What is keratitis?
Keratitis is an inflammatory disease of the cornea of the eye, characterized by ulceration and clouding.
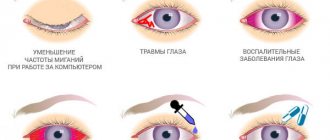
The main symptoms of keratitis are eye pain, redness, lacrimation, photophobia, and decreased visual acuity. Ultimately, the development of keratitis can lead to the appearance of a cataract and loss of visual function.
The main causes of keratitis are injury to the anterior part of the eyeball (chemical, mechanical or thermal), infection of the eye, the presence of various eye pathologies (metabolic disorders, innervation, etc.).
Quite common diseases that accompany keratitis are conjunctivitis (inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye), iritis (inflammation of the iris), cyclitis (inflammation of the ciliary body) and scleritis (inflammation of the sclera).
First aid for a person with an eye injury: how to provide?
Any eye injury is dangerous; you should not hesitate to see a doctor. Treating a damaged eye at home is strictly prohibited - this can provoke negative consequences, including loss of vision. But first aid is necessary.
What does this help consist of? The location of the injury must be:
- rinse to remove contaminants (if the eye injury is not penetrating);
- stop bleeding with a bandage/bandage;
- numb the injury site (apply ice).
Keratitis - symptoms
The severity of clinical manifestations of keratitis largely depends on the type of corneal lesion, as well as the type of infection leading to the development of the disease.
The first signs of keratitis:
- Redness of the eyes;
- Pain in the eyes;
- Increased tear production
Main symptoms of keratitis
- Corneal clouding and swelling;
- Reduced eye specularity;
- Pain in the eyes;
- Photophobia;
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Involuntary twitching of the eye muscles (blepharospasm);
- Dilation of blood vessels in the eyeball, as well as their transformation into a bright red branched tree (vascularization);
- Decreased sensitivity of the cornea;
- The presence of an infiltrate on the cornea, the color of which depends on its composition (if lymphoid cells predominate - grayish, and if leukocytes - yellowish);
- Sometimes, if there is an infiltrate on the cornea, a person may feel a foreign object in the eye.
Infiltrate with keratitis can vary in size and shape - sometimes it is localized in one place, and sometimes it covers the entire surface of the eye. The infiltrate has the property of exfoliating and falling away from the cornea, and erosion is observed in its place.
Deep vessels are dark red and more linear, while red and light red, smaller branch vessels indicate superficial keratitis.
List of drugs and their descriptions
Drops for eye pain are used only for symptomatic treatment. With their help, it is impossible to eliminate the cause of the disease or slow down the spread of the destructive process. The prescription of a particular eye drug is determined by many factors. When choosing medications, the ophthalmologist takes into account the type of pathology, the form and stage of its course, the patient’s age, and the presence of chronic diseases. The doctor takes into account the composition of the drug and the likelihood of adverse reactions.
Indocollier
The French manufacturer produces Indocollir in the form of a clear solution with a yellowish tint. The active ingredient is indomethacin from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Only useful synthetic additives are used as auxiliary components.
Indocollyr for the eyes has a complex effect on the human body:
- reduces the severity of pain;
- relieves acute and chronic inflammatory processes;
- eliminates swelling of the eyelids.
The main indications for its use are surgical miosis (constriction of the pupil), pain that occurs after surgical interventions and accompanying acute ophthalmological pathologies.
Alcaine
This drug is a representative of the clinical-pharmacological group of drugs with local anesthetic activity. The analgesic effect of the drops is due to the presence of proximetacaine in the eye drops. Alcaine is practically not used in the treatment of diseases. Indications for its use are:
- short-term diagnostic measures;
- surgical interventions - removal of cataracts, sutures placed on the conjunctiva or cornea;
- taking scrapings from the mucous membrane of the eyes for further laboratory tests;
- removal of foreign objects;
- determination of intraocular pressure.
The analgesic effect of Alcaine occurs within a few minutes and lasts for about half an hour. When repeated instillation of the eye product, the duration of the analgesic effect is slightly reduced.
Naklof
An ophthalmic drug with diclofenac is used to prevent pupillary constriction during cataract removal and to relieve the inflammatory process after surgery. Indications for the use of Naklof also include cystoid edema of the retinal macula and inflammation of non-infectious origin. NSAIDs are prescribed to patients to treat the following diseases:
- conjunctivitis;
- keratoconjunctivitis;
- corneal erosion.
Anesthetic drops are characterized by pronounced anti-edematous properties. Naklof reduces local temperature, which often rises during the acute course of the inflammatory process.
Lidocaine
Eye drops with lidocaine are produced by many domestic and foreign manufacturers. It is a local anesthetic often used to relieve acute pain from injuries. The drug has an analgesic effect a few seconds after instillation. But it lasts less than an hour, so Lidocaine is not effective for persistent pain. What are the indications for the use of the drug:
- fundus examination;
- examination of the anterior chamber of the eye;
- performing a surgical operation;
- removal of suture material;
- removal of foreign bodies;
- taking a scraping from the cornea.
Lidocaine for the eyes is in demand as a local anesthesia during operations lasting no more than 30 minutes. In other cases, drugs with a long-lasting analgesic effect are used.
Keratitis - causes
Among the main causes of keratitis are:
- Infection of the eye with a viral, bacterial or fungal infection;
- Eye damage – mechanical, thermal or chemical;
- Exposure of the eye to strong winds;
- Metabolic disorders (usually develops against the background of an unbalanced diet, hypovitaminosis, vitamin deficiency, hypothyroidism, etc.);
- Disorders of the innervation of the cornea (control of the nervous system of the cornea);
- Ultra-high production (hypersecretion) of fatty secretion by the meibomian glands;
- Decreased immune system reactivity;
- Wearing contact lenses - sometimes an infection gets under contact lenses (Staphylococcus aureus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, amoeba are especially common), which actually begins to actively multiply in a “closed” space and cause the development of the disease;
- The presence of certain diseases - lagophthalmos (impossibility of completely closing the eyelids), allergies, conjunctivitis, scleritis, iritis, uveitis, blepharitis, scleritis, cyclitis, pathologies in the development of the eye.
Sometimes the cause of keratitis cannot be determined.
Foreign body, bleeding, speck, injury: how to help?
- Foreign object. If there is a large object in the injured eye, you need to fix a protective frame over the eye using improvised means, which will not allow the foreign body to move. A regular paper cup will do. For disinfection, you can take any antibacterial drops (for example, "Levomycetin" 0.25%), then go to see a doctor as quickly as possible.
- Heavy bleeding. The causes of hemorrhages in the tissue of the eyelids or organs of vision are contusions or penetrating wounds. First you need to order antibacterial drops, then cover your eye with a sterile bandage (do not put pressure on the damaged area) and quickly go to the nearest emergency room.
Eyewinker. Small specks often come out on their own with active blinking and lacrimation. But if the speck does not come out, you need to pull back the lower eyelid and examine the eye, rinse it with running water and apply any antibacterial drops. If even after these manipulations you cannot remove the speck, you should seek medical help.- Chemical burn. The damaged eye should be rinsed with running water as quickly as possible. The eyelids should be spread apart with your fingers for more effective rinsing. Then cover the injured eye with a clean napkin and seek help from a doctor.
- Mechanical injuries of the eyelids. The damaged areas are carefully treated with an antiseptic solution, cold should be applied to the eyelid, and a clean/sterile bandage of gauze or cotton wool should be applied to the wound. Next, you should consult a doctor or the nearest emergency room.
Types of keratitis
Keratitis is classified as follows:
By etiology:
1. Exogenous – the cause of the disease is external factors. Divided into:
— Traumatic – the disease is caused by damage to the cornea by mechanical, chemical, thermal or radiation exposure.
— Infectious – the disease is caused by infection of the eye, especially when it is injured or when wearing contact lenses. Depending on the pathogen it may be:
- Viral keratitis - in 70% of cases is caused by herpes viruses - simplex (Herpes simplex) and herpes zoster (Herpes zoster)
- Bacterial keratitis - the most common pathogens are staphylococcus, Pseudomonas aeruginosa
- Fungal keratitis;
- Caused by other types of infection - amoebic or acanthamoeba keratitis, which develops when the cornea is exposed to Acanthamoeba and protozoa.
— Keratitis caused by conjunctivitis, disease of the meibomian glands and other parts of the eyelid.
— Keratitis caused by corneal erosion.
2. Endogenous – the cause of the disease is internal factors. Divided into:
- Infectious keratitis: tuberculous (hematogenous, allergic), syphilitic, herpetic;
- Neuroparalytic – caused by a violation of the innervation of the cornea, and is characterized by a sharp decrease, and then a complete absence of sensitivity of the cornea of the eye;
- Avitaminosis – caused by insufficient intake of vitamins into the body;
- Allergic – caused by allergies;
- Uveal;
- Dystrophic - the cause of the disease is pathologies in the structure of the eye.
3. Idiopathic – the cause of the disease cannot be determined.
With the flow:
- Spicy;
- Subacute;
- Chronic;
- Recurrent.
For corneal damage:
- Central – located in the center of the cornea (eye);
- Peripheral - inflammation is located at the edge of the cornea.
According to the depth of the lesion:
- Superficial – characterized by damage to the upper layer of the cornea, as evidenced by light red small vessels;
- Deep - characterized by damage to the lower layer of the cornea, as evidenced by dark red large vessels.
Special forms of keratitis
Filamentous keratitis is one of the forms of chronic inflammation of the cornea, the development of which is caused by hypofunction of the lacrimal glands (insufficient tear production) and drying of the corneal epithelium. It is characterized by thread-like discharge from the eyes, photophobia, irritation and burning of the eyes, and dry nasopharynx.
Rosacea keratitis is an inflammation of the cornea with the formation of an infiltrate, developing against the background of rosacea on the facial skin (rosacea). Usually accompanied by the presence of silisto-purulent iritis and conjunctivitis, corneal syndrome, and corneal ulceration.
Possible consequences
Whether there will be consequences after the injury depends on how timely the person receives first aid and what degree of severity the injury has. With poor quality or inappropriate treatment, the following problems may arise:
- Blood poisoning;
- Loss of the organ of vision;
- Decreased visual acuity;
- Accumulation of pus in the skull;
- Purulent inflammation of the eyes;
- Iridocyclitis of fibroplastic type;
- Endophthalmitis;
- The appearance of scars;
- Turn of the century;
- Blockage of the tear duct.
To reduce the risk of complications and consequences, you should consult a doctor immediately after receiving an injury and do not self-medicate.
Keratitis - treatment with folk remedies
Important! Before using folk remedies against keratitis, be sure to consult your doctor!
Sea buckthorn. To relieve the symptoms of corneal inflammation, from the first day you can instill sea buckthorn oil into your eyes every hour; in the next 24 hours, instillations should be done every 3-4 hours. Sea buckthorn oil also improves visual acuity.
Aloe. Cut a couple of large leaves of an adult aloe (the plant must be at least 3 years old) and wrap it in paper, put them in the refrigerator for 7 days to infuse. Then squeeze the juice out of the leaves, strain it, pour it into a glass container, and dissolve 1 grain (the size of a wheat grain) of mumi in it?