Eye pain after cataract surgery
The low-traumatic method of phacoemulsification allows you to quickly replace the clouded lens with an artificial lens, restoring the patient’s vision. Complications occur rarely - in 1% of cases, the likelihood of encountering them is low. Most often, the reason that a person’s eye hurts after cataract (removal) is tissue damage during surgery.
Patient's feelings after surgery
Many people are concerned about the question: after a cataract is removed: is pain in the eye normal or a sign of pathology? In the first days after manipulation, damaged tissues naturally send pain signals to the nervous system. During the operation, a microscopic puncture of the cornea is made, and an ultra-thin needle is inserted. Ultrasound is applied through it and the clouded lens is destroyed. The crushed particles are removed and an artificial lens is installed. If an advanced cataract is removed, the pain in the eye will be more noticeable—higher power ultrasound is used to crush dense formations. The body needs time to recover.
Terms of rehabilitation
Most often, there is no pain during cataract removal. However, everyone’s sensitivity is different, so they are considered as normal in the first 2-3 days. It is impossible to give a more specific answer to the question of how much the eye hurts after a cataract. Affects:
- individuality factor;
- thorough adherence to the rehabilitation regime;
- stage of the disease;
- accompanying illnesses;
- features of the operation.
Warning factors
If cataract pain does not subside or even intensifies in the first days, you should contact an ophthalmologist for an unscheduled examination. Other reasons for caution:
- sudden deterioration in visual acuity;
- a sharp increase in body temperature;
- pus and discharge from the eye;
- discharge of mucus.
Prohibitions during the rehabilitation period
Following the patient's instructions, which can be found in the extract, will help reduce the risk of complications. The restrictions are significant, but reasonable.
- For the first 7 days, it is not recommended to go outside without a bandage.
- Do not use cosmetics for 10 days.
- Physical activity and lifting weights over 3 kg are prohibited for 8 weeks.
- Drinking alcohol and visiting saunas and baths are also not allowed.
- massage the eyeball until completely restored;
- be near a fire, oven, fire, fireplace;
- be exposed to cold temperatures (wind, frost);
- watch TV for a long time, read, work on the computer.
This is a period of being gentle with your health in general and your eyes in particular.
SEE ALSO: Complications of cataracts Mixed cataract surgery Tver cataract Free cataract surgery in Novosibirsk Hemorrhage in the eye after cataract surgery
Rules for instilling eye drops
The total period of taking the drugs in the absence of complications and infection is up to 4 weeks with a gradual reduction in dosage.
It is advisable to have a second person do the instillation. To do this, you need to wash your hands, the patient lies down on the couch or sits down and tilts his head back. In this case, your gaze should be directed upward. The assistant pulls back the lower eyelid and drips the drug between it and the eyeball.
If several drops are prescribed, then you need to take a five-minute break between taking them. For maximum effect, the lower eyelid can be pressed against the eyeball for a few seconds through a sterile napkin.
Does your eye hurt after cataract surgery?
Any manipulations on the organs of vision, even if they are carried out using modern techniques, are stressful for the eyes. Complications after phacoemulsification are noted in every fourth patient. So be prepared for them to appear. There is nothing wrong with this, but you will still have to take additional measures to eliminate these consequences.
As a rule, the eye does not hurt after cataract surgery. But sometimes inflammatory processes develop, which lead to pain and discomfort. Moreover, pain can appear not only in the eye itself, but also in the peri-ocular areas: superciliary arches, temples. The reason for this is:
- Infection of eye tissue due to improper selection of medications.
- Swelling or swelling of the retina.
- Bleeding.
- Inflammatory processes.
Often the sensation of pain is accompanied by a burning sensation, itching or increased tearing. This appears almost immediately after the operation is completed. For such complaints, the doctor prescribes therapy that is designed to eliminate the cause of these symptoms. If it does not go away, then the course of treatment is changed, selecting the most adequate method. In some cases, pain is a consequence of increased intraocular pressure. In this case, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Indications for surgical treatment. At what stage is it better to have surgery?
Cataracts cannot be treated with conservative methods. Therefore, in the early stages of the pathological process, many people do nothing, because they are sure that the operation is performed only on overripe cataracts of the eye. As a result, this leads to the fact that over time, vision deteriorates greatly and cannot be restored even through surgery. Today it is not necessary to wait for the cataract to mature (this process can take from 4 to 15 years); the operation can be performed with visual acuity of 0.1-0.2.
When should surgery be done? Indications for surgical treatment of cataracts due to lens opacity are the following conditions:
- overripe cataract;
- swelling cataract;
- phacolytic glaucoma;
- dislocation (subluxation) of the lens.
The operation may also be prescribed if it is necessary to perform ophthalmoscopy for the purpose of diagnosing and treating concomitant eye diseases. In addition to medical indications, we can also highlight some social and everyday issues in which the lens is removed. These include insufficiency of binocular vision, a significant decrease in acuity and a decrease in the visual field.
These functions are necessary for a person to live normally, and therefore are an indication for cataract surgery.
Complications after replacing the lens of the eye for cataracts
Complications after cataract surgery occur in the form of swelling, astigmatism and other physical abnormalities. People who have encountered such an unpleasant eye disease know firsthand that surgical intervention often ends badly, and there are complications after surgery. Eye cataracts still require treatment. And unfortunately, the only way to get rid of the pathology is to perform an operation to remove the lens and replace it with an artificial one. The procedure itself does not take much time and does not pose any threat to life and health, however, to avoid complications, you must adhere to certain rules and recommendations.
Types of complications
Complications after such an intervention can be divided into two categories: some of them arise directly during the operation, and others after it is performed.
Complications that arise after the procedure include the following:
- The intraocular pressure of the eye increases.
- Inflammatory process.
- The retina of the eye peels off.
- Hemorrhage occurs in the anterior chamber.
- The development of a disease such as secondary cataract.
- The new lens shifts slightly to the side.
Below we will look at each type of complication in more detail.
- Inflammatory process. After lens replacement, inflammation or swelling of the cornea and astigmatism almost always occur. That is why, after the operation is performed, the patient must be administered steroid drugs or antibiotics. After two to three days, all symptoms of inflammation should subside.
- Hemorrhage. This complication is rare; in most cases, it is associated with damage to the membrane or cornea of the eye at the time of surgery. As a rule, the patient does not hurt anything, he sees everything, and after a few days there will be no trace of blood left, it will simply resolve. If this does not happen, the doctor will have to forcefully flush the anterior chamber. Additional fixation of the lens is also performed.
- Intraocular pressure increases. This type of complication can occur because the drainage system becomes clogged with drugs of a viscous consistency. The doctor uses them to protect the cornea of the eyes. You can solve the problem by dropping drops into the eye. In rare cases, the specialist makes a small puncture through which the eyes are subsequently washed. Swelling of the eye or cornea and astigmatism are also observed, but it goes away quickly.
- Retinal disinsertion. This complication can be considered one of the most severe; it occurs due to injury during lens replacement. People who develop astigmatism also experience this complication. Many ophthalmologists insist on performing an operation during which the sclera is sealed. If the area of detachment is insignificant, then restrictive laser coagulation can be performed. In addition, due to the fact that the retina is detached, another unpleasant problem arises - the lens moves. Patients complain of astigmatism, the eye hurts greatly, is constantly accompanied by a feeling of discomfort, and swelling occurs. All symptoms last only for a while; after rest, this condition goes away. But with a significant displacement, visual discomfort will occur constantly. In order to solve the problem, it is necessary to perform repeated surgery.
- The lens is completely displaced. Lens displacement is a dangerous and serious complication that requires immediate intervention from specialists. During the operation, the lens is lifted and then securely fixed in its new position.
- Secondary cataract. After surgery, a complication such as the development of secondary cataracts is quite common. This occurs due to the fact that epithelial cells continue to multiply from the damaged lens. In this case, astigmatism is observed, visual acuity drops sharply. In order to solve the problem, you need to perform laser surgery.
Why does swelling occur?
Most patients ask why, after removal and replacement of the lens, corneal edema, eye astigmatism and other unpleasant problems develop. Experts explain it this way: eye tissues react to ultrasound. Corneal edema can occur not only after surgery, but also before it, if the cornea is weakened.
The structure of a mature cataract is hard, so at the time of the operation the ultrasound load will be increased, as a result of which the load on the eye will also increase.
You can remove corneal swelling from the eye using certain procedures or injections prescribed by your doctor. It should be noted that swelling during a sutureless operation is almost always insignificant.
Immediately after the corneal swelling subsides, the eyes will see well. Astigmatism is also treated under the strict supervision of a doctor.
How to avoid complications?
In order to alleviate your condition, speed up the rehabilitation process and prevent the development of even more serious complications, you must follow preventive measures:
- Do not tilt your head down until your doctor tells you to.
- At night, sleep on the side where your good eye is.
- Don't drive.
- You cannot lift weights weighing more than 10 kilograms.
- Take care of your eyes when visiting a bath or sauna, try not to let water get into it.
- Follow all your doctor's recommendations.
- Take vitamins, eat more vegetables and fruits.
- Be sure to give up bad habits, especially smoking.
Throughout the entire rehabilitation period, you should avoid heavy strain on the eyes. You can watch TV or sit at the computer the next day, but no more than two hours.
If the operation is successful, recovery depends only on you. If you follow all your doctor’s instructions and take preventive measures, you will be able to avoid complications, such as astigmatism.
ARTICLES ON THE TOPIC: Clinic of microsurgery and cataracts of the eye Fedorova After cataract surgery, what can you eat? Supplements for the eyes for cataracts Classification of cataracts ICD-10
Can complications arise after a few months?
Some types of complications may “make themselves felt” several months after surgery. The main one is the development of secondary cataracts. This condition usually occurs after 6 months to a year. In this case, the cloudiness does not form on the lens. The capsule, inside of which the intraocular lens is located, suffers. Patients note symptoms typical of cataracts. The complication is characterized by:
- blurred image outlines;
- weakened color rendering of objects;
- the appearance of “floaters” before the eyes.
Why does my eye hurt after lens replacement surgery?
An effective and gentle method of phacoemulsification does not eliminate the risk of complications after replacing the eye lens for cataracts. The advanced age of patients, concomitant diseases, and violation of sterility requirements by medical staff provoke undesirable consequences of the operation.
Intraoperative complications
Eye cataracts are incurable with conservative methods: there are no means that can make the clouded lens transparent again. Phacoemulsification, an operation involving the replacement of a worn-out “biological lens” with an artificial one, can restore lost vision with a minimal percentage of complications. To crush the lens that has lost its quality, an ultra-thin needle is used - a phaco tip, which works under the influence of ultrasound. Microscopic punctures (1.8-2 mm) are made for the needle tip; they do not require subsequent sutures, because heal on their own. Through these holes, the crushed lens masses are removed, and an elastic lens is implanted in their place - an artificial lens substitute. The intraocular lens (IOL) expands inside the lens capsule and provides the patient with high-quality vision for the rest of his life. However, even during such a high-tech operation, there are complications:
- Rupture of the capsule wall and loss of parts of the crushed lens into the vitreous region. This pathology provokes glaucoma, damage to the retina. After 2-3 weeks, a secondary surgical intervention is performed to remove the clogged vitreous.
- Displacement of the implanted lens towards the retina. A malpositioned IOL causes swelling of the macula (the central part of the retina). In this case, a new operation is necessary to replace the artificial lens.
- Suprachoroidal hemorrhage is the accumulation of blood in the space between the choroid and the sclera. This complication is possible due to the patient’s advanced age, glaucoma and hypertension. Hemorrhage can lead to loss of the eye and is considered a rare but dangerous aspect of lens replacement surgery.
Intraoperative problems during phacoemulsification are not excluded, but occur rarely - in 0.5% of cases. Postoperative complications occur 2-3 times more often (1-1.5% of cases).
Complications of the first postoperative weeks
For the first two weeks after surgery, it is necessary to protect the operated eye from bright light, infections and injuries, and use anti-inflammatory drops for tissue regeneration.
Despite preventive measures, complications are possible in the first and second weeks after cataract removal.
Pathologies amenable to conservative therapy
- Inflammatory processes. They are inevitable during operations - this is the body’s response to injury, therefore, upon completion of the surgical intervention, antibiotics and hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs are injected under the conjunctiva, and the eye is irrigated with bactericidal drops for 2-3 weeks. With weakened immunity, symptoms of uveitis or iridocyclitis are added to the usual signs of inflammation (redness, itching).
- Uveitis is an inflammatory reaction of the choroid of the eye, manifested by pain, photosensitivity, spots or fog before the eyes.
- Iridocyclitis is an inflammation of the iris and ciliary zone, which is accompanied by severe pain and lacrimation.
Such complications require complex treatment with antibiotics, anti-inflammatory hormonal and non-steroidal drugs.
- Hemorrhage into the anterior chamber. Associated with minor damage to the iris during surgery. Minor bleeding inside the eye can be treated with additional irrigation and is not painful or interferes with vision.
- Corneal edema. If a mature cataract (with a hard structure) is removed, complications after cataract surgery on the cornea are caused by the increased effect of ultrasound during its crushing. Corneal swelling occurs, which goes away on its own. When air bubbles form inside the cornea, special ointments and solutions and therapeutic lenses are used. In severe cases, the cornea is replaced - keratoplasty.
- Postoperative astigmatism. Surgery changes the shape of the cornea, causing refractive error and blurred vision. It is corrected with glasses and lenses.
- Increased eye pressure. Postoperative (secondary) glaucoma can occur due to various circumstances:
- the remains of the gel-like suspension (viscoelastic) that were poorly washed off during surgery impede the circulation of fluid inside the eye;
- the implanted lens moves forward towards the iris and puts pressure on the pupil;
- inflammatory processes or hemorrhages inside the eye.
As a result, symptoms appear: redness, pain, pain in and around the eyes, tearing, retching and fog before the eyes. The pressure returns to normal after the use of special drops; sometimes a puncture is done to wash the clogged ducts of the eyeball.
Pathologies requiring surgical intervention
- IOL dislocation. During the operation, the cataract (clouded lens) is removed from the capsular bag, where an elastic artificial lens is placed. It straightens itself inside the capsule, and the desired position is fixed by the doctor. If not fixed correctly, the artificial lens can move back, forward, or to the side. In such cases, the patient experiences a double image of distant objects, the eyes quickly get tired, and the unpleasant symptoms do not disappear after rest. This complication is quite severe: surgery is necessary to correct the position of the lens. Otherwise, retinal detachment will occur or glaucoma will develop.
- Rhegmatogenous (related to rupture) retinal detachment. Serious pathology during lens replacement operations. The retinal layer, separating from the wall of the eyeball, ceases to receive nutrition and dies, which leads to complete loss of vision. Provoking factors are:
- intraoperative complications;
- contusions of the operated eye;
- high degree of myopia;
- diabetes mellitus, vascular diseases.
If symptoms of retinal detachment appear: light spots, floaters, a dark veil before the eyes, you should immediately consult an ophthalmologist. Treatment is carried out with laser coagulation, surgical filling, and vitrectomy.
- Endophthalmitis. Inflammation of the internal tissues of the eyeball (vitreous humor) is a rare but very dangerous complication of eye microsurgery. It is connected:
- with infection entering the eye during surgery;
- with weakened immunity;
- with concomitant eye diseases (conjunctivitis, blephatitis, etc.)
- with infection of the tear ducts.
Symptoms: sharp pain, significant blurred vision (only light and shade is visible), redness of the eyeball, swelling of the eyelids. Emergency treatment is required in an inpatient eye surgery department, otherwise eye loss and the development of meningitis will occur.
Remote pathological changes
Undesirable consequences may appear 2-3 months after surgery. These include:
- Cystoid macular edema. Inflammation of the central part of the retina (macula) develops as a result of rupture of the lens capsule during surgery; infections in the vitreous body. Diabetes mellitus, glaucoma, and uveitis often provoke macular edema. The most important part of the retina is affected - the corpus luteum, where light rays are focused and nerve impulses are transmitted to the brain. Early diagnosis of retinal edema is difficult, the symptoms are not clearly expressed:
- blurred vision, especially in the morning;
- blurry wavy image of objects;
- pink tint of the image;
- light aversion.
An accurate diagnosis of macular edema is possible only with optical tomography and retinal angiography. The disease is treated with antibiotics in combination with anti-inflammatory drugs. With successful therapy, after 2-3 months the swelling resolves and vision is restored.
- "Secondary cataract". Late postoperative complication occurs after 6-12 months. The artificial lens, which replaces the removed “biological lens,” works properly, so the name “cataract” in this case is inaccurate. The opacification does not occur on the IOL, but on the capsule in which it is located. On the surface of the shell, the cells of the natural lens continue to regenerate. Shifting into the optical zone, they accumulate there and prevent the passage of light rays. The symptoms of cataracts return: fog, blurred outlines, decreased color vision, spots before the eyes, etc. Pathology is treated in two ways:
- surgical capsulotomy - an operation to remove the clogged film of the capsular bag, during which a hole is made to allow light rays to access the retina;
- cleaning the back wall of the capsule using a laser.
The correct choice of IOL reduces the likelihood of developing complications: the lowest percentage of post-cataract development is achieved by implantation of acrylic lenses with square edges.
Does your eye hurt after cataract surgery?
Any manipulations on the organs of vision, even if they are carried out using modern techniques, are stressful for the eyes. Complications after phacoemulsification are noted in every fourth patient. So be prepared for them to appear. There is nothing wrong with this, but you will still have to take additional measures to eliminate these consequences.
As a rule, the eye does not hurt after cataract surgery. But sometimes inflammatory processes develop, which lead to pain and discomfort. Moreover, pain can appear not only in the eye itself, but also in the peri-ocular areas: superciliary arches, temples. The reason for this is:
- Infection of eye tissue due to improper selection of medications.
- Swelling or swelling of the retina.
- Bleeding.
- Inflammatory processes.
Often the sensation of pain is accompanied by a burning sensation, itching or increased tearing. This appears almost immediately after the operation is completed. For such complaints, the doctor prescribes therapy that is designed to eliminate the cause of these symptoms. If it does not go away, then the course of treatment is changed, selecting the most adequate method. In some cases, pain is a consequence of increased intraocular pressure. In this case, antihypertensive drugs are prescribed.
Consultation with an ophthalmologist
Good afternoon. On December 15, 17, I had surgery on my right eye to replace the lens. There was cataract (immature). A month and a half has already passed. I followed all the doctors’ recommendations as expected for a month. A month later I visited an ophthalmologist, he said everything was fine. He canceled all the drops and allowed me to “live a normal life.” About a week ago, maybe a little more, the right eye again began to react to light, it stings, sometimes hurts, and waters. Sometimes the whole right side of my face ache. Not much, but not very pleasant. There are no visible changes in the eye. Doesn't blush, sometimes it seems like I see worse. I can't figure out what's wrong with the eye. I already regret having the surgery. By the way, the lens is American. The postoperative period was without complications. But what about the eye now? Why does it hurt, sting, or tear? Answer, please. Thanks Is this normal? Patient age: 1976 years
Consultations on this issue are carried out by practicing doctors. Medical education has been verified by the site administration. The service bears full moral and legal responsibility for the quality of consultations.
First stages of the disease
- a feeling of itching in the eyes, a desire to rub them;
- black spots before the eyes;
- painful reaction to bright light;
- a halo forms around light sources;
- all objects appear yellowish;
- Sometimes with farsightedness there is a sudden temporary improvement in vision.
For patients diagnosed with cataracts, a medical history, unfortunately, is rarely written by a doctor from the initial stage. As a rule, people go to the hospital much later. But it is precisely in the first period that conservative treatment can slow down the process of formation of cloudy spots and delay the operation for several years. There are cases when in the initial stage the disease stopped and did not progress, which cannot be said about the next stage.
- Immature cataract. During this period, single spots on the periphery of the lens begin to unite and move towards the central zone. Intraocular pressure increases, because the lens increases in size – “swells”. Visual disturbances become noticeable and typical symptoms occur:
- visual acuity weakens, it is difficult to see small letters and details;
- fog appears before the eyes;
- difficulty distinguishing shades and colors;
- objects become fuzzy and double;
- in the dark, vision deteriorates, and in the light there is pain in the eyes.
Since vision quickly deteriorates, this stage is the main time to seek medical help. The cloudiness reaches a significant size, and conservative therapy has no effect. There is no point in hoping that drops and exercises will stop and reverse the irreversible process of lens clouding - this is a waste of precious time.
Today there is no need to wait for the cataract to mature in order to implant an intraocular lens in its place. On the contrary, late periods of surgery are associated with difficulties in removing a lens that is too dense.
What to do if your eye hurts after cataract surgery?
Cataracts are an eye disease that can only be treated with radical methods. Transparency of the optical system can be restored to a person by surgery.
Possible consequences
Modern eye surgery is characterized by safety and unique precision. Therefore, after treatment, a very small percentage of patients are prescribed repeat operations and additional therapy.
The most common complication occurring in the postoperative period is clouding of the posterior part of the lens remaining on the capsule. It is noted in every 4 operated patients.
Complications that cause pain:
- retinal tumor;
- infection of eye tissue;
- bleeding;
- inflammation.
Complaints after surgery
Since surgery is a surgical treatment, discomfort cannot be avoided. All sensations are individual. Clinics are faced with complaints that the eye hurts after cataract surgery, the eye tingles and itches. These sensations, if you follow all the doctor’s instructions and the correct course of the postoperative period, disappear after a few days.
However, if the painful sensations intensify, it means there is some kind of pathology. Some patients ask why the eye waters after lens replacement. There shouldn't be any tearing. This is a postoperative complication. The nutrition of the cornea may be impaired. Erosion is relieved with drug therapy.
Only following the ophthalmologist’s instructions will help you avoid complications after surgery.
Classification
Based on its origin, cataracts are divided into acquired or congenital.
According to morphology (structure), cataracts are divided into:
- subcapsular, which in turn is divided into anterior and posterior, which is determined by its location under the capsule or in front of it;
- nuclear, which can develop with the deterioration of normal age-related changes, which involves the nucleus of the lens, is often accompanied by myopia, its dense consistency is an indication for surgical removal;
- cortical - covers the posterior, equatorial and anterior parts of the capsule;
- herringbone - this form is quite rare, characterized by many needle-shaped multi-colored deposits in the layers of the lens.
According to the degree of maturity, age-related cataracts are divided into:
- immature - classified as initial senile cataract with partial;
- mature - complete clouding of the contents of the lens;
- overripe - wrinkled anterior capsule due to leakage of lens fluid;
- Morganieva - overripe cataract with liquefaction when the nucleus descends.
Types of intraocular lenses
Intraocular lenses are produced in various types, which differ in refraction. The choice of refraction is influenced by the examination tests and the patient’s desire to see perfectly after surgery without using glasses. In addition to these lenses, which guarantee a clear picture of objects located far and near, artificial lenses have recently begun to be actively used, the effect of which is similar to glasses with built-in progressive lenses and multifocal glasses. They help you see perfectly at any distance. There are also special lenses that can replace curved corneas or that contain multi-colored filters that have a protective function against retinal disease.
There are several types of lenses
Treatment
In the initial stages of lens opacification, the specialist recommends conservative therapy to the patient to prevent rapid progression of the disease. The treatment of cataracts includes the use of eye drops that improve metabolic processes.
Most commonly prescribed medications:
- Taufon or Taurine: contain the amino acid of the same name, which prevents oxidation and clouding of the lens protein.
- Oftan Katahrom: normalize oxidative and energy processes. Active ingredients: Cytochrome C, Adenosine and Nicotinamide.
- Quinax: contains azapentacene, which improves metabolic processes and protects the lens from loss of transparency.
To combat cataracts, ophthalmologists recommend using medications according to a special regimen: 1-2 drops instilled into both eyes three times a day in courses.
Contraindications for the use of conservative therapy:
- Individual intolerance to any component of the drug;
- Pregnancy and breastfeeding period.
In the case of mature or overripe cataracts, the use of drug therapy is unfounded.
When should surgery be performed?
The main indication is considered to be low visual acuity, leading to limited ability to work and discomfort in everyday life. In case of advanced cataracts, this is the only way to restore vision.
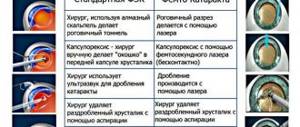
How is phacoemulsification of cataracts performed?
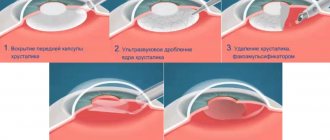
This treatment involves replacing the cloudy lens with an intraocular lens. A fairly small incision is made on the side of the cornea and a small probe is inserted into it. Ultrasound destroys the nucleus of the lens and then removes it. After this, the intraocular implant is inserted onto the capsule, which will support it in place.
The entire operation takes no more than 20 minutes, and the effect is noticeable immediately. Upon completion, the specialist advises the patient to follow certain rules.
Recommendations of an ophthalmic surgeon after cataract removal:
- Lifting weights over 3-5 kg is prohibited.
- Avoid bending down and sudden movements.
- Wear dark glasses in bright sunny weather.
- Do not drink excess water in the first 14 days after the intervention.
- Limit intake of salty, spicy foods.
- Sleep on the non-operated side.
- Avoid driving.
- Do not rub or put pressure on the eye.
- Quitting smoking and alcohol.
This regimen must be followed for about 2-3 months to reduce the likelihood of acquiring postoperative complications.
When it is not advisable to conduct FEC
There are certain contraindications to the operation.
These include:
- Development of an acute infectious disease or exacerbation of a chronic one.
- Condition after myocardial infarction or stroke that occurred at least 6 months ago.
- Inflammatory processes in the organ of vision.
- Malignant neoplasms of the eye area.
- Mental illness or inadequate state of a person.
If there are any, it is recommended to postpone the intervention for some time or cancel it.
Diet
The patient needs to follow proper nutrition for cataracts: he will have to give up a number of foods that provoke the progression of the disease. People who eat large amounts of meat are considered more prone to developing cataracts. To stop the course of the disease, it is recommended to eat food containing nutrients.
List of recommended products:
- Vitamin C: maintains the tone of the eye vessels. There is a lot of it in parsley, strawberries, currants, citrus fruits, and peaches.
- Vitamin E: is an antioxidant, protecting the organ of vision from UV rays and reducing the intensity of the disease. Contained in nuts in large quantities.
- Zinc: affects the absorption of vitamin A and provides support for lens clarity. Red beans, pumpkin seeds, shrimp, and chicken are rich in this microelement.
In old age, it is advisable for a person to eat foods containing small amounts of carbohydrates to reduce the likelihood of developing cataracts. Experts recommend including natural honey in your diet, as it contains microelements and vitamins that are beneficial for the eyes. It is enough to eat 1 tsp per day.