Home » Children » For what reasons does a newborn’s eye fester, what Komarovsky advises and what can be treated
From the first days of a baby’s life, a variety of health problems may appear. The main organs have already formed and are gradually beginning to function at full capacity, but most systems are still at the stage of consolidation.
The first months of life are the period when some health problems arise. One of these phenomena is considered to be pus in the baby’s eye.
To cure this condition, it is recommended to find out why the eye of a newborn baby is festering.
Advice from experienced pediatrician Komarovsky will help overcome difficulties in treating pus.
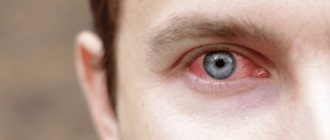
Eye diseases of newborns and infants
In infants, when pressing on the inner corner of the lower eyelid, pus is sometimes released. This is due to the anatomical and physiological characteristics of the organ of vision. Predisposing factors ─ inadequate care, vulnerability of the eye to external infection.
Dacryocystitis
This is an inflammation of the lacrimal sac. In newborns, it develops against the background of blockage and abnormal obstruction of the nasolacrimal duct. The disease is characterized by a unilateral manifestation. Dacryocystitis often recurs and goes away on its own as the baby grows and matures.
Methods of treating the disease in children in the first 3 months of life:
— instillation of antibacterial solutions into the eyes;
- placing ointments in the eyelid;
- gentle massage of the lacrimal sac;
— according to indications, canal probing.
Neonatal conjunctivitis
The immaturity of the infant's immune system leads to the addition of an eye infection. Pathogenic flora that provokes purulent inflammation ─ streptococci, pneumococci, Staphylococcus aureus, chlamydia.
Blennorea
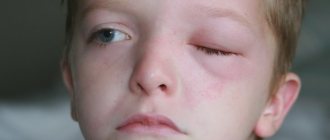
This is an inflammation of the eyes caused by gonococcus. Infection of a newborn occurs during passage through the birth canal from a mother with gonorrhea. Appears 2-3 days after birth. Distinctive signs ─ pronounced swelling of the eyelids, abundant flow of pus from the eyes. In severe cases, the cornea is affected, ulcers are formed, which after healing leave a thorn. A rare complication is blindness.
The development of the disease is facilitated by the absence or violation of prevention rules. Immediately after birth from an infected mother, a silver solution or a penicillin antibiotic is instilled into both eyes of the baby.
Treatment
Regardless of the age of the child, whether he is a newborn or 4, 5, 6 months old, treatment should be comprehensive in accordance with the cause of the disease. For hygienic purposes, wash the eyes with antiseptic solutions. It is possible to use green tea and a solution of potassium permanganate. Rinsing with ordinary boiled water and regular compresses help. For therapeutic purposes, the doctor may prescribe antibacterial eye drops and/or ointments, antiviral eye drops, antihistamines in the form of eye drops or tablets. In the case of neonatal dacryocystitis, timely surgical treatment is necessary.
A baby’s eye may be festering for various reasons. Therefore, at the first signs, you need to contact a specialist to avoid unpleasant consequences.
You can sign up for a comprehensive children's examination by contact numbers or during a personal visit at branches of the Optic-Center ophthalmological clinic.
Causes of purulent conjunctivitis in children after one year and pregnant women
After the first year of life, the production of pus in the eyes is caused by infectious agents ─ viruses, bacteria.
Diseases, the symptom of which is suppuration of the mucous membranes of the eyes:
— influenza, ARVI ─ pathogenic microorganisms penetrate the conjunctiva from the upper respiratory tract;
— sinusitis (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis) ─ inflammation of the paranasal sinuses with subsequent spread of infection;
— seasonal allergies (hay fever) or year-round runny nose (hay fever) ─ pus appears along with profuse lacrimation as a response of the immune system to the introduction of an allergen.
In pregnant women, hormonal regulation in the body is disrupted. The conjunctiva loosens, tear production increases, and the size of the eyeball changes. Women who correct their vision with contact lenses may experience systematic discomfort or pain in their eyes. Consequences ─ purulent discharge from the eye. When the first symptoms of inflammation appear, a pregnant woman must immediately see a doctor.
Advice from Doctor Komarovsky
The first thing pediatrician Evgeniy Komarovsky recommends is to seek medical help.
The doctor will take some pus for examination, and then prescribe the necessary medications, which often include antibacterial drugs and ointments, as well as drops.
Let's consider a few recommendations from a famous pediatrician:
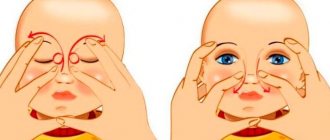
- Eye wash solution. The doctor recommends using various solutions only when warm, so as not to disturb the baby’s delicate mucous membrane. You only need to wipe your eyes with a clean cotton swab, after washing your hands with soap. For the solution, chamomile is used, sold in a pharmacy in dry form. Pour 1 tablespoon of the plant into a glass of boiling water, leave for 20 minutes and carefully treat the pus in the eye.
- Green tea infusion. The doctor recommends using this drug if the eyelid is swollen. In combination with medicinal ointments, the tea infusion will remove pus and bring the eye condition back to normal.
- Komarovsky does not recommend instilling breast milk into the eye, because it will be an additional breeding ground for bacteria.
- Each eye must be wiped with a separate cotton pad to prevent infection of a healthy organ.
- Many mothers are interested in the question of whether it is possible to bathe their baby in the bathtub during suppuration. The pediatrician claims that this procedure is acceptable, but it must be done correctly. It is not recommended for a baby to stay in the bath for a long time. Apply medicinal compositions only after bathing.
After bathing, the baby should be allowed to rest and lie down for 30 minutes under a warm blanket.
Important! Avoid leaving your baby in a draft: existing inflammation of the eye can lead to other infectious diseases.
When the baby is in advanced condition, probing is performed to remove the film blocking the tear duct.
This process is safe and is done under anesthesia. To prevent surgical intervention, provide your child with first aid in a timely manner.
Useful video
Share this post
- Related Posts
- Panties and other ways to quickly and correctly potty train a child
- How to choose the appropriate size of children's clothing: correspondence tables
- How to get rid of constipation in a newborn with different types of feeding at home
- Why does a child walk on his toes, what Komarovsky advises, how to treat and prevent it
- Methods and tips on how to wean your child from sucking a pacifier
- What is the best vitamin D for infants: types and dosage of the drug
Causes of suppuration
Eyelashes that stick together after sleep, purulent discharge in the corners of the eyes - this phenomenon can quite often be found among newborns. The causes of this condition can be both infectious diseases and congenital pathologies. But there is no need to be upset. Most often, it is enough to observe hygiene measures by wiping the child’s eyes every day with a swab moistened with boiled water. This will help avoid infection. If the eye still festers, it is better to consult a doctor.
The most common causes of suppuration are:
- Conjunctivitis of various etiologies;
- Dacryocystitis;
- Blennorea.
A child's eye is very tender and vulnerable.
Therefore, when suppuration appears, it is better not to self-medicate, but to immediately consult a specialist. This will help to correctly assess the disease and begin adequate treatment in a timely manner.
Your nurse will tell you how to care for your newborn’s eyes when you first visit your baby.
Types of discharge from the eyes of a child
If discharge of a certain consistency and color appears from the eyes of a child, especially a newborn, measures should be taken immediately. And it's not about the discharge itself. Whatever caused them can be seriously dangerous.
There are several types of discharge from the eyes. And everyone has their own reason.
We are talking about allocations:
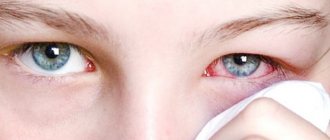
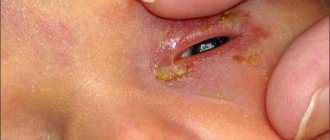
- Purulent mucous. The appearance of bacterial or viral conjunctivitis in a child is accompanied by a large amount of viscous discharge with the presence of pus. Unwashed hands, swimming in the pool, or using shared towels may well contribute to the spread of infection. Yellow or brown discharge sticks the child's eyelashes together so much that when he wakes up, he is simply unable to open his eyes. Sometimes a thin film forms on the surface of the eyeball. Since conjunctivitis of a bacterial nature is easily transmitted by contact, if discharge appears, it is urgent to see an ophthalmologist.
- Liquid ones that resemble tears. They are white or whitish. This usually happens when there is an allergen. Therefore, you will need to consult not only an ophthalmologist, but also an allergist. The sooner the source of the problem is found, the faster the child’s discomfort will go away. For research, the discharge is taken for analysis, and allergy tests are also carried out. Once the diagnosis is confirmed, the child should be kept away from the allergen. In addition, treatment involves the use of antihistamines.
- Discharge that looks like crusts and scales on the eyelids. It is under no circumstances recommended to ignore these discharges in the eyes, because such signs signal the development of blepharitis - an ailment that is not very easy to cope with. But not only scales can indicate blepharitis. The eyelids also become inflamed. The symptoms are caused by demodex mites, an infection that has accumulated in excessive amounts of sebum. Serious consequences can be avoided if you do not delay seeking help.
- Purulent in newborns. If this is present, then conjunctivitis or dacryocystitis cannot be ruled out.
Prevention measures
Compliance with hygiene requirements allows you to avoid suppuration in the eyes. The eyes of a newborn must be washed with boiled water at room temperature in the morning. After returning from the street, the baby should rinse his face and hands. Prepare a separate towel for your child.
It is important to protect a newborn from contact with sick children and adults. If during a walk you need to wipe your baby’s hands or face, use disposable wet wipes.
It is much easier to prevent any disease than to treat it. Therapy in many cases takes a lot of time and requires additional costs.
Conjunctivitis - types and symptoms
Conjunctivitis is an inflammatory disease associated with damage to the conjunctiva of the eye. This disease can be caused by various factors.
There are several types of this disease depending on the pathogen:
- Bacterial;
- Allergic.
- Viral;
Conjunctivitis of viral etiology occurs against the background of viral diseases, most often ARVI.
In this case, all the signs of a cold are observed: fever, weakness, runny nose, cough. Its treatment is aimed at eliminating the virus itself, which is usually dealt with by the immune system.
For more serious types of pathogens, such as herpes, treatment is longer and more serious.
The bacterial type of disease is associated with the penetration of bacteria or microorganisms into the conjunctiva that cause inflammation.
Often occurs as a secondary infection. The duration and severity of the disease depends on the pathogen.
Allergic conjunctivitis occurs when the eye is irritated due to exposure to a substance – an allergen. This is one of the signs of an allergy and, most often, is accompanied by other symptoms: rash, redness of the skin, itching, allergic cough, runny nose.
The main signs of any type of conjunctivitis are:
- Redness of the eyes;
- Swelling and swelling of the eyelids;
- lacrimation;
- Suppuration, which occurs most often with bacterial conjunctivitis;
- Itching, burning.
Treatment of conjunctivitis is associated with determining its etiology. Therefore, it requires specialist consultation.
Causes of dacryocystitis in infants
The eyes of newborns can also fester due to inflammation of the lacrimal sac. The inflammatory process in the lacrimal canaliculus begins due to its obstruction.
Obstruction occurs when the physiological film that covers the lacrimal canaliculi in utero from amniotic fluid entering them does not break through at birth. The same film is used to cover other organs of the baby. Normally, the film breaks with the first cry of the newborn. But it happens that it remains in front of the eyes, blocking the path for the natural outflow of tear fluid. The baby’s accumulating “unshed” tears ultimately cause inflammation in the lacrimal sac.
Immediately after the birth of the child, you need to carefully observe whether there is an outflow of tear fluid from his eyes. If not, we can assume that he has dacryocystitis. This means that the baby needs to be shown to a doctor to make an accurate diagnosis.
Conjunctivitis of newborns, its causes and treatment
Most often, babies become infected with conjunctivitis during childbirth, when pathogenic microbes get into their eyes.
Conjunctivitis can be caused by:
- chlamydia;
- streptococci;
- staphylococci;
- pneumococci and other similar bacteria;
- viruses of measles, influenza, herpes, respiratory infections.
Allergic conjunctivitis can be classified as a separate group. It occurs against the background of general allergization of the body. Allergens can include animal hair, plant pollen, room or clothing dust, household chemicals, food, medications and much more.
When conjunctivitis occurs in a newborn, the following symptoms appear :
- fear of light (the baby tends to close his eyes in the light);
- lacrimation;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- yellow crusts gluing eyelashes;
- purulent discharge from the eyes, especially in the morning.
To avoid complications, conjunctivitis should be treated under the supervision of a doctor!
Each parent is able to provide first aid To do this you need:
- With cleanly washed hands, carefully rinse the newborn’s eyes several times a day with either warm boiled water, or strained tea leaves, or an aqueous solution of furatsilin;
- instill medicinal eye drops (albucid or chloramphenicol).
When washing the eyes, movements should be directed from the outer edge of the eye to the inner. A separate cotton swab is used for each eye.
The same tampon cannot be used twice! After a single use, the tampon should be thrown away!
Drops should be placed in the eyes 1-2 drops at a time, while slightly pulling the lower eyelid down. Some of the medicinal fluid will immediately flow out of the eye. But some - about one drop - will remain. This is quite enough for a therapeutic effect. The procedure should be performed 2 or 3 times a day.
If a newborn's eyes fester due to conjunctivitis of microbial origin , in addition to the listed symptomatic measures, it is necessary to treat the viral or bacterial disease itself.
With an allergic etiology of conjunctivitis, it is important to recognize and remove the factor causing the allergy from the baby. For example, if the allergen is pet fur, it is worth finding other caring owners for the pets. There are a number of tests to identify the allergen; they are prescribed by the doctor.