Increased sensitivity to light is akin to disaster for many. After all, you have to squint, wince, involuntary lacrimation begins, and it’s simply impossible to work on a computer.
Often in such situations, doctors diagnose “photophobia”. But not everyone understands what it actually means. Tatyana Shilova, MD, professor, chief physician of the ophthalmology clinic, told AiF.ru about what to expect from your eyes if you have photophobia, how to recognize photophobia and how to deal with it
Question and answer Does color perception change with age?
What is the essence of the problem?
Photophobia is a symptom of increased photophobia, which is inherent in many diseases of the eye and brain. It is not a separate disease, but rather a symptom of other health problems, such as infection or inflammation, that may irritate the eyes.
It is not uncommon for people who are sensitive to light to experience other associated symptoms, such as headaches and eye pain when exposed to very light or bright environments.
Photophobia, or photophobia, is a medical term that refers to the excessive reaction of the eyes to light that occurs in some people. This condition can be chronic or temporary and can occur in both adults and children. Literally, this is “fear of light,” since “phobia” means fear of something, and “photo” means light. However, it is correct to talk not about fear, but about increased pathological sensitivity to light.
It's not just sunlight that irritates people with photophobia. Light sources such as fluorescent or incandescent lamps may also cause discomfort. As a rule, we are talking about bright and intense light, but there is an unpleasant sensation in the eyes even in dim lighting.
A familiar symptom. What is anisocoria and how often does it occur? Read more
Why does my head hurt and put pressure on my eyes?
A severe headache that presses into the eyes can be a symptom of fatigue. But it also occurs in many dangerous diseases and conditions:
- high intracranial pressure with pain in the eyes develops against the background of a general increase in pressure in the vessels of the head and cavities of the brain. It makes itself felt when moving or static muscle tension. This is manifested by discomfort in the eyes, headache, fever, slow heartbeat. Disorders of the vomiting center occur. Over time, the face and body swell significantly.
- Concussion, especially if it is accompanied by the development of a hematoma. The accumulation of blood in the brain interferes with surrounding tissues, causing headaches that radiate to the eyes. This is a dangerous condition, as the hematoma can burst and be fatal.
- Vascular dysfunction and risk of stroke. The worse the condition of the blood vessels, the harder it is for the brain. When their damage reaches a critical level, a stroke attack will occur.
- Aneurysm. Sac-like dilatation of blood vessels threatens rupture and hemorrhage at the slightest strain. Urgent surgical intervention is required.
- Cervical osteochondrosis. Constant spasm of the neck muscles and immobility of the joints cause pinching of the vessels of the head. This leads to oxygen starvation of the brain, which is accompanied by pain in the head. The pain can radiate to the eyes, shoulders and chest. Most often occurs with a sedentary lifestyle.
- Accommodation spasm and visual impairment in patients with myopia. It occurs when the right or left eye is overstrained and is not corrected by rest. Vision may be lost if there is prolonged contraction of the eye muscles. It hurts to move your head and eyes. Sometimes swelling of the eyes causes the same effect.
Reasons for failure
Our visual analyzer is complex, and problems can arise not only at the level of the eyeball, but also during the passage of impulses in the form of several intermediate processes, and when reaching the cortical analyzing part of the brain.
First of all, photophobia is inherent in acute and chronic inflammatory diseases of the ocular surface, such as conjunctivitis, dry eye syndrome, recurrent erosion and corneal dystrophy, as well as similar conditions. It occurs due to irritation of the nerve endings of the cornea and conjunctiva, which are highly sensitive.
Question answer
Why does the eye twitch?
Also, severe photophobia occurs when there is inflammation of the choroid and sclera, in this case there are complaints of pain in the eyes at rest and when moving the eyes, and headaches from inflammation are often a concern.
With increased intraocular pressure, photophobia also often appears, which is combined with heaviness in the eyes and pain in the temples and head. Such symptoms are inherent in the condition of uncompensated glaucoma and require urgent treatment.
Another eye disease in which light scattering causes photophobia and a desire to squint the eye is cataracts, especially its complicated forms. In these cases, the patient sees poorly on a bright sunny day and is more comfortable in cloudy weather.
There is still no clear explanation for why photophobia occurs when there is inflammation of the optic nerve, brain, or its membranes, but it is believed that the problem is associated with the internal light-sensitive ganglion cells of the retina, which contain melanopsin. These cells detect light and create a sensation of brightness, and they can make the eye more sensitive, including causing pain.
Often, photophobia is a neurological problem that involves the communication system between the eye and the brain, not just the eye. The part of the eye that sends the light sensitivity signal to the brain is different from the part that transmits vision, which is why some people, even if they are blind, may suffer from photophobia.
People with photophobia have less tolerance to any type of light. Additionally, high visual contrast, such as when lights flash or flicker, makes it difficult to perceive, and striped patterns cause more migraines and problems for people with photosensitive epilepsy. On the other hand, fluorescent lights seem to be a leading cause of headaches, migraines, eye strain and seizures.
Glaucoma, cataracts, farsightedness. What eye diseases threaten after 40 years Read more
Treatment
If it hurts you to look at the light, be sure to visit an ophthalmologist for a comprehensive examination.
The specialist will examine the condition of the eyeball using a slit lamp, and if necessary, conduct an ophthalmoscopy - scraping the cornea. Ultrasound diagnostics provides accurate research results.
Alarming symptoms that are a good reason to see a doctor:
- Severe pain - only when exposed to light or for a long time;
- Constant need to wear sunglasses;
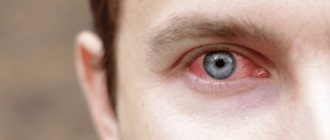
- Hyperemia;
- Migraine;
- Fogging that lasts for a couple of days or more.
Treatment will be carried out by a specialized specialist - for example, an ENT specialist, a dentist, a neurologist. If the pain is severe, you can take painkillers. For eye diseases, you need local and systemic medications, glasses with smoky lenses.
Folk recipes
Basic folk recipes for photophobia:
- Sweet clover - take 40 g of herb per glass of boiling water and boil for a quarter of an hour. Strain and make a compress.
- Eyebright - pour a spoonful of eyebright into a glass of boiling water, infuse it, use it internally, for rinsing and lotions.
- Flax seed - 4 tablespoons, infused in a glass of boiling water, used for rinsing.
- Sea buckthorn oil – used as eye drops.
Necessary therapy
If photophobia is present, the cause must first be determined and only after a diagnosis has been made by an ophthalmologist and neurologist based on an examination, which should include ophthalmological examinations and, quite often, an MRI, can treatment begin.
Some of the available therapies include medications for migraines, antibiotics or antivirals for conjunctivitis and deep vascular inflammation, artificial tears for dry eye syndrome, drugs for bacterial meningitis, and so on.
In any case, to determine the best type of treatment depending on the cause of photophobia, a comprehensive examination by an ophthalmologist and neurologist is necessary.
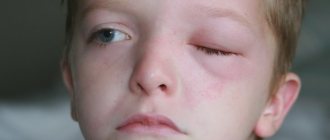
Photophobia in children
Photophobia among children and schoolchildren is not uncommon. The eyes become too sensitive, resulting in a burning sensation, increased blinking, and the child squints. If you notice these symptoms, they are permanent and you need medical help.
The causes of childhood photophobia are fatigue, overexertion, stress, and lack of sleep. The process can be started by previous antibiotic treatment. Photophobia is provided in case of excessive love of the computer.
If your son or daughter complains of the presence of a foreign body with severe pain when exposed to light, check the thyroid gland. With bilateral damage, body temperature often rises.
If there is burning, itching, or lacrimation, we can talk about conjunctivitis - for the treatment to be effective, first conduct a comprehensive health examination.
It is important to correctly identify the cause of the problem and eliminate it - working with symptoms is useless. Parents should also ensure that the child spends moderate time at the computer, TV, gets enough rest, and gets enough sleep.
Walk enough time in the fresh air, keep your diet balanced. Eye gymnastics is useful for children.
How to protect your eyes from the sun?
The easiest way is sunglasses. Ideally, with a frame that fits the face as closely as possible and wide temples, so that as little side and reflected sunlight as possible gets into the eyes. It is especially important to wear them in the summer, in southern latitudes or in the mountains. Moreover, as scientists have found, ultraviolet radiation has a particularly strong effect on the eyes not at noon, as many people think, but in the morning and in the afternoon. So it’s better to watch sunrises and sunsets with dark glasses. Remember: rays that are reflected from water, sand or snow are no less dangerous for the eyes.
Another option for protecting your eyes from the sun is contact lenses with a UV filter. They protect better than glasses from side rays (and many scientists believe that they are much more dangerous than direct rays). However, lenses cannot replace sunglasses: they do not completely cover the eyes and the area around them. Therefore, for those who live in the south, have vision problems or “bad heredity” and spend a lot of time in the sun, doctors often advise wearing both glasses and contacts.
“In Shape” program will tell you more about how to choose contact lenses and how to care for them
In summer, you should not ignore hats: wide brims will also cut off a significant part of the sun's rays. And finally, it is always worth remembering that the less time we spend in the open sun, the better for our health.
Numerous scientific studies by scientists have proven that ultraviolet radiation, if exposed to the sun for a long time and without protecting the eyes, can damage both the eyelids and the surface of the eyes, as well as their entire internal structure, including the lens. UV rays are often the cause of various eye diseases.
Physiological causes of photophobia
Pain from bright light can occur for physiological reasons. The fact is that the organs of vision are designed for a certain load; if the norms are exceeded, this leads to irritation of the mucous membrane and pain. The following factors can provoke pain:
- Exit from a dark room into bright light.
- Working at the computer for a long time or watching TV for a long time.
- Looking at the sun or white snow.
- When seeing a bright light from welding.
- With mechanical irritation of the eyes, for example, with active rubbing with your hands.
In addition, if your eyes begin to hurt in bright light, this may be a natural reaction to a lack of melanin in the body.
In recent years, more and more people have complained of periodic photophobia. Many doctors associate this phenomenon with the use of smartphones.