The eyes see only half - what is the reason?
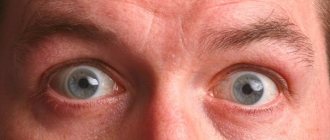
The visual field is the space that is accessible to the perception of one eye when the head and visual organs are stationary. Some people may experience such a defect when half of the view seems to be blocked by a black spot. Simply put, a person does not see with one half of the eye. If such a “half” loss of visual fields is observed in both visual organs, then this may indicate the development of a serious pathology - hemianopsia.
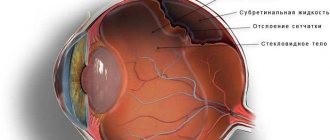
This disorder is explained by damage to certain areas of the visual system, including the area of the brain that is responsible for vision.
The causes of the development of this disease are most often associated with pathological processes in the brain - tumor growth, the development of meningitis, abscesses, impaired cerebral circulation, and traumatic brain injuries.
The main symptom of hemianopsia is the loss of ½ or ¼ of the visual field in each eye and the occurrence of temporary blindness in the corresponding area.
Depending on the cause that caused the pathology, visual field defects may be located differently. With homonymous hemianopsia, there is a symmetrical loss of the visual field only on the left or only on the right in both eyes. For example, a person does not see with the temporal half of the right eye and the nasal half of the left eye.
With the heteronymous or heteronymous type of the disease, the right visual field is lost in one eye and the left in the other (or vice versa). In this case, a person does not see with areas of the eyes located closer to the nose, or, conversely, closer to the temples. If the patient has lost not half, but only a quarter of the visible image, this symptom may also indicate the development of hemianopsia (quadrant type).
Presence/absence of vision problems
It turns out that even small deviations in this area lead to the fact that a person begins to see much worse in the dark than in the light. Ophthalmologists claim that with physiological astigmatism that does not require correction, the ability to night vision is greatly reduced. The same thing happens with myopia and farsightedness. This is explained simply - light does not reach the retina, which is not perfectly flat, since it envelops the back surface of the eye. With myopia, light does not hit the retina directly, but somewhere before it, and the image becomes blurry. With farsightedness, on the contrary, light falls behind the retina. In both cases, its edges are not used, and this significantly reduces the ability to see in the dark. Glasses and lenses, by the way, can only worsen the situation, since part of the already meager light is reflected from their surface, not reaching the eye at all. By the way, the ability to see in the dark depends not only on eye color or vision problems. Oddly enough, it is also influenced by gender. It has been proven that women are able to see more small details in the dark, but in a closer field. Often a lady driving at night cannot understand which side of the road the oncoming car is moving on.
Can hemianopsia be cured?
Since the pathology is not due to ophthalmological reasons, the main treatment is usually carried out by a neurologist, surgeon or oncologist. The essence of therapy is to detect and eliminate the cause that led to loss of visual fields. For this purpose, chemotherapy, surgery and other necessary manipulations can be performed.
Conservative therapy in the treatment of this pathology usually does not help, but there are computer techniques that can improve visual function.
Thus, loss of half the visual field is a serious clinical sign that often indicates hemianopsia. This condition, in turn, may indicate a number of severe brain diseases. Therefore, if you notice a black spot in front of half of your eye, consult a doctor immediately. Early diagnosis in many cases will help save not only vision, but also life (for example, when it comes to cancerous tumors).
Explanation
Due to the rapid switching of the operation of the visual apparatus when the gaze stops at a color other than white, in the absence of deviations, the same picture is observed without changes in brightness or color tint. A necessary condition for obtaining a reliable result is conducting the test while you are awake.
Once the patch is removed from the covered eye, there should be no change in color perception. There may be a temporary increase in the brightness of a closed eye.
Different sensitivity of the visual organs to pictures is not always based on incurable diseases. It is enough to eliminate the influence of provoking factors, which will have a beneficial effect on the restoration of vision. The presence of any changes requires consultation with an ophthalmologist to determine the provoking factors.
Author's rating
Author of the article
Alexandrova O.M.
Articles written
2029
about the author
Was the article helpful?
Rate the material on a five-point scale!
( 3 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5)
If you have any questions or want to share your opinion or experience, write a comment below.
Features of therapy in children and adults
If the pathology is diagnosed early, the chances of a full recovery increase. Thanks to timely surgery to correct the position of the eyeball and correct refraction, it is possible to normalize the functioning of the visual apparatus.
The organ of vision actively develops in childhood. When diagnosing amblyopia in a child, it is important to have surgery before the age of 12. In most cases, pathology is detected during a medical examination for admission to a preschool institution or school. This is the ideal age to eliminate the problem, if you do not delay treatment.
The principle of therapy for adult patients is based on long-term direct occlusion of the healthy eye and stimulation of the foveal zone of the diseased organ of vision. Among the techniques used to eliminate amblyopic manifestations, technology based on the effect of neuroplasticity stands out. It is performed using a computer program that shows the patient different stimuli based on the Gabor spot. The effectiveness of this therapy is an improvement in visual acuity by 2.5 lines.
Why does one eye see brighter in the morning?
In the morning, every person feels slight discomfort in the eyes, which goes away within 1-2 minutes. This is normal. If one eye perceives objects and objects more brightly than the other, and the effect does not go away for a long time, it is recommended to consult a doctor for a thorough examination of the eyeball.
After alcohol
One of the reasons for morning distortions of the visual apparatus may be the negative effects of alcohol if a fair amount of strong drinks were drunk the day before. Ethanol contributes to dehydration of the body, decreased functioning of the tear glands, which provokes dry eye syndrome.
Large doses of alcohol impair vision due to the effects of toxins. Against this background, toxic amblyopia develops. Signs of pathology are especially pronounced during a hangover, that is, in the morning hours.
Why can this happen suddenly?
Symptoms of amblyopia that appear in the morning are often evidence of incorrect head position during sleep. When the face is immersed in a pillow, the visual system is compressed under the weight of its own body.
This leads to disturbances in blood flow to the tissues and cells of the eye, tear production, and slight deformation of the cornea. After waking up, the pinched eye cannot focus on objects. Discomfort is often complemented by bright flashes.
After 5-10 minutes, visual acuity is completely restored. If symptoms do not disappear for a long time, you should make an appointment with an ophthalmologist.
Possible complications
If treatment is not started promptly, the progression of lazy eye syndrome will rapidly continue until complete loss of functionality. Problems with complications also concern those patients who did not receive full treatment or refused traditional therapy or surgery. Therefore, the issue of early diagnosis and quality treatment should be a priority.
Children require special attention. In the presence of pathological processes, treatment cannot be delayed. Lost time results in irreversible changes, which subsequently negatively affect the quality of life.
Diagnostic methods and therapy
Making a diagnosis requires:
- Visometry (tables are used to determine the level of acuity).
- Perimetry (thanks to a certain device, the boundaries of the visual fields are revealed).
- Refractometry.
- Skiascopy (refractive power is determined using a light beam and a mirror).
- Ophthalmoscopy (the doctor uses an ophthalmoscope to examine the bottom of the eye).
- Ophthalmometry (the radius of curvature of the cornea is determined using an ophthalmometer).
- Study of binocular vision (synoptophore and four-point color test are used).
The method by which the pathology will be eliminated is determined by the level and type of refractive errors. Visual dysfunction is usually corrected with glasses or contact lenses. But this method is not suitable for every patient. It is necessary that the difference in refractive power should not be more than 3 diopters.
The selection of lenses is carried out for each specific case separately. It is necessary to wear them correctly and periodically undergo examination by an ophthalmologist, receiving the necessary consultations from him.
A patient who wears lenses may suffer from:
- epithelial edema;
- keratitis;
- damage to the corneal layer.
If conservative methods prove useless, the doctor decides to perform laser surgery. It is also prescribed to patients whose degree of illness is high. After surgery, it may take a week or two for the improvement to become apparent.
There is no need to panic when anisometropia is diagnosed. If detected early, the problem can be completely eliminated, especially if there is a mild degree of the disease.
Different perceptions of the organs of vision do not always indicate the presence of a pathological condition.
The difference in color perception may not be significant, which indicates a certain normal vision.
A significant difference in the color display of the picture is a reason to seek medical help.
The reasons for different perception of shades are congenital or acquired. With hereditary pathology, both eyes are affected. In the case of acquired color blindness, unilateral progression of the disease is observed. Color perception disorders develop against the background of a pathological condition in the body:
- retinal diseases;
- disturbances in the functionality of the central nervous system;
- jaundice;
- improper use of medications;
- poisoning by chemical components or their compounds;
- due to cataract removal;
- prolonged exposure to ultraviolet rays on the visual apparatus.
There are several types of acquired color transmission disorder from the eyes to the brain:
- Xanthopsia. Surrounding objects become yellow.
- Cyanopsia. The picture is perceived in blue shades.
- Erythropsia. Vision is colored in red shades.
The appearance of acquired disturbances in the sensitivity of color images is temporary. Elimination of the pathological condition occurs after reducing the impact of provoking factors.
Complete loss of color perception by the visual organs is characterized by additional pathological conditions:
- decreased level of vision;
- central scotoma.
Incomplete blindness to some shades of colors occurs. This color perception is classified according to shades:
- Protanopia. Insensitivity of the eyes to the color red.
- Deuteranopia. The visual organs do not recognize green shades.
- Tritanopia. It is difficult for the visual apparatus to recognize the color blue.
Complex color blindness may occur. For example, only blue or green shades are not perceived.
Common pathological conditions are protanopia and deuteranopia.