Only through vision is a person able to contemplate beauty and communicate with the world around him. However, over time, your eyes may begin to fail. Vision problems can be very diverse, so it is worth excluding serious pathologies. To do this, you should consult a doctor.
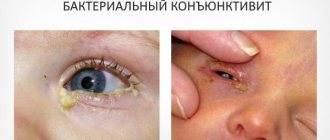
Some believe that if the capillaries in the eye burst, then this is only a temporary phenomenon. However, such symptoms may indicate quite serious health problems, which only an experienced specialist can accurately determine. Therefore, you should not ignore this problem.
What is the function of capillaries in the eyes?
The capillary is the thinnest blood vessel in the human body. It communicates with veins and arteries. There are millions of capillaries in everyone's body, which are also found in the eyes. Depending on the work of these vessels, a person’s vision remains clear or he or she develops certain problems.
If the capillaries are in poor condition and do not cope with their tasks, then this leads to the fact that the body begins to starve, since it is not saturated with oxygen and the necessary nutrients and components at the proper level.
Treatment of rosacea
The first way to eliminate burst blood vessels on the face is a comprehensive examination by a doctor. Drug therapy for a disease is an additional method in the treatment of a disease using a hardware method. This includes drugs that act on blood vessels and strengthen them. Here is the following list:
- Alpha-linoleic acid Omega-3 improves vascular elasticity well. The fatty polyunsaturated amino acids included in the composition remove sclerotic plaques in the blood vessels.
- The drug Ascorutin helps to reduce the penetration of blood vessels into the surface layer of the skin and reduce their fragility. The cream contains vitamin C and P.
- Alpha tocopheron, Pinogen, Gingo biloba. These antioxidants help remove harmful waste products from the body.
It is necessary to seek help from an experienced cosmetologist who can offer the following manipulations:
- Laser therapy. This salon procedure is inexpensive, but in advanced cases you will have to pay more.
- Photorejuvenation. To be cured, a full course of therapy is necessary, and for the first effect, several procedures are sufficient.
- Ozone treatment. A very effective method of therapy for severe disease. The procedure is not very pleasant, since ozone is injected under the skin. To eliminate vascular mesh on the face, you need to undergo a full course of therapy in the clinic.
- Sclerotherapy. This treatment depends on the type of vessels affected. If the capillaries are blue, this is due to an increase in venules.
Why do blood vessels in the eyes burst?
Such minor hemorrhages have probably happened to every person at least once. However, when the eye is red, the capillaries have burst, and no additional unpleasant symptoms are observed, the person prefers to wait a while until the unpleasant redness goes away on its own. Although the eye looks scary at such a moment, such a problem does not cause serious physical discomfort. Should you panic if the capillaries in your eye burst? What to do in such a situation?
If this is the first time this happens, then don’t worry too much. The redness will actually go away on its own within a few days. However, when blood vessels begin to burst with enviable frequency, such a phenomenon may indicate more serious problems. In this case, you should definitely visit an ophthalmologist and clarify the reasons for what is happening.
Typically, the doctor first conducts a standard examination and listens carefully to the patient. He also needs to examine the fundus and familiarize himself in detail with the patient’s medical record. A specialist needs to know for sure whether the capillaries burst under the eyes or just inside the visual organs, what preceded the appearance of unpleasant symptoms, and any other information that will help determine the cause of the redness. Sometimes such symptoms are accompanied by fever, dizziness, the appearance of “spots”, etc.
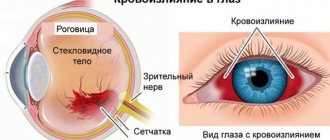
Symptoms of bleeding, visible and felt
Bleeding in the eye is noted primarily visually.
- In mild cases it looks like a hyperemic stripe, in worst cases it looks like a red spot on the conjunctiva.
- The size and shape of a spot or stripe may be different, but in all cases it stands out in a bright red color; it is impossible not to notice it when looking at yourself in the mirror.
- If several vessels burst at once, redness in the eyes can fill the entire conjunctiva.
- Most cases end with only redness, but sometimes people also notice dryness or a slight burning sensation in the area of the injured eye. Some discomfort may be felt.
When capillaries burst due to internal reasons, being one of several symptoms of a particular disease, other unpleasant phenomena may be observed. In the event of a surge in pressure, for example, in addition to redness of the eyes, headaches and spots before the eyes, weakness and poor health are observed. Usually only one eye is affected; cases where capillaries burst in both visual organs at once are rare.
Helpful: Displaced calcaneal fracture
Capillaries burst in the eye: internal causes
If we talk about such factors, then quite often this happens with the development of arterial or intracranial hypertension. As a rule, when frequent redness occurs, doctors suspect this pathology first. During a hypertensive crisis, a sharp jump in pressure occurs, which the fragile blood vessels of the eye cannot withstand. That's why they burst first. If we talk about additional symptoms, such seizures are often accompanied by nosebleeds.
If a person with hypertension has severely burst capillaries in the eye, this is a clear signal that they need to check their blood pressure and more closely monitor their health. If blood pressure increases very strongly and sharply, this can lead to more serious consequences. Capillaries can burst not only in the eyes, but also in the brain.
If a person has burst capillaries in the eye and this is not the first time this has happened, then it is also worth checking for diabetes. With such a disease, pathological conditions associated with the functioning of blood vessels often develop, which become thinner and are characterized by increased fragility. Sometimes doctors diagnose diabetic retinopathy, which is characterized by problems with the vascular system of the visual organs. If this problem is left unattended, the patient’s vision will only worsen over time. There is a risk of complete blindness.
It is also worth excluding ophthalmic type pathologies. If a benign or malignant formation appears in the eye, this may well provoke numerous ruptures of blood vessels. An inflammatory disease can also lead to similar symptoms. If the patient has additionally burst capillaries around the eyes, this may be a sign of conjunctivitis, glaucoma, keratitis and other pathologies that require prompt treatment.
Similar symptoms can also appear against the background of hematological diseases. Redness of the eyes sometimes indicates leukemia, lymphoma, hemophilia, etc. Also, these ailments are accompanied by additional symptoms in the form of the appearance of hematomas with slight pressure on the skin.
When speaking about why the capillaries in the eye burst, one should not exclude the possibility of developing vitamin deficiency or immunodeficiency. Often, due to the fact that the human body lacks certain useful components (for example, vitamins), this can lead to blood vessels losing their elasticity.
Ontogenesis
The cellular elements of the capillary wall and blood cells have a single source of development and arise in embryogenesis from the mesenchyme. However, the general patterns of development of blood and lymphatic capillaries in embryogenesis have not yet been sufficiently studied. Throughout ontogenesis, blood capillaries are constantly changing, which is expressed in the desolation and obliteration of some capillaries and the new formation of others. The emergence of new blood cells occurs by protrusion (“budding”) of the wall of previously formed cells. This process occurs when the function of a particular organ is enhanced, as well as during organ revascularization. The process of protrusion is accompanied by the division of endothelial cells and an increase in the size of the “growth bud”. When a growing cell merges with the wall of a pre-existing vessel, perforation of the endothelial cell located at the top of the “growth bud” occurs and the lumens of both vessels connect. The endothelium of capillaries formed by budding does not have interendothelial contacts and is called “seamless.” By old age, the structure of the blood vessels changes significantly, which is manifested by a decrease in the number and size of capillary loops, an increase in the distance between them, the appearance of sharply tortuous blood vessels, in which narrowing of the lumen alternates with pronounced expansions (senile varicose veins, according to D. A. Zhdanov), and also a significant thickening of the basement membranes, degeneration of endothelial cells and compaction of the connective tissue surrounding the K. This restructuring causes a decrease in the functions of gas exchange and tissue nutrition.
Blood capillaries are present in all organs and tissues; they are a continuation of arterioles, precapillary arterioles (precapillaries) or, more often, lateral branches of the latter. Individual cells, uniting with each other, pass into postcapillary venules (postcapillaries). The latter, merging with each other, give rise to collecting venules that carry blood into larger venules. An exception to this rule in humans and mammals are sinusoidal (with a wide lumen) liver blood vessels, located between the afferent and efferent venous microvessels, and glomerular blood cells of the renal corpuscles, located along the afferent and efferent arterioles.
Blood vessels K. were first discovered in the lungs of the frog by M. Malpighi in 1661; 100 years later, Spallanzani (L. Spallanzani) found K. in warm-blooded animals. The discovery of capillary pathways for blood transport completed the creation of scientifically based ideas about the closed circulatory system laid down by W. Harvey. In Russia, the systematic study of calculus began with the studies of N. A. Khrzhonshchevsky (1866), A. E. Golubev (1868), A. I. Ivanov (1868), and M. D. Lavdovsky (1870). Dat made a significant contribution to the study of anatomy and physiology. physiologist A. Krogh (1927). However, the greatest successes in the study of the structural and functional organization of cells were achieved in the second half of the 20th century, which was facilitated by numerous studies carried out in the USSR by D. A. Zhdanov et al. in 1940-1970, V.V. Kupriyanov et al. in 1958-1977, A. M. Chernukh et al. in 1966-1977, G.I. Mchedlishvili et al. in 1958-1977 and others, and abroad - E. M. Landis in 1926-1977, V. Zweifach in 1936-1977, E. M. Renkin in 1952-1977. , G. E. Palade in 1953-1977, T. R. Casley-Smith in 1961-1977, S. A. Wiederhielm in 1966-1977. and etc.
Blood cells play a significant role in the circulatory system; they provide transcapillary exchange - the penetration of substances dissolved in the blood from vessels into tissues and back. The inextricable connection between the hemodynamic and exchange (metabolic) functions of blood cells is expressed in their structure. According to microscopic anatomy, cells have the appearance of narrow tubes, the walls of which are penetrated by submicroscopic “pores.” Capillary tubes can be relatively straight, curved, or coiled. The average length of the capillary tube from the precapillary arteriole to the postcapillary venule reaches 750 µm, and the cross-sectional area is 30 µm2. The caliber of the blood cell on average corresponds to the diameter of the erythrocyte, but in different organs the internal diameter of the cell varies from 3-5 to 30-40 microns.
Rice. 2. Schematic representation of the structure of the wall of the blood capillary: 1 - endothelial membrane; 2 - basal membrane, consisting of a basement membrane (3) and pericytes (4), red blood cells (5) are visible in the lumen of the capillary. Rice. 3. Electron diffraction pattern of a fragment of the wall of a blood capillary from the parotid salivary gland: I - part of an erythrocyte in the lumen of the capillary; II - endothelial cell (1 - cytoplasm, 2 - micropinocytotic vesicles); III - basement membrane; IV - pericyte, located deep in the basement membrane (3 - cytoplasm, 4 - nucleus, 5 - contact of the pericyte process with the endothelial cell). Rice. 4. Electron diffraction pattern of the elements of the wall of blood capillaries: a - intracerebral capillary (1 - glycoprotein coating, 2 - endothelial cell); x 60,000; b — intercellular contact in the endothelial membrane of the glomerular capillary of the kidney (1 — cytoplasm of neighboring endothelial cells, 2 — contacting cytolemmas, 3 — intermembrane space); x 90,000; c and d — glomerular capillaries of the kidney (1 — open fenestrae; 2 — diaphragmatic fenestrae in the cytoplasm of endothelial cells); X 70,000; d — wall of the sinusoidal capillary of the liver (1 — intermittent contact between adjacent endothelial cells 2); x 35,000.
As electron microscopic observations have shown, the wall of the blood vessel, often called the capillary membrane, consists of two membranes: the inner - endothelial and the outer - basal. A schematic representation of the structure of the blood vessel wall is presented in Figure 2, a more detailed one is shown in Figures 3 and 4.
The endothelial membrane is formed by flattened cells - endothelial cells (see Endothelium). The number of endothelial cells limiting the lumen of the cell usually does not exceed 2-4. The width of the endotheliocyte ranges from 8 to 19 µm and length - from 10 to 22 µm. Each endotheliocyte has three zones: peripheral, organelle zone, and nuclear-containing zone. The thickness of these zones and their role in metabolic processes are different. Half of the volume of the endothelial cell is occupied by the nucleus and organelles - the lamellar complex (Golgi complex), mitochondria, granular and non-granular network, free ribosomes and polysomes. The organelles are concentrated around the nucleus, together with the Crimea they form the trophic center of the cell. The peripheral zone of endothelial cells performs mainly metabolic functions. Numerous micropinocytotic vesicles and fenestrae are located in the cytoplasm of this zone (Fig. 3 and 4). The latter are submicroscopic (50-65 nm) holes that penetrate the cytoplasm of endothelial cells and are blocked by a thinned diaphragm (Fig. 4, c, d), which is a derivative of the cell membrane. Micropinocytotic vesicles and fenestrae involved in the transendothelial transfer of macromolecules from the blood to tissues and back are called large “burrows” in physiology. Each endothelial cell is covered on the outside with a thin layer of glycoproteins it produces (Fig. 4, a), the latter play an important role in maintaining the constancy of the microenvironment surrounding endothelial cells and in the adsorption of substances transported through them. In the endothelial membrane, neighboring cells are united using intercellular contacts (Fig. 4, b), consisting of cytolemmas of adjacent endothelial cells and intermembrane spaces filled with glycoproteins. These gaps in physiology are most often identified with small “pores” through which water, ions and low molecular weight proteins penetrate. The throughput capacity of the interendothelial spaces is different, which is explained by the peculiarities of their structure. Thus, depending on the thickness of the intercellular gap, interendothelial contacts are distinguished as tight, gap and intermittent types. In tight junctions, the intercellular gap is completely obliterated over a significant extent due to the fusion of the cytolemmas of adjacent endothelial cells. At gap junctions, the smallest distance between the membranes of neighboring cells varies between 4 and 6 nm. In intermittent contacts, the thickness of the intermembrane spaces reaches 200 nm or more. Intercellular contacts of the latter type in the physiological literature are also identified with large “pores”.
The basal membrane of the blood vessel wall consists of cellular and noncellular elements. The noncellular element is represented by the basement membrane (see), surrounding the endothelial membrane. Most researchers consider the basement membrane as a kind of filter with a thickness of 30-50 nm with pore sizes equal to 5 nm, in which the resistance to penetration of particles increases with increasing diameter of the latter. In the thickness of the basement membrane there are cells called pericytes; they are called adventitial cells, Rouget cells, or intramural pericytes. Pericytes have an elongated shape and are curved in accordance with the outer contour of the endothelial membrane; they consist of a body and numerous processes that entwine the endothelial membrane of the cell and, penetrating the basement membrane, come into contact with endothelial cells. The role of these contacts, as well as the function of pericytes, has not been reliably elucidated. It has been suggested that pericytes participate in the regulation of the growth of endothelial cells K.
Other reasons
Not only serious pathologies can lead to such symptoms. Often a person is faced with the fact that the capillaries in his eye have burst due to:
- Fatigue, lack of sleep, eyestrain. This can happen if you work at a computer for a long time, watch TV or use tablets, smartphones and other gadgets. Reading books at night is also very harmful, as it leads to severe strain on the visual organs.
- Excessive physical activity. People who are actively involved in sports often experience burst capillaries in the eye. If you give preference to strength training, this may well lead to redness. In women, blood vessels can burst due to strong efforts during childbirth.
- High temperature. Fever often accompanies colds. Against this background, deformation of blood vessels often occurs.
- Allergic reactions.
- Taking large doses of alcoholic beverages. This often leads to the fact that the vessels begin to rapidly narrow and expand. If a person suffers from chronic alcoholism, then there will be redness not only in the eyes, but also on the skin underneath them. This is due to the appearance of swelling.
Reasons for appearance
The vascular network on the face indicates a disturbance in the body's circulation and stagnation of blood in small capillaries. Both men and women suffer from the disease.
Important! There is no need to start treating a disease without specifying why it arose!
The causes of rosacea (dilated blood vessels) are varied.
- Abuse of bad habits - alcohol and smoking have a bad effect on the entire body.
- Temperature fluctuations and changes.
- Unhealthy environmental situation.
- Disorders in the circulatory system (heart disease).
- A person works a lot and rests little.
- Depression, apathy.
- Overheating (long exposure to the scorching sun)
- Thyroid gland dysfunction (hormone problem).
- Heredity.
Important! the appearance of a fine mesh on the face is the result of diseases of certain organs, and in order to be cured, you need to know the cause.
Cuperosis is characterized by the appearance of small vessels on the face in the surface layer of the skin due to impaired blood flow and wear of the capillary walls. It can warn of serious disorders in the body and, in addition, makes the face aesthetically unattractive.
People at risk for the disease:
- Mothers of many children.
- Newborn children (lack of subcutaneous fat).
- Workers in hazardous production.
- Working outside in winter.
- Anyone who is overweight.
- With high blood pressure.
The reason for the appearance of small vessels can be ordinary physiology, for example, a woman is carrying a child, childbirth and the onset of menopause - under the influence of hormones, blood vessels burst on the face and red spots form.
When an elderly person suffers from this disease, there is no need to take special measures for treatment. Body tissues age over time, and blood vessels become fragile. For prevention, it is advised to drink vitamin C and other multivitamins, and prescribe a diet and special creams.
In order not to aggravate the process of rosacea, you need to eat right, follow a daily routine, and give up smoking and alcohol.
External effects on the eyes
Such factors also often cause redness of the organs of vision. Vessels can burst due to strong gusty winds, bright sun or high atmospheric pressure. It is also worth making sure that the air in the room is not too dry. If a person spends a long time in front of a fire or in a smoky room, he may also notice the appearance of redness.
People sensitive to changes in temperature should refrain from visiting saunas and steam baths.
A foreign object can also cause the capillaries in the eye to burst. What to do in such a situation? Under no circumstances should you try to remove it yourself. Otherwise, the cornea of the eye may be damaged. Therefore, it is necessary to consult a doctor immediately.
Lymphatic capillaries
Lymphatic capillaries (Fig. 5 and 6) are a system of endothelial tubes closed at one end, which perform a drainage function - they participate in the absorption of plasma and blood filtrate (liquid with colloids and crystalloids dissolved in it), some blood elements (lymphocytes) from tissues , red blood cells), are also involved in phagocytosis (capture of foreign particles, bacteria). Lymph. K. drains lymph through the system of intra- and extraorgan lymphatic vessels into the main lymphatic collectors - the thoracic duct and the right lymphatic duct (see Lymphatic system). Lymph. K. penetrate the tissues of all organs, with the exception of the brain and spinal cord, spleen, cartilage, placenta, as well as the lens and sclera of the eyeball. The diameter of their lumen reaches 20-26 microns, and the wall, unlike blood vessels, is represented only by sharply flattened endothelial cells (Fig. 5). The latter are approximately 4 times larger than the endothelial cells of blood cells. In endothelial cells, in addition to the usual organelles and micropinocytotic vesicles, there are lysosomes and residual bodies - intracellular structures that arise during the process of phagocytosis, which is explained by the participation of lymph. K. in phagocytosis. Another feature of lymph. K. consists in the presence of “anchor” or “slender” filaments (Fig. 5 and 6), which fix their endothelium to the surrounding collagen protofibrils. Due to their participation in absorption processes, interendothelial contacts in their walls have a different structure. During the period of intense resorption, the width of the interendothelial gaps increases to 1 μm.
How long does it take for broken blood vessels to last?
First of all, it all depends on why exactly the capillaries began to rupture. The small vessels themselves recover quite quickly. However, if we are talking about a more serious pathology, then this process may take much longer.
If this happened against the background of a stressful situation or severe fatigue, then it is enough for the person to take a sedative and have a good rest. In this case, the organs of vision will no longer resemble the eyes of a vampire within a few hours. The same applies to situations when a person has been in front of a computer or TV for too long.
In case of mechanical injury, it will take longer. It all depends on the extent of the damage. Usually the vessels are completely restored within a couple of weeks.
Dry mucous membranes – are these symptoms dangerous?
What to do if bleeding is observed against the background of dry mucous membrane of the organ of vision - everyone should know this. This can occur after conjunctivitis, with microtrauma, in the postoperative period. In this case, it is recommended to use eye drops to speed up healing and to moisturize the retina. If you are seeing a doctor because of an eye disease, he will prescribe and indicate such drops, but if not, you can consider the following solutions.
For minor injuries, Visin drops help, they moisturize and accelerate the disappearance of small hematomas. For injuries and after conjunctivitis, Defislez is used; it is often prescribed by doctors. Taufon can help with inflammation, eye problems due to excessive fatigue, and Emoxipin can be used for a long period. If dryness bothers you, you can choose one of these medications to eliminate discomfort and speed up eye healing.
Treatment of burst blood vessels
First of all, it is necessary to determine why exactly the capillaries began to burst in the eyes. If we are talking about overwork or long work at the computer, then in this case it is enough to wait a little and give the visual organs a rest. After some time, their condition will be restored without any additional funds. However, you need to be sure that the causes of redness are not caused by anything serious.
If a person has burst capillaries in the eye, only a doctor can best determine how to treat the damaged vessels. However, in some situations a person urgently needs to get rid of a problem. In this case, the following drops will help:
- "Hyphenlease." This product is also commonly called “artificial tears.” These drops will help if the organs of vision are too tired and are not naturally moistened.
- "Visine." Quickly relieves fatigue and redness.
- "Taufon". These drops have a vasoconstrictor effect. However, it is better not to use them without a doctor's prescription. This is explained by the fact that if you narrow the blood vessels, this may not always have a positive effect.
Cold and compresses that can be prepared from natural herbal mixtures will also have a positive effect.
However, you need to understand that self-medication can only relieve symptoms. If a person suffers from a more serious illness, then he will need complex therapy, which will be aimed at solving the problems that caused such symptoms.
Non-pathological causes and help
Even prolonged visual strain in the absence of rest for the eyes can put a strain on the capillaries beyond normal, which will lead to their rupture. Often the causes of microbleeds in the eye are, at first glance, ordinary actions and events that a person, as a rule, does not pay attention to.
By the way. Going to the sauna, drinking alcohol, hypothermia or overheating, being in the wind, carrying furniture, a quarrel accompanied by emotional screams and ending in tears - all this can help a capillary in the eye burst.
There are many non-pathological causes
- If you regularly do not get enough sleep, get plenty of rest, get enough sleep, try to go to bed earlier and sleep for at least eight hours, observing the conditions for quality sleep.
- Reduce the load in case of constant physical overexertion that has caused damage to the capillaries.
- Avoid stressful situations that cause increased emotionality.
- Rest your eyes more often during visual stress, do gymnastics, and take care of high-quality lighting.
- Do not abuse alcohol and quit smoking until the walls of the blood vessels are completely thinned.
- If your capillaries are weak, do not go to the bathhouse or sauna.
- Take vitamins that will make the walls of blood vessels more elastic and stronger.
Red whites of the eyes - what to do
By the way. If for some reason your capillaries have fragile walls, it is necessary to constantly prevent hemorrhages and not be in a situation in which the vessels may be damaged.
Video: Why blood vessels burst in the eyes
If the redness does not go away
First of all, don't panic. If no treatment measures produce a visible result, then the remedy for redness may have been selected incorrectly. In this case, it is not the symptoms that need to be treated, but the pathology itself that causes them. The use of drops in such situations either gives a very short-term effect or does not have any positive effect at all.
Also, rupture of blood vessels could be caused by injury or bruise. In this case, the healing process takes quite a long time, even if the person uses drops and traditional medicine.
If vascular rupture occurs periodically, then it is worth visiting a specialist and accurately determining the causes of the symptoms.
Methods for studying capillaries
When studying the condition of the walls of capillaries, the shape of capillary tubes and spatial connections between them, injection and non-injection techniques, various methods of capillary reconstruction, transmission and scanning electron microscopy (see) in combination with methods of morphometric analysis (see Medical morphometry) and mathematical modeling; For intravital examination of K., microscopy is used in the clinic (see Capillaroscopy).
Pathology of K. - see articles Inflammation; Capillary circulation; Microcirculation, pathology; Edema; Permeability.
Bibliography:
Alekseev P. P. Diseases of small arteries, capillaries and arteriovenous anastomoses, L., 1975, bibliogr.; Kaznacheev V.P. and Dzizinsky A.A. Clinical pathology of transcapillary exchange, M., 1975, bibliogr.; Kupriyanov V.V., Karaganov Ya.L. and Kozlov V.I. Microcirculatory bed, M., 1975, bibliogr.; Folkov B. and Neil E. Blood circulation, trans. from English, M., 1976; Chernukh A. M., Alexandrov P. N. and Alekseev O. V. Microcirculations, M., 1975, bibliogr.; Shakhlamov V. A. Capillaries, M., 1971, bibliogr.; Shoshenko K. A. Blood capillaries, Novosibirsk, 1975, bibliogr.; Hammersen F. Anatomie der terminalen Strombahn, Miinchen, 1971; Krogh A. Anatomie und Physiologie der Capillaren, B. ua, 1970, Bibliogr.; Microcirculation, ed. by G. Kaley a. BM Altura, Baltimore ao, 1977; Simionescu N., Simionescu M. a. Palade GE Permeability of muscle capillaries to small heme peptides, J. cell. Biol., v. 64, p. 586, 1975; Zweifach BW Microcirculation, Ann. Rev. Physiol., v. 35, p. 117, 1973, bibliogr.
Ya. L. Karaganov.
Is there a risk of losing vision?
Because of the vessels themselves, it is almost impossible to lose the ability to see. However, often redness of this kind becomes a signal that a person is suffering from a particular disease. In this case, visual disability can be quite easily acquired. If you do not start the necessary treatment, there is a risk of going blind if the patient is diagnosed with one of the diseases in an advanced stage:
- Hernia of the eye.
- Severe allergies.
- Cataract.
- Glaucoma or conjunctivitis.
What it looks and feels like
The white of the eye changes color, turning red spotwise, partially or completely. In some cases, it literally becomes filled with blood, and sometimes only “rusty” spots or reddish streaks appear on the surface of the protein. All these are signs of a ruptured capillary, one or more. Usually the redness goes away on its own after three to five days, but if it does not go away or occurs again, a visit to an ophthalmologist is inevitable.
By the way. If the burst capillary is located in the visible part of the white, not covered by the eyelid, then the redness will be clearly visible, but if the rupture occurs in a segment that is not visible, the person may not notice microhemorrhages if he does not pay attention to the sudden heaviness and feeling of obstruction in the eye .
Bleeding in the eye
Many people do not feel when a capillary bursts. Others or a mirror can tell them that they have a red eye. But some people, even with a single damaged capillary, experience a headache, fever or chills, dizziness, and “floaters” appear in the eyes.
The fact that the eye becomes frighteningly red and looks unaesthetic is not scary. The danger arises not when the protein has already turned red, but at the moment the capillary ruptures. And, of course, the reasons that lead to a break can pose a danger.
Burst of a blood vessel in the eye
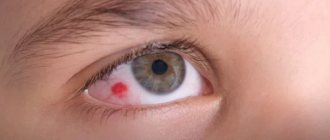
Capillaries burst in a child's eye
In such a situation, you should not panic. There are several conditions when such redness in babies is the absolute norm. If a child has burst capillaries in the eye due to lack of sleep or fatigue, prolonged crying, reactions to irritants (for example, a lot of dust has accumulated in the children's room), coughing or spending a long time in front of the computer or TV, then you need to give the child a little rest.
However, there are situations where such symptoms may cause concern. Therefore, you should be more attentive to the baby. If the capillaries around a child's eyes burst, this may be caused by:
- Infectious diseases (for example, influenza or acute respiratory infections).
- Mechanical damage and foreign matter entering the eye (children are often careless when playing).
- Pathologies of the visual organs.
- Severe physical stress (even though children look energetic, they also need proper rest).
- Increased body temperature.
- Diabetes mellitus.
- Lack of vitamins and minerals (usually an exacerbation begins in the spring).
Prevention
It is worth noting that the organs of vision are highly sensitive, so you need to take care of your eyes. First of all, you need to adhere to the correct daily routine. This means that a person should get a good night's sleep and allow himself to sit for a very long time at night in front of the computer or TV. Sleep is very important not only for the eyes, but also for the entire body as a whole.
It is important to monitor your diet. The diet must be balanced. You should give up junk food and try to eat only products of natural origin. It is recommended to eat as many vitamins as possible. It is especially worthwhile to press on blueberries, carrots and black currants. These products are rich in components that are essential for good vision.
It is not recommended to drink a lot of alcohol and smoke. You should also avoid strenuous physical activity and stressful situations. A person should lead an active lifestyle, but should not spend all their time in the gym. It is best to give preference to walks or light jogging in the fresh air.
Nervous stress can lead not only to eye problems, but also negatively affect a person’s overall health. If you cannot avoid such situations (for example, work is associated with stress), then you need to choose natural light sedatives.
It is also worth undergoing examination and consulting with doctors at least once a year. They will be able to promptly identify this or that pathology at an early stage.
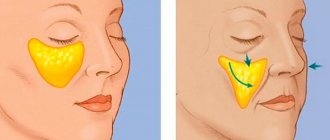
How to remove burst blood vessels on the face at home. How to remove burst blood vessels on the face
Vessel burst: reasons
As a rule, the cause of burst blood vessels on the face is hypo- and avitaminosis (lack of vitamins P, C, K); unhealthy diet (abuse of fatty foods, sweets); diseases of the cardiovascular, digestive, endocrine systems; taking hormonal medications, including contraceptives; smoking; chronic stress; pregnancy; obesity; heavy physical activity; poor skin care (overdrying); tanning without skin protection; sudden changes in temperature, especially in the presence of predisposing congenital factors.
Damage to blood vessels may also be due to heredity. The structural features of the skin and vascular walls are often transmitted through the female line and can bring a lot of troubles (varicose veins, spider veins, increased vascular permeability, unhealthy complexion - pallor or, conversely, redness)
What to do. if blood vessels on the face burst
Folk remedies, as well as “medicinal cosmetics” are ineffective in this case. They may help to slightly reduce visible defects, but they will not radically solve the problem. Modern cosmetology has special techniques that can return the skin to its previous appearance in the shortest possible time.
Laser treatment. Laser radiation glues the vascular walls and makes the vessel invisible, since blood no longer circulates in it. This method is highly accurate, does not involve healthy tissue, and does not leave cosmetic flaws.
Phototherapy. The principle is the same, but the active agent is pulsed light. The effectiveness of the method is high, but a certain number of procedures are required, and the result appears only after a few weeks.
Electrocoagulation. The same “gluing” of the vessel, only with the help of current. This method is gradually becoming a thing of the past, although the effect is good and the risks are relatively small. But if there is a laser, why take any risks?
Cryodestruction. Cauterization of the vessel with liquid nitrogen. The effect is good, but there are many cosmetic risks. In medicine, this method is often used, but in cosmetology it has recently been extremely rare.
Prevention of vascular problems
Removing broken blood vessels on the face alone will not solve the problem once and for all. A comprehensive approach is required, including identification and elimination of risk factors to avoid relapse.
If you smoke, quit this bad habit. Vascular problems will only progress due to smoking; no other measures can neutralize the harm of nicotine.
Normalize your diet: give up fast food, caffeine, alcohol, carbonated drinks. Eat as many fresh vegetables and fruits as possible.
Proper skin care. It is important to avoid overdrying, tanning without protective equipment, and temperature changes. You need to wash your face with warm water. Rough peelings should not be done. Use masks and facial massage with caution. Use only high-quality hypoallergenic cosmetics.
You should consult your doctor about taking medications containing vitamins C, K and P. This will strengthen the vascular wall, reduce “fragility” and increased vascular permeability.