Retinal detachment is a serious eye disease that most often requires surgical intervention. But even surgery does not guarantee that detachment will not occur again. Therefore, it is necessary to comply with all requirements and contraindications during the recovery period and after it.
The most important contraindication for those who suspect retinal detachment: under no circumstances should you delay seeing a doctor or self-medicate! This disease can progress rapidly. It cannot be treated with traditional methods, and incorrectly selected drugs can only aggravate the patient’s condition. Symptoms that require you to seek qualified help as soon as possible:
- sudden deterioration of vision;
- the appearance of a cloudy veil before the eyes that does not disappear when blinking, or a “blind spot”;
- partial or complete loss of lateral vision;
- the appearance of floating dots, flies, flashes, spots.
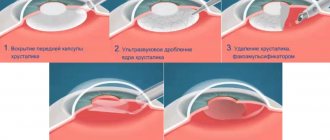
Execution method
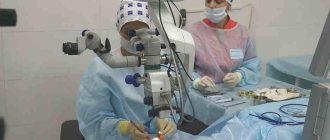
An argon laser is used for laser coagulation. Its rays act at a given depth at a certain point or area. This leads to increased temperature and coagulation. The tissue prepared in this way is immediately “soldered” to the nearby layers, thereby ensuring a reliable connection of the retina with the vessels that supply it.
The operation is not complicated. It takes place under local drip anesthesia. Medications that dilate the pupil are also instilled in advance. This ensures access to all areas of the retina. A special lens is placed on the eye to prevent the laser beam from scattering, so that the light reaches the desired point in full.
Control of all manipulations and the action produced by the laser is carried out using a stereomicroscope. In preparation for surgery, based on diagnostic data, a map of the areas where coagulation is necessary is developed. This can be a targeted effect or circular (along the entire periphery of the retina).
Cost of laser coagulation of the retina
| Barrage of the macular zone | 4,200 rub. |
| Barrage of holey defect in the macular zone | 5,000 rub. |
| Barrage of the exudative detachment zone | 6,700 rub. |
| PLKS of the 1st category of complexity (includes barrage of 1-2 lesions without laser cerclage) | 4,000 rub. |
| PLKS of the 2nd category of complexity (includes barrage of more than 2 lesions without laser cerclage) | 4,500 rub. |
| PLKS 3 category of complexity (includes barrage of lesions with laser cerclage) | 7,800 rub. |
| PLKS carried out in two stages, stage I | 7,000 rub. |
| PLKS, carried out in two stages, stage II | 3,700 rub. |
| Barrage of local detachments during PLKS of categories 1-3, carried out in one stage | 2,900 rub. |
| Barrage of local detachments during PLKS performed in two stages | 1,500 rub. |
| Barrage of the retinal detachment zone, stage I | 6,000 rub. |
| Barrage of the retinal detachment zone stage II | 4,500 rub. |
| Focal laser photocoagulation of the retina | 5,200 rub. |
| Sectoral laser coagulation of the retina | 5,700 rub. |
| Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina Stage I | 6,800 rub. |
| Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina stage II | 4,700 rub. |
| Panretinal laser coagulation of the retina stage III | 3,700 rub. |
Sign up for a consultation >>>
Advantages
Laser coagulation is a completely non-contact treatment method. Micro-instruments are not used during the operation, and the surgeon’s hands do not come into contact with the eye. The laser, being an absolutely precise and sterile instrument, minimizes many risks: infection, bleeding, subsequent scarring, and inaccurate movements.
In this regard, laser treatment can be performed on an outpatient basis in a “one day” mode. General anesthesia and hospitalization are not required. The operation lasts no longer than 20 minutes, then the patient can go home. Laser coagulation does not impose significant restrictions during the rehabilitation period, and therefore does not make changes to the patient’s usual lifestyle. With some exceptions, you can continue working immediately.
In some cases, repeated laser coagulation may be required. In order to analyze the effectiveness and assess the sustainability of the results obtained, it is recommended to undergo regular examination by an ophthalmologist.
Indications for coagulation and contraindications
Manipulation is prescribed for the following pathologies:
- degenerative retinal disease;
- detachment of the inner membrane of the eye;
- impaired blood flow (retinal veins, postocclusive retinopathy);
- severe degree of myopia (myopia);
- diabetic retinopathy;
Laser coagulation is often prescribed to patients with severe myopia for the further possibility of vision correction. If there are direct indications, it can be prescribed to women during pregnancy.
Contraindications are not absolute; a preliminary instrumental study is carried out to assess the risks of the operation.
Patient reviews about treatment
In 90% of cases, reviews from patients who have undergone this treatment are positive. Laser intervention may be accompanied by pain or discomfort (depending on the treatment area and the patient’s pain threshold). There were mild attacks of nausea and dizziness, which were short-lived. The majority of patients indicated the absence of complications and side effects.
Laser photocoagulation is low-traumatic and quite effective in preventing retinal detachment.
The manipulation does not require special preparation from the patient; therapy is carried out on an outpatient basis. Fomenko Natalia Ivanovna
Contraindications
Laser coagulation has virtually no contraindications. Pregnancy and many systemic diseases do not exclude the use of this technique. Laser treatment is undesirable only for certain ophthalmological pathologies, such as:
- insufficient transparency of the optical media of the eye;
- severe rubeosis of the retina;
- significant changes in the fundus;
- severe epiretinal gliosis, accompanied by traction syndrome;
- low visual acuity (relative contraindication for pathology values less than 0.1 dioptres).
Who should not undergo laser vision correction? Contraindications for surgery
Laser correction is the most modern method of vision restoration, but it has a number of contraindications. Restrictions for this operation are divided into two main groups. They are absolute and relative. The former prohibit the procedure, while the latter are a temporary obstacle to it.
Today, the development of scientific and technological progress is proceeding by leaps and bounds. Therefore, the list of both those and other contraindications is constantly changing.
Strict restrictions that were previously considered absolute, thanks to innovation, are gradually becoming temporary. Currently, the list of contraindications for laser correction looks something like this.
Very often, a temporary contraindication is the condition of the retina. In this case, the doctor may prescribe a strengthening procedure - cauterization of the retina with a laser. After which the patient is allowed to undergo laser correction.
Relative contraindications to laser vision correction
- This operation is not recommended for children. This time limitation is easily explained. The thing is that children’s visual organs are still forming and growing - their structure changes (usually this happens before the age of 18). In this case, laser correction is not so much dangerous as it is pointless - no doctor can guarantee lasting results for a small patient. But most likely, modern non-surgical therapeutic measures will be offered, aimed at improving vision and adapted to age-related changes.
- Doctors warn pregnant women, as well as young mothers during lactation – breastfeeding – against surgical intervention. Even if the child is “artificial”, it is still not recommended to carry out this procedure in the early postpartum period. From the very beginning of pregnancy until the end of breastfeeding, female hormonal levels work in an enhanced mode. This fact can significantly slow down the healing of the eye. Moreover, after laser correction, the patient is necessarily prescribed antibiotic eye drops, which can pass through the placenta or breast milk into the child’s body and harm him.
- If the patient’s vision has rapidly deteriorated over the past year, then this circumstance may also become a relative contraindication to laser correction. You will be asked to play it safe and treat your eyes with various therapeutic methods, monitor their condition and wait until your vision stabilizes.
- Inflammatory processes in the organs of vision can also become a temporary obstacle. Surgery at this time can have a lot of negative consequences, in particular, significantly increase inflammation and slow down postoperative tissue recovery.
- A temporary contraindication to laser correction is dystrophic changes in the retina. In order to get rid of problems of this kind, patients are recommended to undergo laser coagulation - a procedure that prevents retinal detachment. It is aimed at strengthening it in a non-contact way. Laser photocoagulation can be restrictive, that is, preventive, or therapeutic, depending on the severity of the problem.
- If the patient has diseases that cause weakened immunity, then most likely he will be offered to undergo vision correction surgery until complete recovery. Interruptions in the functioning of the immune system will make the healing process of the eye take a long time, and can also cause various complications.
All of the above contraindications are temporary in nature, and therefore do not impose a categorical ban on laser correction.
However, there is a list of reasons why laser vision correction cannot be done.
Absolute contraindications to laser vision correction
- People suffering from advanced diabetes mellitus, unfortunately, will not be able to improve their vision with laser correction. Such an operation is also denied to those who suffer from various systemic diseases - rheumatism, rheumatoid arthritis, bronchial asthma, AIDS. With such ailments, the operated eye will take a long time to heal, and in the future there may be various complications and even a decrease in visual acuity.
- For the same reasons, doctors do not undertake to operate on patients with skin problems - psoriasis, neurodermatitis, eczema, as well as those whose skin is prone to the formation of keloid scars.
- Mental and neurological abnormalities are absolute contraindications for laser correction. The behavior of patients with such ailments is unpredictable, and therefore can complicate the operation and prolong the rehabilitation period.
- The list of absolute contraindications to surgery includes serious eye diseases, such as optic atrophy, cataracts, and glaucoma. However, some patients suffering from these ailments are sometimes allowed laser correction at some stages of the disease.
- The list of absolute contraindications also includes keratoconus, a disease in which the cornea of the eye protrudes into a cone and becomes thinner. If the thickness of this part of the eye is less than 450 microns and if there are penetrating scars of the cornea in the optical zone, laser correction cannot be done, otherwise it will become even thinner and will simply tear over time, causing blindness.
Of course, any operation has contraindications, but most have no reason to refuse to improve the quality of their vision.
All you need is to carefully study the list of contraindications, conduct a comprehensive diagnosis, and most importantly, visit an experienced ophthalmologist!
After operation
The effect of drops that dilate the pupil gradually weakens within 2-3 hours after surgery. As this happens, normal visual acuity is restored. In the first hours, there may be some redness and irritation in the eye. These phenomena pass on their own within 24 hours.
After surgery, it is recommended to wear sunglasses continuously until strong chorioretinal adhesions are formed.
After the procedure, you cannot drive and you must exclude other activities that require increased concentration.
The recovery period after undergoing laser coagulation of the retina lasts from 7 to 14 days. During this period, it is necessary to follow the instructions that the patient receives from the ophthalmologist when going home. The most common of them impose restrictions excluding:
- activities associated with sudden movements, vibration, falls (including sports and active recreation);
- body bending, heavy lifting, excessive muscle tension;
- visual stress, especially at close range;
- alcohol consumption;
- taking large volumes of liquid, as well as eating spicy and salty foods;
- thermal and water procedures (visiting a bathhouse, sauna, swimming pool, solarium, swimming in open water).
Under certain circumstances, after laser coagulation there remains some risk of developing new foci of degeneration and retinal detachment. Patients with diabetes are at risk. After surgery, all patients are recommended to visit an ophthalmologist monthly for a preventive examination for six months. Then the frequency of visits is reduced to quarterly. If the condition remains stable, the doctor transfers the patient to a regimen recommended for healthy people - examination by an ophthalmologist once a year. It is necessary to inform the doctor about the fact of undergoing laser coagulation of the retina, if this is not indicated in the medical record.
In case of complicated heredity, preventive annual examinations are especially important for early diagnosis of the possible onset of the disease. Timely detection of the onset of trophic disorders of the retina will allow laser coagulation to be carried out before signs of degeneration appear and to avoid its ruptures and detachment.
In what cases is the use of lenses contraindicated?
The likelihood of complications after surgery is negligible, but still present. In this case, you need to stop wearing lenses for a while until the problem is resolved.
- short-term swelling of the cornea;
- inflammation of the iris;
- the appearance of dark spots in the field of vision.
After coagulation, the patient must be observed by a doctor every month for a year.
The Lenzy.ru online store offers a wide selection of high-quality optical products from popular global brands. We will promptly answer your questions and help you place your order. We wish you successful purchases!
Advantages and disadvantages
Laser surgery has its advantages, the most significant are:
- safety, painlessness and bloodlessness;
- non-contact treatment;
- minimal time investment;
- reducing the risk of recurrent retinal detachment;
- no need for hospitalization;
- minimum restrictions and complications;
- rapid restoration of vision after filling.
A significant disadvantage of this therapeutic method can be considered headaches after it.
Disadvantages include the discomfort that the patient experiences during the procedure; some complain of photophobia. For several days after the procedure, many people have headaches and eyes, and in the postoperative period there are many inconvenient restrictions that are important to strictly observe, otherwise surgical treatment will not bring the desired results. After laser correction for the treatment of retinal detachment, you cannot engage in certain sports. For professional athletes this is a significant drawback, but such a ban is necessary if an adult wants to maintain normal vision.