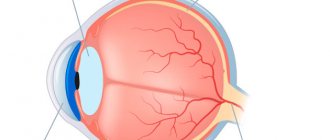
Operations to remove the cloudy lens of the eye have been performed for a very long time. However, in the past there was a practice of waiting for the cataract to mature. This was due to the lack of high-tech materials and safe methods for removing the lens substance that had become unusable. It was possible to remove it completely and properly only in the later stages of cataract development, when the “cataract is mature” and the lens substance becomes quite dense.
The patient, meanwhile, progressively lost his vision, sometimes even to the point of light perception. He was forced to seriously limit his range of interests, spending almost all his time at home, exposing himself to unnecessary risks, acquiring more and more new diseases and feeling constant discomfort from the rapid decline in his quality of life.
Thanks to modern medical technology, today there is no need to wait for cataracts to mature. If visual function decreases even at an early stage of the disease, ophthalmologists recommend immediate surgical treatment.
When is lens replacement prescribed for myopia?
Lens replacement for myopia is prescribed in the following cases:
- 1) High myopia – from -15 to -20 D
- 2) Refractive errors
- 3) Changing the shape of the lens
- 4) Hereditary lens diseases
- 5) Lens opacities
- 6) Contraindications to laser vision correction.
- 7) Patient's reluctance to wear glasses or contact lenses
Lens replacement for myopia is performed only on patients over 18 years of age.
Until this age, the eye continues to grow and its systems and tissues are in the process of formation.
Also, surgery is not performed if vision is rapidly deteriorating - myopia must first be “stabilized”. Remember - surgery is a last resort method, it is prescribed only when other methods of combating the disease have not been effective. In the early stages, they try to correct vision with glasses, scleroplasty, and keratotomy.
Consequences of manipulation
Before the introduction of this technology, complications after cataract surgery occurred more frequently. This happened because it was necessary to wait for the lens to fully mature. In this state, it became denser, which complicated the process. Therefore, ophthalmologists believe that cataracts must be eliminated immediately. This factor contributed to the invention of phacoemulsification.
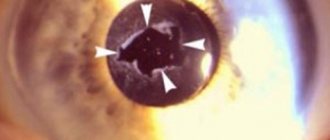
This is a new and safe method that has maximum effect in the treatment of cataracts. But any operation has its own certain risks of complications. Secondary cataracts are more common. The first sign of this complication is a cloudy appearance of the posterior capsule.
The frequency of occurrence of the secondary form depends on the material from which the replacement lens is made. When using IOLs made of polyacrylic, complications occur in 10% of cases. When using silicone lenses, consequences are observed in 40% of cases.
Sequence of lens replacement surgery for cataracts
Most often, secondary cataracts occur when using lenses made of polymethyl methacrylate. The reasons for its appearance, as well as preventive measures, are still unknown. Scientists are trying to figure out how this effect occurs after lens replacement. This is known to occur due to the movement of epithelial tissues into the space that lies between the lenses and the posterior capsule.
Epithelium is the cells that remain when the lens is completely removed. They can form deposits that make the patient's vision blurry. It is believed that fibrosis of the lens capsule leads to the occurrence of secondary cataracts. In this case, the complication is eliminated using a YAG laser. They make a hole (in the center of the clouded area).
After surgery, cataracts cause another complication - an increase in intraocular pressure (IOP). It occurs immediately after the intervention. It may occur due to incomplete washout of the viscoelastic. This is a substance that protects the internal structures of the eye. The cause of increased IOP after cataract removal may be a shift of the IOL towards the iris. But this phenomenon can be easily eliminated if you use glaucoma drops for 2-3 days.
Normal intraocular pressure is 20 mmHg. Art.
Prevention of elevated IOP is very important, as this condition leads to the development of glaucoma
Other negative phenomena
Irvine-Gass syndrome, or cystoid macular edema, occurs in 1% of cases. But when using the extracapsular technique, the likelihood of pathology occurring increases to 20%. There is a risk group for this complication that includes diabetics, people with uveitis and wet AMD.
The likelihood of occurrence increases if the posterior capsule is ruptured during cataract extraction. After the lens is removed, a complication may arise in the event of vitreous loss. You can get rid of the pathology with the help of corticosteroids, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, angiogenesis inhibitors. If conservative treatment does not give the desired effect, vitrectomy is prescribed.
The eye may swell after lens replacement. This complication is called ocular edema. It occurs when the pumping function of the endothelium is damaged during surgery. Damage can be either chemical or mechanical in nature.
During swelling of the eye, a person sees blurred. But with a favorable outcome, the complication goes away on its own.
The postoperative period may be accompanied by corneal edema, which normally disappears 3-5 days after the intervention
But the development of pseudophakic bullous keratopathy can also occur. This process is characterized by the presence of bubbles in the cornea. To eliminate them, hypertonic solutions and ointments are prescribed. It is possible to use therapeutic contact lenses. If therapy does not help, the cornea will need to be replaced.
Foggy eyes can also appear with astigmatism. The postoperative type of the disease occurs after IOL implantation. The complexity of astigmatism directly depends on the method used to eliminate the cataract. The severity is influenced by the length of the incision, its location, the presence of sutures and problems encountered during the operation.
If the degree of astigmatism is small, then it can be corrected with glasses or lenses. But when the eye is watery and the degree of astigmatism is high, it is necessary to perform refractive surgery.
In rare cases, a complication such as IOL displacement occurs. According to statistics, the percentage of manifestation of this complication is very small even several years after the operation. Contributing factors are:
- weakness of the cyanogen ligaments;
- pseudoexfoliation syndrome.
In very rare cases, displacement of the artificial lens may occur, this happens due to weakness of the zonules of Zinn.
Other pathologies
Rhegmatogenous retinal detachment is a common occurrence during IOL implantation. Its occurrence is associated with various problems discovered during surgery. The appearance of pathology is facilitated by the presence of diabetes mellitus, myopic refraction, and previous surgical intervention.
In most cases, this disease is caused by intracapsular cataract extraction. Less commonly, the cause is extracapsular cataract extraction. But the smallest percentage of cases of such a complication is observed during phacoemulsification. To detect this complication early after surgery, it is necessary to periodically visit an ophthalmologist. This condition is treated in the same way as other detachments.
During the operation, unforeseen complications may occur, which include choroidal hemorrhage. Blood pours out from the nutrient vessels of the retina. This condition is observed with hypertension, a sudden increase in IOP, atherosclerosis, and aphakia. The cause of the disease may be an eyeball that is too small, old age, or an inflammatory process.
The bleeding may stop on its own. But there are cases when it led to complex consequences, as a result of which patients lost an eye. It is necessary to apply complex therapy to eliminate bleeding. Additionally, corticosteroids, cycloplegic and mydriatic drugs, and antiglaucoma drugs are prescribed. Sometimes surgery is indicated.
Choroidal hemorrhage
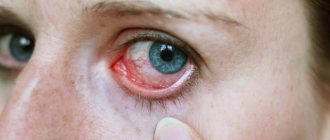
If cataract surgery is performed, complications may present in the form of endophthalmitis. They can cause a sharp decrease in vision, which leads to its absolute loss. According to statistics, the frequency of occurrence is 0.13-0.7%
Factors contributing to the occurrence of pathology include wearing contact lenses, a prosthetic fellow eye, and the use of immunosuppressive therapy. If an infectious process has begun in the organ, it is manifested by severe redness of the eye, increased photosensitivity, painful sensations and deterioration of vision.
For prophylaxis, preoperative administration of 5% povidone-iodine is indicated. Additionally, an antibacterial agent is injected into the eye. The quality of disinfection of the instrument used for surgery plays an important role.
How is the operation performed?
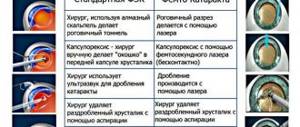
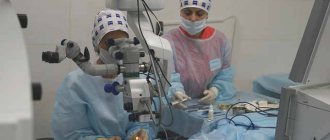
Replacement of the lens of the eye for myopia is carried out using the phacoemulsification method, which practically does not cause complications.
The operation takes 15-30 minutes and is performed under a microscope on an outpatient basis.
Through an incision, ultrasound is used to emulsify the patient's lens and then remove it. In its place, an intraocular lens (an artificial lens) is implanted, which will subsequently be responsible for focusing the image on the retina. Sometimes it becomes necessary to install not one, but two lenses, which is also not a big problem. IOLs for myopia and other operations on the lens are selected individually, taking into account the patient’s vision characteristics. Only a doctor can do this.
Obtaining a quota for an operation within a short time: is it possible?
The process of obtaining a quota for an operation can really be speeded up, although this is not always possible. People who are familiar with this whole system recommend the following:
- Please indicate in your application the specific hospital where you want to have surgery. Of course, this medical institution must be included in the list of government clinics providing medical care of a similar nature. Contact the hospital's quota committee and find out if there are any available quotas.
- Try to communicate as often as possible with the supervisor of the governing body in which the issue of allocating a quota is being considered.
- Provide two packages of documents: one to the management, the second to the clinic’s quota committee.
- You should not focus on the best hospitals in the city, especially if you live in large cities such as St. Petersburg and Moscow.
- Lines at clinics can be long. Some patients wait for a quota for years.
- Pay for the procedure yourself, and subsequently return all or part of the amount by contacting the Ministry of Health. Please note that domestic implants, which are installed according to a quota, are cheaper. You can only get your money back for them. The state does not pay for imported IOLs.
Possible complications
Complications during surgical treatment of myopia (myopia) are associated primarily with the course of the underlying disease. The fact is that with myopia, the eyeball becomes enlarged, which affects all systems of the visual organ. There may be:
- 1) Dystrophic changes in the retina
- 2) Retinal tears due to thinning
- 3) Reducing the thickness of the outer shell of the eye (sclera)
- 4) Retinal detachment
That is why lens replacement for high myopia is prescribed only after a thorough examination and taking into account all possible consequences.
The optimal age for surgery is after 40 years.
By this time, the ability to accommodate is partially lost, and the first signs of cataracts may appear. After surgery, the patient needs to visit an ophthalmologist regularly to monitor his vision and detect complications at the earliest stage.
For what ophthalmopathologies is a quota for eye surgery issued?
You can receive a quota for high-tech treatment of an eye disease in the following cases:
- Inflammation of the retina and choroid, cysts and neoplasms, hemorrhages in the eyes against the background of destructive processes in the cornea, lens or vitreous body;
- Rupture or detachment of the retina with its subsequent deformation;
- Congenital or secondary glaucoma, which is accompanied by various complications, for example, inflammatory processes;
- Defects that were the result of surgery inside the eyeball;
- Dangerous injury to the eyelid, eye (mechanical or chemical burn);
- Benign and malignant tumors of the orbit;
- Congenital anomalies of the lens, cornea, muscle tissue and other parts of the eyeball;
- Anomalies of the eyelids, defects in the structure of the lacrimal apparatus;
- Changes in the structure of the anterior chamber of the eyeball, which are caused by cataracts;
- Secondary cataract, which causes diseases of the retina, choroid, and lens.
The procedure for obtaining quotas and the list of diseases covered by preferential treatment are changing. New rules may be established every year. You should clarify all these questions with lawyers or monitor changes in legislation yourself.
If you approach this issue thoroughly, then getting a quota is quite possible. However, you should not risk your health. Cataracts are a very serious pathology that can permanently deprive a person of vision. Therefore, it is better to spend a little money, part of which can then be returned through the appropriate structures.
After operation
Replacing the lens for myopia is a fairly well-established operation. The postoperative period is usually well tolerated. The patient is discharged the next day after the follow-up examination, and vision is restored almost immediately. However, it is necessary to observe some precautions, which are mainly related to the need to protect the operated eye from damage. Recommended:
|
How to apply for a quota for an operation?
There are two ways to obtain a quota for cataract surgery: by contacting the medical institution where the procedure will be performed, and through the health authority. In any case, you will first have to make an appointment with your local doctor, who will give you a referral to an ophthalmologist. He will prescribe all the necessary diagnostic procedures and prescribe treatment. The ophthalmologist will tell you how to obtain a quota for the operation and subsequently make a decision on hospitalization.
The next stage is collecting documents. They are endorsed by the chief physician of the medical institution where the patient was examined. The patient will need:
- referral from hospital;
- an extract from the card with a full description of the diseases with a note about the need for surgical treatment of cataracts;
- test results, fluorography, ECG, otolaryngologist and dentist reports;
- photocopy of passport;
- copies of certificates of compulsory medical and pension insurance.
After collecting all the documents, they must be taken to the local health authority. This institution has a special commission that distributes quotas for cataract operations and for the treatment of other diseases. The commission reviews the patient’s package of documents within 10 working days. The meeting usually takes place without the participation of the patient. If a positive decision is made, the documents are sent to the hospital where cataract surgery will be performed.
Hospitals providing high-tech treatment have quota committees. Here the documents are studied for another 10 working days. At the meeting, a date for hospitalization of the patient must be set. It is worth understanding that deadlines are not always met. Often there is a long wait. The quota commission at the hospital informs the curator from the health department about its conclusion. Within three weeks, he must contact the patient to schedule an appointment with him. The final stage of obtaining a quota for cataract surgery is providing the patient with a document indicating the name of the clinic and the date of hospitalization.
As you can see, the procedure for obtaining a quota is quite lengthy. The patient should be patient. Don't forget that in reality everything will be more complicated. You may be placed on a waiting list for a surgery quota.
Is there any way to speed up the registration process?
Cost of lens replacement for myopia
The cost of replacing a lens for myopia is determined mainly by the cost of an artificial lens. You can choose a monofocal lens - it is cheaper, but you will need glasses for correction, since you will only see well at a certain distance. If you give preference to a multifocal lens, then you will not need glasses - such an lens has several focusing points for different distances. The price also includes consumables. You can find out the exact cost in our price list in the section on cataract surgery - phacoemulsification.
How can you save money on cataract surgery?
Treatment costs will be significantly reduced if you have a voluntary health insurance policy. It gives the right to free diagnosis and treatment in a hospital. The operation itself will also be free, but the intraocular lens will be paid for by the patient. There are several types of IOLs. Today they are made of soft materials and resemble regular contact lenses. An IOL is also called an artificial lens.
If you wish, you can pay for the installation of an aspherical, toric or even multifocal lens.
It will also compensate for the corresponding refractive error, for example, astigmatism. There are even intraocular lenses with UV protection. They are expensive, but provide the clearest possible vision, which can be completely lost with cataracts. Before making a decision, visit several clinics to find out prices for surgery.
Reviews about lens replacement for high myopia (myopia)
It is safe to say that after replacing the lens, myopia completely disappears and the patient returns to normal vision. Only sometimes people who have undergone surgery complain of minor discomfort in the eyes - double vision of objects from some angles or cloudiness of objects at certain distances.
In general, only about 5% of patients note inconvenience or side effects that have appeared in reviews.
We also note that everyone’s body characteristics are different and this may affect the postoperative period. You can read reviews in the corresponding section of the site. The surgical procedure is the same as for the treatment of cataracts.
Recovery period
You can read in detail about the types and progress of the operation
Here. This article focuses on characteristics and behavior in the postoperative period.
Every patient expects that after radical treatment his life will change. This is not entirely true - recovery requires time and adherence to medical recommendations. What are the nuances:
- At the end of the procedure, numbness in the eye is acceptable - this is a consequence of the local anesthetic. It will go away on its own in 1-2 hours.
- Postoperative prescriptions typically include antibiotic eye drops to prevent bacterial infections, as well as topical anti-inflammatory agents to minimize swelling. You will be provided with detailed printed instructions for all appointments. If necessary, a prescription will be issued.
- In the daytime, especially with good insolation, the use of sunglasses is recommended.
- At home, it is advisable to stay in bed for 1-2 days and try to rest more.
- Do not touch, rub or scratch your operated eye. Do not remove the protective bandage yourself, unless otherwise advised by a specialist. Try not to sleep on the side of the injured eye.
- You can return to normal daily life within 2-3 days. But it is advisable to avoid heavy lifting and intense physical activity.
The norm is poor vision, glare and flickering on the 1-4 postoperative days. Then all patients note gradual positive dynamics. The speed of recovery varies from person to person.
Preparing for surgery
Surgical replacement of the lens is carried out after a surgeon has examined the patient and determined the need to treat the ophthalmological disease surgically. Before carrying out the manipulation, the patient must pass all the necessary tests and consult with other specialists noted by the attending physician to ensure there are no contraindications.
Antibacterial drops should be instilled into the eyes on a schedule 3-5 days before surgery to minimize the risk of eye infection. The doctor will give other special recommendations during the preliminary consultation.
Contraindications for surgery
The natural lens is replaced surgically. And like any other operation, this manipulation has a number of contraindications. The possibility and expediency of the procedure is indicated by the attending physician when compiling a medical history and based on the results of a preliminary examination of the patient.
It is not recommended to replace the lens in the following cases:
- for inflammatory and infectious eye diseases;
- if decompensated glaucoma was previously diagnosed, lens replacement can be carried out after normalization of intraocular pressure;
- decompensation of general condition;
- Pregnant women and women during lactation do not undergo surgery.
The procedure for replacing the lens in ophthalmology is considered a generally safe procedure, so in extremely rare cases side effects occur after the operation. The main thing is to follow all the recommendations of your doctor.