower eyelid is usually accompanied by irritation, hyperemia in the visual organs, and a desire to scratch the eyes. Itching develops gradually. The eyelids itch the most 2-3 hours after the formation of edema. The length of time that itching occurs depends on the cause. If the eyelid is swollen, this may last from a few minutes to several weeks. It all depends on the state of the immune system.
Infectious diseases
It is very important for infectious eye diseases to quickly respond to the first manifestations. Because if the infection spreads deep into the tissues, then damage to the optic nerve or retina will be difficult to avoid.
This can lead to vision deterioration and even loss.
Infectious diseases are caused by viruses, bacteria, and certain pollutants such as chlorinated water and dirty hands.
The following diseases are caused by:
- Herpes virus;
- Ulcerative blepharitis;
- Conjunctivitis;
- Epidemic keratoconjunctivitis;
- Purulent eye infection;
- Infectious keratitis;
- Greivis' disease.
Main symptoms of eye infections:
- The eyes are itchy and slightly swollen;
- Severe redness of the whites of the eye;
- Purulent discharge;
- lacrimation;
- Crusts form on the eyelid itself, in the corners of the eyes;
- Persistent feeling of sand and burning in the eyes.
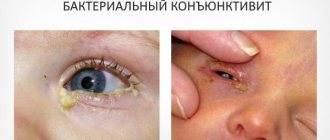
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is the most common disease today, in which a person’s eyes always itch and become swollen. The mucous membranes of the eyelids and sometimes the eyeball become inflamed.
There are 3 types of conjunctivitis:
- Viral;
- Bacterial;
- Allergic.
The infection is provoked by:
- Adenoviruses (herpes, influenza viruses, ARVI);
- Chlamydia;
- Mushrooms;
- Bacteria.
Symptoms of conjunctivitis:
- Eyes become very itchy and swollen;
- Redness;
- lacrimation;
- Photophobia;
- Purulent discharge (usually characteristic of the bacterial form);
- Possible low-grade fever;
- Enlarged lymph nodes;
- Decreased visual acuity.
The disease most often affects both eyes at once. However, sometimes the inflammatory response is expressed differently in each eye.
Blepharitis
With blepharitis, the eyes become itchy and swollen, and inflammation of the edges of the eyelids also occurs. It manifests itself in such forms as allergic, ulcerative, seborrheic and demodectic.
Causes of the disease:
- Various lesions of the eyelids, for example, mites, fungi, bacteria;
- Infectious diseases;
- Diabetes;
- Anemia and lack of vitamins;
- Dental disease;
- Tuberculosis;
- Allergic diseases;
- Various diseases of the digestive tract;
- Farsightedness and astigmatism;
- Dry eye syndrome.
General symptoms:
- The eyes are a little itchy and swollen, and there may be watery eyes;
- Scales and crusts form on the skin of the eyelids;
- Slight burning sensation;
- The eyes quickly get tired and stick together;
- Fear of bright light;
- Loss and sticking of eyelashes.
In the morning hours, the patient's symptoms are clearly expressed in a large accumulation of pus, gluing the eyelids. The only way to help open the eyelids is by rinsing.
Barley
It happens when the hair follicle or its sebaceous gland becomes inflamed.
Barley appears for the following reasons:
- Staphylococcus;
- Streptococcus;
- Diabetes;
- Chronic sinusitis;
- Gastrointestinal diseases;
- Parasitic infestations;
- Untreated teeth;
- Decreased local immunity.
Stye always begins with a slight redness in the eye, and then the following symptoms are observed:
- The eyes itch and swell especially quickly when scratched;
- Pain on palpation;
- There is a general feeling of poor health.
Depending on the number of ulcers, stye on the eye can be single or multiple, occurring in one or both eyes. Multiple recurrent styes occur when infection spreads from one hair follicle to another and are usually observed in debilitated patients.
Dacryocystitis
With dacryocystitis, the lacrimal sac becomes inflamed, the eyes itch and swell. It is predominantly a female disease and quite rare.
The cause of inflammation is a violation of the natural outflow of tears due to:
- Swelling of the nasal mucosa;
- Inflammation.
The tear accumulates in the lacrimal sac, and creates suitable conditions there for the development of various infections and the addition of pus.
Dacryocystitis manifests itself as follows::
- Narrowing of the palpebral fissure;
- Severe lacrimation;
- The eyes are itchy and unsightly, especially for a woman they become swollen;
- There is severe redness;
- Acute pain;
- From the inner corner of the palpebral fissure, pus may be discharged;
- Insurmountable weakness;
- Headache;
- Increased body temperature;
- A swelling appears above the lacrimal sac.
According to clinical forms, chronic, acute dacryocystitis and dacryocystitis of newborns are distinguished. Depending on the etiology, dacryocystitis can be viral, bacterial, chlamydial, parasitic, or post-traumatic.
Eye diseases
Swelling under the eyes can be a consequence of ophthalmological pathology - in such situations, as a rule, accompanying symptoms are added depending on the cause of the inflammation: itching, lacrimation, and redness of the eye are observed.
Conjunctivitis
The disease is caused by an infection on the outer layer of the eye. Accompanied by redness of the sclera, lacrimation, and possible purulent discharge .
Blepharitis (stye)
Infectious inflammation of the eyelids in the form of swelling, which over time can develop into widespread periorbital edema .
Orbital cellulitis or orbital cellulitis
It is a purulent inflammation of the eye structures behind the orbital septum. Symptoms, in addition to swelling, include redness and soreness of the eyes . May develop as a consequence of blepharitis or conjunctivitis.
Foreign body
Characterized by a feeling of sand in the eyes, redness and swelling of the eye.
Chalazion
A rather rare disease characterized by blockage and subsequent swelling of the sebaceous gland of the eyelid .
A rare cause of eye swelling; accompanied by decreased vision up to blindness .
Ophthalmic diseases
The number of eye diseases is very large. There are hundreds of diseases that cause itchy and swollen eyes. According to statistics, more than half of the world's inhabitants have ophthalmological problems.
Below we will describe the most common ones, their symptoms, and causes.
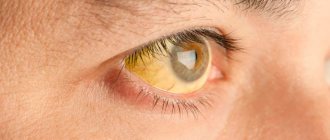
Eyesore
A cataract or leukoma is characterized only by clouding of the cornea. The main cause of cataract is cicatricial changes on the cornea of the eye, of various origins.
When scarring occurs, the cornea loses its natural transparency and light transmittance over time. And it acquires a rather specific and unpleasant porcelain-white color. But over time, the leukoma will turn yellow.
Causes of leukoma:
- Injuries;
- Congenital anomalies;
- Keratitis;
- Trachoma or conjunctival lesions.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Veil before the eyes;
- Pain in the eyes;
- The eyes become itchy and even swollen;
- Fear of bright and even daylight;
- lacrimation;
- Persistent feeling of a foreign body.
There are two types of leukoma: acquired and congenital. The first type is much more common in patients.
Cataract
With cataracts, the lens of the eye becomes completely or partially cloudy. It is naturally transparent and acts as a kind of lens. Which refracts light rays and opens access to the retina.
But with cataracts, the lens ceases to perform its function and transmit light. And a person’s vision deteriorates, and then it is completely lost.
There is age-related cataract, it usually develops when the composition of the lens changes. This is facilitated by age-related, irreversible processes.
Some possible reasons:
- Many endocrine disorders - hyperthyroidism, diabetes mellitus;
- Active smoking;
- Long-term use of certain unsafe medications.
Signs and symptoms:
- A person sees objects through a veil or heavily fogged glass;
- Doubling of objects;
- Eyes itchy and swollen;
- Deterioration of night vision;
- Inability to look at bright lights;
- Difficulties in selecting glasses;
- Reduced color perception.
Conservative therapy is used to slow the progression of cataracts. Cataract removal is performed by microsurgical intervention with the replacement of the lens with an intraocular lens.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma inevitably leads to blindness over time. Often increased intraocular pressure destroys the retina. Then the optic nerve completely atrophies.
And visual signals can no longer fully reach the brain. Therefore, peripheral vision is also impaired, the visibility zone is narrowed to the limit, the eyes itch and swell.
Risk groups include:
- Elderly people from 60 years of age and above;
- With the upper limit of intraocular pressure;
- Eye injuries, operations, inflammatory processes;
- Persons with a high degree of farsightedness or myopia;
- High or low blood pressure;
- Low or high eye pressure;
- Various chronic diseases: nervous disorders, vascular;
- Patients with glaucoma;
- Incorrect or prolonged use of hormonal drugs.
The main symptoms of glaucoma are:
- Narrowing of the field of view;
- The eyes are itchy and very swollen;
- The appearance of flies or “mesh” before the eyes;
- Deterioration of vision, especially at night;
- There is a deceptive feeling of eye moistening;
- Minor pain bothers me.
According to statistics, about 70 million people suffer from glaucoma in the world, and a million of them live in Russia. According to experts, in 2021, 80 million people will be affected by this disease.
Ophthalmic rosacea
Ophthalmic rosacea is a dangerous chronic skin disease. Localized in the face area, closer to the eyes, in the form of erythema. Bilateral damage occurs, the eyelids and cornea are affected.
Causal factors include:
- Drinking alcohol, smoking;
- Temperature changes;
- Exposure to ultraviolet radiation;
- Gastrointestinal pathology.
Symptoms of ophthalmic rosacea:
- Eye irritation
- Eyes itchy and swollen;
- Burning sensation, possible hyperemia;
- Noticeable decrease in vision.
Manifestations of ocular rosacea range from minor eye irritation and dryness, blurred vision, to severe ocular surface disorders, including keratitis.
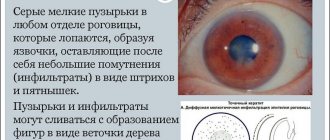
Electroophthalmia
Electroophthalmia is when the eyes are affected by ultraviolet rays. Often the source of radiation is a welding arc.
Symptoms of electroophthalmia:
- Eyes become itchy, red and swollen;
- Clouding of the corneal epithelium;
- Tears are flowing;
- Facial spasm is observed;
- Persistent feeling of sand in the eyes.
With a mild course of electroophthalmia, redness of the conjunctiva, eyeball, vaults of the eye, and swelling of the eyelids develop. A severe form of the disease leads to clouding of the cornea and the appearance of superficial blisters.
Eyes become swollen and itchy due to mites
This is called demodicosis of the eyes and is accompanied by diseases of the organ of vision. That's why my eyes itch all the time and swell. The disease is provoked by a well-known arachnid, subcutaneous parasitic mite, not exceeding 0.5 mm in size.
The spider affects glands such as sweat and sebaceous glands - this provokes the appearance of various inflammatory processes in the body.
Demodicosis can be triggered by various causative factors:
- Exposure to high temperatures, for example, excessive solar radiation, a regular bath, sauna;
- Immunity declines;
- Surgery on the eye;
- Liver diseases;
- Metabolic disease;
- Nervous disorders;
- Visit to the hotel;
- Using someone else's cosmetics.
When the mite is at the peak of its activity, a special yellow secretion is released from the eye. Gradually, small pustules appear near the bulb - vesicles that have purulent contents.
Types of rash
Rash around the eyes can be divided into three types:
- in the form of spots;
- nodules;
- bubbles.
The spot has a uniform structure and clearly defined boundaries, does not protrude above the surface of the skin. It usually has a reddish tint, which actually distinguishes it from healthy skin, which is why it also has another name - a red rash under the eyes.
The nodules protrude above the surface of the skin and also change its color. They may occur against the background of a certain disease or local inflammatory process. There is a type of nodule on which a blister can form. The structure of the rash can be both dense and soft.
The bubble forms directly on the skin, or even thicker. Consists of three parts: cavity, bottom and tire. Inside the cavity there is serous content. It develops independently, without any additional changes to the skin.
Wearing contact lenses
With poor vision, many people prefer lenses to glasses. This is convenient, of course, and invisible to others.
During adaptation, you will feel discomfort, your eyes will itch and swell. When wearing contact lenses for a long time, you can easily damage the delicate mucous membrane.
When infected, the eyes will begin to:
- itch;
- The whites will turn red;
- Discharge appears;
- Watery eyes appear;
- Pain and feeling of a foreign object in the eye.
You need to properly care for your lenses:
- Follow the replacement schedule;
- Wash and disinfect in a timely manner;
- Put on only with clean hands.
Spending prolonged periods of time in front of a computer or television screen
When you spend a long time at the computer, your eyes quickly get tired, itchy, swollen, and can become inflamed. The mucous membrane is naturally protected by the tear film.
But with reduced secretion, the film quickly becomes thinner and the person involuntarily begins to experience discomfort:
- Slight burning sensation;
- Visual acuity decreases;
- Eye diseases appear;
- Eyes itchy and swollen in the morning;
- A small veil appears before the eyes;
- A headache begins.
To avoid the unpleasant consequences of being at the computer, you need to take hourly breaks.
In moments of rest:
- Do eye exercises, for example, blink intensely and move them in different directions;
- Instill “artificial” tears, this is an over-the-counter drug.
Other diseases that make the eyes itchy and swollen
Other ophthalmic diseases that cause itchy and swollen eyes:
- Amblyopia occurs when one eye dominates the other. The functioning of the brain and organ of vision is impaired;
- Retinal dystrophy is a severe damage to the eyeball, i.e., death of the retina;
- Astigmatism is a pathology of the lens or cornea;
- Presbyopia - age-related farsightedness;
- Colorblindness is the inability to distinguish colors;
- Keratoconus - leads to thinning of the cornea;
- Myopia - inability to see objects at a distance;
- Farsightedness is the inability to focus on nearby objects.
Congenital and acquired somatic pathologies
There are a number of somatic diseases that cause swelling and puffiness of the eyes:
- glaucoma,
- cataract,
- gastrointestinal pathology (liver disease),
- metabolic and endocrine diseases (diabetes mellitus).
Glaucoma is a chronic eye pathology, the development of which is caused by neurovascular disorders and impaired circulation of intraocular fluid.
Cataracts, in which the cornea becomes cloudy, can be caused by both genetic defects and previous inflammation and trauma. It may also present in the early stages with itching and swelling of the eyelids.
Diabetes mellitus, in severe cases, leads to eye damage, so if the eyelids itch and itch, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist.
Eyes become itchy and swollen in children
If you notice that your child's eyes are itchy and swollen, be sure to take action. Because this is an alarming symptom and a consultation with a pediatrician is necessary here.
Often the doctor quickly removes the discomfort, and everything returns to normal. But in some cases, emergency and even surgical care will be required.
Here is a list of the main reasons why the eyes itch and swell in children:
- The child cried for a long time and rubbed his eyes;
- Due to the bite of a mosquito , midge and other insects;
- Allergic reaction of the body , in which nasal congestion does not go away;
- There may be a foreign body in the eye , for example, a speck of dust or a midge;
- Due to simple overvoltage . The following can have a negative impact: TV, computer, gadgets, school studies. You need to teach your children to take at least short breaks on time and give some rest to their eyes;
- Barley is a purulent inflammation, the whole eye can swell, the child actively scratches the eyes, but they do not redden much;
- Congenital obstruction of the lacrimal canal - the corners of the eyes may become very itchy and swollen in infants. Because the mucous membrane dries out;
- Conjunctivitis can be of any origin, the causes of its occurrence are different: fungi, viruses, various bacteria. With conjunctivitis, the eyes are especially itchy and even swollen;
- During wound healing . The child’s body produces a special healing substance that provokes such symptoms;
- Abscesses of the eyelid and lacrimal sac lead to the accumulation of purulent masses in the tissues, the eyes quickly swell and constantly itch. Pus is formed during the development of many ophthalmological diseases or untreated sinus diseases (infectious).
Diagnostics
If your eyes are itchy and swollen. You should immediately contact an ophthalmologist. This will help avoid serious complications and even loss of vision.
The doctor will take the following measures:
- Conduct an examination and test your vision;
- Examines discharge from the eyes;
- Determine whether there is an allergy;
- Eliminates infectious origin of ailments;
- Assess the condition of the fundus;
- Conducts pupillary reaction to light;
- Prescribe treatment if necessary and determine the date of the next appointment.
Treatment methods
Let's look at methods of treating the main diseases that cause itchy and swollen eyes.
Treatment of an allergic reaction
The main method of treatment is the use of medications.
Two categories of drugs are used for treatment:
- Drugs that relieve symptoms;
- Drugs that eliminate the allergen.
The most popular drugs:
- Kromofarm - recommended for use in the form of drops. Apply four times a day, 1 or 2 drops. In rare cases, apply eight times. The main contraindications are children under five years of age, breastfeeding, as well as pregnancy and hypersensitivity. The cost in pharmacies ranges from 100 to 300 rubles ;
- Visin Alergy is an effective drug that can be administered both intranasally and conjunctivally. It is recommended to administer the drug intranasally. Drops can be used from the age of six. Before use, you must thoroughly clean your nasal passages. It is necessary to do two inhalations twice a day. Sometimes prescribed four times a day. Contraindications: children under six years of age, breastfeeding and pregnancy, as well as hypersensitivity. The cost of the drops is 300 rubles .
Kromofarm Vizin Alergy
Treatment of unpleasant symptoms when wearing contact lenses
If your eyes become swollen and itchy, then you need to consult an ophthalmologist. The doctor will prescribe other lenses. And the doctor may also prescribe medications to eliminate discomfort - lubricating and moisturizing drops.
The most popular drug is Hilo-Komod drops.
Place one drop of the drug in each eye three times a day.
If necessary, increase the frequency of use.
Hilo-Komod drops are prescribed from the age of 18.
The cost is 700 rubles .
Treatment for cataracts
Cataracts are a dangerous eye disease. Sometimes surgery is required to treat cataracts. Cataracts can lead to complete blindness. You cannot treat this disease on your own. Only a doctor can prescribe drugs to treat such a disease.
The most commonly prescribed drugs are:
- Quinax eye drops - drops are used 3 times a day, two drops in one eye. Quinax should not be used by children, during pregnancy, with sensitivity to chemicals or while breastfeeding. The cost varies from 700 to 800 rubles ;
- Oftan Katahrom - the drug is used three times a day, you need to instill 1-2 drops. Contraindications: pregnancy, breastfeeding, individual sensitivity to any components. Can be used from 18 years of age. The average cost is 250 rubles .
Quinax
Oftan Katahrom
Eye treatment for prolonged screen time
Most prescribed drugs:
- Systane drops - used 1-3 times a day, one or two drops in each eye. Contraindications: individual intolerance, as well as pregnancy. Cannot be prescribed to children. The cost is 400 rubles ;
- Oftagel - apply 1-4 times a day, one drop. It is not recommended for children or those with sensitivity to the components of the drops. Cost 250 rubles .
Systane Oftagel
Treatment for the appearance of barley
Most prescribed drugs:
- Albucid eye drops - apply 2-3 drops into the affected eye 5-6 times. Contraindications: hypersensitivity to components and pregnancy. Cannot be used by children under three years of age. Average cost 80 rubles ;
- Hydrocortisone - ointment is used before bedtime, the product is placed in the conjunctival cavity behind the lower eyelid. Cannot be used by children under two years of age. The average cost is 90 rubles .
Albucid
Hydrocortisone
Treatment for glaucoma
Glaucoma is a chronic disease in which the optic nerve atrophies.
Therefore, instillation of anti-glaucoma drops, for example, Timolol, is indicated.
You need to drip 2 times a day, one drop. Timolol should not be used by children under three years of age.
Contraindications: sinoatrial blockade, lactation, bronchial asthma, dystrophic diseases.
The average cost is 60 rubles .
Treatment for ophthalmic rosacea
For drug treatment, Tetracycline ointment is used.
Apply 3-4 times a day. The course of treatment lasts 5-7 days.
Contraindications include pregnancy, lactation, kidney and liver dysfunction, and various fungal diseases.
Prohibited for use by children under eight years of age.
The average cost is 150 rubles .
Treatment for electroophthalmia
- Cyclomed - cycloplegic drops, which are instilled 1 drop up to 4 times a day. It is permissible for children to use the drug, but only with a doctor’s prescription. Contraindications: high sensitivity to components, glaucoma, pregnancy, intestinal obstruction. Average cost 600 rubles ;
- Tobradex - antibiotic drops are suitable for various infections. Application: instill every 2 hours for the first 3 days, then 1-2 drops every 4-5 hours, treatment for no more than 8 days. It can be prescribed even to newborn children. Contraindications: fungal diseases, microbacterial infections, pregnancy and viral conjunctivitis. The average cost is 250 rubles .
Cyclomed
Tobradex
Treatment of diseases causing red, swollen eyes
The first thing you need to do is find out why the eye is swollen and what could be causing this problem. Despite some different symptoms, this matter is best left to the doctor. Only after the diagnosis is made, a course of treatment is prescribed.
Conjunctivitis
Due to the fact that this disease has a different initial nature (viruses, bacteria, allergies), the final list of drugs will vary.
- In case of bacterial conjunctivitis, the eye is initially washed from accumulated pus using a solution of Furacilin or potassium permanganate. Afterwards they are treated with any bactericidal agent (Ciprofloxacin, Sodium Sulfacyl, Oletetrinovaya ointment or Levomycytin).
- Viral conjunctivitis is treated with antiviral drugs, eye drops with the active ingredient interferon (Actipol, Ofalmoferon). To prevent bacterial infection, it is recommended to rinse with Chlorhexidine or Furacilin.
- Therapy for allergic conjunctivitis involves identifying and eliminating the allergen. If necessary, antihistamine eye drops Allergodil, Okumetil, Visin can be applied topically.
Barley
Rinsing with a solution of penicillin, furatsilin, potassium permanganate. It is strictly forbidden to squeeze out pus, this will provoke further spread of the infection! Lubricating the skin of the eyelids, placing antibacterial ointments behind the eyelids: Levomycytin, Tetracycline, Albucid. Immunostimulating drugs are often prescribed.
Treatment at home with folk remedies
Of course, you can treat your eyes at home with popular folk remedies, but you should not believe only in the magical power of folk recipes and abandon modern medicine.
Do not forget to make sure that you are not allergic to the product used or its components.
Let's consider treatment with folk remedies.
Treatment of eye pressure
Aloe flower will help treat eye pressure.
Directions for preparation and use:
- Tear aloe (2 leaves) by hand and pour 250 ml of boiling water;
- Boil for one minute;
- Cool and strain;
- Rinse your eyes with this decoction up to 5 times a day for two weeks;
- Then you need to take a break for half a month and undergo treatment again;
- Take 3 courses and there will be no trace of the disease;
- This remedy has no contraindications;
- For children from 6 years of age.
Treatment of demodicosis of the eyelids
For demodicosis of the eyelids, it is worth mixing:
- 2 g combustible sulfur;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of birch tar;
- 2 tbsp. spoons of interior lard (be sure to melt).
Directions for preparation and use:
- Mix all ingredients;
- Put on fire and boil for 2 minutes;
- When it cools down a little, pour into a jar;
- Be sure to lubricate your eyelids with the resulting mixture at night;
- In the morning, wash off the residue;
- The course of application is at least 2 months;
- Use with caution for people with sensitive skin and a predisposition to allergies;
- Suitable for use from 15 years of age.
Treatment of conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is treated with herbal infusions.
Take 1 tbsp. spoons of herbs, necessarily chopped:
- snapdragon;
- marshmallow root;
- black nightshade leaves.
Directions for preparation and use:
- Pour 0.5 liter of boiling water;
- Cover and leave until cool, filter;
- Instill 2 drops 1 time per day until healing.
An infusion of cornflowers also helps:
- Take 1 tbsp. spoon of flowers and pour 1 cup of boiling water;
- Wash the eyes with a slightly warm solution every morning for ten days;
- This remedy is very effective for conjunctivitis and also has no contraindications;
- It should not be used by young children without a doctor.
Treatment for the appearance of barley
Barley can be easily cured at home; use one of the methods described below. Moreover, they are harmless, and even small children can be treated with eggs. The first method can only treat adults.
The first way is to eat 4 dry baskets of tansy per day, washed down with plenty of water.
Second way:
- Boil the egg;
- Take out half of the white and apply it to the eye;
- Keep until it cools down.
Another effective way is to apply boiled flaxseed in a gauze bag to the barley.
Treatment for glaucoma
For glaucoma, flower pollen is a great help, which should be taken 15 g per day for a month.
Using a compress for treatment:
- Mix 2 tbsp. l. fresh nettle and 1 tsp. lily of the valley flowers;
- Pour 1 tbsp. water and leave for 8 hours;
- Add 0.5 tsp. soda, stir;
- Make compresses 2 times a day, for at least 10 minutes;
- Contraindicated for children and pregnant women.
Blueberries improve vision and prevent seizures. You can drink teas or eat fresh berries in unlimited quantities. It has absolutely no contraindications, and is especially useful for children and adults.
Medicines for itching and swelling of the eyelids
Rarely do patients manage to cope with itching and swelling of the eyelids at home 100%. Even if you suppress the symptoms of the disease, there is no guarantee that it will not arise again. For complete cure, consultation with an ophthalmologist, dermatologist, allergist-infectious disease specialist and therapist is required. For injuries accompanied by swelling of the eyelids, the patient is prescribed a consultation with a traumatologist.
An integrated approach to treatment always gives good results. For this purpose medications are used:
- Antihistamines. They are used to relieve the symptoms of allergies, as well as other diseases accompanied by itching. Drops of Opatanol, Visin, Okumetil and so on are used for these purposes. You can use ointments, injections, tablets.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs. They also come in different forms. Most often used in the form of drops and ointments. Doctors often prescribe drugs based on Indomethacin - Indocollir, Diklo-F and so on. The use of anti-inflammatory drugs is indicated for almost any infection.
- Ointments. In this form, the medicines are quite convenient to use, especially during night sleep, when the eyes are resting and the drug is fully working. Ointments that are recommended include Hydrocotrizone, Tetracycline, and so on. They are used to treat blepharitis and conjunctivitis.
- Antibacterial agents. Used to treat bacterial infections. It is recommended to use Levometicin and Tsipromed in the form of drops.
All medications are used after medical prescription and under the strict supervision of doctors.
Prevention
The following simple tips will help you avoid dangerous situations:
- Do not touch your face with your hands, especially outside the home;
- Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene;
- Visit an ophthalmologist regularly, especially after 40 years of age;
- Protect your eyes from adverse conditions (use glasses);
- Take breaks when working at the computer;
- Moisturize the mucous membrane with special drops;
- Eat properly;
- Use proven cosmetics;
- Drink at least 2 liters of water per day;
- With demodicosis, you need to sleep on pillows made of synthetic fillers;
- Play sports or at least take daily walks in the fresh air;
- Complete abstinence from alcohol, cigarettes and trips to the solarium.
Redness around the eyes and itching: causes and treatment
As a rule, any pathological processes or changes in the body are reflected on a person’s face in a variety of manifestations, and therefore it is very important to monitor not only your health, but also lead a correct lifestyle. It is with the help of these simple measures that you can forget about itching around the eyes and keep your face not only beautiful, young, but also healthy for a long time.
One of the manifestations of many ailments is skin redness, swelling and severe peeling. But in order to eliminate such symptoms, it is necessary to establish the exact cause that provoked their appearance.
Human physiology
Quite often, a person’s skin around the eyes itches due to normal physiological characteristics, which are always individual.
With sensitive or very dry skin, simple exposure to natural factors, for example, strong wind, hot sun or, conversely, low temperatures (frost), is often enough to cause a red spot and severe irritation to appear under the eyes. In such cases, the skin begins to itch and peel without any particular reason.
People with these skin types are recommended to use special creams daily that have not only a nourishing, softening, moisturizing, but also a protective effect. You should use such creams before every time you go outside, and not just in the morning or before bed.
Cosmetics
In women, itching under the eyes, as well as around them, can occur when using low-quality or simply unsuitable cosmetics. There can be several reasons for this phenomenon, for example:
- content of any harmful substance in cosmetics;
- individual allergies to certain components;
- use of low-quality cosmetic products;
- using toilet or laundry soap to wash your face (it dries the skin very much);
- using the wrong skin cleanser;
- using a cream that is not suitable for age or has expired.
When applying any inappropriate cosmetic or care product, as well as decorative cosmetics, a burning sensation occurs almost immediately, the skin under the eyes begins to itch, and a rash and swelling may appear.
For people with this problem, it is best to give preference to hypoallergenic products or cosmetic lines for sensitive skin and for children.
[[!ms2Gallery?]]
If, when using cosmetics, red spots appear under the eyes, discomfort, a feeling of tightness of the skin, itching, pain, tingling, you need to urgently take action:
- It is necessary to clean the entire surface of the face from applied cosmetics, using special products and warm water. You should not use soap, as it will significantly worsen the condition of the skin, increase irritation and other symptoms.
- It is very important to quickly relieve inflammation by applying a compress of a warm decoction of chamomile or other medicinal herbs to the face, and after that you need to treat the skin with a special healing cream based on natural ingredients, while avoiding the skin around the eyes; it is better to apply baby cream to them.
- You cannot use those products that caused a negative reaction again in the future, and if the problem occurs frequently, it is best to consult a dermatologist to select the right cosmetics.
Other factors
Very often, the causes of redness of the skin, as well as itching around the eyes, are constant stress, vitamin deficiency, improper, unbalanced diet, lack of proper rest, chronic lack of sleep, and constant eye strain.
When working for a long time at the computer, sewing, embroidery, beading, knitting or simply reading a book, as well as during any other activity that requires strong eyestrain, a person’s eyes begin to itch from simple fatigue. With a lack of vitamins, the skin often peels off.
Therefore, before drawing conclusions about the presence of certain diseases, it is worth thinking about your lifestyle, the characteristics of your daily work, the sufficiency of rest; perhaps, many things in your lifestyle will require adjustments and changes.
Diseases of the eyes and internal organs
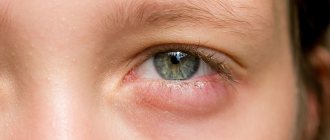
In some cases, eyelid hyperemia, itching, swelling and puffiness may be symptoms of various eye diseases, such as:
- Blepharitis. This disease has an infectious etiology and is caused by certain microbes entering the eye area.
- Conjunctivitis. The disease is also caused by microbes, but is distinguished by the presence of severe inflammation of the eyelids, their redness, severe swelling, crust formation, and purulent discharge from the eyes.
- Demodecosis. Caused by a special demodex mite. An important symptom is irritation and itching, localized along the ciliary edge, and red rashes and peeling of the skin may appear.
- Barley or meibomite. It is a kind of abscess in the eyelid area, located near the eyelashes of the upper or lower eyelid. The disease is caused by an infection, and its treatment consists of accelerating the ripening of the tumor and its rupture.
Quite often, the condition of the eyes is reflected in numerous internal diseases, for example, diabetes mellitus, problems in the digestive or endocrine system, insufficient functioning of the immune system, and liver diseases. All this can cause not only itching in the eyelid area, but also redness of the skin, swelling, irritation, dryness, and the formation of dark circles under the eyes.