Why does my head hurt and put pressure on my eyes?
In order to begin treatment, you need to find out exactly why your eyes and head hurt. Preliminary diagnostics can be performed on special resources.
You will need to answer several questions about the location of the pain and all its manifestations. As a result, in just a few minutes you will receive a list of diseases that could cause discomfort.
Under no circumstances should you prescribe treatment based on self-diagnosis. It does not replace consultation with a specialist, but only helps to understand how serious a particular symptom is.
Diagnostics
To independently determine the answer to the question of why your head and eyes hurt, you should analyze your lifestyle. Perhaps the cause of headaches is non-compliance with an elementary regimen or a healthy lifestyle.
Tired eyes
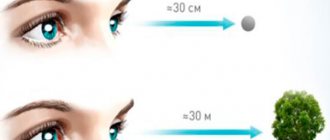
Overwork from working at a computer for a long time or being in a room with artificial lighting can cause severe eye fatigue. Eye strain causes inflammation of the optic nerve. This is what can cause pain in the frontal part of the head and temples. If you ignore pain symptoms, the headache will only get worse and can have more serious consequences.
To avoid overwork, take short breaks from work. It will be enough to just get distracted for 5 minutes and look out the window, watch the birds or people.
The main thing is to keep your eyes moving during this time. You can also use special eye drops to relieve tension in the blood vessels of the eyeball.
During your lunch break, you can do a little gymnastics for your eyes - close your eyes and rotate your pupils in different directions.
Doctors give an impressive list of reasons. In most cases, timely initiation of treatment allows you to quickly and completely get rid of the unpleasant syndrome.
The main thing is not to delay going to the doctor, not to try to solve the problem with the help of painkillers and not to get carried away with traditional medicine without the permission of a specialist.
Overwork
In this case, blurred vision and decreased visual acuity are observed, pain is localized in the temples and back of the head. Red eyes appear dry or, on the contrary, become very watery. If you ignore the condition, it will be accompanied by general weakness, weakness, dizziness and nausea.
Migraine
Blurred vision: causes
It must be said right away that a sharp decrease in vision is almost always a symptom of some disease. The causes of eye problems can be both direct eye pathologies: diseases of the cornea, lens, retina, and general diseases.
Among the eye diseases that most often lead to a sharp decrease in vision are retinal detachment and rupture, macular degeneration, inflammation or ischemia of the optic nerve, rupture or blockage of a vessel.
Also, a common cause of the development of this symptom is diabetic retinopathy, a complication of diabetes mellitus in which damage to the vessels of the retina occurs. With this disease, vision loss is usually irreversible.
In addition, a sharp deterioration in vision can occur with retrobulbar neuritis, intracranial hypertension, intoxication of the body and other pathological conditions.
Tired eyes
Have you become forgetful and is it bothering you a lot? Well, it’s better to seriously understand this phenomenon, because the reasons leading to “leaky memory” can be very serious.
Clinical refraction test (performed by an optometrist or ophthalmologist)
In the case of acute corneal lesions (erosion), corneal ulcers, keratitis, herpes zoster involving the eye, an acute attack of glaucoma, anisocoria will be present, but symptoms such as eye pain and redness of the eye will be much more pronounced.
Rare diseases that lead to the development of anisocoria include hereditary optic neuropathies (Leber's hereditary abiotrophy) and corneal scarring due to vitamin A deficiency.
Examination for blurred vision
In medical language this phenomenon is called amaurosis. Vision loss may be a consequence of retinal detachment or ischemia and other eye diseases (for example, glaucoma or uveitis), damage to the optic nerves, or bilateral damage to the visual cortex.
Patients with acutely developed visual impairment should be urgently hospitalized. At the same time, the information that the emergency doctor is able to collect about the development of vision loss is important and helps to quickly establish a diagnosis at the hospital stage.
In this article we will look at what it is and what are the causes of this disease.
Causes of acute vision loss
Retinal and optic nerve lesions
Sudden loss of vision in one eye usually results from damage to the retina and other structures of the eye or the optic nerve. One of its common causes is a transient circulatory disorder in the retina.
Typically, patients complain of a veil that suddenly falls in front of the eye and sometimes covers only part of the field of vision. Sometimes sensory disturbances and transient weakness in opposite limbs are simultaneously observed.
The duration of the episode ranges from several minutes to several hours.
Sharp loss of vision: what to do, causes, treatment of sudden deterioration
A person's vision may suddenly or gradually deteriorate. With gradual changes in refraction, they do not become noticeable immediately. But an unexpected drop in vision can frighten, cause panic and even lead to depression. The reasons for the deterioration can be caused by external or internal factors. Let's try to figure out why visual acuity decreases and how to deal with it.
- the outlines of objects are blurred;
- distant objects are difficult to see;
- fog or a veil appears before the eyes, etc.
You should not try to determine on your own why the visual center began to function incorrectly. The reasons may be related to both eye diseases and pathologies of other organs.
A decrease in visual ability occurs:
- on one eye - this indicates vascular pathology, various defects in eye tissue and other local causes;
- in both eyes at once - this indicates neurogenic disorders.
Visual function may deteriorate briefly, but significantly, due to eye strain: prolonged work or games at a computer monitor, watching TV.
- the appearance of flashes, sparks, spots before the eyes;
- double contours of objects;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eyes, such as sand or debris;
- rapid fatigue of the visual apparatus;
- pain in the eye area;
- poor vision at night, in twilight.
A person with refractive error begins to squint, but sometimes even these tricks do not help, and the contours of objects continue to blur.
In addition to decreased visual function, there may be other symptoms that you should pay attention to:
- irritability, behavior changes;
- pale skin;
- dizziness;
- weakness in the body and limbs;
- headache;
- nausea, etc.
Only a doctor can determine why vision decreases after a comprehensive eye examination. The reason does not always lie within the area of expertise of the ophthalmologist, but he will recommend which specialists should still be consulted.
A gradual decrease in visual acuity comes with age, but there is no cause for concern. It is associated with changes in the tissues of the eyeball.
Sometimes the visual function is fully preserved when a person looks straight, but when the gaze moves to the side, the focus is lost. The same thing can happen when the light level changes.
- Various injuries to the visual organs. This may include burns from chemicals, damage to the mucous membranes and deeper tissues of the eye by foreign bodies.
- Hemorrhages into the retina. Damage to the walls of blood vessels is caused by too much physical exertion, overexertion during childbirth, a predisposition to vascular fragility, and other factors.
- Detachment, retinal tears. Occurs as a result of trauma during childbirth.
- Infectious eye diseases. Usually the infection affects both eyes at once. The most common diseases: blenorrhea, keratitis, conjunctivitis.
- Retinal migraine. Occurs due to dysfunction of the main artery of the retina. As a result, blind spots may form when viewing.
- Optic neuropathy. Most often it is diagnosed in only one eye; usually the patient with this lesion of the visual apparatus does not experience pain.
- Macular degeneration. The disease affects the retina. It is believed that the cause of its occurrence is a lack of vitamins.
- Diabetic retinopathy. Almost 90% of diabetic patients experience visual impairment over time. Damage to the vessels of the retina occurs, which leads to the fact that it is insufficiently supplied with blood.
Among eye diseases, myopia, farsightedness, and astigmatism negatively affect visual function. Another important factor is age-related tissue changes.
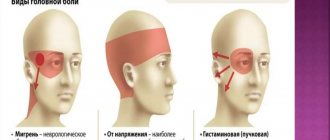
Types of headaches
Physiological and pathological conditions that are accompanied by pain in the head and eyes often have additional specific symptoms. Some patients constantly have pain in a certain part of the skull, for others it is difficult to determine the localization of the symptom, for others it is difficult to even move their eyeballs.
The type of sensations, frequency and time of their occurrence, duration - all this helps the doctor when making a diagnosis. Systematic or prolonged attacks of eye pain and headache are usually accompanied by a number of striking clinical manifestations.
Some of them affect the human psyche or lead to a decrease in the quality of his life.
Migraine is a chronic disease that is accompanied by periodic attacks of severe headaches. Most often, this disease affects people aged 25 to 55 years. Women are three times more likely to suffer from it than men. Residents of megacities are more sensitive to headaches than residents of rural areas. In general, every tenth inhabitant of our planet is familiar with the symptoms of this disease.
The disease has various manifestations and is divided into two large groups.
Classic migraine
A headache attack is preceded by a so-called aura. It may manifest itself:
- in slight discomfort
- lethargy,
- drowsiness,
- feeling of numbness in the limbs,
- auditory, tactile and visual (flashes, waves, blind spots) hallucinations.
The aura begins an hour before the attack and lasts 15-30 minutes.
Common migraine
Causes
A headache does not always mean the presence of a disease.
It can also occur as a response to negative environmental factors (lack of oxygen, stuffiness, smoke), due to long hours of work, hunger, hangover or lack of sleep. However, this symptom should not be ignored, because headaches can also be the result of a variety of diseases of the brain, nervous system and internal organs.
Viral gastroenteritis
Any inflammatory process in the body causes headaches, including infectious lesions of the stomach and small intestine - viral gastroenteritis. Rotavirus is the cause of 40% of cases of acute intestinal infections in children under 14 years of age and 55-60% in children under 5 years of age.
Inflammation begins after various viruses enter the gastric mucosa:
- rotaviruses - one of the main causative agents of gastroenteritis;
- caliciviruses - released into the external environment along with the feces of an infected person;
- intestinal adenoviruses, especially dangerous for young children;
- astroviruses, transmitted mainly by contact.
The main symptoms of acute viral gastroenteritis:
- diarrhea,
- nausea and vomiting,
- headache,
- general weakness,
- tachycardia.
As the disease progresses to the chronic stage, periodic headaches persist and stomach pain appears after eating. Diagnosis is based on taking a medical history and identifying the pathogen.
Brain aneurysm
A pathological protrusion of the walls of blood vessels supplying the brain is called an aneurysm. The danger of the disease is that a person may not suspect a “time bomb” in his own head for a long time and only learn about it when a blood vessel ruptures. Very often, an aneurysm is diagnosed during a routine medical examination.
Thinning and stretching of the vessel wall can lead to hemorrhagic stroke - bleeding in the brain. Risk factors for developing an aneurysm include heredity, trauma, cardiovascular disease, and bad habits (Fig. 1).
Figure 1. Factors that increase the risk of aneurysm. Source: MedPortal
The headache caused by an aneurysm is caused by the pressure of the blood-filled sac-like bulge on the nerves and surrounding tissue. Attacks of pain are similar to migraines and most often affect the back of the head.
Stroke
A stroke is a vascular accident that damages parts of the brain. Acute cerebrovascular accident occurs either due to a decrease in the lumen of the cerebral arteries (cerebral infarction or ischemic stroke) or due to rupture of a vessel and hemorrhage in the brain (hemorrhagic stroke).
A sharp headache is characteristic of a hemorrhagic stroke. The rupture of a vessel and blood pressure on the nerve endings of the meninges cause severe suffering to a person. Pain during a stroke has different localization, affecting the back of the head, the forehead or the entire head (Fig. 2).
Figure 2. Symptoms of a stroke. Source: MedPortal
Pain during an ischemic stroke may be absent or mild.
Important! At the first sign of a stroke, you should immediately call an ambulance! Doctors may have only 4.5 hours to save a patient.
Brain tumor
Neoplasms in the brain, regardless of etiology, always cause headaches. This is due to the fact that as the tumor grows, it begins to put pressure on the nerve endings located inside the skull and affects the meninges and blood vessels. Pain is also caused by increased intracranial pressure due to an enlarging tumor.
The intensity of pain depends on the size of the tumor and its location. In the initial stage of the disease, a person does not feel any discomfort and does not consult a doctor. When symptoms become severe, the tumor is often quite large and affects large areas of the brain.
If the neoplasm affects peripheral vessels, painful attacks are migraine-like. Sometimes the pain syndrome is accompanied by nausea, clouding of consciousness, and convulsive seizures.
Hypertonic disease
People suffering from high blood pressure often complain of headaches in the back of the head. The pain may be throbbing, pressing or aching.
Pain in hypertension is due to the fact that when blood vessels lose elasticity, the blood flow puts pressure on the vascular nerve endings. This pain is typical for older people who have suffered from hypertension for a long time.
At a younger age, a person may not experience any unpleasant symptoms of high blood pressure and learn about the problem only during a routine medical examination.
Increased intracranial pressure
Intracranial hypertension is a neurological diagnosis associated with impaired circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. The causes of high blood pressure are most often associated with the presence of other diseases or due to reasons not directly related to the brain:
- the use of vasoconstrictors, antibacterial, hormonal and some other groups of drugs;
- vascular atherosclerosis, hematomas, blood clots and other obstacles to the cerebrospinal fluid;
- stroke, encephalitis and other disorders of the nervous system;
- renal pathologies;
- brain tumors and hematomas;
- toxic lesions;
- problems with the endocrine system;
- congenital pathologies, for example, hydrocephalus.
Headache is the main symptom of increased intracranial pressure, but a comprehensive examination is required to determine the causes of the pathology.
Cervical osteochondrosis
Cervical osteochondrosis and the pain associated with it are our retribution for long hours spent at the computer and reluctance to walk. Causes of degenerative-dystrophic lesions of intervertebral discs and muscle spasms:
- overweight and obesity,
- poor nutrition,
- stress and emotional stress,
- excessive zeal in the gym and incorrect technique for performing strength exercises,
- sedentary work.
All of them are directly related to the wrong lifestyle. Damage to the cervical vertebrae and intervertebral discs can also be a consequence of trauma and congenital abnormalities of the spine.
Without proper treatment, osteochondrosis can be accompanied by increasing pain in the head and back, poor circulation and the formation of a hernia.
Neck myogelosis
Very severe headaches occur with myogelosis - thickening of the muscles in the neck, although painful nodules can also appear in other parts of the spine. Seals occur due to changes in the structure of muscle protein; they are easily palpated.
The main causes of myogelosis:
- sedentary work, sedentary lifestyle,
- hypothermia and drafts,
- nervous tension causing muscle spasms,
- scoliosis.
Myogelosis can develop against the background of cervical osteochondrosis, herniated intervertebral discs and inflammatory processes in the musculoskeletal system. Risk factors also include arterial hypertension, injuries and sprains, and professional sports.
Myogelosis headache torments a person with any turn of the head or change in body position. The disease is difficult to diagnose because its symptoms are similar to many other spinal pathologies.
How to determine astigmatism yourself: symptoms of disease development
The symptoms are closely related to each other. The brain has an optic chiasm, through which pain or inflammation can be transmitted to the eyeball.
In addition to this nerve, the brain gives an impulse to the oculomotor and facial nerves, which also innervate the orbit, and with the development of pathological processes, they spread pain.
The causes of such pain can be different. These include the following:
infectious, inflammatory processes (sinusitis, sinusitis, sinusitis, meningitis, meningoencephalitis, brain abscesses, herpetic damage to the facial and vagus nerve);- vascular pathologies (arterial hypertension, hypotension, ischemic brain damage, pre-stroke, thrombosis of blood vessels in the neck and head, hematomas, hemorrhages);
- skull injuries, concussions;
- neurological causes (osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, intervertebral hernia of the neck, migraine, cluster, tension headaches, neuritis of the facial nerve, inflammation of the optic nerve, retrobulbar neuritis);
- ophthalmological diseases (cataracts, myopia, eye injuries);
- oncological causes (brain tumors, optic chiasm, spread of metastases of malignant neoplasms).
Child with poor vision
Eye pathologies are not uncommon today. Vision problems occur in older people, adults and even children.
According to statistics, one of the most common disorders is astigmatism.
Important: How to determine astigmatism #8212; Only the doctor knows. However, you can suspect the presence of this disease yourself.
With astigmatism, a refractive error occurs. Light rays are not focused correctly on the retina #8212; and as a result, a person sees a blurry image.
This is how an astigmatist sees
Vision problems are indicated by characteristic symptoms that should never be ignored.
To prevent the development of pathology at an early stage, you need to contact an ophthalmologist when you detect the first alarming signs.
Only timely diagnosis and a well-chosen course of treatment will help maintain high visual acuity.
Signs of astigmatism in adults
Symptoms appear from the first day of development of the pathology. However, a person does not always immediately notice vision problems.
For a long time, astigmatism occurs in a mild form, so no significant changes for the worse are noticeable.
Many patients ask: “How do I know if I have it?” As the disease progresses, characteristic complaints appear.
The most common symptoms of astigmatism in adults are:
- blurred image;
- double vision;
- headache;
- sensitivity to light;
- poor vision at dusk;
- squinting to improve visual acuity;
- rapid eye fatigue;
- tilting the head to improve image quality;
- feeling of constant tension in the eyes.
Why does vision deteriorate in one eye?
A sharp decrease in the quality of vision can be associated with a number of reasons that are known to many: hereditary pathologies, mechanical damage to the retina and lens, infectious diseases. But what if it only deteriorates in one eye? Vision can decline in a person of any age - both a child and an elderly person. The deterioration may be temporary or chronic and may be treatable with medication or surgery alone.
First, you need to determine the reason why one eye has become worse at seeing.
Causes
If vision drops sharply in only one eye, this may indicate the following pathologies (including quite rare ones):
- Leber syndrome (a hereditary disease to which men are more susceptible);
- stroke;
- retinal detachment;
- acute form of glaucoma, which is accompanied by painful symptoms;
- disease of the lens, developing to myopia, farsightedness, cataracts and other disorders.
Ophthalmologists include retinal detachment among the most common causes of sudden deterioration of vision in one eye. This disease is often recorded in older people.
After fifty years, the vitreous body of the eye becomes less strong and elastic, which is the background of which detachment occurs. The retina, which does not come into contact with the vessels, causes a sharp drop in vision, and only in one eye.
The only method to solve this problem is surgery.
In addition, the unwise use of tablets and smartphones also causes a decrease in the quality of vision in one eye.
Reading from gadget screens while lying down is especially dangerous: the maximum load falls on the eye on the opposite side of the body.
It should be noted that the deterioration in this case is short-term, but constant use of equipment in this position can lead to more serious consequences.
What to do
Only an experienced and qualified ophthalmologist will name the exact reason. The doctor will conduct a comprehensive examination and diagnosis, during which the patient’s age, characteristics of his lifestyle, his blood pressure, glycemic index, atherogenicity index and, of course, individual eye parameters will be taken into account.
Pregnancy and symptoms
After conception, a woman’s body may react unconventionally: ripples will appear in the eyes, and then a headache will develop. This may be a consequence of hormonal changes and other changes in the body in preparation for the upcoming birth.
At these moments, pressure increases, the position and structure of blood vessels changes. A woman may experience aching headaches and glare in her eyes. However, in addition to the normal state, this may also be a consequence of a pathological process:
- a sharp decrease or increase in blood pressure;
- decreased hemoglobin;
- ophthalmological diseases that destroy the retina, lens or other parts of the eye;
- cervical osteochondrosis;
- poisoning by toxins or other harmful substances.
These pathologies are dangerous for the condition of the pregnant woman and the fetus. Even if the symptoms are mild, it is recommended to undergo a full examination.
Migraine as a cause of symptoms
Try to be outdoors as much as possible, observe the world around you, and experience more positive emotions. You should not overuse analgesics, otherwise it will negatively affect other internal organs.
When the first signs of a headache appear, try to relax and sit in a comfortable position for a couple of minutes with your eyes closed. This will slightly reduce the inflammation of the optic nerve, and the headache will not be as intense.
The next migraine attack will be less painful if you drink 100 ml of aloe infusion with chicory juice during meals. Also, steam baths will be effective for relieving migraine attacks. Pour water and vinegar in equal proportions into a container and bring to a boil. As soon as steam begins to form, you need to tilt your head over the container and take at least 70 deep breaths.
If the headache is caused by overstrain or eye fatigue, touch your forehead to the cool glass of the window. This will help neutralize the electrostatic charge that accumulates on the skin and leads to painful sensations.
— abuse of alcoholic beverages, drugs and medications;
- smoking tobacco products, which not only affects visual and hearing acuity, but also affects verbal and visual memory;
- lack of certain vitamins and minerals in the body;
— infectious diseases and diseases of internal organs;
— metabolic disorders;
- severe head injuries.
This is how an astigmatist sees
Symptoms
Symptoms of the condition depend on the underlying cause that caused decreased visual acuity and headache.
The most common signs are:
- poor health, loss of strength;
- double vision;
- increased blood or intraocular pressure;
- the eyes become tense, dry mucous membranes and overwork of the eyeballs may develop;
- migraine occurs.
A person may have only a headache or be accompanied by the above symptoms.
Methods for diagnosing the disease: why do your head and eyes hurt?
To diagnose a pathological condition and establish the exact clinical form of the disease, a number of measures are carried out with a detailed account of all associated symptoms. Thus, for retinal (reticular) migraine, one of the most important criteria is the absence of ophthalmological disorders other than attacks.
A regular migraine can be combined with atrial scotoma (ocular migraine) because the nutrition of the brain is disrupted.
Diagnosis is carried out on the basis of:
- A thorough external eye examination by an ophthalmologist.
- Analysis of pupillary reactions.
- Research of the existing field of view.
- Computer examination of the hemispheres using tomography.
- Pathology assessments by a competent neurologist.
- Characteristics of motor functions of the eyes.
- Ophthalmoscopy.
This is how an astigmatist sees
Treatment of severe vision loss
In order to prescribe the correct treatment for a sharp deterioration in vision, it is necessary to accurately identify the cause of the pathological process. This often requires a full ophthalmological examination.
Treatment depends on the type of disease; it can be conservative or surgical. In no case is it permissible to self-medicate; therapy for a sharp decrease in vision should be carried out only by a qualified ophthalmologist.
After accurately determining why the head and eyes hurt, the doctor selects individually appropriate treatment.
As an independent disease, headaches are quite difficult to cure. Migraine is practically untreatable, so it is best for a person suffering from attacks to consult a neurologist for a more accurate diagnosis and recommendations for preventing attacks.
To avoid possible complications, you should give up all bad habits - quit smoking, drink coffee on an empty stomach, drink strong alcoholic drinks. Daily walks in the fresh air will be an excellent prevention against headaches.
Massage and acupuncture will help relieve tension in the neck and shoulders, which will make it much easier to get through the next migraine attack. Massaging your temples in a circular motion can help reduce migraine pain. A massage on the inside of the palm will help relieve pain in the eyes and head caused by overwork.
Two glasses of warm water and 10 minutes of relaxation in a comfortable position can relieve vascular spasms and relieve you of headaches.
If the headaches are chronic, then antidepressants or sedatives and medications are sometimes prescribed to alleviate the condition.
Blurred vision #8212; it is a common problem that affects thousands of people every day. This disorder can have many causes and is sometimes associated with serious medical conditions, so it is best to consult a specialist.
Often blurred vision is accompanied by nausea, headaches, and fatigue, so it is better to understand what causes this condition and how it can be avoided.
If you can’t see objects well, can’t distinguish people’s faces, can’t read, and letters on the monitor screen blur in front of you, then you definitely need to consult a doctor.
In this article we will tell you what may be causing blurry vision and how you can cure it.
Causes of blurred vision
So, let's look at the possible causes of blurred vision and the most common symptoms that accompany it.
It is necessary to begin therapy after identifying the causes of the disease; self-administration of analgesics, antispasmodics and NSAIDs can lead to addiction and exacerbation of symptoms. You can get rid of unpleasant sensations without medications:
- massage your temples and head;
- do gymnastics for the neck and eyes;
- take a walk outside or ventilate the room well;
- use a cold compress from a decoction of medicinal herbs or plain water - apply it to the sore spot and on the eyes;
- take a contrast shower;
- sleep for 1-2 hours in a cold room without access to light.
If your head starts to hurt, you need to measure your blood pressure to make sure there are no dangerous factors.
When using drugs, their purpose and effectiveness should be taken into account. For mild attacks, you can take Aspirin, Indomethacin, Analgin or Ibuprofen and Paracetamol.
Doctors also recommend using medications to treat regular migraine attacks between relapses. For this purpose, new antidepressants, a group of anticonvulsants, and drugs based on propranolol are prescribed.
Treatment
Therapeutic measures are based on the cause that caused the disorder:
- prescription of glasses and lenses that correct decreased visual acuity;
- drugs against glaucoma, cataracts, prescribed in the form of drops;
- medications that lower blood pressure;
- anti-inflammatory drugs;
- surgical methods to restore damaged tissues;
- surgical removal of malignant and benign tumors.
If any serious systemic disease is detected, specific therapy is prescribed. After complete healing, the headaches will go away on their own.
Symptom prevention: to avoid headaches and eye pain
Often headaches and ripples in the eyes are just signs of an unhealthy lifestyle. Here's what you can do to get rid of them without drugs:
- try to drink as much clean drinking water as possible - a natural prevention of dehydration, which affects 80% of the population;
- alternate between work and rest; if you want to sleep 12 hours, sleep for that long;
- eliminate caffeine, cigarettes and alcohol for a while; if the pain goes away, try not to introduce them into everyday life;
- spend more time in the fresh air and try to ventilate the premises.
Moderate physical activity is the best prevention of headaches not associated with pathological causes.
If a person is often bothered by a headache, which is preceded by ripples in the eyes, it is necessary to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. This can be caused by both serious organ diseases and ordinary fatigue.