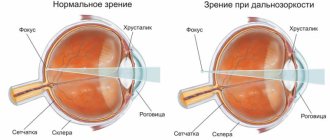
Reduced visual acuity at dusk or “night blindness” is characterized by insufficient function of cells (rods in the retina). Rod cells are responsible for the perception of black and white vision (twilight), and cone cells are responsible for color vision.
This condition is manifested by the fact that in low light a person’s ability to distinguish objects, shapes and colors decreases. This leads to disorientation in space and narrowing of visual fields. Sometimes this can cause complete loss of vision if there is a sharp transition from a light space to a dark one. With night blindness, the most difficult color to distinguish is blue. The peculiarity of this decrease in vision is that in daylight visual acuity is not impaired.
Set up and wash the car
Before an overnight voyage, you need to carefully prepare for the trip.
Wipe the windows and headlights from layers of dirt and dust. Often road dust acts as a filter, cutting off an important part of the spectrum. This is especially true for xenon headlights, which need washers like air. Halogen lamps operate at warmer frequencies, but crystal clarity does not hurt them either. When everything is ready for a long journey, it is worth lowering the brightness of the instrument panel. Outside the city, the illumination of the highway decreases sharply, bright instruments begin to dazzle. Their brightness control is usually hidden under the steering column. And groping for it on the way entails a loss of attention. In general, it is better to set everything up in advance.
Article on the topic Speed slalom. How not to change lanes on the road
More lighting
Even before night falls, that is, at dusk, you need to take care of the visibility of your car yourself. The low beam headlights must be in good working order. If only one headlight is on, it can mislead others about the distance and location of your car. This means that drivers may act inappropriately. For example, someone will overtake you head-on, mistaking a car with one headlight for a distant truck in the night. If it is impossible to cancel the trip, then the left headlight should be on. These are the requirements of the traffic rules. In addition, you can turn on the fog lights.
Can nyctalopia be cured?
Treatment depends on the type and causes of the disease. Congenital hemeralopia is almost untreatable. For other types, taking vitamins and proper nutrition help. The doctor also prescribes drops and ointments.
If the disease is caused by any vision pathologies, surgery may be required. The following operations are carried out:
- laser coagulation;
- antiglaucomatous procedures;
- phacoemulsification of cataracts;
- laser correction;
- lens replacement, etc.
There are also folk methods: decoctions and tinctures of medicinal herbs, taking berries with the necessary vitamins (sea buckthorn, blueberries). These methods cannot replace comprehensive medical treatment and should only be a supplement to it.
Stay away from "one-eyed"
If you have already met such a “one-eyed” person, then it is better to stay closer to the right side of the road. It is impossible to predict what kind of vehicle is rushing towards you. This could be a motorcycle, a “blind” truck, a tractor with a protruding trailer, or other rural homemade products. “One-eyed”, whose dimensions are extremely difficult to estimate, must be feared.
What is the fine for turning off headlights at night? More details
Capture the electronic navigator
The navigation system will be very useful on a long journey. Usually on autumn nights, and even in cloudy weather, visibility drops to its maximum, which is why the route configuration is not visible. If you turn the map as close as possible, you can use the screen to monitor upcoming turns and their degree of steepness. This will help when planning overtakings. By looking at the map from time to time and guided by markings or signs, you can choose a relatively safe area for the maneuver. But don't forget to look at the road too!
Article on the topic
What the driver cannot do. What medications are dangerous to take while driving?
Weakness, blurred vision, feeling unwell
Julia
161 views
January 2, 2021
Good afternoon. In early November, I had a mild form of coronavirus. Kt1-8%. I am 27 years old. I have already written many times. 3 weeks after the illness, I felt worse, dizziness began, which did not go away throughout the day, my head was spinning from morning to evening (objects around me did not spin). Sometimes it seemed like I was going to faint. But she never fell. Severe weakness in the body, pressure drops and rapid heartbeat, I heard my heartbeat. I didn’t sleep well at night and had insomnia. In my life I have VSD, astheno-neurotic syndrome. I'm a suspicious person. I had an MRI, ultrasound scan, thyroid hormones - everything was normal. I began to worry very much about my well-being, because the problem had not been identified and my health was not getting better, I was afraid that something serious would happen, I began to feel uncomfortable being around or falling asleep alone, thinking that I would get sick and there was no one around. There was a feeling of fear and anxiety. I went to a psychiatrist and they prescribed me Eglonil and Bellataminal. I drank for 2 weeks and began to sleep normally. It seemed to be getting better, but then my period started and I felt worse, again dizziness, weakness, pressure surges and tachycardia. I also sometimes had internal tremors in my body. I could have been such a coward all day from morning to evening. I went to a neurologist and she took Eglonil away and told me to take Teraligen, added betaserc and left bellataminal. I took Teraligen for 3 days, but from the first day of taking it, my vision began to blur, as if there was no focus, fog in my head, as if everything was floating in my head and eyes. Not double, no. After 3 days of taking Teraligen, I quit it, I thought my eyes were swimming from it, but this problem still hasn’t gone away and bothers me very much. I began to worry more about my eyes and the fog in my head, I cried every day and still cry to this day, because I don’t understand what’s happening. Then I went to another psychiatrist, they prescribed me 1/4 haloperidol, 1/4 finlepsin, 1/4 phenazepam, 1/4 azafen 3 times a day, she said that although the drugs are scary, they work well in such dosages for people with anxiety disorders. I was afraid to drink them, I didn’t drink anything at all for 2 days, but my vision also remained blurry, near focus is normal, if I look to the side it’s blurry, or at the phone screen. And there’s some kind of fog in my head. Dizziness doesn't bother me yet. I took haloperidol 1/8 and phenazepam 1/8 at night, for starters. I didn't sleep well. I had difficulty falling asleep and waking up at night. But I didn’t take this drug anymore, the instructions for it were too scary. I decided not to take this treatment. In addition, for the last 2 days my blood pressure has been fluctuating, 140/100, 130/90. I feel very bad, severe weakness, in my body, in my legs, my legs hurt and twisted, I cried again. Yesterday I went to the neurology hospital. Then they put me on an antihypertensive drip, gave me half a tablet of fensitate at night, half a tablet of Selectra and 5 glycine. I drank it all, and in the morning I felt very nauseous, which is why I forcibly vomited and went to the toilet. I have a stomachache. Could this be from these pills? In recent days I have lost my appetite again and I eat little. According to the chronicle - gastroduodenitis, esophagitis, reflux. Why do I feel bad every day, please help me! I want to note that I don’t have attacks that go away and I feel fine until the next attack. I feel sick all day every day. Why does the pressure fluctuate? Why are my eyes blurry and my head foggy? What else is worth examining? Should I take some hormones, check my kidneys and adrenal glands? help me please
The question is closed
weakness
Blurred vision
Remember the upstarts
On long straights, where the road goes exactly along one line, you shouldn’t relax either. You may not see oncoming traffic due to the terrain. The fact is that the road often does not go strictly horizontally, but in giant waves; not only passenger vehicles, but also trucks can hide in the lowlands. In general, if lights flash in the distance, you should not relax, hoping that it was “just your imagination.” A hidden car can jump out of complete darkness at the most unexpected moment.
Vision "at age"
When we are young, we do not attach importance to how well our body works.
But its resources are limited, and over the years we will experience not the best changes, including vision problems. When to expect them and how to deal with them?
This is the norm
One of the first signs of age-related changes in vision is presbyopia. This is what doctors call the progressive deterioration of the eye's ability to focus on close objects. Presbyopia makes it difficult to read small print, especially in low light.
To see the letters, you have to hold the book away, and you feel eye strain.
Another symptom of presbyopia is a temporary deterioration in vision when looking from a nearby object to a perspective that goes into the distance, for example, from a mobile phone screen to a landscape passing through a car window.
The problem is less noticeable in bright sunlight, when the pupil becomes smaller.
The reason for these changes is the hardening of the lens due to a natural decrease in the level of the protein that maintains its transparency, alpha-crystallin. People over the age of 35 are at risk for developing presbyopia, but changes usually occur in those who have crossed the 40-year mark.
It is impossible to avoid them: they will affect everyone. To a greater extent, vision will deteriorate in those who read a lot, work with a computer, and to a lesser extent in representatives of professions that do not require strain on the visual analyzer.
It’s easy to normalize the situation: lenses allow you to instantly restore visual acuity. In addition, surgical treatment effectively corrects presbyopia. However, whether the game is worth such a traumatic and expensive candle will have to be decided individually.
Through a cloudy glass
Much later, age-related changes in vision appear, and primarily cataracts. It develops in more than half of older people over 80 years of age.
It is caused by clouding of the lens of the eye due to the accumulation of proteins or pigment, which reduces the transmission of light to the retina at the back of the eye.
Cataracts develop slowly, sometimes over several decades, affecting one or two eyes. It is accompanied by disturbances in both visual acuity and color perception: the world around becomes faded, objects lose their outlines, and a halo appears around them. Vision becomes much worse in bright light and in the dark.
In severe cases, blindness can occur: in 50% of cases it is associated precisely with clouding of the lens.
In the initial stages, vision can be improved with the help of lenses, but the only effective treatment is surgery to replace your own cloudy lens with an artificial, but transparent one. It can be performed at any stage of the disease.
The operation, as a rule, does not cause difficulties and is performed on an outpatient basis, under local anesthesia. Significant improvement in vision occurs in 9 out of 10 patients. The likelihood of developing cataracts can be reduced by preventing factors that damage the lens by stopping smoking and wearing sunglasses with a UV filter.
Under high pressure
Unlike the first two conditions, glaucoma is a disease. Its cause is damage to the optic nerve and, as a result, loss of vision. Glaucoma ranks honorably second after cataracts among the most common causes of blindness.
As a rule, glaucoma is accompanied by increased intraocular pressure. In such cases, the disease develops slowly and its symptoms progress gradually. First, peripheral vision deteriorates, and then central vision. If left untreated, blindness occurs.
At the same time, progression can be stopped with the help of eye drops that reduce intraocular pressure, and the sooner therapy is started, the better. Therefore, it is very important to diagnose the disease as early as possible.
In order not to miss the problem, those who are at risk for developing glaucoma should have their eyes checked at least once a year. Risk factors include increased intraocular pressure, heredity and high blood pressure.
Macular degeneration of the retina
Over the age of 50, macular degeneration of the retina may develop. Risk factors for the disease include heredity, smoking, high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, high cholesterol, obesity and exposure to UV rays.
In the early stages there are no manifestations. Symptoms, or rather, the symptom appears as it progresses, taking away the opportunity to lead a full life.
The main symptom of macular degeneration of the retina is deterioration or loss of central vision in one or both eyes. Sometimes it can be accompanied by visual hallucinations that have nothing to do with mental illness.
In 2015, macular degeneration of the retina was diagnosed in more than 6 million people worldwide. This is much less compared to other age-related diseases. However, the problem should not be downplayed.
Monitor air luminosity
You can predict the appearance of an approaching car by the reflected light of its headlights. From distant spotlights, especially LED ones, the surrounding atmosphere slightly luminesces. The glow runs in front of the car and is noticeable from afar, even when it disappears behind the hills. In addition, light is reflected from the treetops and even from low-lying clouds. Therefore, it is necessary to carefully monitor the condition of surrounding objects. If there is even minimal luminosity, then difficult overtaking risks turning into trouble.
Don't go blind
When an oncoming car approaches, it is better to turn your gaze to the very edge of the right side of the road. Then you can avoid short-term blinding by headlights, especially if some boor did not want to switch the “far” to the “near”. The anterior hemisphere will still be visible with peripheral vision, and by moving the pupil to the side, it is possible to avoid direct rays hitting it. In addition, the boundary between the asphalt and the roadside is visible much better than the sliding white markings.
What safety rules should be followed in thick fog? More details
Treatment of decreased visual acuity at dusk, “night blindness”
If the cause of night blindness is a disease, then treatment is aimed at eliminating it. However, congenital night blindness cannot be treated.
For people who suffer from night blindness, doctors recommend the following:
- Taking vitamin A - the dose should be calculated by an ophthalmologist because vitamin A is toxic in large quantities;
- Periodically examine peripheral vision;
- To absorb vitamin A, it is recommended to adjust your diet and enrich it with fatty acids.
Slow down
Before passing oncoming traffic, it is better to slow down so that the braking distance fits the length of the space illuminated by the headlights. This is especially true after switching distant spotlights to low beam. For example, you drive fast with powerful LED lamps and see everything perfectly 150 meters ahead, but after pulling the lever towards you, night falls on the surrounding area and the road ahead is enveloped in a black blanket. All objects on the road, holes, pieces of vulcanized tires, as well as animals now jump out of the darkness 40-60 meters from the car. It is better to slow down to 70 km/h. Calculating a safe speed is simple. It takes 1 second to make a decision, and during this time the car will jump about 19 m, but for braking another 31 m is needed. It turns out 50 m, and this is exactly the length of the path to a complete stop for passenger cars on dry asphalt at a speed of 70 km/ h.
Article on the topic
7 tips to combat fogging car windows
Watch out for flashing headlights
Wild animals pose a particular danger at night. They are poorly visible in the dark and can unpredictably throw themselves under the wheels. But there is a good way to detect them. Usually moose can stand on the side of the road or right on the asphalt and stare at the lights of vehicles. It is difficult to notice them from afar. But if the road bends, then in the light of oncoming headlights you can see the rapid flickering of some objects. These could be bushes or animals. Under no circumstances should flickering be ignored. It is better to reduce the speed to 50-60 km/h.
Why does night blindness occur?
In modern medicine, congenital and acquired night blindness is determined. If a person is diagnosed with congenital night blindness, then we are talking about a genetically determined disease. The acquired form of the disease is a functional illness.
Acquired hemeralopia develops in humans due to the influence of a number of factors. First of all, the causes of hemeralopia may be diseases of the retina. These are pigmentary degeneration and retinal detachment , as well as inflammatory processes . Night blindness in humans can develop due to degenerative processes of the macula, disorders of the choroid, inflammatory processes of the optic nerve, and myopia . Sometimes treatment for hemeralopia is given to patients who are later found to have cataracts or glaucoma . Sometimes decreased vision in the evening is observed in a person who has recently received a traumatic brain injury. Also, similar visual impairments can occur if a person constantly works in very poor lighting or reads in incorrectly set light. In some cases, nyctalopia can be caused by exposure to ultraviolet radiation on the eyes. This occurs due to exposure to bright sun and the influence of dazzling snow on the eyes.
Another important factor that can provoke night blindness is a lack of vitamins A and B2 in the human body. This explains the fact that night blindness is often observed in people suffering from general vitamin deficiency .
If we are talking about risk factors for the development of nyctalopia, then in this case the age factor should be noted. After forty years, a person experiences a slowdown in all processes that occur in the body. As a result, the nutrition of the retina deteriorates, and vision in the twilight decreases.
Do not immediately overtake large vehicles
If a yellow flashing light looms ahead, you need to be extremely careful and pull to the side of the road. Yellow flashing lights, in addition to road services, also belong to carriers of large cargo. Large industrial objects like to be transported at night on multi-wheeled platforms, when the roads are relatively clear. These could be industrial boilers, iron towers or other bulky structures. Such platforms are dangerous when turning, as they “cut” the trajectory and climb into the oncoming lane. Well, when overtaking flashing slow-moving vehicles, it is better to use straight and clearly visible areas.