Possible reasons
Pain in the eye when blinking is a symptom of a large number of ophthalmic problems. The most common ones are:
- foreign body in the eye;
- overstrain of the optic nerve;
- mechanical damage to the upper eyelid;
- blepharitis;
- conjunctivitis;
- iridocyclitis;
- myositis;
- neuritis.
If pain is felt not only when blinking, but also when pressing on the eyelid, then the cause may be eye fatigue.
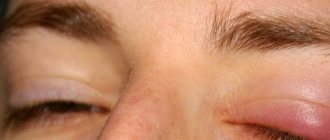
When a mechanical or infectious lesion of the eyelid occurs, the following symptoms occur: the eyelid becomes red and swollen, and an inflammatory process develops.
In case of infectious diseases, both eyes need to be treated, despite the fact that only one hurts.
The cause of pain when blinking can also be non-compliance with the rules of wearing contact lenses or glasses, obstruction of the lacrimal ducts, abscess, boil, or phlegmon.
If the inflammatory process is localized in the area of the tear ducts, then the corner of the eye hurts when blinking. This pathology is called canaliculitis.
If the upper eyelid hurts when pressed, then the cause may be a boil. The eyelid swells and a cone-shaped abscess forms. Without treatment, the pain intensifies, and an abscess of the eyelid develops. The pain can radiate to the corner of the eye, to the upper and lower parts. You need to be treated with antibacterial drugs.
An abscess is a complication of a carbuncle or boil.
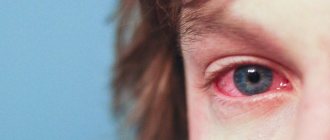
Conjunctivitis
This is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eye. It can be caused by fungi, viruses, infections, and allergies.
Symptoms:
- pain when blinking;
- sensation of a foreign body, sand in the eye;
- pain, burning;
- redness of the mucous membrane;
- lacrimation;
- purulent discharge from the eye, sticking of eyelashes;
- swelling of the eyelids
Conjunctivitis is a contagious disease and both eyes need to be treated.
For a bacterial infection, antibacterial drops are prescribed, for example, Tobrex or Albucid. Viral conjunctivitis is treated with Floxal, Ciprofloxacin, Oftadek, and allergic conjunctivitis is treated with antihistamine drops Allergodil or Ketotifen. Read more about conjunctivitis →
Myositis
This is inflammation of the eye muscles due to overexertion, hypothermia or mechanical damage.
Severe swelling and severe pain occur when blinking. Not only the eyeball hurts, but also the eyelids, and a headache occurs. There is a restriction in pupil mobility.
Treatment is with corticosteroid drugs. If conservative therapy is not effective, surgery is resorted to.
Blepharitis
This is a chronic inflammation of the eyelid margin, which is manifested by the following symptoms:
- pain when blinking, especially in the corner of the eye or the eyelid itself;
- swelling and redness of the eyelid;
- itching and burning of the skin around the eye;
- lacrimation, photophobia;
- crusts and scales on the skin of the eyelids.
The disease is difficult to treat, so it is important to get rid of the disease before it becomes chronic. Therapy depends on the type of pathogen. These can be antibacterial, anti-mite, antiallergic or hormonal drugs. Massage is effective. Correcting nutrition and increasing immunity is important. Read more about blepharitis →
Iridocyclitis
This is an inflammation of the iris and choroid of the eyeball. More often, the inflammatory process is of infectious origin. Treatment depends on the pathogen. This may be antibacterial or antiviral therapy.
Characteristic symptoms of the disease:
- pain when blinking;
- change in the shape of the pupil, its narrowing;
- lacrimation, photophobia;
- change in iris color;
- decreased visual acuity;
- redness of the eye.
Palpation of the eye causes pain to the patient.
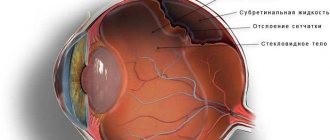
Glaucoma
This is a serious disease that leads to blindness. In addition to pain when blinking, there is:
- double vision when trying to look at an object more clearly;
- blurred vision;
- pain when pressing on the eyeball;
- blurred vision in the dark.
Treatment depends on the stage and type of glaucoma. In most cases this is surgery.
Barley
With this disease, one eyelid is affected, so the patient only has pain in one eye. If the stye pops up from below, then the lower eyelid hurts.
It swells, turns red, it hurts for a person to blink, and the body temperature rises. Since barley is a purulent-inflammatory disease of the sebaceous gland, a swelling with purulent contents forms on the eyelid.
What to do? It doesn’t matter where the abscess has formed, you cannot open it yourself. Eye drops and ointments will help. With proper treatment, the stye will go away in 3-4 days.
Chalazion
This is a benign tumor that appears due to chronic inflammation of the sebaceous gland in the eyelid. Main symptoms:
- pain when blinking;
- swelling and redness of the eyelid;
- round swelling on the eyelid.
The disease is similar to stye, but after 1-2 days the pain goes away and the lump begins to enlarge. Treatment should be carried out by an ophthalmologist. For small tumors, surgical removal can be avoided. Read more about chalazion →
Neuritis
This is inflammation of the optic nerve. The only symptom of this disease is eye pain when blinking. Over time, visual acuity may decrease.
The patient needs a full examination and hospitalization in the ophthalmology department.
Foreign body
A speck, dust, sand or splinter can get into the eye, causing pain. In this case, the pain is cutting, tearing and redness of the mucous membrane appear. After removing the foreign body, all symptoms disappear.
If an infection occurs, then antibacterial therapy will be needed, otherwise an inflammatory process will develop and the pain will only intensify.
Eye fatigue
The cause of pain can be overexertion. When working at a computer or watching TV for a long time, the cornea dries out, causing pain. Most often both eyes hurt.
What you can do yourself
Treatment of diseases with symptoms of pain in the lower eyelid is carried out with medication or surgery. And as soon as this sign appears, you should contact an ophthalmologist for examination and identification of the cause.
Note! Self-medication in case of damage to the eyelid is excluded, as there is a risk of infection of the eye and even loss of vision.
To reduce pain before visiting a doctor, you can use medicinal decoctions to wash the eyes.
Diseases of other organs and systems that may be accompanied by eye pain
The eye may hurt when blinking, not necessarily due to eye diseases. Other reasons:
- Sinusitis. If pain in the orbital area intensifies when blinking or pressing, this may be a sign of chronic sinusitis. When the paranasal sinuses become inflamed, the pain is pressing and the inflammatory process spreads to the tissues that surround the eyes.
- Crohn's disease. This is a chronic inflammatory disease of the gastrointestinal tract that can last more than 6 months and affect any part of the digestive tract. One of its symptoms is pain when blinking one eye.
- Infectious diseases (ARVI, colds). The infection affects not only the respiratory tract, but also the organs of vision. The eyes water, the muscles ache, which causes pain when blinking. The sensations pass simultaneously with other symptoms of the disease.
With sore throat, herpes, rhinitis and otitis media, there is a high probability of damage to the organs of vision. For treatment, you need to contact an ENT specialist. If your eye hurts when blinking, you need to drip Levomecitin drops and smear the eyelid with Oxolinic ointment.
You should not ignore painful sensations when blinking. They may indicate severe problems that can result in vision loss. Need qualified medical assistance.
Author: Oksana Belokur, doctor, especially for Okulist.pro
Lower eyelid hurts when closing eyes
In the case of blepharitis, the main signs will be redness and swelling of the eyelid with increased pain when closing the eye.
When infected with molluscum contagiosum, small yellow-white nodules appear on the eyelids. This disease is more often diagnosed in young children and is treated by removal or cauterization with iodine.
An ulcerative lesion of the cornea is the result of a complication of conjunctivitis or traumatic injury to the eye. This will be accompanied by pain in the lower eyelid when closing the eye and touching it, lacrimation and blurred vision.
Purulent inflammation of the inner membranes of the eye, endophthalmitis, is characterized by a decrease in eye pressure, accumulation of purulent exudate, pain and swelling of the eyelid.
Causes
The most famous causes of swelling of the lower eyelid under one eye:
- Allergy. The symptom is the result of the use of inappropriate cosmetics, medications or exposure to dust particles or food products.
- Lack of sleep . With systematic lack of sleep, the upper and lower eyelids swell. Therefore, it is necessary to observe the correct work and rest schedule.
- Infection. The cause of swelling of one organ of vision may be an inflammatory reaction provoked by an infection. Excessive fluid accumulation occurs with blepharitis and conjunctivitis. In this case, the eyelid turns red, when touched, one feels warmth, tenderness of the skin and painful sensations.
- Styes rarely form on the lower eyelid. The pathology manifests itself as swelling, hyperemia, and a noticeable lump. After a few days, a yellow spot appears in the middle; this is pus.
- Swelling under the organ of vision on the right/left side occurs due to the inflammatory process of the facial nerve.
- An insect bite (bee, wasp, midge or other insect) is manifested by this symptom. Together with their saliva, a toxic component penetrates into the tissue, causing hyperemia, itching and pain. Swelling appears instantly.
- Lesions caused by herpes viruses are characterized by ulcers, hyperemia, and increased body temperature. The lower eyelid swells, pimples appear on it with contents inside.
- With pathologies of the kidneys and cardiovascular system, the process of removing fluid from the body is disrupted, and osmotic pressure begins to increase, which leads to increased swelling.
- The cause may be leakage of cerebrospinal fluid.
- The problem may be due to a non-inflammatory process. Uncomfortable sleeping position, lying on one side, unsuitable bedding material are all non-inflammatory causes. Accompanied by pale skin, body temperature does not rise.
- Puffiness under the eye indicates a fatty hernia. It does not disappear in the morning and is not eliminated by home remedies.
- Disturbed functioning of the endocrine system under the influence of hormones leads to slight swelling under the eyes.
- Scratching with dirty hands causes bacteria to settle under the lower eyelid. Infection penetrates into minor microcracks, leading to redness and swelling. The eyelid gets hot. Dirty hands can cause swelling of the lower eyelid of one eye.
- Damage to the lower eyelid as a result of eyelash extensions or tattooing also manifests itself as swelling.
- The cause of the swelling may be a complication after applying Botox to the cheekbones to correct the shape of the face.
The cause of swelling may also be prolonged exposure to ultraviolet radiation, disruptions in the hormonal system, ARVI, sore throat and consumption of seafood.
Treatment
Medicines
Drug therapy is carried out in the presence of a pathological process, if the eyelid hurts, swells, turns red, or barley (furuncle) has formed. Eye diseases cannot be treated on your own; before using any medications, you must visit a specialist.
Non-surgical eye treatment in 1 month.
Medicines include drops, ointments, intramuscular injections and lotions. If swelling is caused by bacteria, painkillers, antibiotics, vitamins and antiseptics are prescribed for external use.
Treatment with antiseptics is carried out if papules or wounds form under the eyelid. Antiviral medications are prescribed to combat the underlying pathology.
Hydrocortisone and tetracycline ointment are used if pain appears under the lower eyelid. Prednisolone, Celestoderm and Levomycetin drops help cure infectious diseases.
If swelling is caused by an allergic reaction, Claritin, Tavegil or Zodak are prescribed.
Furunculosis is treated with sedatives, antibiotics, and anti-inflammatory drugs. At the time of opening the abscess, it is important not to introduce infection into the eyes, so you cannot squeeze out the boil or stye yourself.
Physiotherapy
Microcurrent therapy restores microcirculation and metabolic processes in tissues. Current treatment is used for severe swelling of the face, age-related skin changes and pigmentation.
Physiotherapy is contraindicated for cancer and infectious problems, herpes and unhealed scratches.
Home treatment
Chamomile is widely used by traditional healers against puffiness under the eyes. It soothes the skin, so it is suitable if the lower eyelid is swollen and itchy. Chamomile accelerates regeneration processes and relieves inflammation if the eyelid is swollen due to blepharitis.
Suitable for preparing infusions that are taken orally or made into lotions. Chamomile is beneficial in combination with green tea.
Other useful recipes:
- Brew strong tea. Strain and cool. Soak a cotton pad in the liquid and apply to the lower eyelids for 10 minutes.
- Grate the cucumber. Squeeze the mixture lightly and wrap it in cheesecloth. Apply the compress to the swollen area for 15 minutes.
- Raw potatoes are an excellent anti-inflammatory agent that helps reduce swelling after a blow. Use similarly to cucumber. If the swelling needs to be eliminated quickly, just cut the potato in half and apply the cut side to the swelling.
- Apply badyagi gel to the problem area. Leave for 15 minutes, rinse with warm water.
- A sage compress helps relieve swelling. 1 tsp. Pour boiling water over medicinal herbs and leave. Heat one part, leave the other cold. Use the hot and cold parts alternately, soaking a cotton swab in them, and applying them to your eyes for 2-3 minutes.
- Mix equal amounts of chopped herbs - dill, chamomile and parsley. Zali
Pain when pressing, like a bruise
Often, uncomfortable feelings in the eyes are expressed not only when blinking, but also when pressing the closed eyelid. A common reason that the eyes hurt like a bruise is fatigue and eye fatigue.
In exceptional situations, such a failure can occur in people who do not follow the rules for wearing lenses.
The most severe factor of discomfort when blinking and pressing can be an indicator of the formation of cancer. As a rule, such neoplasms arise in the posterior lobe of the eyeball. In this case, the discomfort is continuous and increases with pressure on the eye.