Why does a child often have pus in his eyes?
Reasons for the discharge of pus from the eyes of a child: eye diseases, improper care of the baby, colds. If a child's eyes fester after sleep, then this is not a reason to worry. During the day, small dust particles enter the organ of vision, and at night during sleep they are removed. This is a protective function of the body. In the morning it is enough to wash the child.
What else often causes festering eyes in children? The cause may be inflammatory diseases of the visual apparatus of a viral or infectious nature:
Conjunctivitis
Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the visual organ. Viral in nature (herpetic, adenoviral) - occurs when the immune system is weakened. Often occurs against the background of ARVI. The discharge is scanty, transparent, mucous in nature.
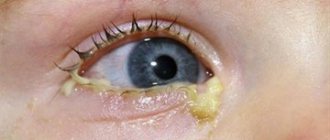
Bacterial conjunctivitis (staphylococcal, streptococcal, gonococcal) - occurs when a secondary infection is attached. In infants, infection occurs when passing through the infected birth canal of the mother. It is characterized by the discharge of yellow pus from the child's eyes. It will fester profusely, sometimes with an unpleasant odor.
Blepharitis
Inflammation of the ciliary edge of the eyelids. Blepharitis is most often caused by a staph infection. Discharge from a child's eyes is accompanied by swelling of the eyelid margins, redness and itching. The eyes begin to fester, the eyelashes stick together, and a yellowish crust forms on them. Occurs most often after dust gets into the eyes, after hypothermia.
Dacryocystitis
Dacryocystitis is inflammation of the lacrimal sac due to blockage of the excretory duct. There is nowhere for the tear fluid to flow, an infection occurs, and as a result, inflammation. The lesion is one-sided, i.e. one eye will fester.
Dacryocystitis in newborns develops in the first days of life and is called primary. The reason is anomalies in the development of the nasolacrimal duct. The baby's eye becomes very suppurated, crusts form, and a painful swelling is observed in the corner of the affected organ.
Secondary dacryocystitis - in older children. The manifestations are the same: the eye festers, pain is felt.
Barley
Barley is a purulent inflammation of the hair follicle, sebaceous gland and surrounding connective tissue. Associated with decreased immunity, hypothermia and the addition of pathogens. Symptoms: round, dense formation on the eyelid, lacrimation, pain. Low temperature (low-grade fever) is possible. It begins to fester after the outbreak is opened.
Uveitis
Inflammation of the choroid of the organ of vision. Uveitis is caused by viral or infectious causes, and is also possible due to allergic reactions. The disease occurs acutely with the onset of eye pain. The pain spreads to half of the head. Accompanied by blepharospasm (difficulty opening the eyelid), photophobia, lacrimation, and blurred vision.
The pupil becomes sluggish and reacts poorly to light. Visually – redness, swelling, drooping eyelid. Yellowish or transparent pus is released from the child's eye (depending on the cause).
Other reasons
Causes not related to eye inflammation:
- Colds of viral origin. The reason that pus collects in the corner of the eye is the addition of a secondary infection. Most often - streptococci and staphylococci. The symptoms of the underlying disease come to the fore: the child becomes lethargic, drowsy, has a runny nose, pain or sore throat, headache, muscle aches, body temperature rises above 38 degrees, and eyes fester.
- Allergic reactions. The most common allergens: plant pollen, animal dander, chicken protein, honey, citrus fruits. There is a clear relationship: symptoms appear after contact with the allergen. Parents notice that the baby’s eyes are swollen, festering, red, and watery. Itching and sneezing may occur.
- Mechanical damage. Symptoms are associated with injury or foreign body penetration under the eyelid. In this case, the child’s eye waters and purulent discharge may appear. It will fester a second time when pathological microorganisms enter and inflammation develops.
- Lack of hygienic child care. Occurs in dysfunctional families. In this case, not only do the eyes fester, but there are also other signs of poor care for the baby.
Associated symptoms
Pus accumulating in the eyes of children is not the only symptom of conjunctivitis, dacryocystitis, or the same allergy. The discharge is accompanied by a number of characteristic signs that help the doctor more accurately determine the diagnosis, and therefore not make a mistake in choosing treatment methods. These diseases are characterized by the following symptoms:
purulent discharge that accumulates in the corners and prevents the child from opening his eyes in the morning; photophobia; with adenoviral conjunctivitis, the temperature may rise, appetite may decrease, headaches, enlarged lymph nodes, runny nose, and sore throat; redness of the mucous membrane of the eye; tearfulness; characteristic blisters on the edges of the eyelids - this is how herpetic conjunctivitis manifests itself; swelling of the eyelid; a film on the mucous membrane, which is under no circumstances recommended to be removed at home; if a child’s eyes are very purulent, he complains of itching and there is a simultaneous runny nose - these are signs of an allergic reaction; sleep disturbances, appetite disorders; moodiness, irritability; eyelids glued together in the morning; formation of yellow crusts; pain, complaints of burning; deterioration of visual acuity.
This does not mean that all of the above symptoms will be present: everyone’s body is different, and so are the diseases. But most often, 5–6 of these signs, when occurring simultaneously, poison the baby’s life. And parents simply have to know what to do if their child’s eyes fester: show him to an ophthalmologist as soon as possible. He exclusively prescribes treatment.
What to do if a child’s eyes are purulent
Dr. Evgeniy Komarovsky spoke about suppuration in a child’s eyes in his program. The mucous membrane in children is sensitive to viruses and bacteria, as well as allergens.
To find out the causes and prescribe effective treatment, Dr. Komarovsky recommends monitoring your child. After what does the eye begin to fester? After visiting a kindergarten and having contact with sick children? Or after contact with animals? Maybe after changing washing powder or other household chemicals? Are there other symptoms: cough, fever, sore throat?
Next, the question arises: how to treat the child?
1. Viral colds. Therapy is aimed at the underlying disease.
- "Ingavirin" is an antiviral drug. Prevents the reproduction of viruses, increases the activity of interferons, stimulates the immune system. Approved for children over 7 years old. Take 1 capsule (60 mg) 1 time per day. Packaging the drug will cost 350–400 rubles.
- "Kagocel" - activates the production of interferons, stimulates the body's defenses, and suppresses the proliferation of viruses. Suitable for children over 3 years old. Dosage depends on age. Up to 6 years - 1 t. 2 times a day for 2 days, then 1 t. 1 r/day. - 2 days. General course – 4 days. Over 6 years old - the first 2 days, 1 t. 3 times a day, the next 2 days, 1 t. 2 times a day. Course – 4 days. The cost of 1 package of tablets is 250–480 rubles.
- “Anaferon for children” is a homeopathic medicine that improves the baby’s immunity. Prescribed from infancy and older. On the first day of illness, 1 t every 30 minutes, then 1 t 3 times a day. until the condition normalizes. Infants should dilute the medicine in warm boiled water. Priced at approximately RUR 200/pack.
- “Albucid” is an addition to the main treatment as an antiseptic so that the eye does not begin to fester. Eye drops for children 10% - for children under 2 years old, 20% - for children over 2 years old. Instill 1–2 drops every 2–4 hours. The cost is about 50 rubles.
2. Allergic reactions are treated with antihistamines. They relieve swelling, redness, itching.
- "Cetrin". Prescribed 1 t. 1 r/d or 1/2 t. 2 r/d. Allowed from 6 months. 150–200 r/pack.
- "Suprastin". Take 1/2 t. 2 times a day. or 1/4 t. 3 r/day. Allowed for use from 3 years of age. 1 package of the drug costs 100–130 rubles.
- "Zodak" - eye drops for children over one year old. The dosage regimen depends on age. 1–2 years: 5 drops 2 times a day. Costs from 160 rubles. 2–6 years: 5 drops 2 times a day or 10 drops 1 time a day.
- 6–12 years: 20 drops either at a time or divided into 2 doses.
- Over 12 years: the same dose 1 time per day in the evening.
3. Mechanical damage. The first stage is to remove the foreign body. To prevent the eye from starting or stopping to fester, use:
- "Albucid", eye drops. They have an antiseptic effect. Directions for use: age 2 years and less - 10% drops 1-2 every 2-4 hours, age over 2 years - 20% drops in the same dosage. Price about 50 rubles.
- "Tobrex", drops for children under one year of age and older for pus in the eyes. They belong to the group of antibacterial drugs and have a bactericidal effect. Needed to prevent secondary infection caused by microorganisms that have penetrated into the damaged visual organ. 1–2 k. every 6 hours. The price is approximately 200 rubles.
4. Inflammatory diseases of the organ of vision. Drops with an antimicrobial effect are prescribed:
- “Floxal” – instill 1–2 drops into the conjunctival sac 2–4 times a day. Duration of treatment is 7–14 days. Price: 170–220 rubles.
- Tobrex, eye ointment. Place under the lower eyelid 2-3 times a day. A strip of ointment 1–1.5 cm. Course up to 10 days. The ointment will cost 170–200 rubles.
- "Albucid". Infants are prescribed at a concentration of 10%, over 2 years - 20%. 1–2 k. 6–12 r/d. 1 bottle costs 50 rubles.
- "Acyclovir" is an antiviral eye ointment for herpetic lesions. Has a detrimental effect on herpes viruses. Place under the lower eyelid 5 times a day. Use during the entire period of illness plus 3 days after symptoms have passed. Cost 50–100 rubles.
- In case of dacryocystitis, it is additionally necessary to massage the lacrimal sac to normalize the outflow of tear fluid. The massage is performed with clean hands. Light pressure movements of the fingers are carried out from the inner corner of the eye up and down. The correctness of the massage is indicated by an improvement in the outflow of pus, i.e. the eye begins to fester intensely. After the massage, use topical antimicrobial agents.
5. If purulent discharge is the result of poor hygiene, what should you use to wash your eyes with? Infusions of soothing herbs are suitable for rinsing: chamomile, string. They will relieve inflammation. After 2-3 days the eyes will stop festering. We will talk about this in detail below.
Additionally, we invite you to watch a video where an ophthalmologist will talk about the causes and treatment of eye suppuration in a child:
How to cure children at home?
It is better to seek medical help from a specialist than to treat children at home. The doctor will make a correct diagnosis, refer you for laboratory diagnostic tests, and prescribe treatment. With properly selected drug treatment, the eyes will quickly stop festering. If you decide not to go to the clinic, then you should know how to wash a festering eye:
- Chamomile solution. Recipe: Pour boiling water over 1 filter bag of chamomile. Let sit for 10–15 minutes. Cool the solution to a warm temperature, and then either rinse or rinse for 10 minutes. Apply a cotton pad soaked in chamomile to the closed eye that is festering. Repeat the procedures 2-3 times a day.
- A decoction of the string. Pour one glass of boiling water over the packet of string and let it simmer for 2-3 minutes. Cool slightly and rinse eyes with warm broth 3 times a day.
- Celandine decoction. You can use both leaves and flowers. Prepare the decoction in the same way as the succession decoction. Washing is done at least 3 times a day.
Prevention
To prevent your baby’s eyes from starting to fester, it is important to follow preventive measures:
- A full night's sleep. For young children, naps are also necessary.
- Healthy balanced diet. The diet should contain fruits and vegetables rich in vitamins and microelements, dairy products, meat and fish dishes. It is advisable to limit sweet and canned foods to the maximum.
- Compliance with personal hygiene rules: regular washing in the morning and evening, additionally if necessary.
- Teach children not to rub their faces with dirty hands.
- Maintaining immunity: hardening, good nutrition, outdoor games, walks in the fresh air.
- See a doctor in the early stages of the disease, when it has just begun to fester.
If the visual organ begins to fester, then it is necessary to promptly treat it in order to prevent the development of complications, such as visual impairment, partial and complete blindness, sepsis, when pathogens penetrate the bloodstream. This problem is dealt with by pediatricians and ophthalmologists.
Share the article with your friends. Tell us about your experience in the comments. All the best. Health to you and your children.
How to protect your baby?
Preventing the development of conjunctivitis is quite simple. It is necessary to teach your child the rules of hygiene from an early age; he should know that he should use only his own towel, wash his hands after returning from a walk, try not to touch his face and especially his eyes with dirty hands.
Young children should periodically wash their eyes with a warm chamomile decoction for preventive purposes. This solution has disinfecting properties and helps prevent the development of inflammation.
Festering eyes in a child of any age is a rather alarming symptom. If you notice the appearance of purulent discharge, you must take your child to see a doctor. The specialist will identify the cause of the inflammation and prescribe appropriate treatment. Moreover, the sooner treatment measures are taken, the faster recovery can be achieved.