Eye drops are medications for topical use that have a certain effect on the mucous membrane of the organs of vision. The prescription of drugs may be different:
- antibacterial;
- antiviral;
- vasoconstrictors;
- moisturizers and so on.
Before using any medication, you must read the instructions. The abstract always describes the algorithm for instilling drops into the eyes: scheme, dosage, frequency of use and duration of treatment. If you use an over-the-counter product on your own without visiting a doctor first, you must strictly follow the step-by-step instructions.
Why are drops placed in the eyes?
For children and adults, topical vision medications are prescribed for a variety of reasons. Most often they are eye diseases such as conjunctivitis, blepharitis, cataracts, glaucoma and the like. The use of medications is indicated before diagnostic or therapeutic procedures. Also, some products are used for daily care and maintenance of visual health. Medicines will be effective only if you follow the algorithm for putting drops into the eyes. Deviation from step-by-step instructions can lead to various complications. Let us consider in more detail how local treatment of the organs of vision should be carried out.
Drops
Often the package of eye drops already contains a special pipette that helps dispense the solution. With these systems, one or more drops can be precisely instilled (with a gap between drop formations). It is advisable that the procedure be performed by an assistant, as this will allow the patient to relax the eye muscles and improve the effect of the drug on the body. However, there are situations when the patient experiences discomfort and fear before the procedure, and therefore closes his eyes reflexively. In this case, the patient himself must instill the solution, following all the doctor’s instructions. The main features of this procedure are discussed step by step below. To better understand how to properly instill medicine into the eyes, you should look at additional photographic materials.
Hand hygiene
Before putting drops into the eyes of an infant, small child or adult, you must wash your hands thoroughly. If you miss the first point of the step-by-step instructions, then there is a possibility of introducing a new infection. As a result, the patient will not only not recover, but his health will only worsen.
Hand hygiene involves thorough washing using antibacterial soap. After this, wipe your palms dry and, if necessary, use sterile gloves. Additional protective equipment (gloves) are more often used in medical institutions. If you carry out the instillation procedure at home, then simply wash your hands.
Preparing the medicine
The technique of instilling drops into the eyes involves preparing a medicine. Many drugs must be stored in the refrigerator after opening. Applying a cold solution to the mucous membrane of the eye may seem uncomfortable. It is especially not recommended to conduct such experiments with children. If you store the drops in the refrigerator, then hold them in your palms for 10-15 minutes before using. Do not heat medicinal solutions.
If the container with the drug has a pipette, then it must be used individually. It is unacceptable to give medicine to other family members for treatment. If you need to use it by several people, you should stock up on individual pipettes. They must have a blunt end.
Place drops in the eyes and place eye ointment behind the lower eyelid.
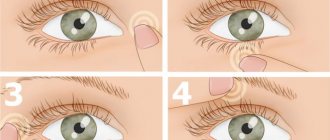
· Instillation of drops into the eyes Execution algorithm: 1. Explain to the patient the procedure for carrying out the manipulation, obtain his consent. 2. Sit the patient on a chair facing the light with his head slightly thrown back or lay him on his back without a pillow. 3. Wash your hands hygienically and put on sterile gloves. 4. Examine the patient’s eyes, if necessary, preliminarily perform an eye toilet. 5. Take the medicine into the pipette with your right hand, and take a sterile gauze pad in your left hand. 6. Pull back the lower eyelid with your left hand using the left gauze pad. 7. Invite the patient to look up (if possible). 8. Slowly release 1-2 drops of the medicine into the conjunctival sac, closer to the nose. 9. Invite the patient to close the eye (the medicinal solution should not leak out), remove excess medicine with a cotton ball. 10. In the same way, drop drops into the other eye. 11. Place the used dressing material and pipettes in containers with disinfectant. solution. 12. Remove gloves and place in a container with a disinfectant solution. 13. Wash hands and dry.
Placing eye ointment behind the lower eyelid
Take a sterile gauze pad or ball in your left hand. The lower eyelid is pulled back using a ball (napkin); the patient should be asked to look up. The ointment is squeezed out of the tube behind the lower eyelid, from the inner corner of the eye to the outer. The lower eyelid is released, the remaining ointment is removed with a napkin (ball). The used ball should be placed in the tray provided for it. The ointment is applied in the second eye in the same way. At the end of the procedure, the used material is disinfected, the gloves are removed and immersed in a container with a disinfectant solution.
31) Irrigate the oral cavity and wipe the teeth of a seriously ill patient
The manipulation is performed in the following sequence: - the patient’s head is given an elevated position so that he does not choke; - turn their head to the side; - place a towel under the cheek, place a kidney-shaped basin at the corner of the mouth; — fill a can or syringe with one of the indicated disinfectant solutions; - ask the patient to open his mouth; - irrigate the inside of the opposite cheek with a stream from a spray can; - turn the patient’s head to the other side and, going to the other side of the bed, repeat the procedure. 8. If plaque is detected on the tongue, the patient is asked to stick out his tongue. Use the fingers of your left hand to grasp the tip of your tongue using a napkin. Using a spatula taken in the right hand, remove plaque. Take a cotton ball moistened with an antiseptic solution with tweezers and treat the tongue. Take a clean ball, moisten it with glycerin or petroleum jelly, or borax in glycerin and lubricate the tongue. 9. If cracks are found on the lips or corners of the mouth, then the red border of the lips and the corners of the mouth should also be lubricated with glycerin or petroleum jelly, or borax in glycerin.
Brushing the patient's teeth (conscious patient):
prepare: rubber gloves, a glass of water, toothpaste, a soft toothbrush, Vaseline, a towel, a container for collecting rinsing water, a garbage bag; Explain to the patient the course of the upcoming procedure; help the patient turn his head to the side; place a towel on the patient's chest; wash your hands, put on gloves; place a container for collecting rinsing water on a towel, under the patient’s chin; ask the patient to hold the container with his hand, take water into his mouth and rinse his mouth; moisten the toothbrush with water and apply toothpaste to it; clean the patient’s upper teeth, conditionally dividing all the teeth on the upper and lower jaws into 4 segments (it is better to start brushing the teeth from the upper jaw); Place the toothbrush on the buccal surface of the upper teeth at approximately an angle of 45°; Using a “sweeping” motion from top to bottom, move along each segment at least 10 times; clean the chewing surfaces of the upper teeth; position the brush perpendicular to the upper teeth, brush their palatal surface with careful, “sweeping” movements, from top to bottom (all 4 segments); brush the lower teeth (cheek muscle and chewing surface) in the same way, and then the patient’s tongue; help the patient rinse his mouth with water; lubricate the patient’s lips with Vaseline; hold the container at the patient’s chin, wipe the chin if necessary; remove the container, towel; remove rubber gloves; Wash the hands.
During manipulation
The algorithm for instilling drops into the eyes involves alternately introducing the drug into each visual organ. To do this, you must follow the following instructions:
- take a sterile napkin and use it to pull down the lower eyelid;
- ask the patient to look up;
- with the other hand, insert the required amount of medicine, provided for in the instructions, into the conjunctival sac;
- ask the patient to close his eyes;
- blot any spilled water with a napkin or sterile cotton swab.
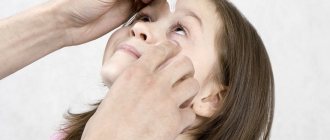
The algorithm for instilling drops into the eyes of a newborn is somewhat different. A small child will certainly resist during manipulation and will not want to look up at your guidance. To treat a newborn's eyes, follow these rules:
- place the baby on your left elbow, holding the baby’s arms with the same hand;
- take a pipette with medicine in your right hand;
- Use the ring finger of your right hand to slightly pull down the lower eyelid and inject the drug;
- The baby will involuntarily close his eyes, and at this time you can wipe away the remaining medicinal substance.
Preliminary procedures
If discharge from the eye sticks together the eyelashes and eyelids, then it is necessary to carry out an additional cleansing procedure. To carry it out you will need gloves, 2 trays, several sterile cotton swabs and an antiseptic solution.
Procedure steps:
- Clean your hands thoroughly and put on gloves.
- Place about 10 swabs on the bottom of a sterile tray and add an antiseptic solution.
- Squeeze the tampon a little and wipe the eyelid edge of the eyelid, directing movements from the outer corner to the bridge of the nose or from top to bottom, discard the used tampon.
- Repeat wiping with other tampons 5-6 times.
- Carefully remove any remaining antiseptic using light movements.
- Remove your hands from gloves and wash them.
In childhood, unwanted responses to medications are more common, so you should carefully select an antiseptic solution.
After the procedure
Having learned how to properly instill drops into your eyes, you will be able to carry out daily manipulation without the involvement of medical professionals. After the procedure, wash your hands again and disinfect the pipettes, if possible. Repeat the manipulation as many times a day as recommended by your doctor or instructions. Do not exceed the prescribed dosage.
Some medications require compliance with certain rules after applying the drops:
- refusal to drive a vehicle (since the medicine reduces visual acuity, such drugs are usually used before diagnostic procedures);
- restrictions on the use of contact lenses (for a few minutes after application or the entire course of treatment);
- additional use of ointments or topical eye medications.
Preparation for the procedure
Before you begin the procedure of instilling drops, you need to prepare:
- First of all, especially if the manipulation is performed at home, you need to carefully read the instructions for the drug. You need to pay attention to literally everything: the shelf life of the drug, dosage, method of use, age restrictions.
- Choose a place for the procedure. It is important that there is sufficient lighting. It is necessary to take care of a place for the patient - this can be a chair, or a place where you can sit reclining.
- If you have to put drops in your eyes, you need to stock up on a mirror.
- Hands should be washed thoroughly with soap and then dried with a clean towel.
- If the pipette is not included with the drops, then it is stored in a separate bottle and disinfected after instillation.
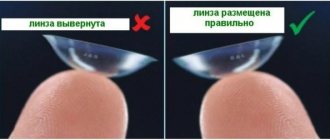
- Before instillation, contact lenses are removed from the eyes. They can be returned to their place no earlier than 20 minutes after the procedure. Each drop has its own instructions on this matter.
- If you need to instill several types of drops, it is important to maintain an interval. It should also be indicated in the instructions, but most often it is 5-15 minutes. Each individual medicine requires its own pipette.
- If it is also necessary to apply ointment, then this is done after instillation.
- The medicine should not be cold; it must first be brought to room temperature.