Causes
There are two categories of reasons that can provoke the appearance of lacrimation and redness - infectious and non-infectious.
Non-infectious causes include:
- foreign body in the eye;
- increased eye strain;
- poor correction;
- improper use of contact lenses;
- cosmetical tools;
- lack of sleep;
- alcohol intoxication;
- smoking;
- mechanical, thermal injury;
- exposure to direct sunlight;
- poor composition of tear fluid;
- exposure to toxic substances;
- obstruction of the tear ducts;
- obstruction of the lacrimal ducts;
- anatomical blockage (abnormal valve);
- allergic conjunctivitis;
- dry eye syndrome;
- glaucoma;
- smoothing of the cornea.
These factors are not associated with infection. Less often, this condition is not a disease in nature, but the influence of irritating factors. The effects of dust, smoke, pungent odors and cold wind quickly disappear after they are eliminated.
Infectious causes:
- bacterial conjunctivitis;
- viral conjunctivitis;
- iritis;
- blepharitis;
- uveitis;
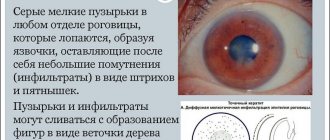
- keratitis.
Infectious pathologies appear quickly and do not go away on their own. The first symptoms appear after a few days.
Inflammatory diseases
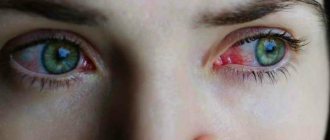
Any inflammatory process can be accompanied by morning pain in the eyes. One of the most common inflammatory diseases is conjunctivitis. It can be bacterial, viral or allergic in nature, caused by eye injury or poor hygiene. With conjunctivitis, in addition to pain in the eyes in the morning, other symptoms often appear:
- discharge of pus, which literally “glues” the eyelashes together and prevents the eyelids from opening;
- redness of the eyes;
- photophobia.
The complex of these symptoms most often indicates that you have developed an inflammatory disease, and you need the help of an ophthalmologist. Your doctor will prescribe appropriate eye drops, ointments, and other treatments that will help relieve or eliminate your symptoms over the next few days or even hours. Usually, a day or two after the start of therapy, opening your eyes in the morning no longer hurts.
However, you should remember that many types of conjunctivitis are infectious, and even after starting treatment you can infect your loved ones. Therefore, so that your family does not wake up the next morning with pain in their eyes, during the period of illness it is important to observe personal hygiene especially carefully.
Treatment
Therapy for redness and lacrimation is determined after diagnosis. Treatment depends on the cause of these symptoms. Infectious pathologies are treated differently. Medicines are prescribed depending on the type of pathogen detected.
Conjunctivitis
Bacterial
In acute bacterial conjunctivitis, one visual organ is initially affected, and after 2–5 days, signs of the inflammatory process spread to the second eye. The main symptoms of acute CD:
- mucous, mucopurulent and purulent discharge;
- swelling of the connective membrane;
- feeling of a foreign object;
- pain that increases as the disease progresses;
- enlargement of preauricular lymph nodes.
Acute CD is treated with topical antibiotics. Moxifloxacin, Tsiprolet, Normax, Gentamicin, Trimethoprim, Polymyxin or Fluoroquinolone are prescribed. If there is no response after 2-3 days, this means that the infection is caused by a virus, antibiotic-resistant bacteria, or is allergic in nature.
Chlamydial bacterial conjunctivitis alternates between periods of remission and exacerbation. The disease manifests itself with a small amount of discharge, a minimal level of pain, itching, lymphadenitis, chemosis and the appearance of follicles on the inner surface of the upper or lower eyelid.
Chlamydial CD is difficult to treat, since the infection caused by chlamydia is prone to protracted and recurrent course, and is also accompanied by numerous complications. Treatment is based on the use of the following antibiotics:
- Phloxal;
- Ciprofloxacin;
- Colbiocin.
Systemic treatment with antibacterial agents lasts 12 days, for extraocular chlamydia - up to 3 weeks.
Gonococcal CD has a very severe course. It manifests itself as redness of the conjunctiva, pain in the eyes, significant swelling, keratitis, up to the formation of ulcerative lesions on the cornea and its perforation, and enlargement of the pre-auricular lymph nodes.
GBC is treated with Ceftriaxone, Ciprofloxacin topically in the form of ointment or drops, and saline irrigation. With GBC, the patient’s sexual partners are also treated. They take oral antibiotics for gonorrhea and chlamydial infections.
Viral
The disease begins in one eye. Then redness, watery discharge and a feeling of irritation in the eye quickly spread to the second organ of vision. Patients develop:
- photophobia;
- chemosis;
- fibrin pseudomembranes;
- blurred vision.
Therapy begins with the removal of purulent discharge. Wash the eyes with a solution of boric acid or potassium permanganate. Additionally, antiviral drugs are used. These include medications based on oxoline, tebrofen and florenal.
Treatment with folk remedies is possible; a good doctor will advise the use of home remedies and describe in detail the method of preparing them.
Allergic
AK is an inflammatory reaction caused by the body's immune reactions in response to contact with an allergen. Clinical picture:
- itching;
- redness;
- nasal congestion;
- eyes water;
- increased photosensitivity;
- blepharospasm;
- formation of follicles or small papillae.
Treatment depends on the specific allergen and requires skin testing. For mild cases, cold compresses and moisturizing drops are sufficient. In severe cases of an allergic reaction, anti-inflammatory and antiallergic drugs are prescribed.
Barley
Involves purulent inflammation of the hair follicle. Hordeolum is manifested by pain, swelling of the eyelid, redness, itching and lacrimation. Sometimes the temperature rises and a headache appears. Barley is treated with drops, allowing it to quickly ripen and break through.
It is recommended to rinse with calendula tincture. Throughout the entire period of therapy, antibiotics are prescribed - Tsiprolet or Levomycetin, and eye ointments are used along with drops.
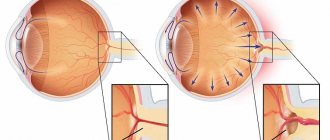
Glaucoma
The disease is characterized by increased intraocular pressure, which causes destruction of retinal cells, atrophy of the optic nerve and irreversible blindness. Signs:
- the appearance of rainbow circles;
- fatigue;
- deterioration of peripheral vision;
- the appearance of a translucent or opaque spot in the field of view.
Therapy begins with the use of eye drops that lower IOP. If medications do not help, they resort to trabeculoplasty using an argon laser.
Iritis
Symptoms:
- pain that increases with palpation;
- swelling of the iris;
- constriction of the pupil;
- eyes water;
- slow reaction to light;
- cloudiness of the anterior chamber moisture;
- hemorrhages or changes in iris color;
- smoothing contours.
Iritis is treated with antiallergic and anti-inflammatory drugs. Hydrocortisone is prescribed for external use. It is recommended to apply warm compresses to reduce inflammation.
Blepharitis
The clinical picture of blepharitis: sensation of a foreign body in the eye, heaviness of the eyelids, pain, itching, increased sensitivity to light sources, lacrimation, redness of the eyelids and dry eyes.
Blepharitis is treated with antibiotics and corticosteroids. For the meibomian form of the disease, massage of the eyelids and lubrication with a solution of brilliant green are prescribed.
Uveitis
The pathology is manifested by inflammation of the choroid of the tract.
The patient is concerned about hyperemia, pain, blurred vision, photophobia, floaters, loss or distortion of visual perception. Uveitis is a disease of infectious origin, therefore it is treated with corticosteroid drops, mydriatic agents and drugs that lower IOP.
Oral corticosteroids are prescribed if inflammation has spread to the vitreous, retina or choroid.
Other possible diseases
Clinical manifestations and treatment features of other pathologies that cause redness and lacrimation:
- Ectropion is an inversion of the eyelid, characterized by dryness, an increase in the mucous membrane in size, lacrimation and maceration of the skin. It is treated with surgery.
- Entropion is an inversion of the eyelid, accompanied by ulceration, scarring of the cornea, redness, and lacrimation. Therapy is based on surgery.
- Dry eye syndrome is characterized by itching, burning, irritation, a feeling of fatigue and tension. Treated with moisturizing drops. Therapy is selected individually, since keratoconjunctivitis sicca has many causes.
Inadequate rest
Morning eye pain is often experienced by people who sleep less than 6 hours. In such a short period, the visual organs do not have time to fully rest and relax. If a person regularly does not sleep at night, fatigue accumulates and serious visual disturbances can occur. In addition to the number of hours of sleep, it is necessary to monitor its quality. Experts strongly recommend sleeping in a room with tightly curtained windows and switched off light sources. The eyes can only fully rest in complete darkness. Even weak radiation from a smartphone or split system does not allow the visual organs to completely relax, which is very important for relieving symptoms of fatigue and maintaining eye health.
The problem can be solved by high-quality darkening of the bedroom, as well as a review of sleep and rest patterns.
Causes of sharp stabbing pain in the eye
Stinging eyes can occur for many reasons: they can range from simply unpleasant sensations in the eye to rather sharp, unpleasant nagging pains. The most common causes of a watery and itchy eye can be:
- overwork of the eye muscles, which may be caused by contact lenses or glasses simply not fitting;
- the problem can also be caused by a headache due to overexertion or stress;
- eye diseases;
- eye injury;
- a foreign body that has entered the eye, which sometimes has to be removed only by an ophthalmologist.
Whatever the reason that caused pain in the eye, you need to remember that this sensitive organ signals problems that have arisen.
It hurts the eyes: treatment with folk remedies
You can also treat pain in the eyes using folk remedies. There are a variety of compresses and lotions. We present effective traditional medicine for the treatment of pain in the eyes:
Brew a spoonful of chamomile, mint, plantain or linden leaves in one glass of hot water. Let it brew for 5-10 minutes, then soak a cotton pad in the infusion, apply it to your eyes, and leave for 20 minutes; Finely grate a raw potato, wrap it in gauze, apply it to your eyes for 20-30 minutes; Squeeze the juice from dill, moisten a cotton cloth, and apply to your eyes for 15-20 minutes.
Prevention of pain in the eyes
As you know, any disease is easier to prevent than to eliminate. Therefore, in order not to think about how to treat pain in the eyes, we recommend that you take preventive measures.
They consist of observing a rest regime for the eyes, getting full sleep, and performing special gymnastics for the eyes. Try not to spend a lot of time at the computer; if this cannot be avoided, then instill moisturizing drops, for example, Oftagel. It is sold in pharmacies without a prescription.
Avoid dusty and smoky places, as tobacco smoke and dust irritate the eyes. Use humidifiers at home. You can prevent pain in the eyes if you follow the drinking regime. Drink 1.5-2 liters of pure still water a day. Your diet should consist of high-quality foods rich in vitamins and minerals. Include fresh fruits and vegetables in your diet, and avoid vitamin deficiency.
Organize your workplace correctly; it should be well lit. While working at the computer, be distracted every 15-30 minutes, give your eyes a rest, blink more often. Don’t forget to wash off your makeup at night, use only an individual towel, and don’t be nervous, because disruptions in the nervous system negatively affect the health of your eyes and the body as a whole.
Methods for relieving the condition of tearing and pain in the eyes
You can drink apple cider vinegar, diluted in a ratio of 1 tsp. per 200 ml of water. Eye strain can be neutralized by massaging the earlobes, temporal bone and the area behind the ears. A compress of infusions of mint, dill and chamomile relieves tired eyes. Brewed tea bags are useful for toning the skin around the eyes. The face should be washed alternating with warm and cool water, and you should finish washing with cool, but not cold water - this will give the skin freshness and a renewed appearance, and cool water will reduce the risk of the development of harmful bacteria on the mucous membrane of the eyes.